TRICUPISD STENOSIS & REGURGITATION
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
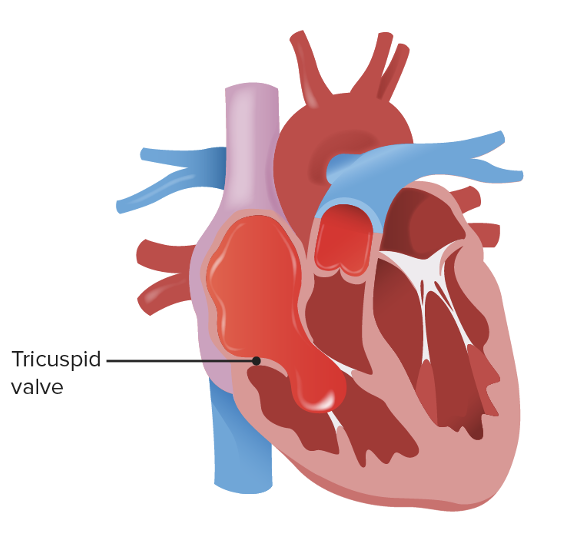
This is?
Normal Tricuspid valve
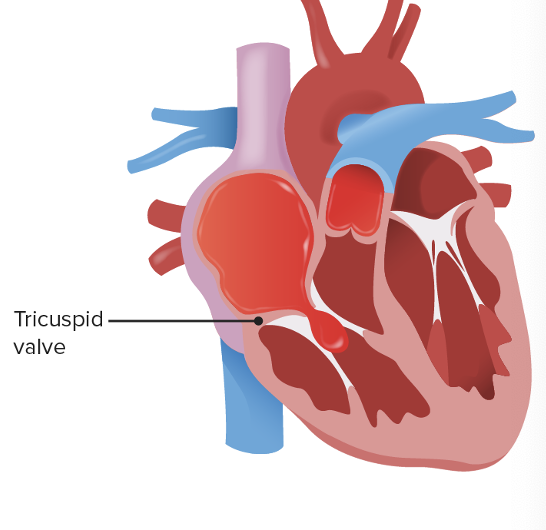
This is?
Tricuspid Stenosis
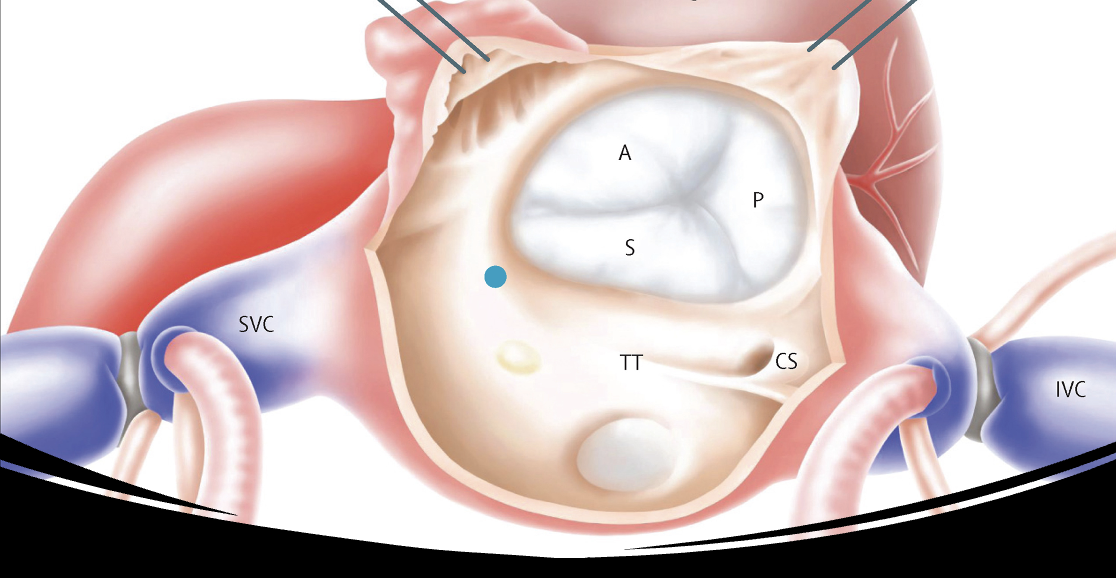
What are the TV Structure?
Anterior leaflet, Posterior leaflet & Spetal leaflet
Is a conditon in which the valve between the RV & RA does not function properly.
Often occurs with other heart problem.
Causes a reduction of blood from the RA into the RV.
A narrowing of the TV that impedes diastolic flow traveling from RA > TV > RV
This causes the RA to become enlarged, decreasing the amount of blood entering the RV.
This is?
Tricuspid Vlave Stenosis
What is the most common cause of TS?
Rheumatic Fever
What are the ETIOLOY?
•Congenital heart problems
•Heart attack or coronary heart disease
•Congestive heart failure
•Endocarditis—heart infection
or inflammation
•Trauma to the heart
•Secondary aka functional TS (wire/pacemaker, clot/tumor/veg)
This is?
Carcinoid (always combined with TR)
What are the SIGN & SYMPOTMS of TS?
ascites
abdominla swelling
jaundice
peripheral edema
right upper quadrant pain
What are the COMPLICATION of TS?
Usually not isolated disease state. Evaluate other valve for stenosis
Increased risk IE
If clot/tumor, increased risk of embolization
Decreased cardiac output
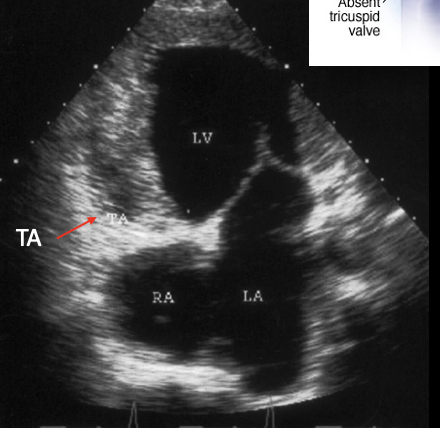
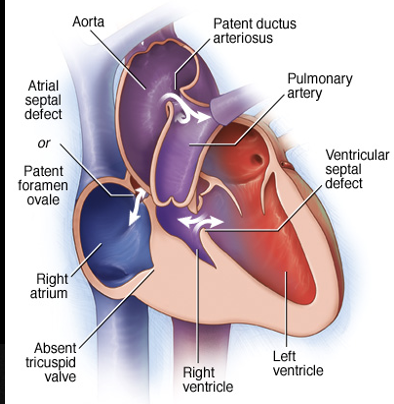
is a condition present at birth (congenital heart disease), a solid wall of tissue blocks the blood flow between your right heart chambers.
This is?
Tricuspid Atresia
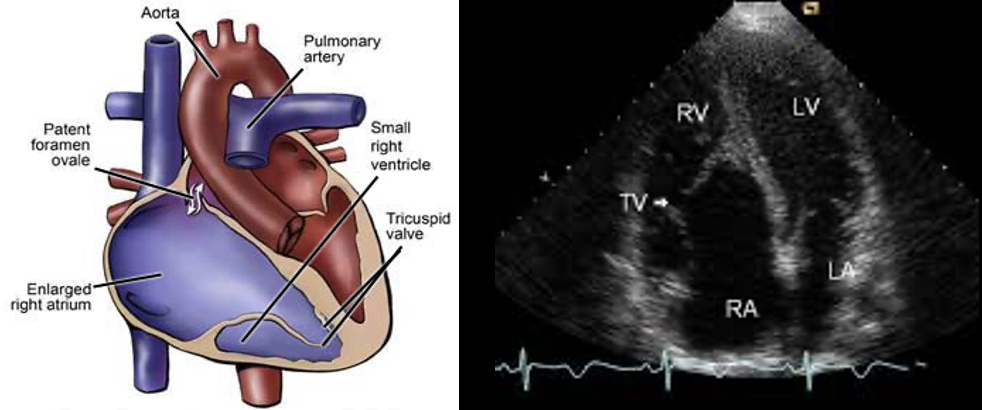
_________in which a malformed tricuspid valve sits lower than normal in the right ventricle, causing blood to flow back into the right atrium (TR).
Ebstein’s Anatomy
is a consequence of the effects of excess hormone production. Serotonin in high concentrations entering the heart from the liver causes fibrosis, particularly in the tricuspid and pulmonic valves, resulting in right-sided heart failure.
Nearly 40% of patients exhibiting the carcinoid syndrome will develop ………………….. with fibrotic endocardial plaques and associated heart valve dysfunction that classically involves the tricuspid valve.
On an echocardiogram this presents a thickening and retraction of the tricuspid valve leaflets during systole. The right-sided image demonstrated severe tricuspid valve regurgitation.
Carcinoid Haert Disease
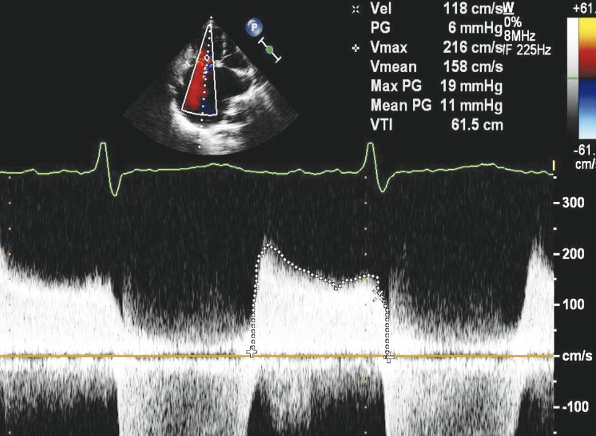
What is the MURMUR of the TS?
•a mid diastolic murmur can be heard during auscultation
•creates diastolic rumble with an opening snap that varies with respiration
What is the 2D ECHO for TS?
thickened leaflets
restricted motion
diastolic doming
decreased TVA
right atrial enlargement
dilated IVC
What is the M-MODE for TS?
thickened leaflet
multiple echoes
decreased leaflet mobility
anterior motion of posterior TV leaflet
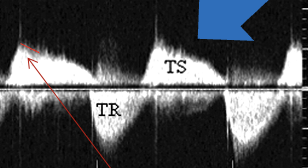
What is the CFD of TS?
Turbulent diastolic flow that travels from RA → narrowed TV → RV
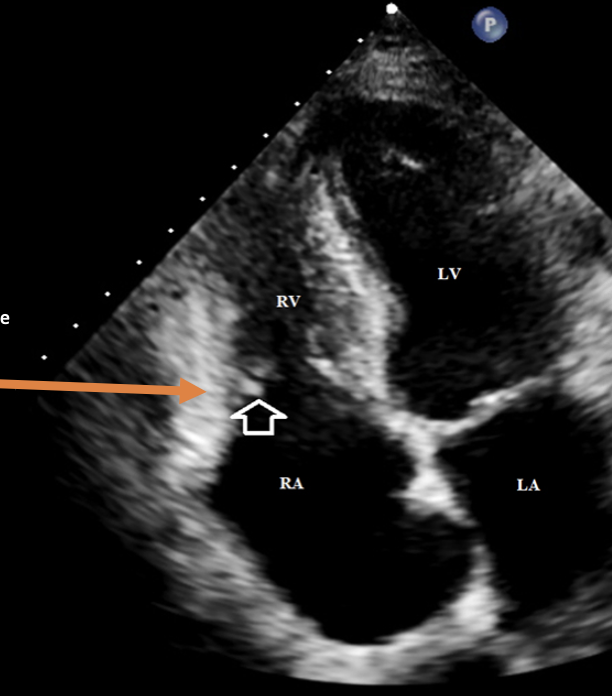
? TR
1 is?
RVIT
2 is?
Apical 4CH
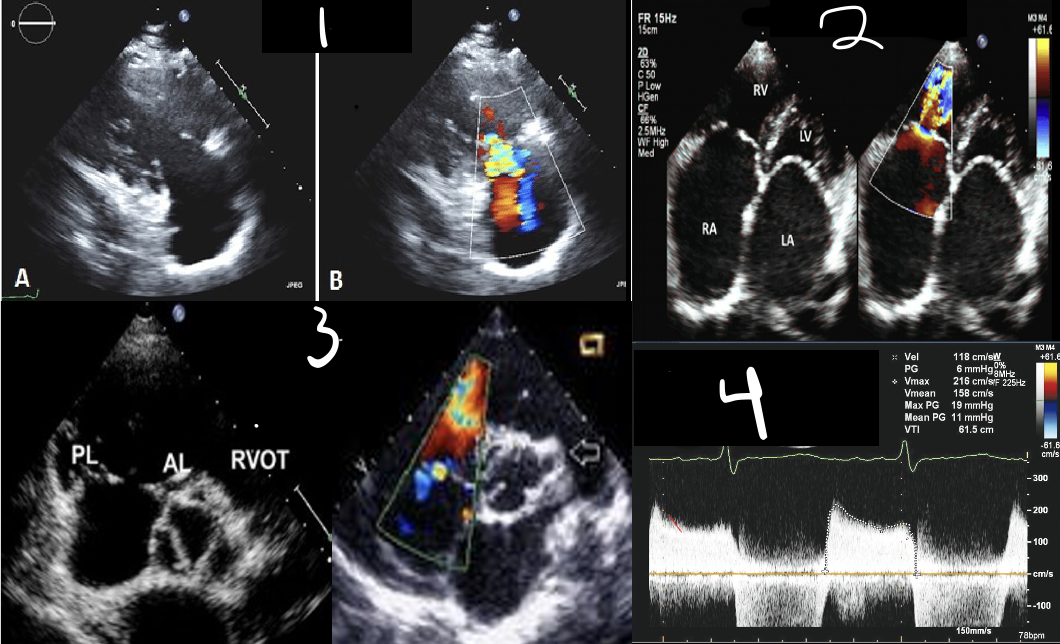
3 is?
SAX A0 & TV
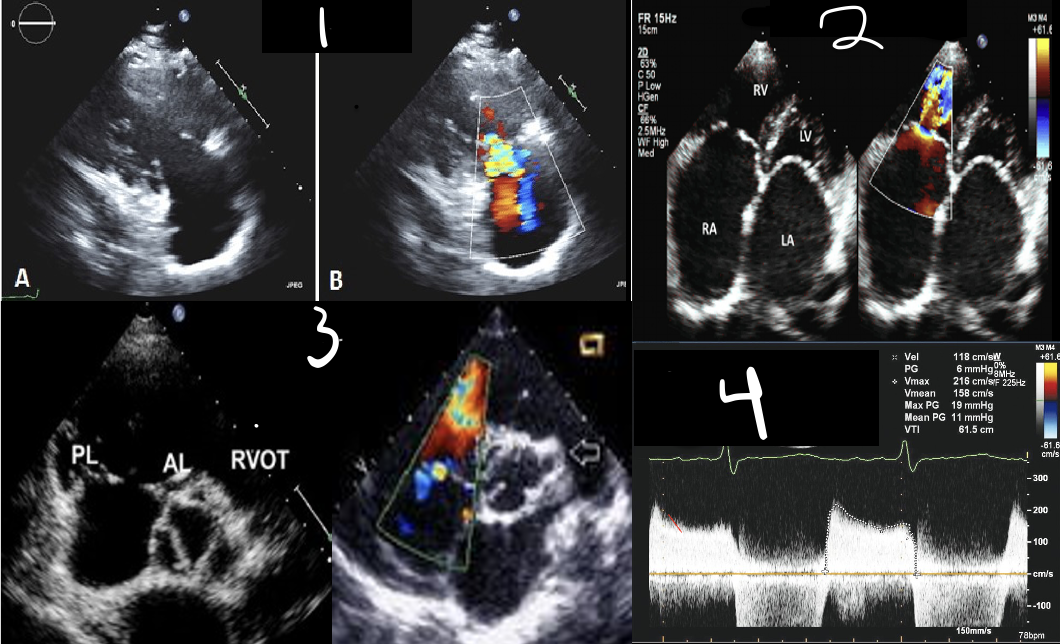
4 is?
Spectral Doppler
Normal Flow is Antegrade
Use TV package (E/A velocity)
1.Measure peak E velocity and Decel slope
•>1 m/s suggestive of high velocity
2. Measure peak A wave
TV INFLOW (PW)
TS = ?
Antegrade Flow
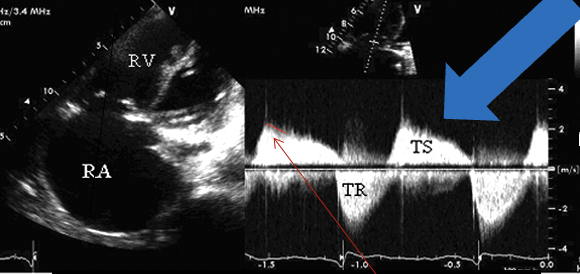
The blue arrow is ?
DECREASED E-F SLOPE
OBTAIN TVA USING
PHT METHOD
NORMAL TVA 7-9 CM
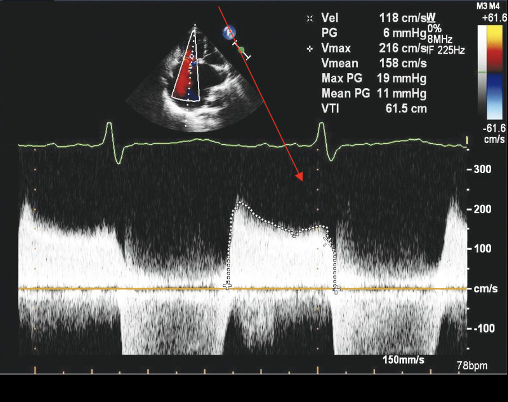
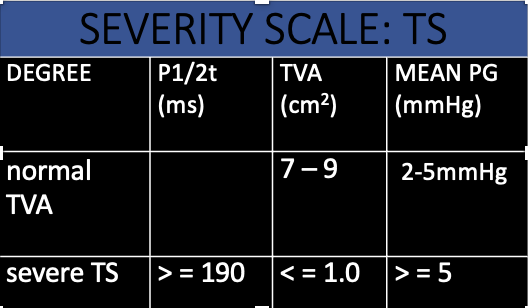
This red arrow is?
Trace E & A Wave to obtain MEAN PG
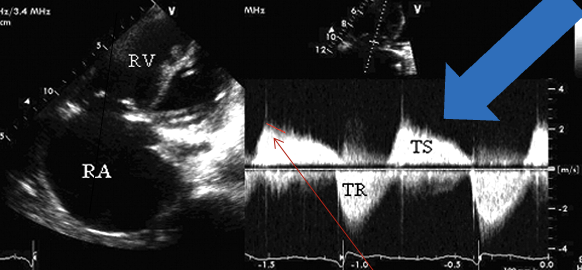
This red arrow is?
Severity scale : TS
TVA = ?
190/PHT
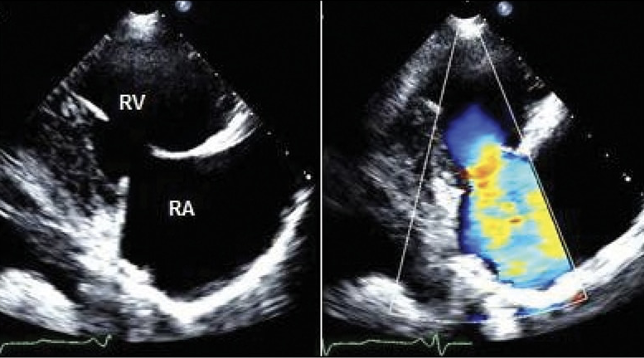
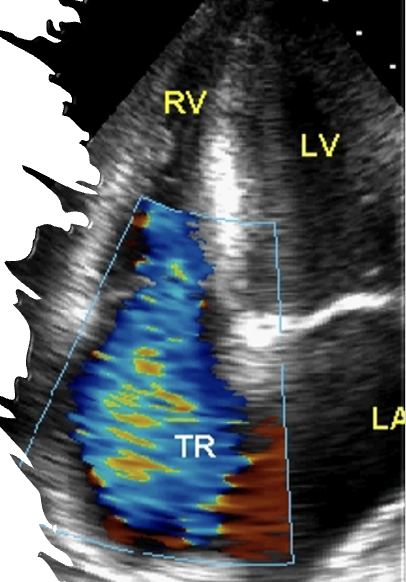
is leakage of blood backwards from the right ventricle into the right atrium during systole; may be acute, chronic or intermittent.
Tricupisd Regurgitation
As the right ventricle contracts to pump blood forward to the lungs, some blood leaks backward into the right atrium, increasing the volume of blood in the atrium. As a result, the ______________, which can change the pressure in the nearby chambers and blood vessels.
right atrium can enlarge
What is the causes of TR?
Trace/mild TR common
Myxomatous degeneration (primary TR)
Rheumatic TR/TS (primary TR)
TVP (20% have MVP)
Carcoid heart disease (primary TR)
Congenital TR
Endocarditis
Ebstein’s Anomaly
Proshetic valve dysfunction
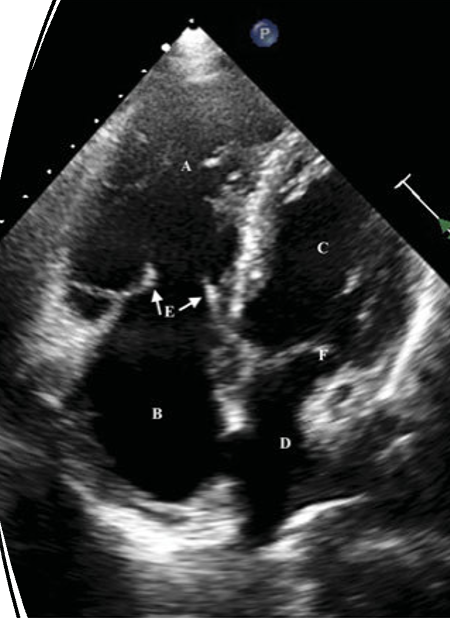
_______________ occurs when large amounts of vasoactive substances such as serotonin, tachykinins, and prostaglandins reach the right side of the heart, consequent to reduced hepatic metabolism from extensive metastatic liver involvement of the carcinoid tumor.
Carcnoid heart disease
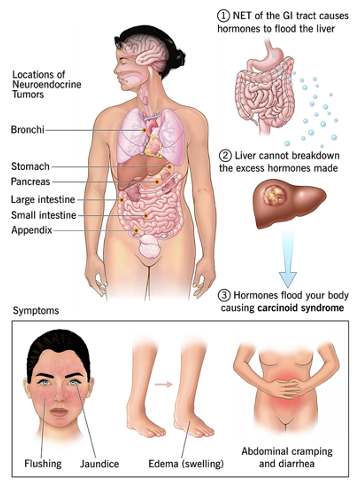
This is?
Carcinoid Syndrome
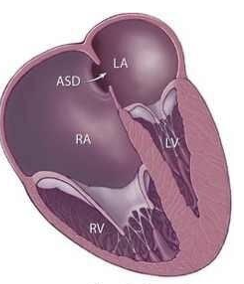
_________________occurs as a baby develops in the womb. The exact cause is unknown. The use of certain drugs (such as lithium or benzodiazepines) during pregnancy may play a role. The condition is rare.
Ebstein’s Anomaly
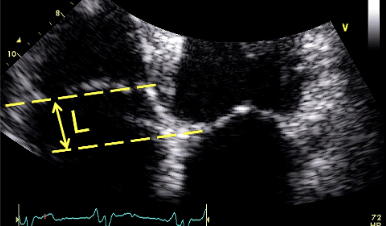
Index = L / BSA
This is?
> 8mm/m² Ebstein Anomaly
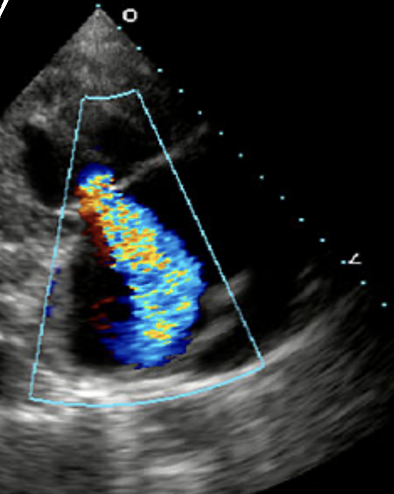
The most common cause of Tricuspid Regurgitation is?
Secondary (functional)
An increase in size of the right atrium or right ventricle, causing annular dilatation
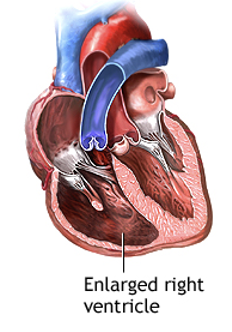
What are the Secondary Causes of TR?
Pulmonary HTN (Abnormal high blood pressure in the lungs)
RV Dysfunction. Lt Heart Disease(such as mitral stenosis)
Pulmonary Stenosis
What are the symptoms of TR?
•often doesn't cause signs or symptoms until the condition is severe. You may be diagnosed with this condition when having tests for other conditions
•Noticeable signs and symptoms of tricuspid valve regurgitation may include:
•Fatigue
•Declining exercise capacity
•Swelling in your abdomen, legs, or veins in your neck
•Abnormal heart rhythms
•Pulsing in your neck
•Shortness of breath with activity
What is the MURMUR of TR?
Holosystolic murmur
Increase with inspiration
TR murmur that is more easily heard with inspiration is referred to as the : ?
Rivero-Carvallo’s sign
What are the treatment options of TR?
Usually, secondary problem
Annuloplasty
TV Replacement
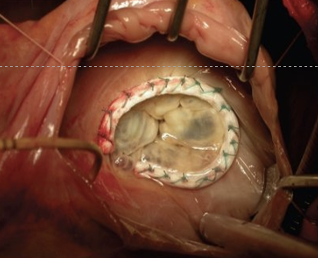
What is this?
Annulopasty
What are the COMPLICATION/SIGNS & SYMPTOMS of TR?
•Enlarged RA, RV, IVC, Hepatic veins, SVC & Neck veins
•leg & abdominal swelling
•liver enlargement & portal HTN
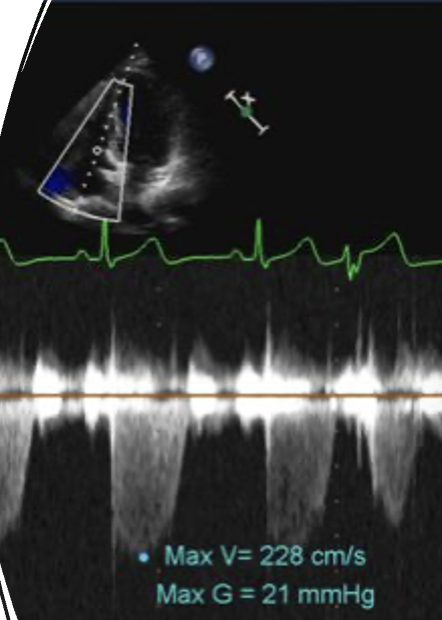
__________is used to estimate right side pressures in the vessels leading to the lungs. This is used to determine pulmonary hypertension.
Right Ventricular Systolic Pressure (RVSP)
What is the formula of the RVSP?
TR Vmax + PAP - RVSP
•PAP elevation
•caused by another disease
•not a disease of pulmonary vessels
•identified by:
-elevated SPAP
-elevated PVR (The resistance the RV must overcome
This is?
Pulmonary Hypertension (PHTN)
•Chronic, an incurable subgroup of PH
•PAP elevation
•Caused by pulmonary vessel disease
•Identified by:
-elevated SPAP (> 25 mmHg at rest or > 30 mmHg with exercise)
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
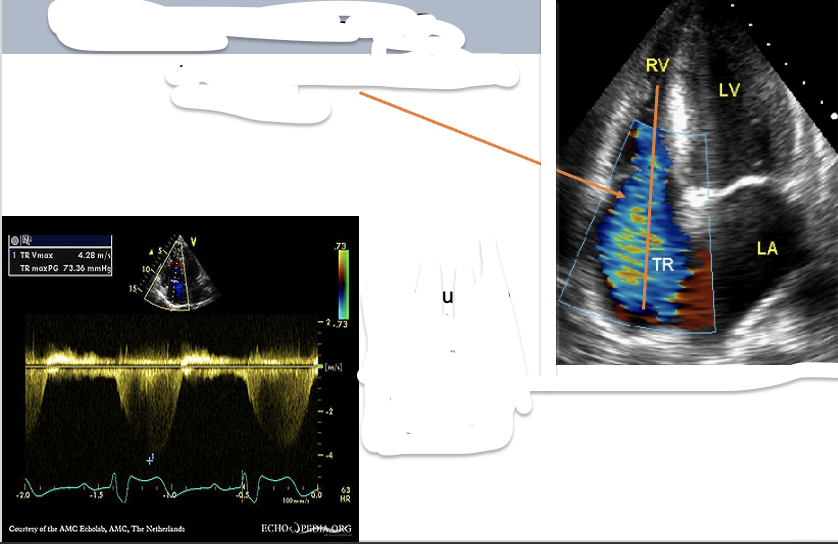
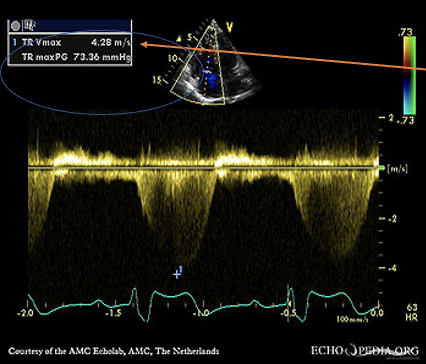
How to obtain the RVSP/SPAP?
TRMax PG + RAP = RVSP
1. Place the CW cursor through the TR color jet
2.Measure the tricuspid regurgitant waveform to achieve the tr velocity
3.The machine will use the TR Vmax velocity and turn it into a pressure gradient. This is done by using the bernoulli equation
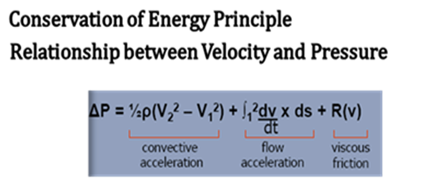
This is?
Bernoulli Equation

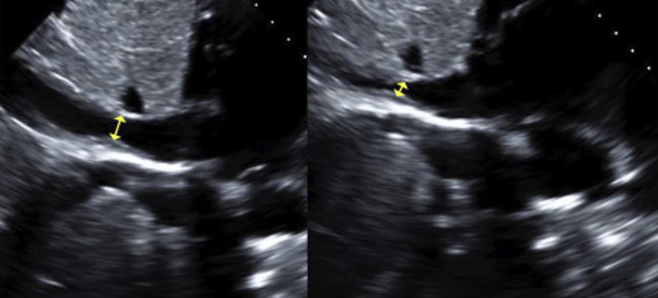
Evaluate the IVC to achieve the ____________?
Right Atrial Pressure
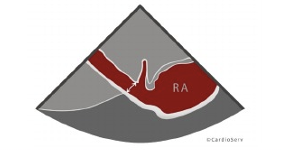
open IVC to its fullest
perpendicular to vessel
1-2 cm away from RA
inner -to- inner
abnormal >2.1 cm
Measure IVC
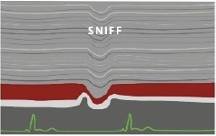
patient must stiff
M-mode perferred
do not measure at Ra junction
normal >50%
abnormal <50%
IVC Collapsibility
What is determined by the TR?
RVSP / Systolic Artery Pressure (SPAP)
TR Max PG + RAP = RVSP/SPAP
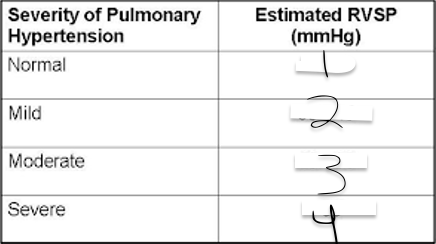
1?
<35
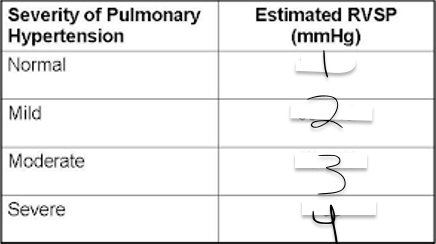
2?
35-45
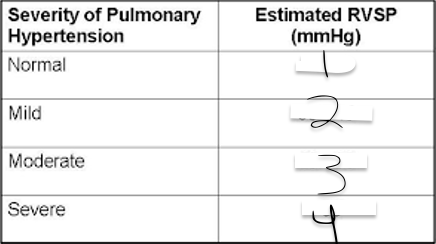
3?
46-60
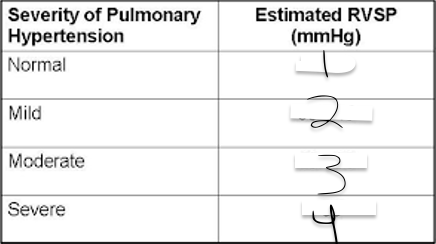
4?
>60
Normal RAP, 3mmHg, Normal IVC Size, what is the Collapse?
Normal
Intermediate RAP, 8mmHg, Normal IVC Size, what is the Collapse?
Abnormal
Intermediate RAP, 8mmHg, Abnormal IVC Size , what is the Collapse?
Normal
High RAP, 15mmHg, Abnormal, what is the Collapse?
Abnormal
What is the assessment of TR by ECHO?
2D, COLOR, SPECTRAL
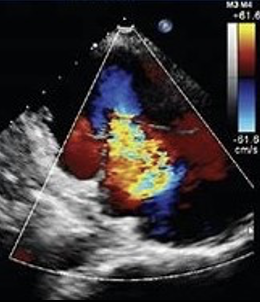
This is?
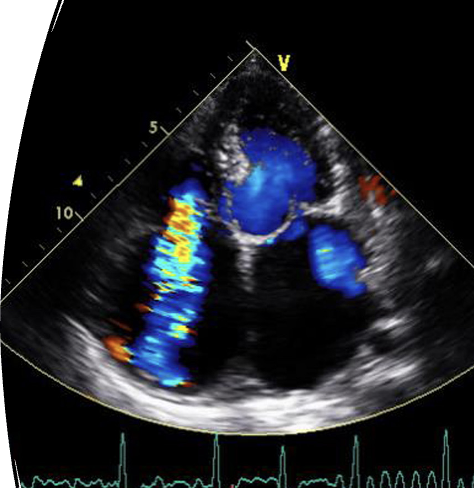
TR in RVIT
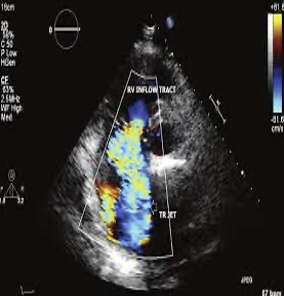
This is?
TR in SAX AO
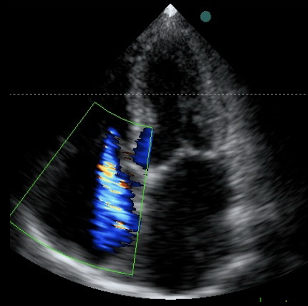
This is?
TR in 4CH
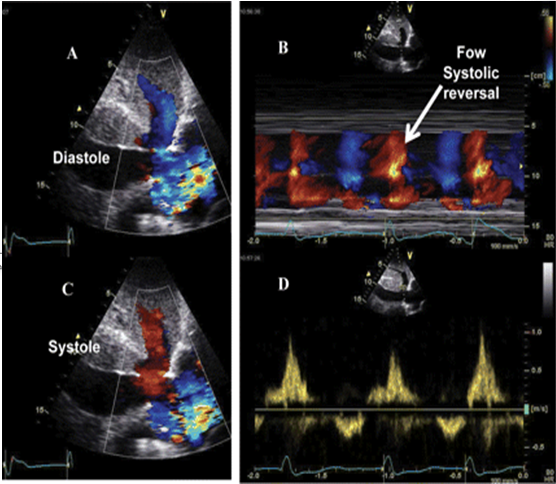
Normal hepatic vein flow travels away from the transducer towards the IVC and is encoded in ______
Blue
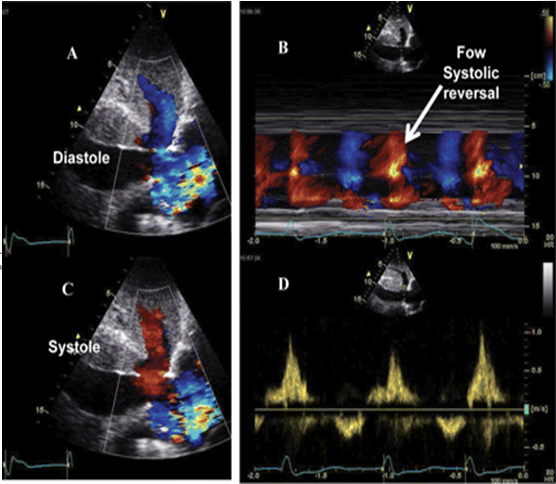
TR flowing into the IVC & Hepatic veins will flow towards the transducer during systole and is encoded in _________
Red
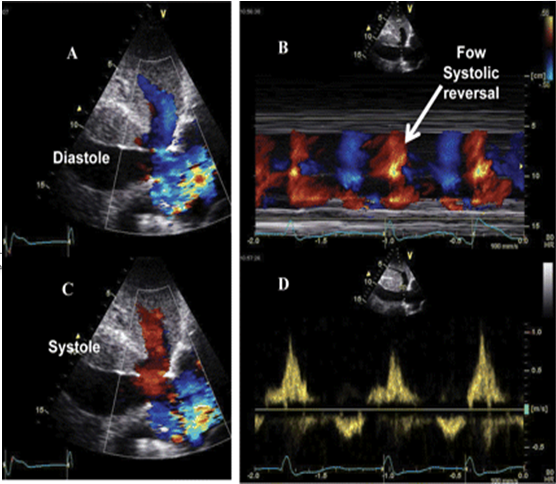
On the spectral waveform, this systolic flow will appear a_______
above the baseline (antegrade)
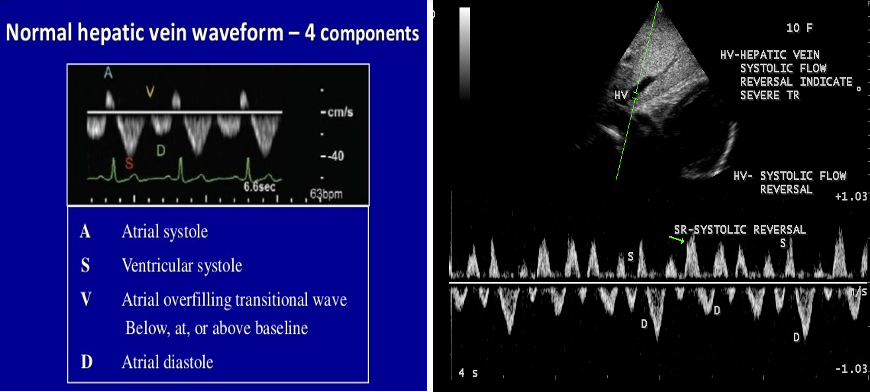
The hepatic vein waveform can be __________________
reflective of the severity of TR present
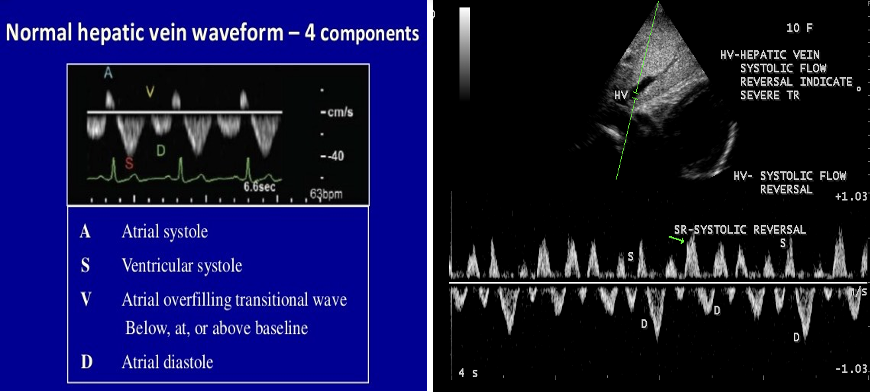
The more severe the regurgitation, the ________________________
more pulsatile the hepatic waveform becomes.
How to prove Severe TR?
Hepatic vein Flow Reversal
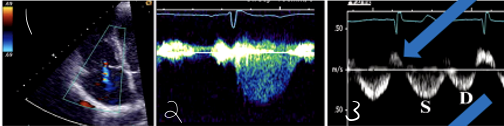
1?
Mild TR in Color Doppler
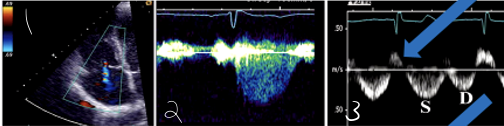
2?
Mild TR CW Doppler
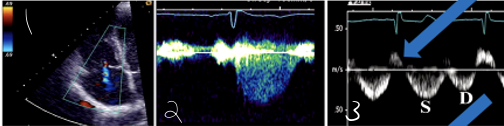
3?
Mild TR in Hepatic Vein Flow (PW)
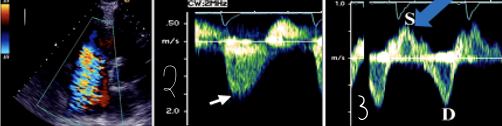
1?
Severe TR in Color Doppler
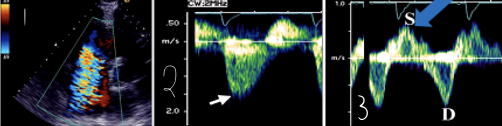
2?
Severe TR in CW Doppler
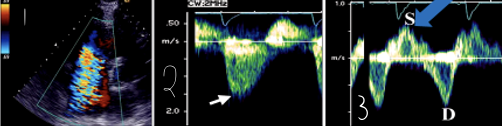
3?
Severe TR in Hepatic vein Flow (PW)
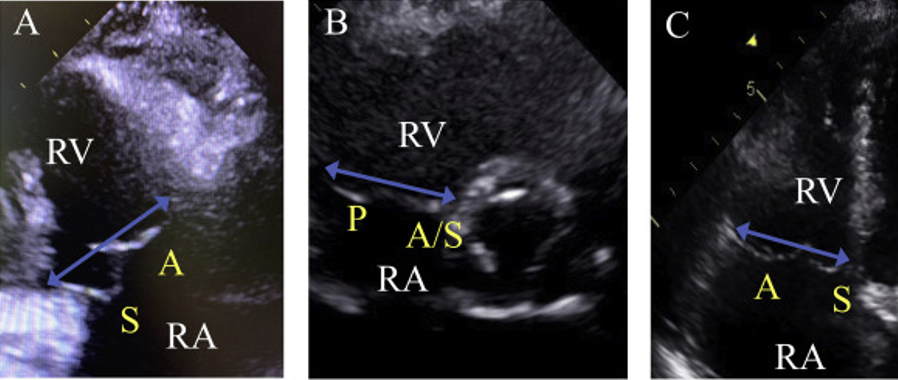
_____________is an infrequent echocardiographic finding that is most commonly associated with mitral valve prolapse.
Trcuspid Valve Prolapse
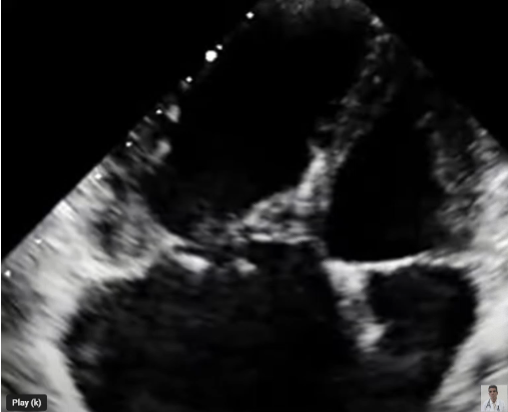
TR caused by____________is most often post-traumatic, is caused by endocarditis or is a consequence of a myxomatously degenerated valve.
TV Flail