Biology Unit 1: Biomolecules
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
electronegativity
atoms ability to attract electrons
atom vs ion vs molecule
atom: smallest unit of an element, ion: charged atom or molecule, molecule: two or more atoms bonded together
cohesion vs adhesion
Cohesion: Water is attracted to water, and Adhesion: Water is attracted to other substances
polar vs nonpolar
polar covalent bonds involve partially positive and negative ends due to unequal sharing of electrons, and nonpolar covalent bonds have equal or nearly equal distributions of electrons, allowing for a neutral molecule
polymer vs monomer
polymers are formed from multiple monomers connected together - monomer is a single subunit of a macromolecule - ex.glucose, while polymer is a large molecule formed from repeating subunits
functional group
a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule
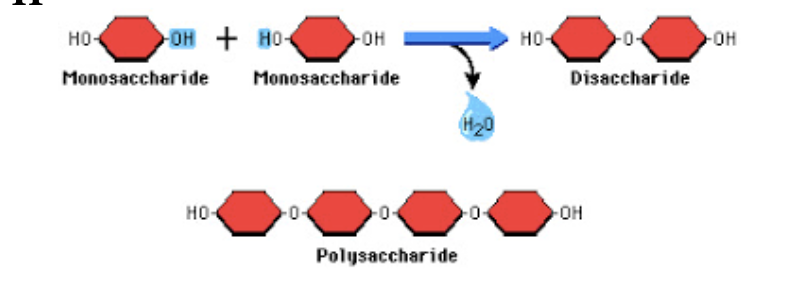
dehydration synthesis
aka polymerization - building polymers
removing H20 (water) molecules to attach molecules
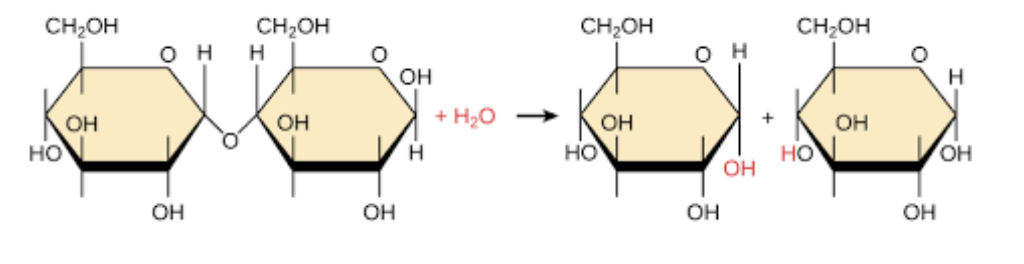
hydrolysis
aka depoylmerization - breaking polymers apart
adding. H20 molecules to break bonds
macromolecules
biomolecules are an example
made by polymerization - making large molocules from smaller molocules
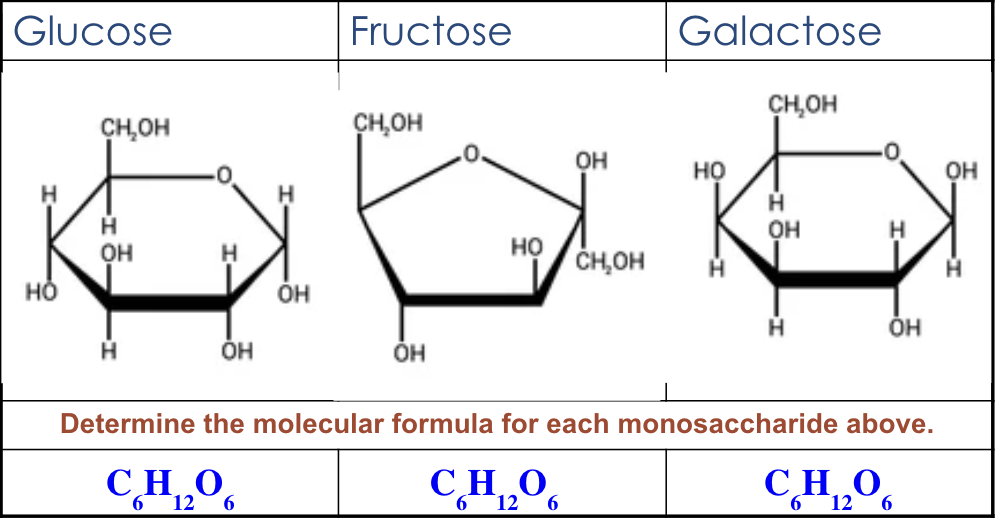
carbohydrates - what is it? polar v nonpolar? elements inside + ratio? monomer and polymer examples? functions?
sugars - starch, cellulose
CHO - 1:2:1
usually polar
monomer: monosaccharides (glucose)
polymers: disaccharides (sucrose), polysaccharides (starch, glycogen - long term storage - cellulose)
functions: store short term energy, structural support such as cell walls in plants
protein - what is it? polar v nonpolar? elements inside + ratio? monomer and polymer examples? functions?
meats, eggs, beans, nuts
made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur.
monomers: amino acid
polymers: polypeptide
functions: muscles, hormones, immune system, transport, enzymes, storage, structural, receptors (signaling + communication)
lipids - what is it? polar v nonpolar? elements inside + ratio? monomer and polymer examples? functions?
wax, oil, fats
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen - mostly C+O
monomers: fatty acids and glycerol
polymers: triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
functions: store energy (long term), insulation, organ cushioning, makeup cell membranes, waterproofing
nucleic acids - what is it? polar v nonpolar? elements inside + ratio? monomer and polymer examples? functions?
rna and dna
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
monomer: nucleotides (a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen containing base)
polymer: dna, rna
function: store + transmit genetic information
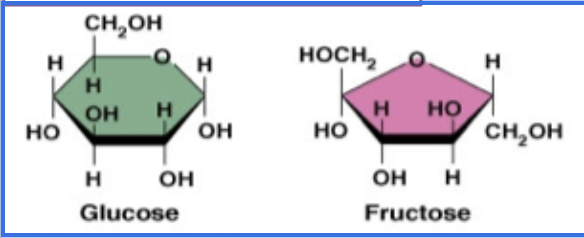
these are examples of?
monosaccharides
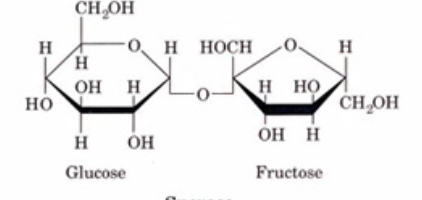
these are examples of?
disaccharides
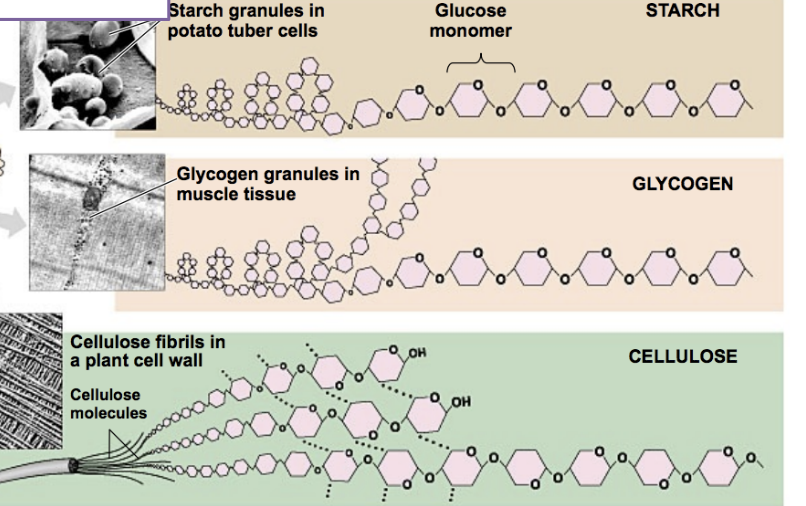
examples of?
polysaccharides
why does shape matter in biomolecules?
determines function
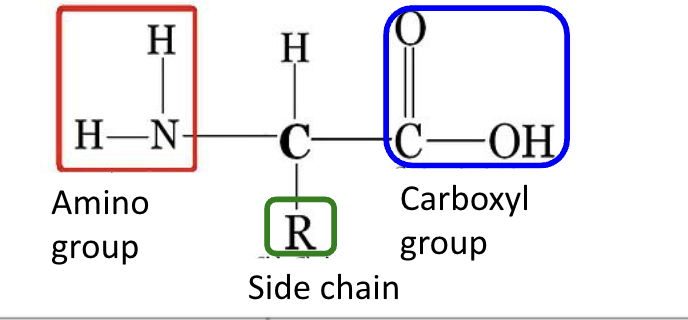
primary structure of protein
amino group, side chain (R ), carboxyl group
amino acids
building blocks for proteins
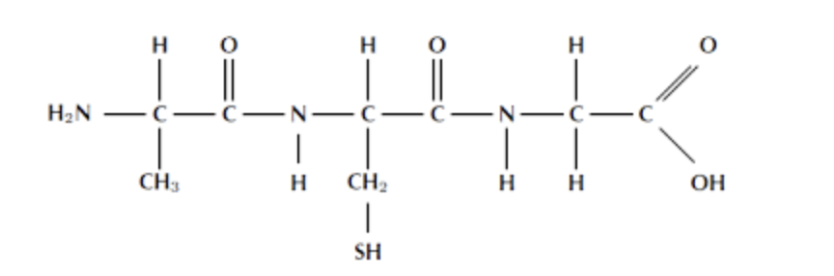
what is this
polypeptide - long chain of amino acids, help to create proteins
peptide bond
covalent bonds of amino acids to create proteins
nucleotide
a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen containing base
unsaturated vs saturated fats
UNSATURATED: fatty acids contain 1 or more double bonds between C atoms (liquid at room temp, plant based oil) -BENT FIGURE
SATURATED: fatty acids have only single covalent bonds between C atoms (solid at room temp, animal based oils) - STRAIGHT FIGURE
cis vs trans bonds
cis - on same side, trans - on opposite sides
trans fat
maufactured fats
positive control vs negative control
positive control: contains what material is being tested for, negative control: does not contain what material is being tested for
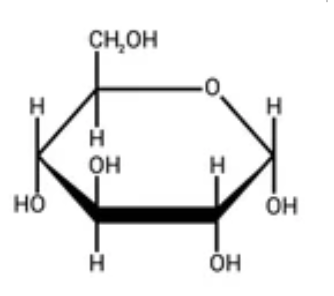
glucose - monosaccharide - C6H1206
how are hydrogen bonds different than other bonds?
weak bond formed between a (partial) positively charged hydrogen atom and other (partial or full) negatively charged atoms
six main elements that make up all living things?
CHNOPS
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur
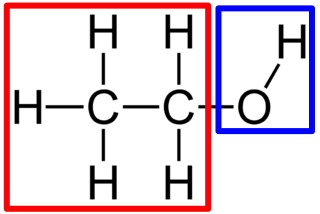
hydroxyl group
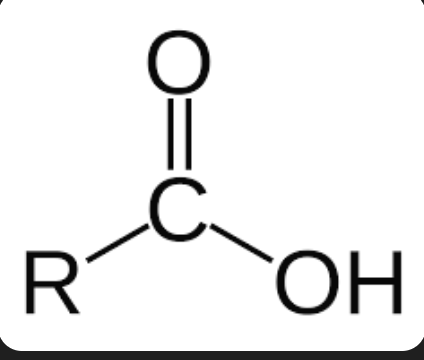
carboyxl group
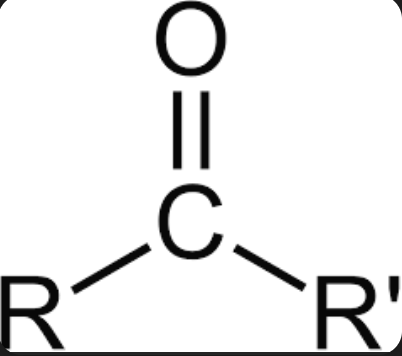
carbonyl group
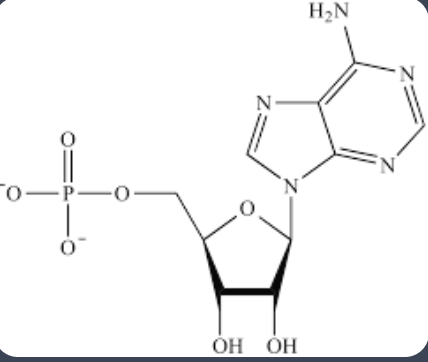
phosphate group
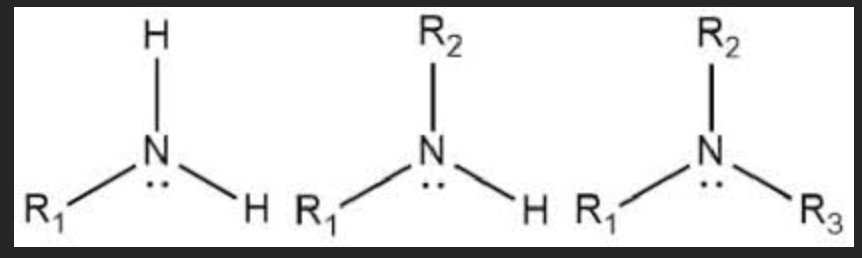
amine group
how do functional groups affect the structure and behavior of organic molecules?
physical properties (polarity, solubility, and boiling point) and chemical reactivity (acidity, basicity, and the types of reactions)
why is carbon so versatile?
carbon has four valence electrons so it can make four bonds
carbon skeletons - “backbone”
bond with it self as well as HNO
what is this
hydrolysis
what is this
dehydration synthesis
what part does water play in reactions?
when water is added in a reaction, one molecule gains OH and one gains H, and the bond is broken
when water is removed in a reaction, one molecule loses OH and one loses H, and a bond is made
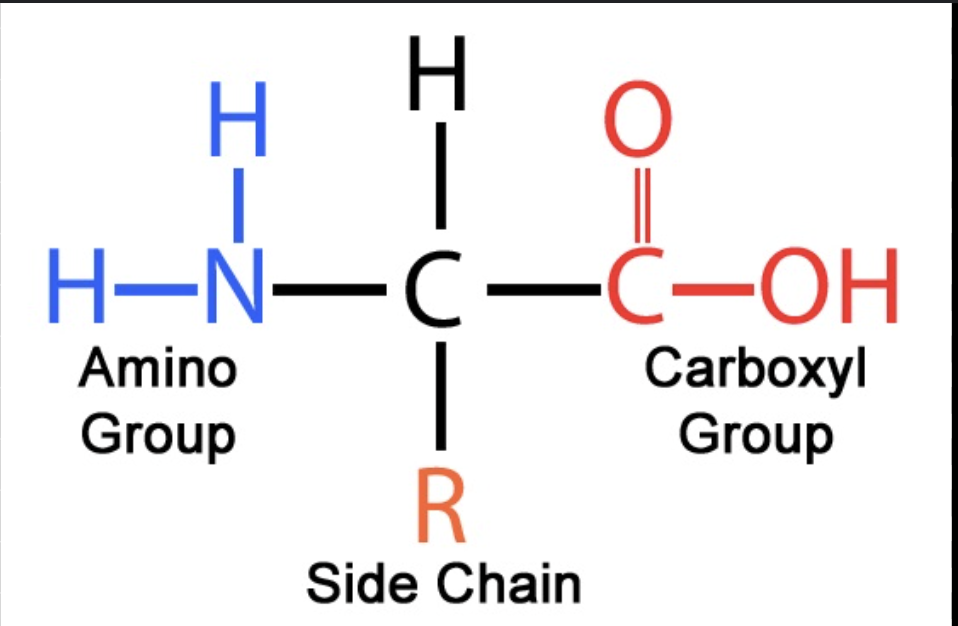
amino acids
chart of each macromolecule