BIO EXAM 2
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
What is the correct species name of humans?
Homo sapiens
A phylogeny contains fish, lizards, salamanders, and lampreys. Fish, lizards, and salamanders all contain jaws. Lampreys do not have jaws. 'Jaws' are considered a:
shared derived character
A virion (single virus particle) typically consist of which three components?
capsid, nucleic acid core, envelope
Which of the following is NOT one of the competing hypotheses for how viruses evolved?
Tranposable exobiosis: Transposable elements gained an envelope protein from their host bacteria which allowed them to persist outside the cell
Which is NOT a potential strategy to combat a human virus such as SARS CoV-2?
phage therapy
Which is NOT true of Gram negative bacteria
turn purple when stained because more stain sticks in their thick cell wall
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. (t/f)
True
An organism that can survive and grow at high temperatures (80-120c) are ___ and are classified
extremophiles/archaea
During travel to central Africa, you contracted an infection with symptoms of fever, weakness, and lethargy, along w blood sample and finds parasitic protozoa. You are most likely infected with organisms belonging to which clade?
Excavata (e.g., Trypanosoma)
Which Eukaryote clade contains red algae, green algae, and all land plants?
Archaeplastida
Prokaryote
no nucleus, no organelles, cells 1 um diameter, cell division by binary fission, flagella that spin
Eukaryote
flagella that wave side to side, chromosomes organized by histones, mitosis, meiosis, nucleus, mitochondria, cytoskeleton
What is the correct level of taxonomic classification for Protists?
None of these. Protist is an informal designation.
Endosymbiotic theory accounts for the origin of which component of a eukaryotic cell?
mitochondria
Which of the following was derived from an ancestral cyanobacterium?
chloroplast
fungi usually ____ their food
absorb
An unknown organism can be excluded from classification as a fungus if it
has chlorophyll and cell walls made of cellulose
Mycorrhizal fungi growing in association with plant roots and providing more water and/or nutrient uptake
mutualistic
Without fungi, human civilization would not have
All of the above (Wine, beer, bread, penicillin)
The nonvascular plant clades (including moss) require liquid water for fertilization during sexual reproduction
flagellated sperm must swim to fertilize the egg.
What characteristic do plants, algae, and some bacteria have in common that is not shared with fungi or animals?
They are photosynthetic
The most direct ancestors of land plants were probably
green algae
In land plants (and some algae), the sporophyte and gametophyte exhibit different levels of ploidy: Sporol
diploid, haploid
Which is the most recent plant adaptation to have evolved?
flowers
What is a fruit?
a mature ovary
are not classified as a gymnosperms.
flowering plants
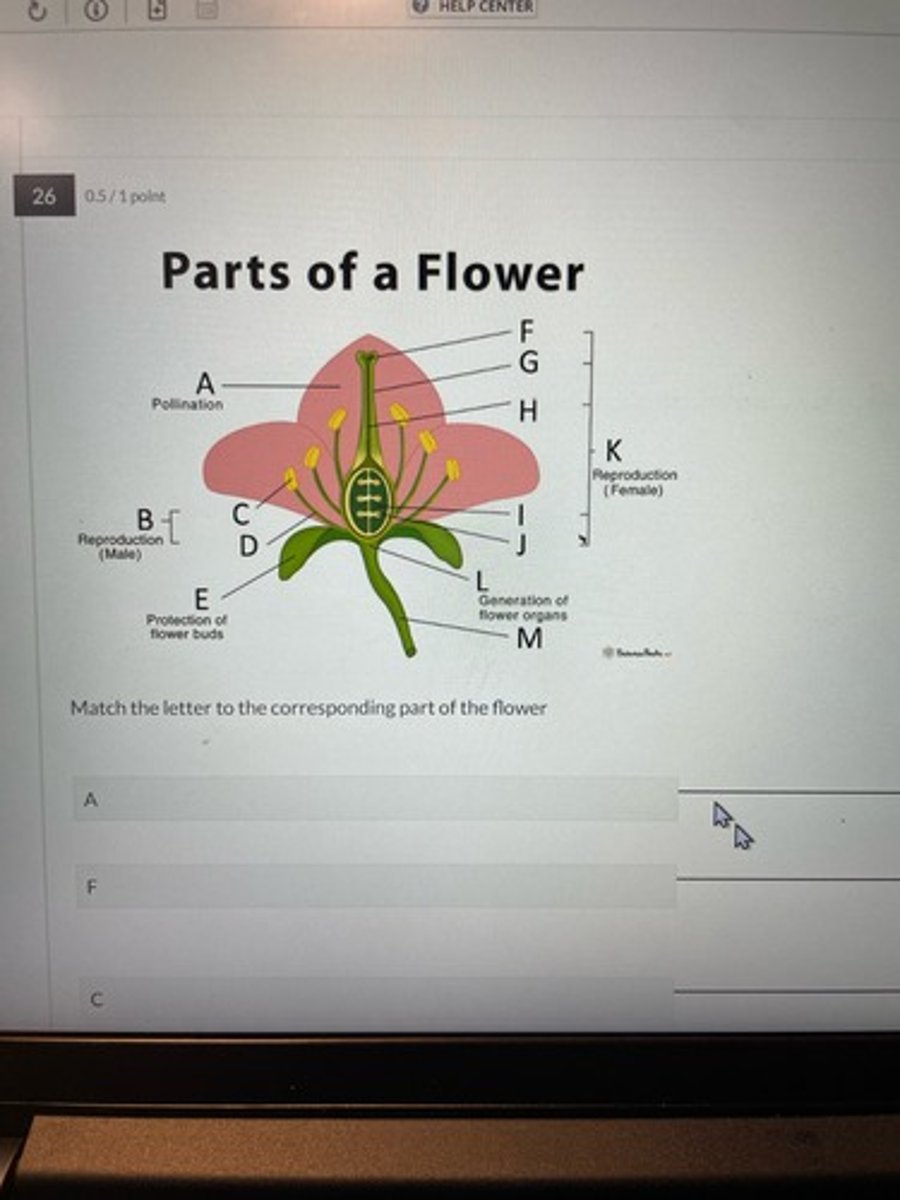
Parts of a flower
A: petal
F: stigma
C: anther
K: carpel
G: style
B:stamen
The last common ancestor of fungi and animals was most likely a
single celled eukaryote
All animals have true tissues. (t/f)
false
What defines radial symmetry?
Any plane of symmetry passing through the center of the organism splits it into equal halves.
What happened during the Cambrian explosion?
Most living phyla of animals rapidly appear in the fossil record.
How many of the animal phyla include unicellular animals?
0
What do fungi and arthropods have in common?
Both groups use polysaccharide chitin for support.
Which of the following is NOT a key advantage provided by the exoskeleton of terrestrial arthropods
it grows with the arthropod throughout its life
Myriapods provide first fossil evidence of animals on land. Myriapods belong to which phylum?
Arthropoda
Animals (such as butterflies or beetles) that undergo radical changes between larval and adult stages are
Holometabolous
The echinoderms are most closely related to the
Chordates
Which of the following is found in all major groups of vertebrates?
skull
The earliest known mineralized (bony) structures in vertebrates are associated with
feeding
Jawless fishes (cyclostomes) include:
hagfish and lamprey
Which statement about the amphibians is FALSE?
They lay yolky eggs with a protective shell.
Which is NOT a member of the amniote clade?
apoda (legless amphibians called caecilians)
Which of the following is a reason that it is important to understand the causative organism of a disease?
antibiotics are an ineffective therapy for viral infections
viruses
chicken pox, influenza, aids, covid-19, ebola
Bacteria
strep throat, e coli, cholera, bubonic plague, tuberculosis, salmonella, lyme disease, typoid fever
protist
chagas disease, trichomoniasis, giardia , malaria
Animnal
dog heart worm, tapeworm
rank order(domain, kingdom, gensus..)
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, gensus, species
What is the spillover effect?
when a virus evolves to infect a new species
Whats a primary goal anocated with bioremedation
to clean up areas polluted with
Domain
The biggest classification level, encompassing billions of organisms.
Species
The smallest classification level, representing one kind of organism.
Example of Human Classification
Eukarya → Animalia → Chordata → Mammalia → Primates → Hominidae → Homo sapiens
Memory trick for classification
Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Soup
Viruses
Viruses are not cells and not alive on their own; they must invade a host cell to reproduce.
Composition of Viruses
Made of DNA or RNA + protein coat.
Spillover Event
When a virus evolves to infect a new species, e.g., bat virus → human virus.
Vaccines
Help prevent infection by viruses.
Antiviral drugs
Slow virus copying.
Phage therapy
Does NOT work on viruses because phages only kill bacteria.
Regressive theory of virus origin
Viruses used to be bigger life forms, then lost parts.
Progressive theory of virus origin
Viruses started as pieces of DNA that escaped cells.
Virus-first theory
Viruses existed before any cells did.
Bacteria
Prokaryotic organisms with loose DNA inside the cell, can be helpful or harmful.
Gram Stain
A method to determine the type of cell wall a bacteria has.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Stain purple, have a thick cell wall, easier to kill with antibiotics.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Stain pink, have an extra outer layer, harder to treat.
Superbugs
Bacteria that antibiotics no longer kill because they evolved resistance.
Prokaryotes
Bacteria that lack a nucleus and organelles, reproduce via binary fission.
Eukaryotes
Organisms like plants, animals, fungi, and protists that have a nucleus and organelles.
Protists
Eukaryotes that are NOT plants, animals, or fungi; they are a mixed group.
Important Protist Diseases
Malaria, Giardia, Chagas Disease, Trichomoniasis.
Endosymbiotic Theory
Eukaryotic cells formed when one cell swallowed another, leading to mutual living.
Slime Molds
Protists that can resemble fungi; include plasmodial and cellular slime molds.
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms with chitin cell walls that absorb food from the environment.
Fungi Sexual Cycle
Includes plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis to produce spores.
Plant Evolution Order
Mosses → Ferns → Gymnosperms → Angiosperms.
Animal Evolution & Body Plans
All animals are multicellular and eukaryotic; body cavities form in the mesoderm layer.
Symmetry in Animals
Radial symmetry can be cut evenly many ways; bilateral symmetry has one cut for equal halves.
Chordates
All chordates have a notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and post-anal tail.
Mammals
Divided into monotremes, marsupials, and eutherians based on reproductive traits.
What is a primary goal associated with bioremediation?
to clean up areas polluted with toxic compounds by using bacteria
Which of the following is correctly described as a primary producer
diatom
green algae differ from land plants in that some green algae
are unicellular
Which clade best fits this description? Phytoplankton with silica (glass) shells that are mined from fossilized sediments for use as abrasives and other purposes. These algae also make a significant contribution to oxygen production.
diatoms
According to the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells, how did mitochondria originate?
alpha-proteobacteria
Endosymbiotic theory accounts for the origin of which component of a eukaryotic cell?
mitochondria
Many multicellular fungi form super-organisms through __ followed by __
plasmogamy/karyogamy
Which of these is not a common fungal pathogen of plants?
ringworm
To which group does the fungus responsible for global amphibian declines belong?
chytridomycota
As you stroll through a moist forest you are most likely to see a
gametophyte of a moss
The tall ferns that we typically see in the tropics and temperate woodlands are the
sporophytes
A trend seen throughout the evolution of the land plants is for the sporophyte generation to become __ and more independent for the gametophyte and the gametophyte generation to become ___ and more dependent
increased, reduced
Not all plants have seeds. What advantage do seeds provide a plant?
Plants with seeds are not dependent on water for reproduction
Which land plant clade has the greatest number of species?
angiosperms
Pollination happens when male gametophyte is transferred to a female gametophyte. (If all goes well, fertilization will follow this step, resulting in a new sporophyte generation.) Pollen can be transferred from a male strobilus to a female strobilus, or from a male flower (or flower part) to a female flower (or flower part). Pollination is part of the life cycle in
gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Which of the following is NOT a feature common to most animals?
asexual reproduction
Which is a shared derived character of animals belonging to the bilaterian clade?
three embryonic germ layers
The body cavity of coelomate animals develops within the
mesoderm
All animals have true tissues.
False