Locomotion and Spinal Reflex
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is nociceptive reflex
Pain reflex or flexor reflex where stimulation of pain endings will cause flexion of affected muscle to WITHDRAW from stimulus
What is the pathway for flexor reflex
Passes interneuron of spinal cord → Spread to agonist muscle to withdraw → Inhibit antagonist (reciprocal inhibition)
What is after discharge
How long muscle contraction is sustained after reflex
What is crossed extensor reflex
Affected arm is flexed away from stimuli while the unaffected contralateral arm is extended
Between flexor and extensor, which has a longer afterdischarge
Extensor reflex
What is positive supportive reaction
pressure on footpad in decerebrate animals causes limb to extend against pressure applied to balance
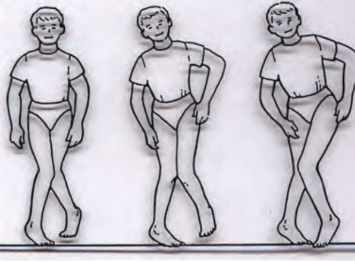
What type of lesion might this patient have
UMN lesion which causes hypertonia → Legs become stiff
What is magnet reaction
Pressure on one side causes extension in that direction
What is cord righting reflex
When animal is laid on its side it will move to try to get into standing position starting from the hea
What is body on body righting reflex
If the head cannot be moved back upright, the body may move upright first
Which phases of the gait cycles are both feet on the ground
Heel strike and pre-swing
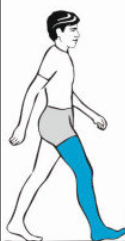
Which muscles are used in heel strike
Tibialis anterior, gluteus maximus
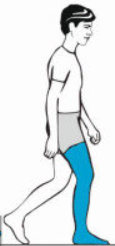
What muscles are used in loading response
Quadriceps femoris
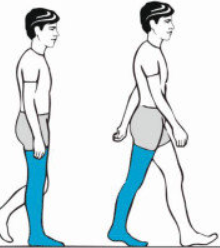
What muscles are used in midstance and terminal (heel off) stance
Triceps surae
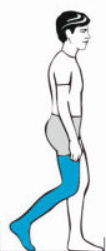
What muscles are used in preswing
Deep plantarflexer, toe flexors, rectus femoris
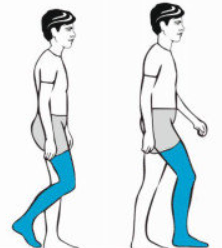
What muscles are used in initial and mid swing
Contralateral abductor of hip, iliopsoas and rectus femoris
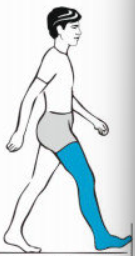
What muscles are used in terminal swing
Hamstring, quadriceps femoris, tibialis anterior
Which parts of the running cycle contributes to higher running speed
Float and swing phases

Describe the walk (and etiology)
Normal walk
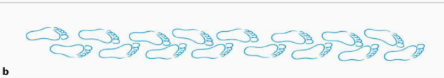
Describe the walk (and etiology)
Short step and stride length + small step width; caused by spinal cord lesion (hypertonia and spastic)
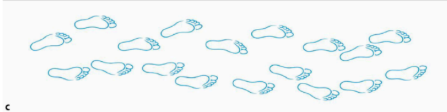
Describe the walk (and its etiology)
Short step and stride length + variable step width; cerebellar lesion → Ataxia

Describe the walk (and the etiology)
Short step and stride length + small step width but similar to normal gait; Parkinsonism or senile gait
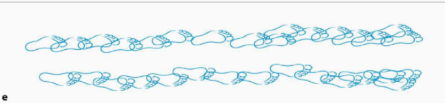
Describe the gait (and its etiology)
Very short step and stride + small step width; magnetic gait caused by frontal lobe lesion