Cancer Biology: Hallmarks, Cell Cycle, and Molecular Mechanisms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the 'Multistep Nature' of cancer?
Cancer is the accumulation of multiple genetic mutations over time, each providing a 'Hallmark' advantage.
What are the 6 original 'Hallmarks of Cancer'?
Self-sufficiency, Insensitivity, Evading Apoptosis, Limitless Replication, Angiogenesis, Invasion/Metastasis.

How does a cell achieve 'Self-sufficiency in growth'?
By constitutively activating pathways like EGFR, Ras, or Raf.
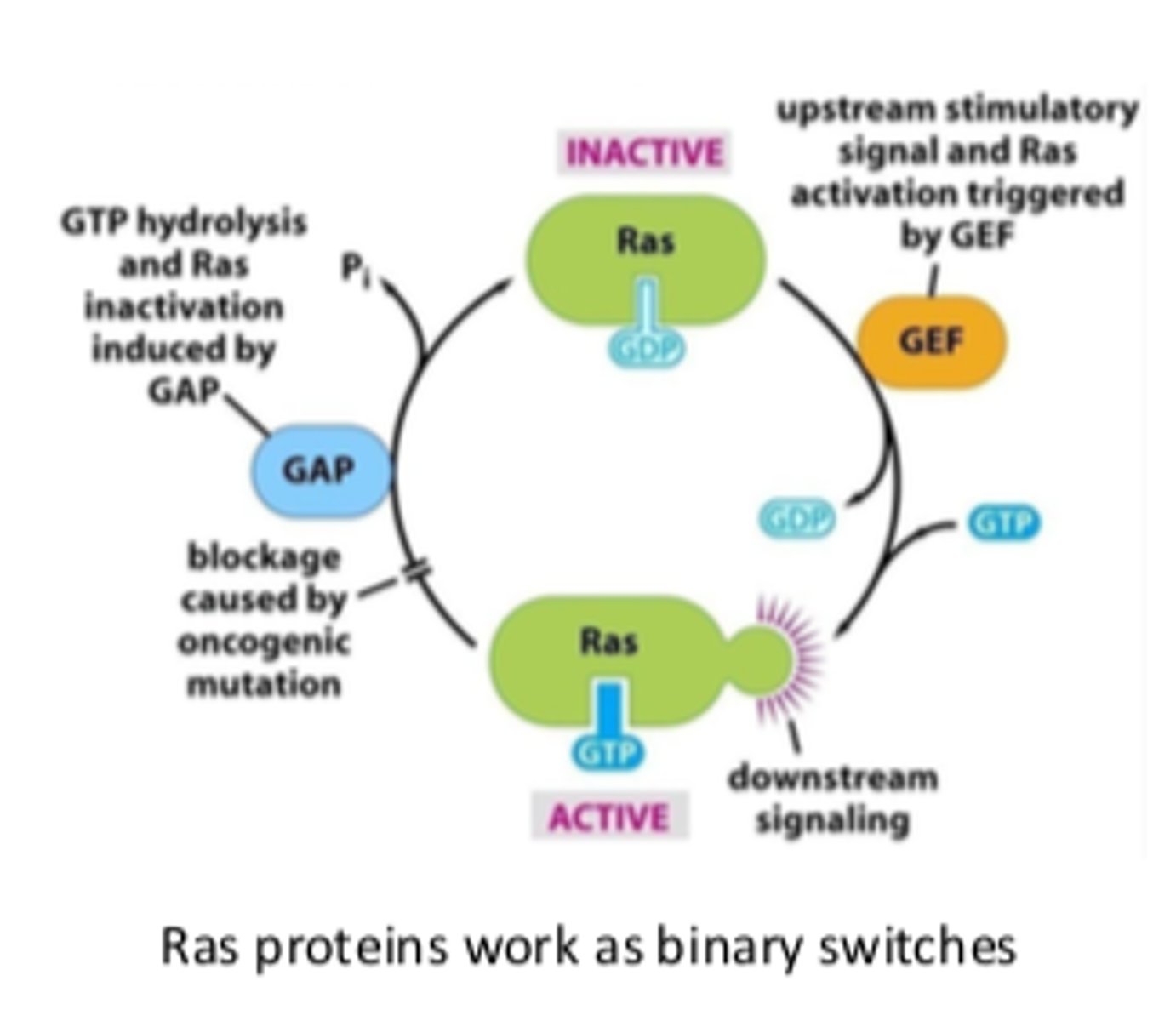
What is the 'Restriction (R) Point' in the cell cycle?
The 'Master Gate' in the G1 phase controlled by pRb; once passed, the cell must divide.
How does HPV's E7 protein 'break the brakes'?
E7 binds to pRb, forcing it to release E2F, bypassing the G1 checkpoint.
Why is p53 called the 'Guardian of the Genome'?
It senses DNA damage and triggers DNA Repair, Cell Cycle Arrest, or Apoptosis.
How does HPV's E6 protein 'silence the guardian'?
E6 binds to p53 and targets it for degradation, preventing the cell from stopping division.
What does a high 'N:C Ratio' look like on an H&E stain?
The nucleus is disproportionately large compared to the cytoplasm, indicating a malignant cancer cell.
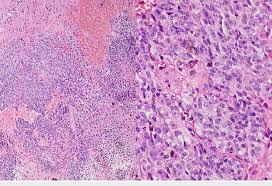
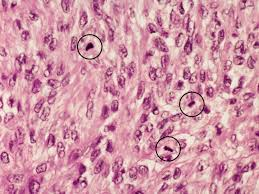
What is a 'Mitotic Figure' and what does it indicate?
It looks like 'spilled ink' or a 'tangled ball of wool' and indicates active cell division.
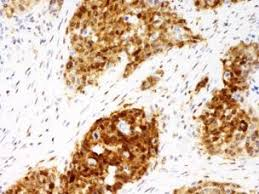
What does strong brown nuclear staining in a p53 IHC indicate?
It indicates Mutant p53, which is stable and accumulates in the nucleus.
What is a 'Koilocyte'?
A cell with a dark, shrunken nucleus surrounded by a clear 'halo', a marker for HPV infection.
What molecular 'scissors' enable 'Invasion and Metastasis'?
MMPs (Matrix Metalloproteinases) digest the basement membrane, allowing cells to invade tissues.
What is 'Sustained Angiogenesis' and what molecule triggers it?
The tumor growing its own blood supply, triggered by VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor).
How do cancer cells achieve 'Immortality'?
By reactivating Telomerase, which rebuilds the ends of chromosomes.
What is the '11th Hallmark' (Altered Differentiation)?
Loss of normal cellular differentiation, with tumour cells remaining primitive and undifferentiated.
How do you identify 'Invasion' in a histology photo?
Look for clusters of tumor cells that have crossed the Basement Membrane into the Stroma.
What is the difference between 'Inactivation' and 'Deletion' of p53?
'Deletion' means no protein is made; 'Inactivation' means a broken protein is made.
Why is the 'Window of Opportunity' vital for HPV/Cancer?
It allows screening to catch cells at the 'Pre-cancer' stage when they are still curable.