1 - Transient Vision loss 2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
bilateral vision loss/blur episodes with sudden onset that last 2-3min
+/- diplopia if brainstem involved
+/- dizziness
+/- HA
+/- drop spells
+/- ataxia
+/- bilateral numbness of face, mouth
+/- nystagmus
+/- Wallenberg's or Foville's
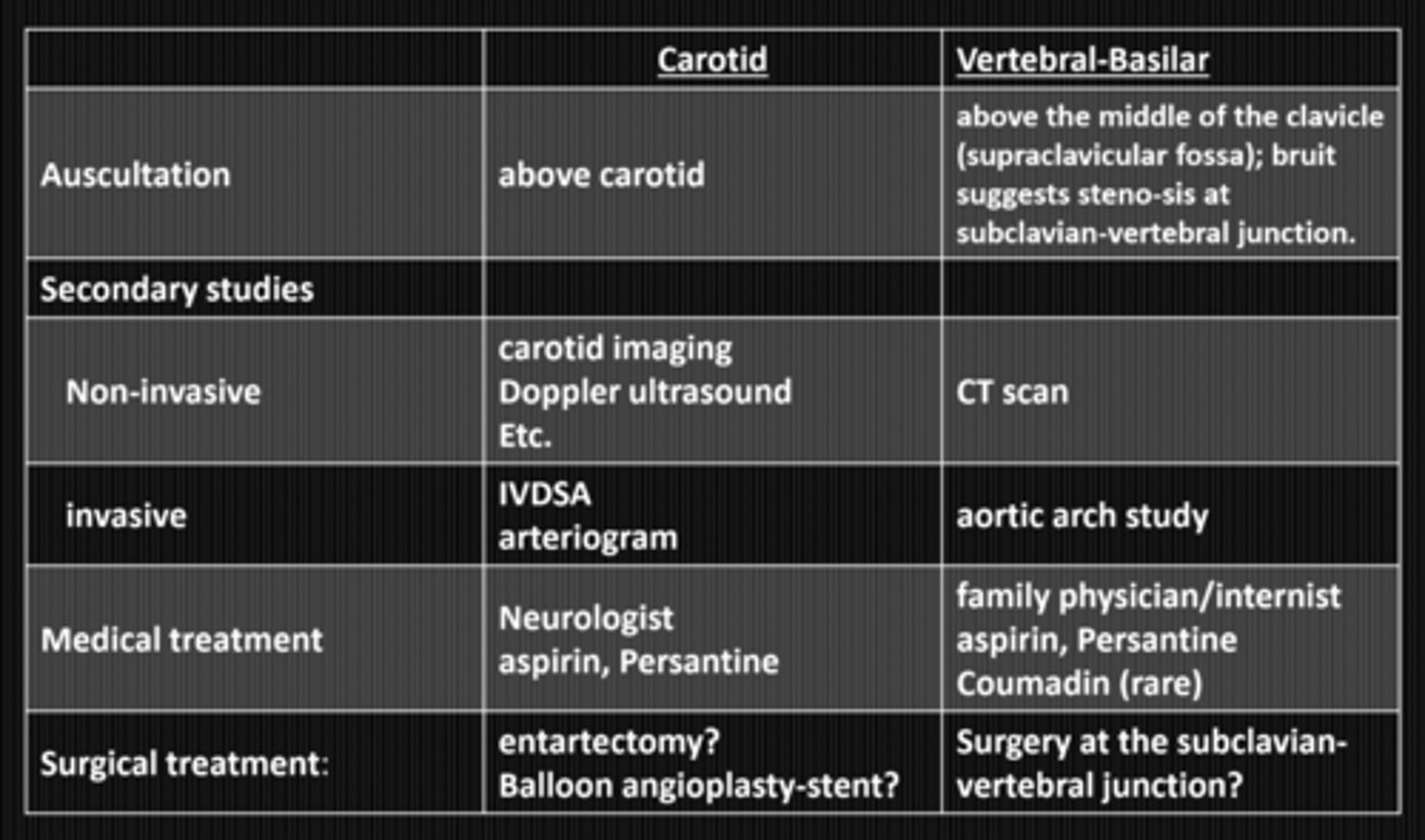
What are some symptoms of vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
same as amaurosis fugax from carotid artery disease
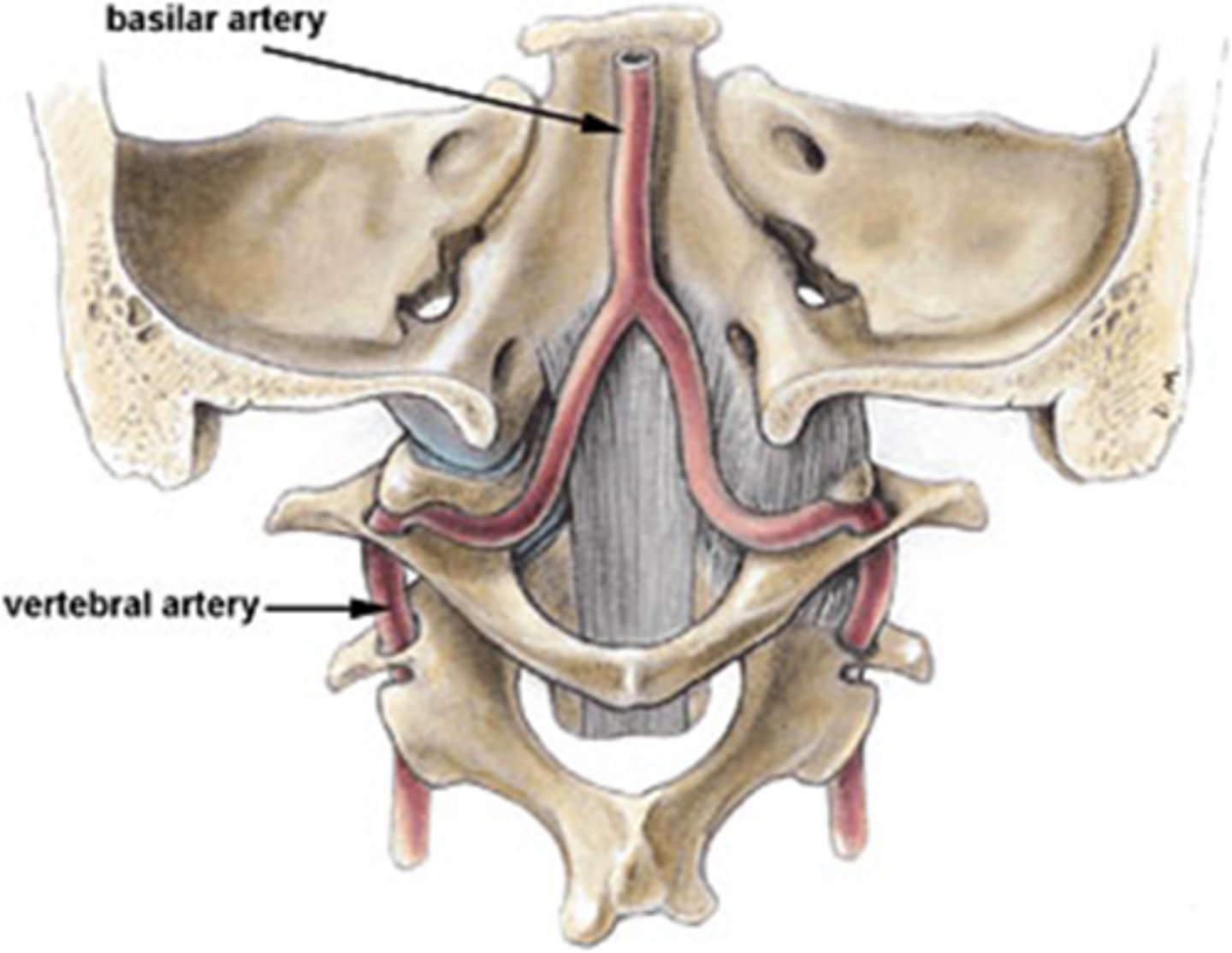
What factors of systemic health and vital statistics contribute to vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
normal
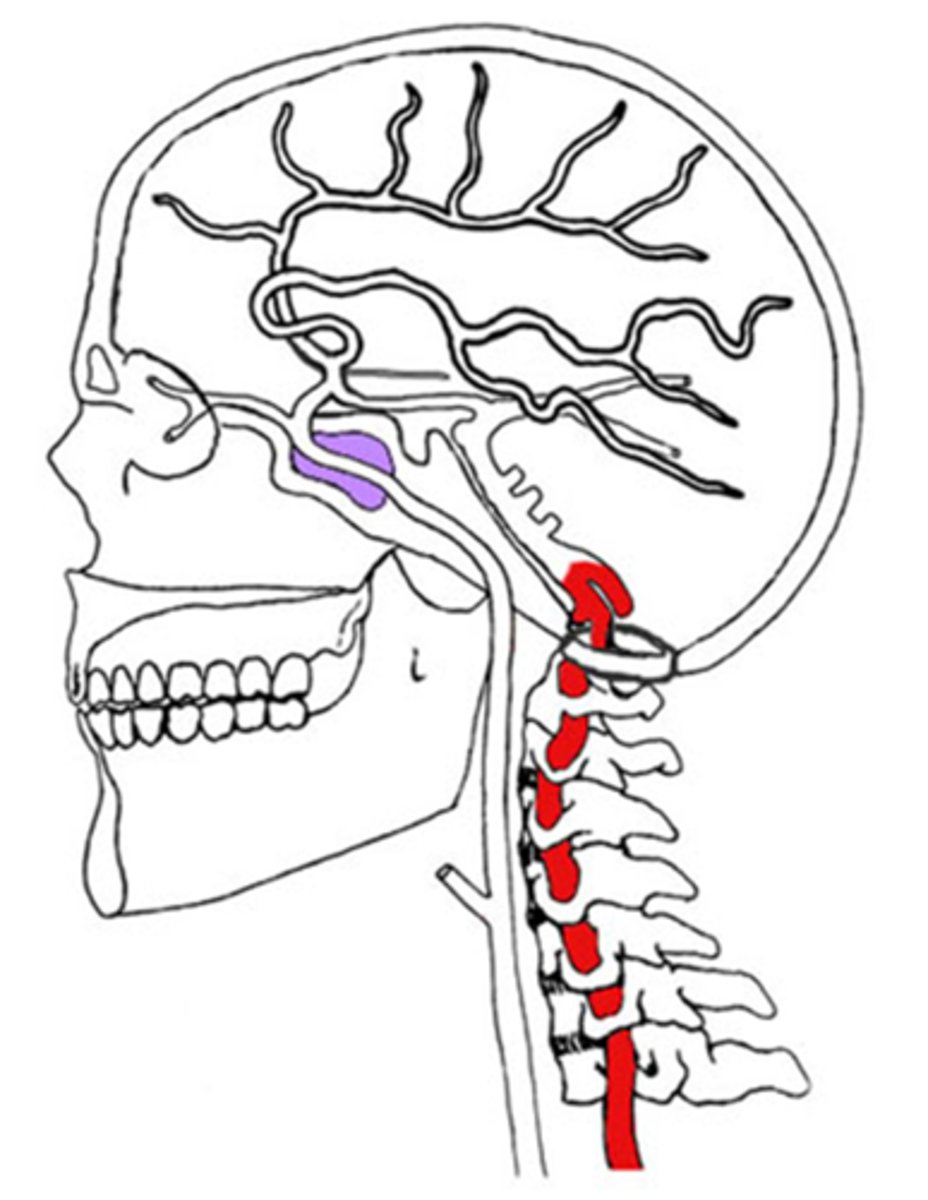
How does vertebral-basilar insufficiency appear upon examination?
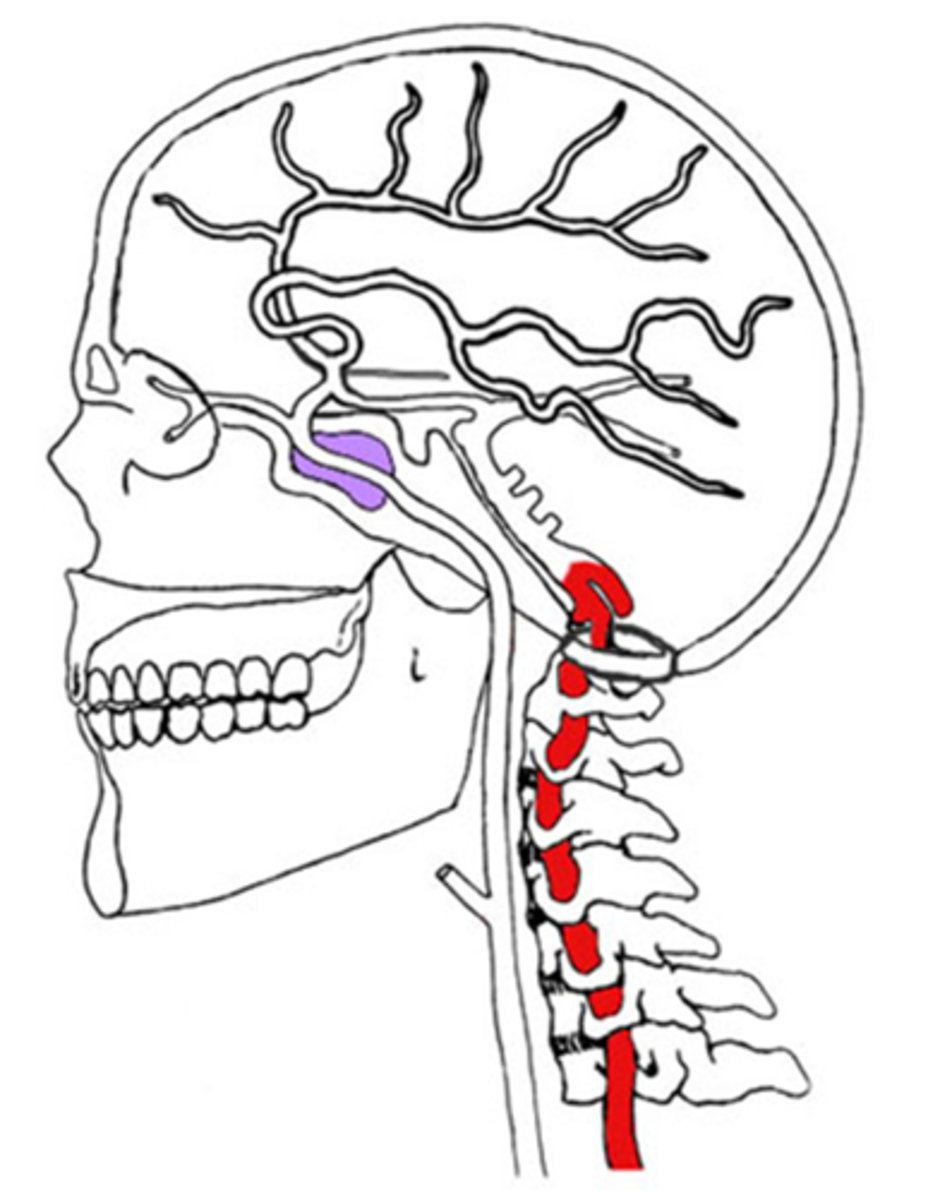
atherosclerosis of the vertebral-basilar artery = lack of blood supply to the post cerebral artery = occipital cortex infarcts
What is the etiology of vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
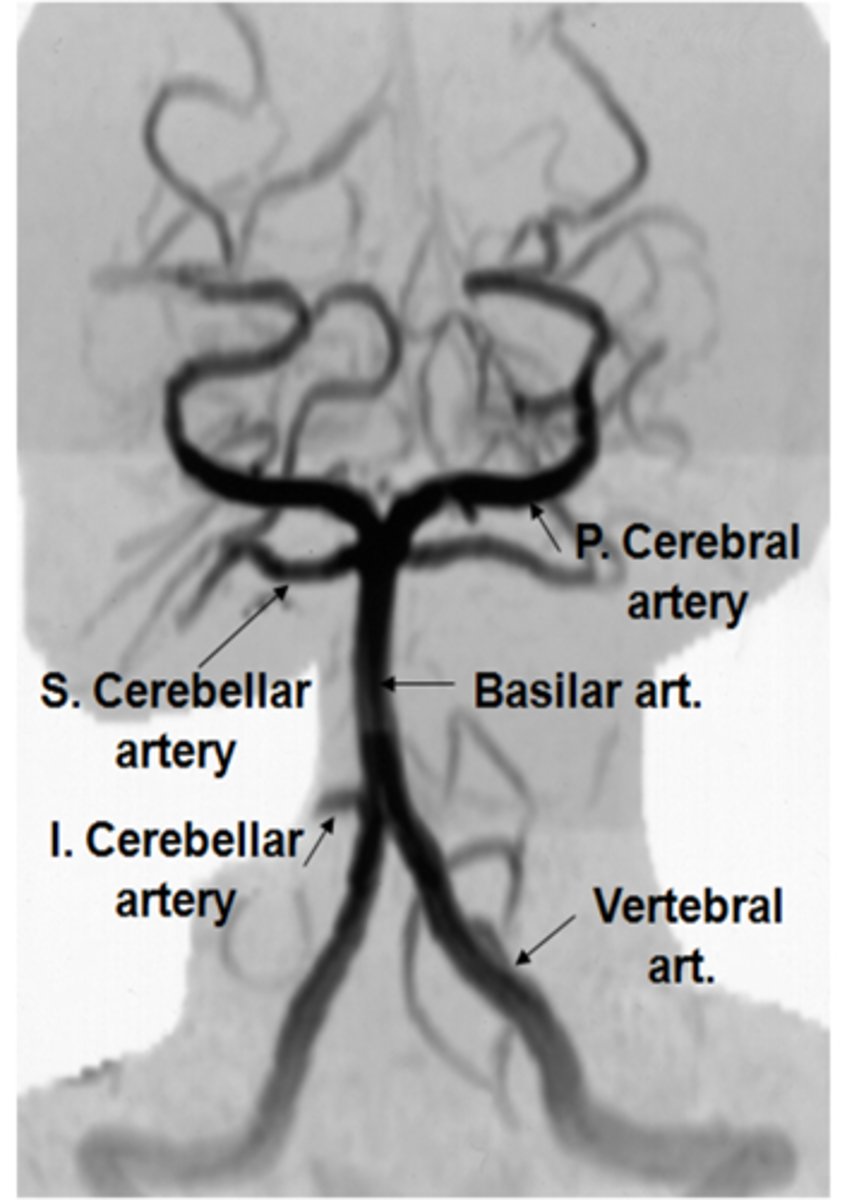
thrombo-embolic process = something is blocking blood flow
hemodynamic process = blood from 2 ICAs and 2 vertebrals cannot access brain = anoxia
What are the 2 theories about TIAs in the posterior circulation via vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
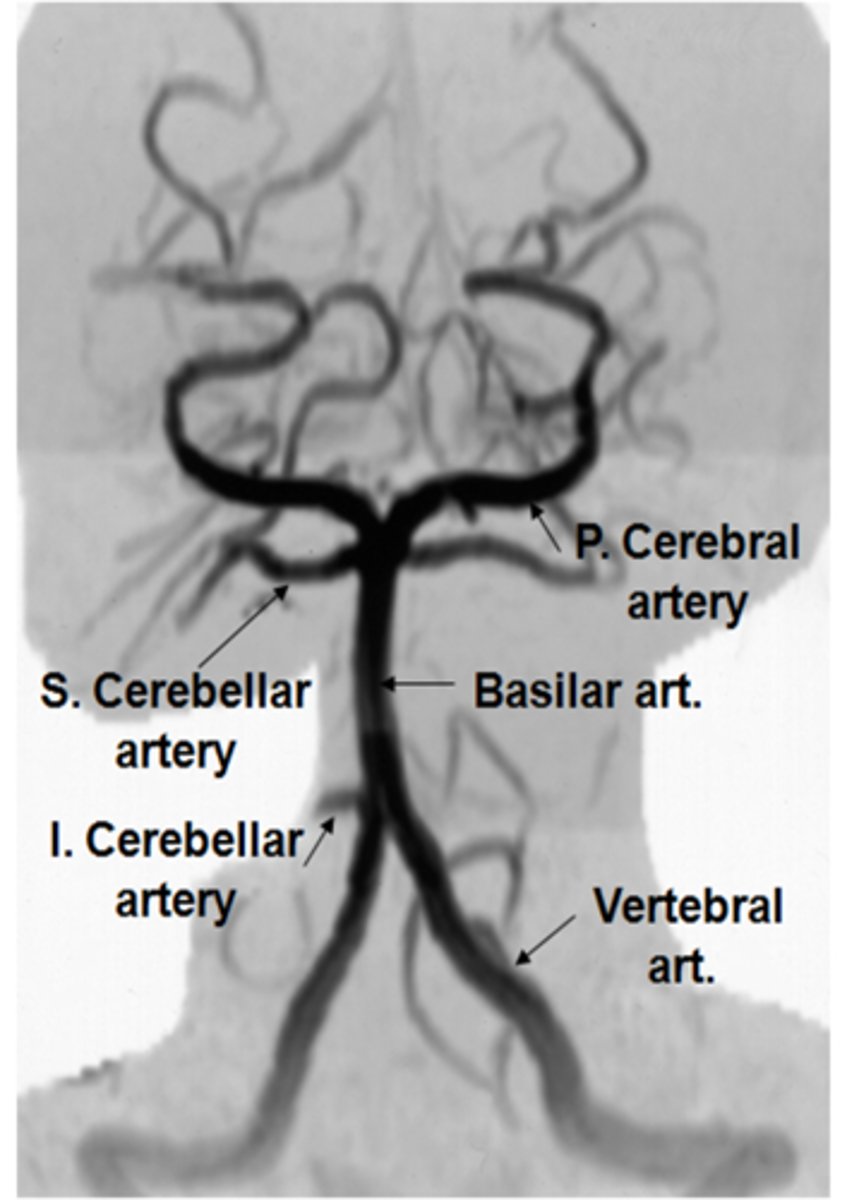
CBC
2hr post-prandial BG
lipid profile
electrolytes
CT scan
What lab / non-invasive studies should we do in vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
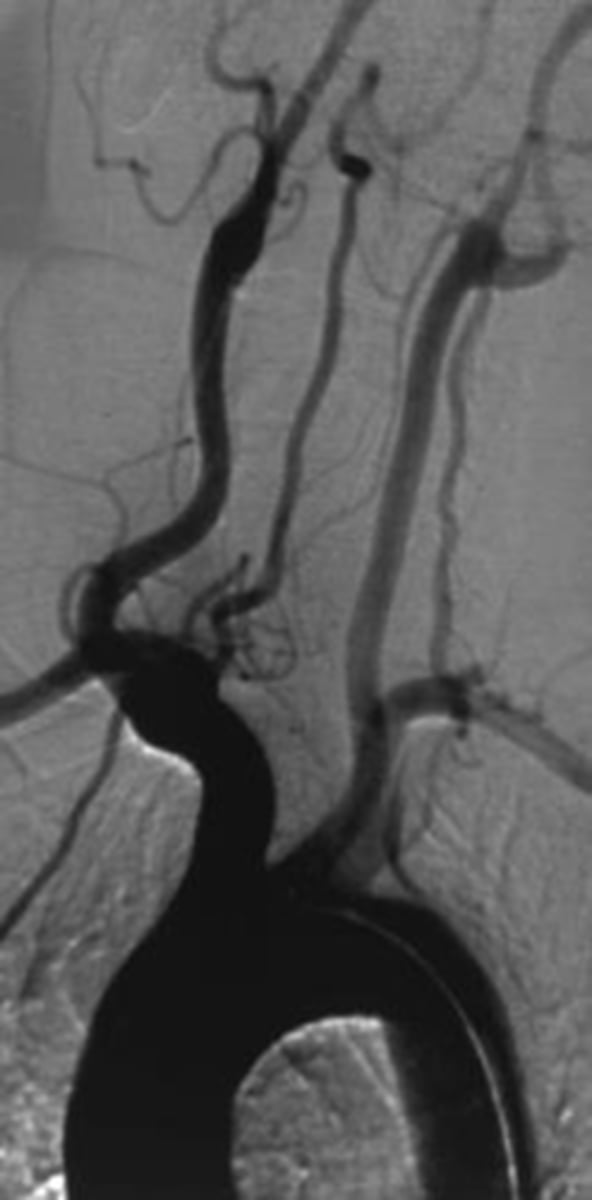
aortich arch angiography
NOTE: invasive studies are NOT recommended
What invasive studies should we do in vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
medical tx (same as for carotid artery disease) = aspirin, persantine, coumadin
NOTE: surgical tx not recommended bc atherosclerosis is diffuse throughout vascular system
What are the 2 tx options for vertebral-basilar insufficiency?
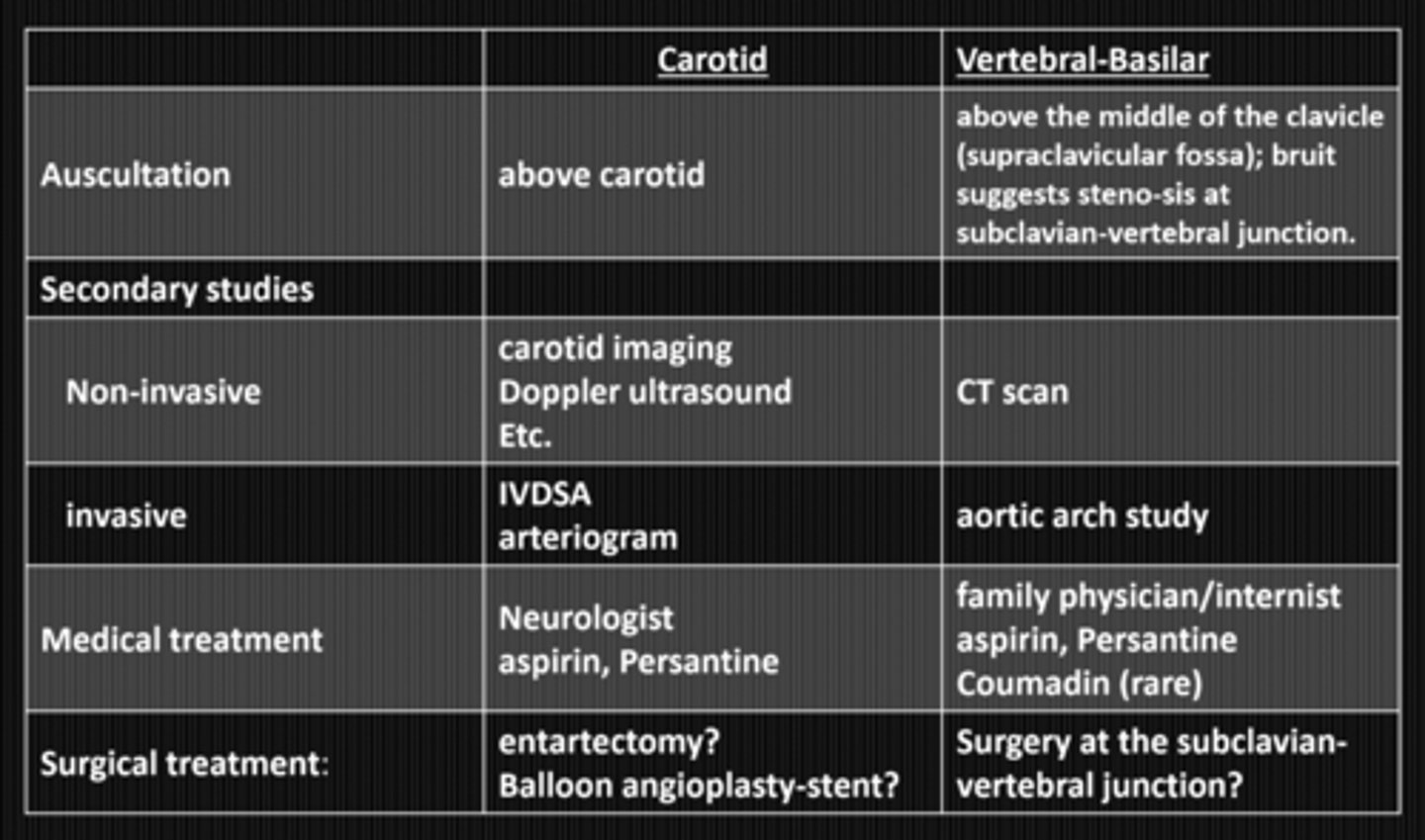
no = VBI has less risk of stroke compared to carotid disease
Does vertebral-basilar insufficiency have the same risk of stroke as carotid artery disease?
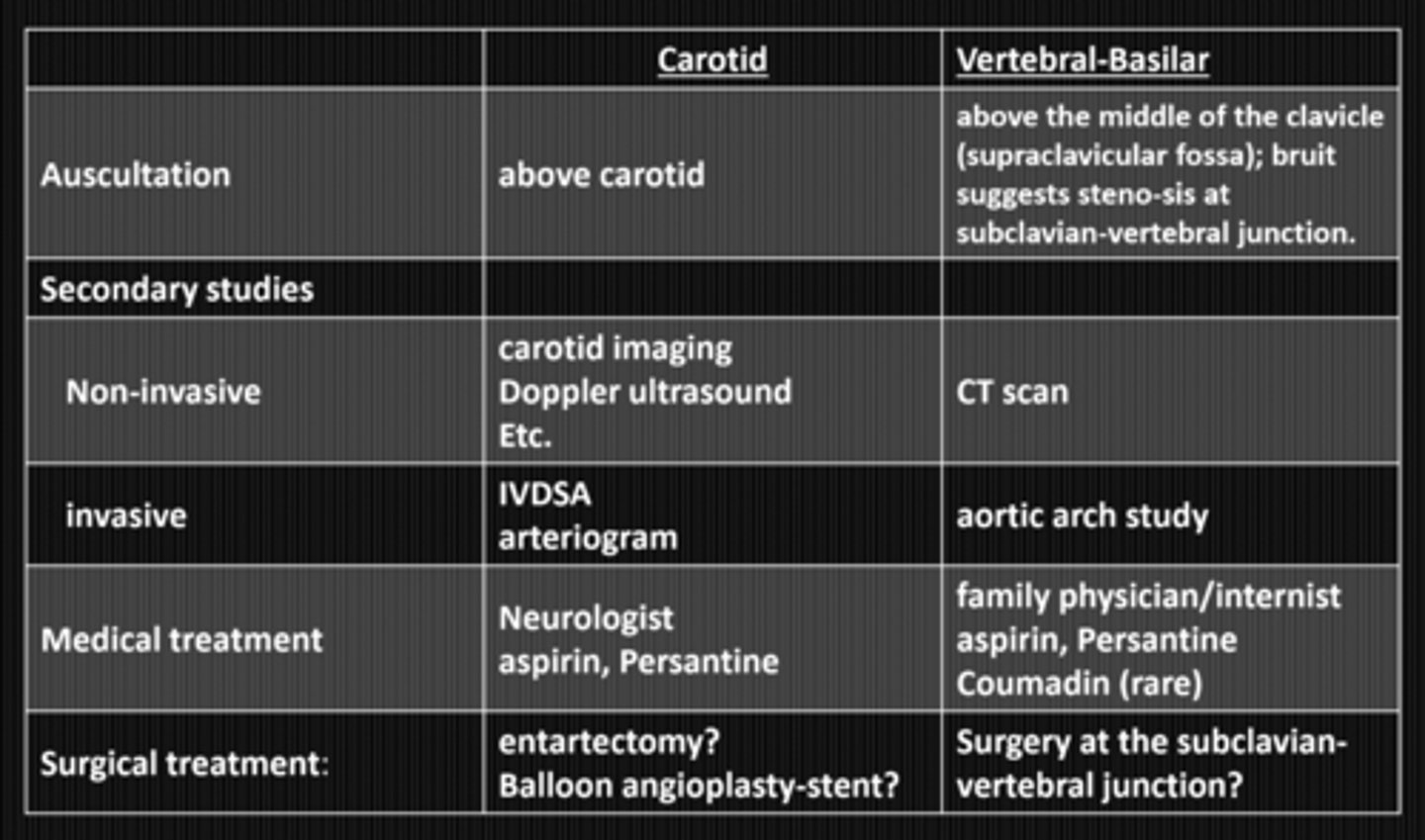
PCP or neurologist
Who should we refer someone with vertebral-basilar insufficiency to for tx?
disseminated disease of the aged = beginning with low grade fever, anorexia, malaise, weight loss = 1-2wks later severe unilateral or bilateral fronto-temporal or occipital pains, scalp tenderness, bilateral visual loss
What occurs in GCA?
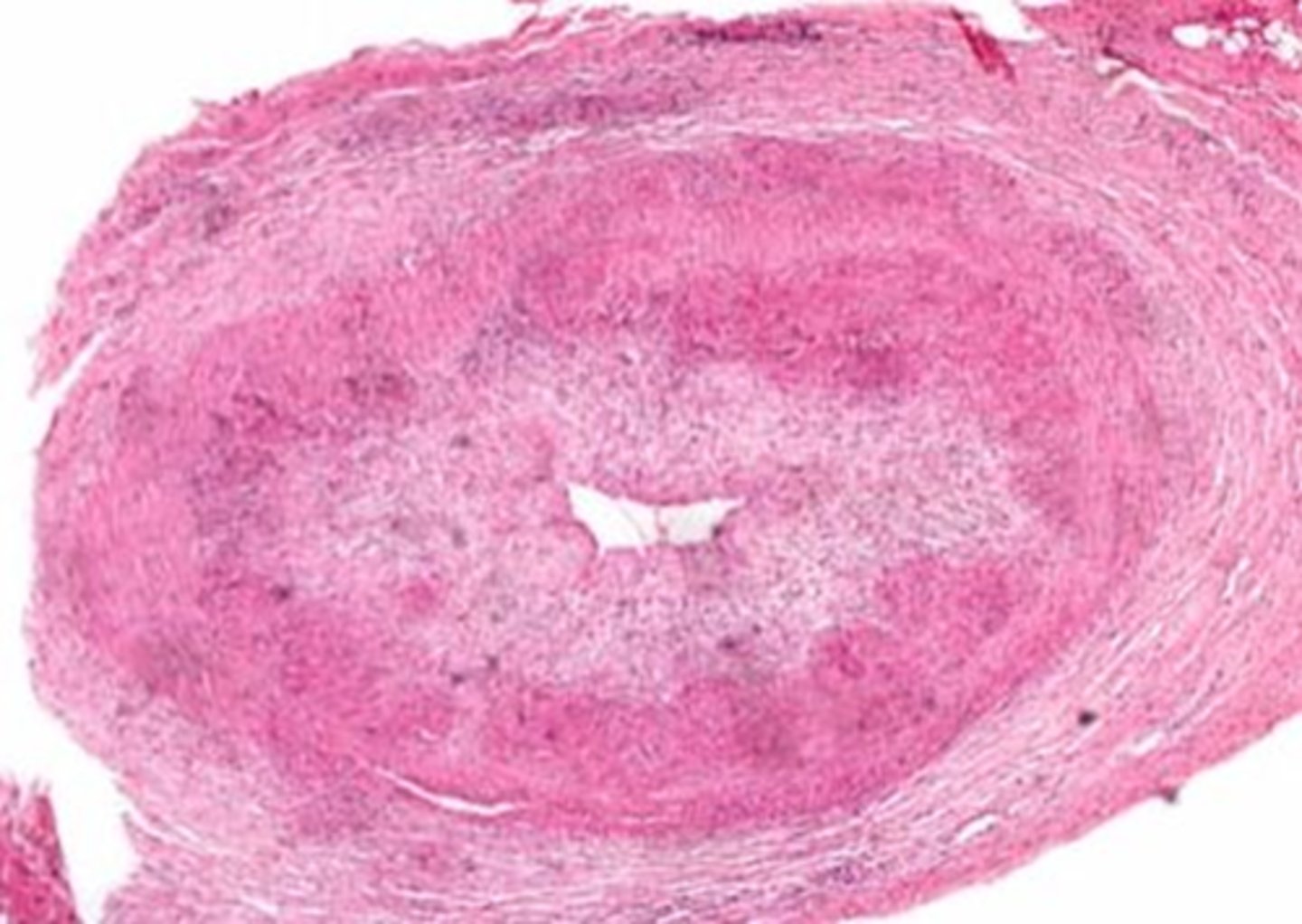
granulomatous inflammation = plasma cells, lymphocytes, giant cells infiltrate the temporal artery = acellular thickening of the tunica intima = destroys the inner elastic membrane and occludes the artery lumen = blocks off post ciliary arteries = infarcted ONH
What is the pathophysiology behind GCA?
painful, sudden, monocular vision loss that may be transient (2-3min) or permanent NLP
+/- scalp tenderness
+/- jaw claudication
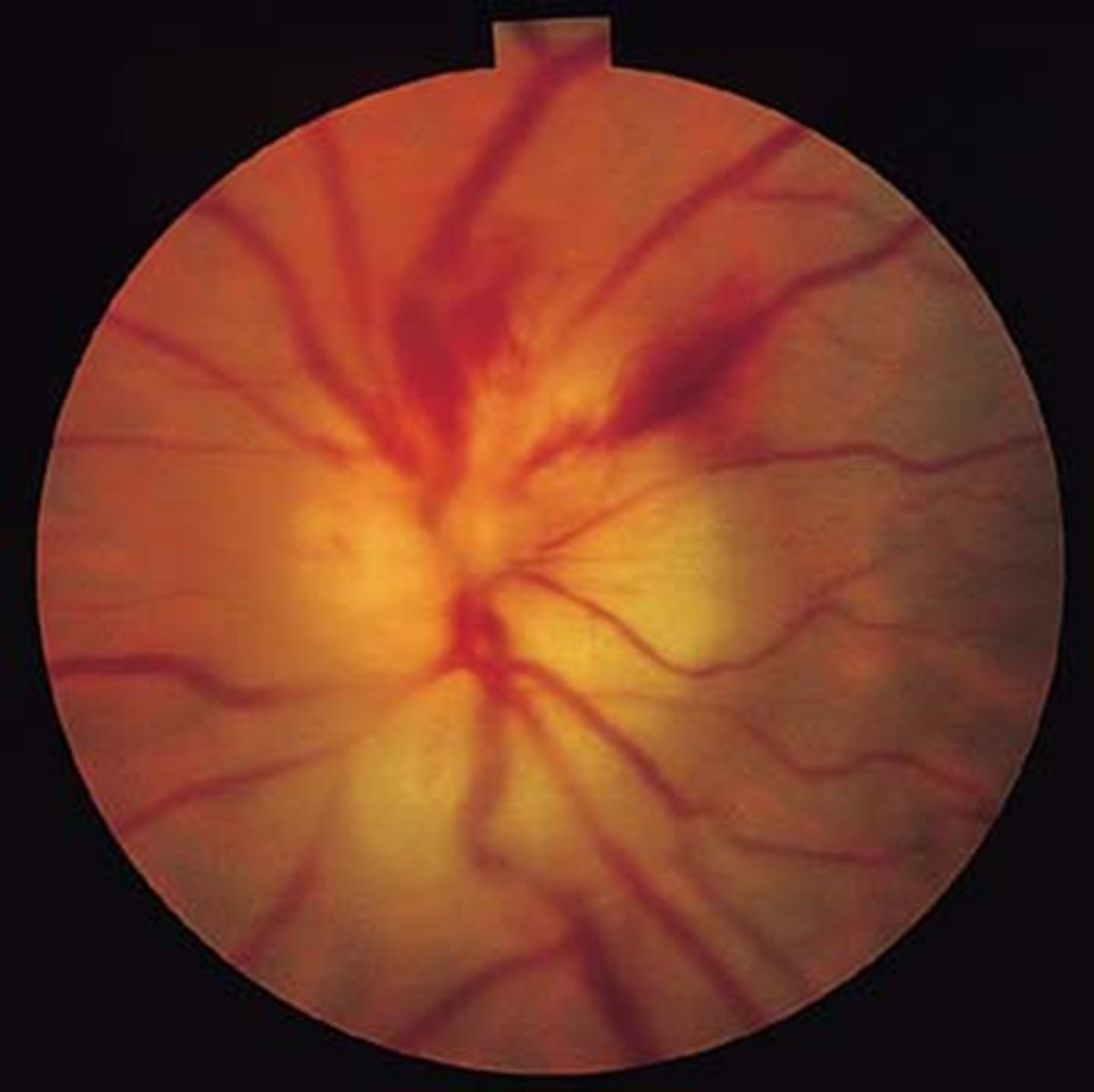
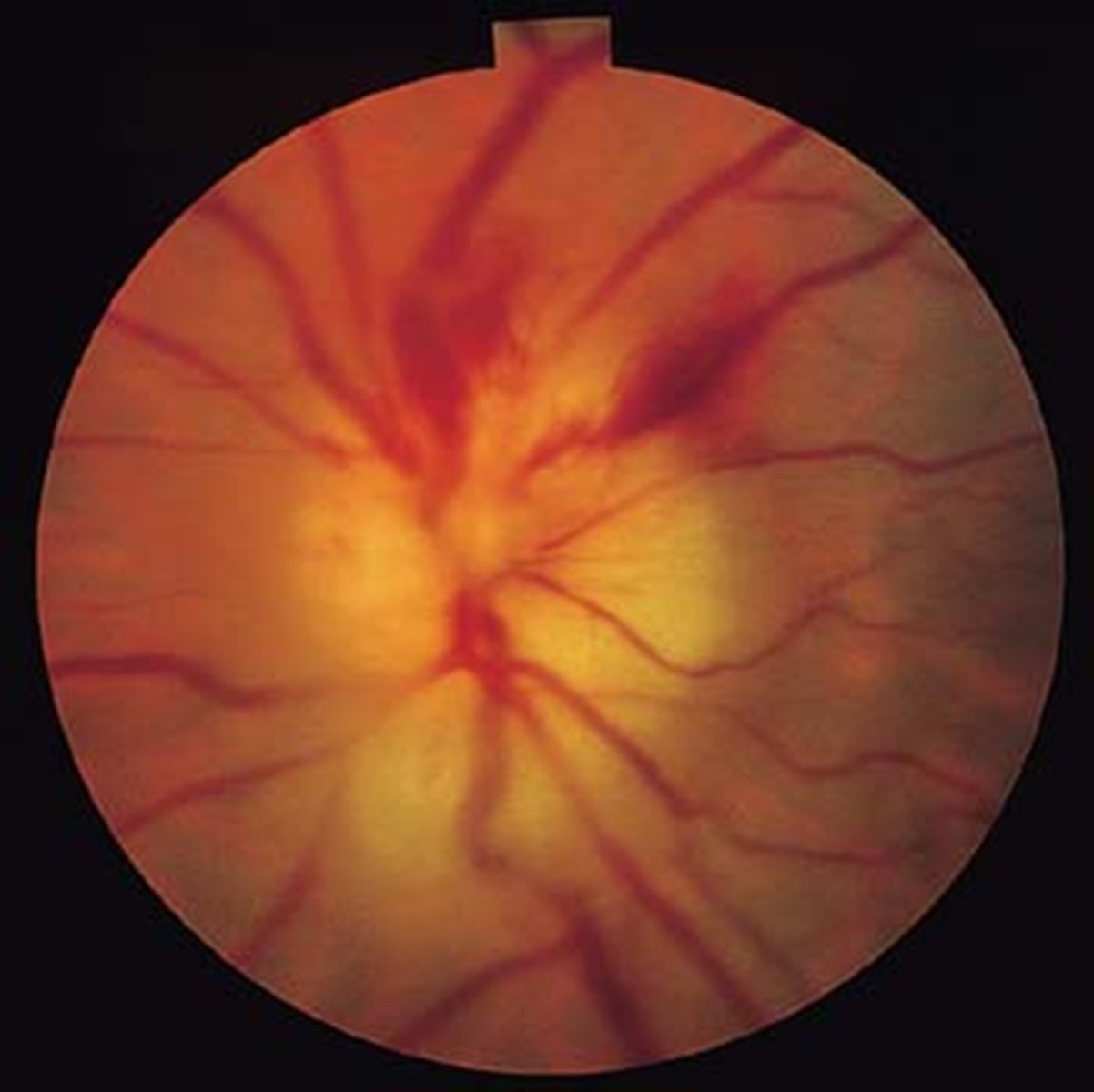
pale, swollen ONH = AAION
+/- hemes at the disc
+/- CN III palsy with pupil involvement
What are some S/S of GCA?
NLP
amaurotic pupil and APD
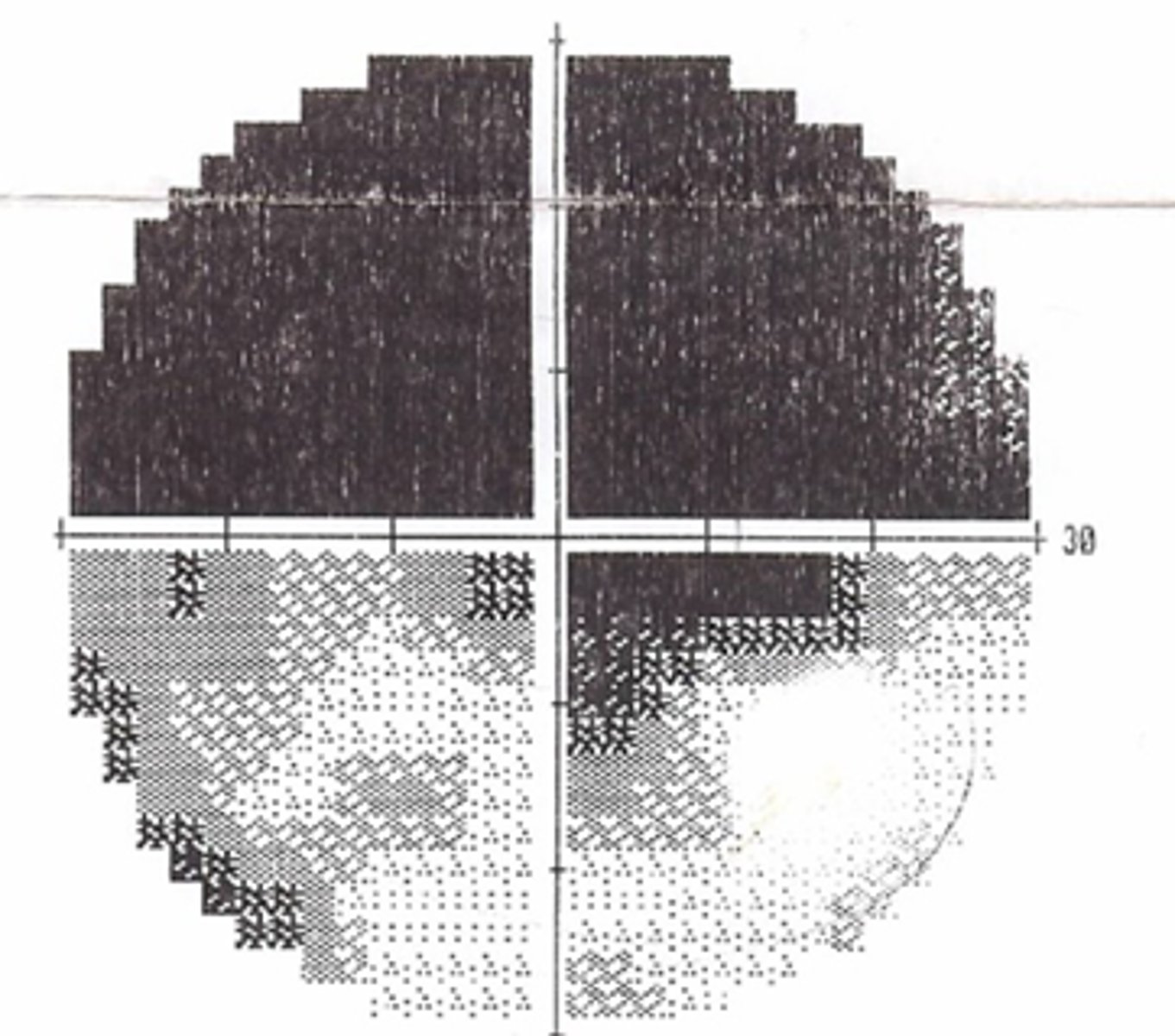
altitudinal hemianopia if not NLP
AAION = disc edema, APD, vision loss, alitudinal scotoma
What main things will we see during our exam in GCA?
polymyalgia rheumatica = RA that affects axial skeleton = pain in shoulders and hips
malaise
weight loss
fever
What do pt's with GCA often have in their Hx?

age 65+
Caucasians
females
What demographics do we typically see GCA in?
bloodwork with Westergen ESR, CRP STAT
temporal artery biopsy to look for mast cells, giant cells and loss of inner elastic lamina
What tests do we run for pt's with GCA?
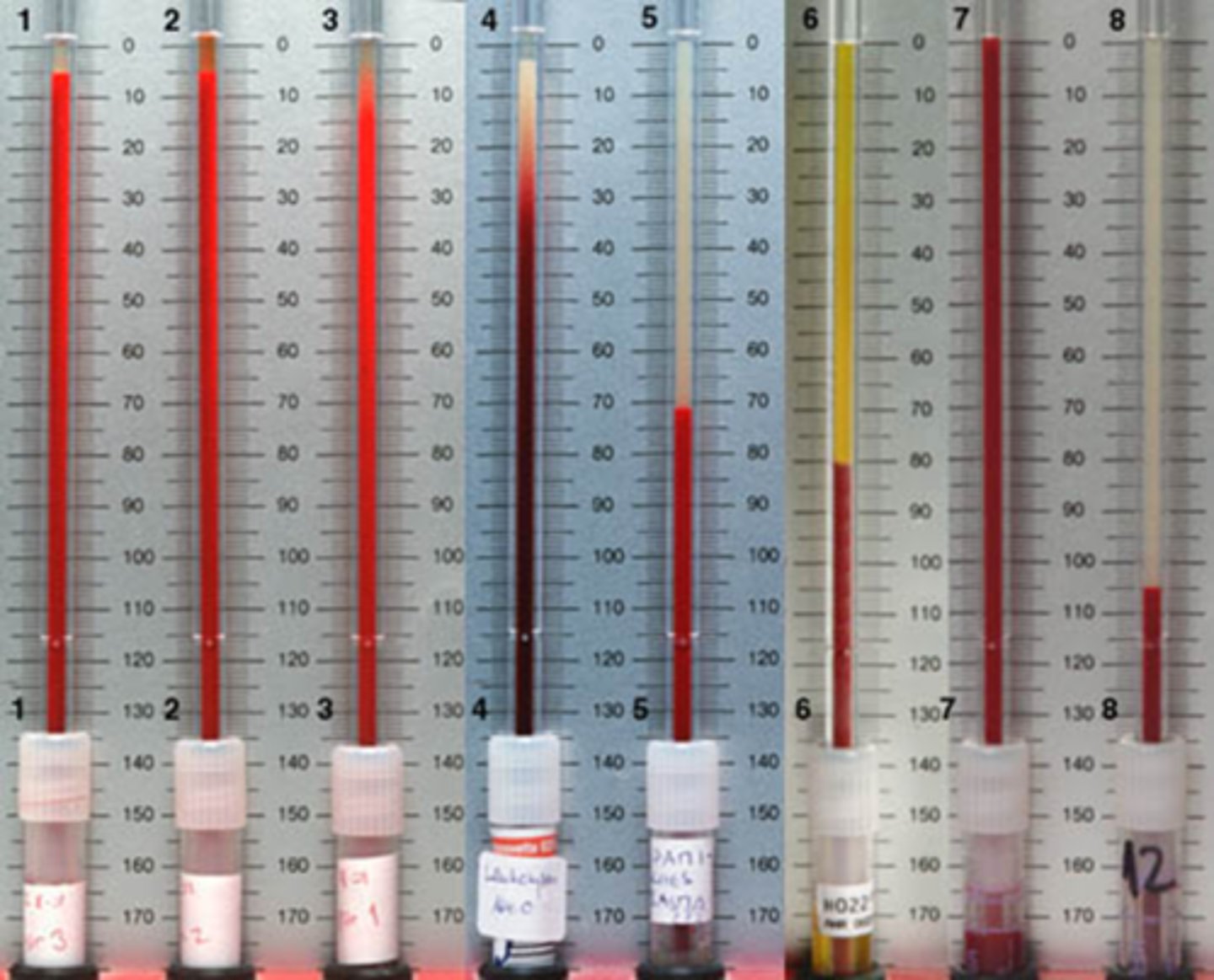
males = age / 2
females = (age + 10) / 2
Recall: what is the normal max value of ESR?
oral steroids STAT = 40-60mg of prednisone qday x 1 year
Actemra (tocilizumab) = IV administration of IL-6 blocker weekly with steroid taper
What is the tx for GCA?
chemical diabetes
osteoporosis
depression
psychosis
Recall: what are some side effects of oral steroids?
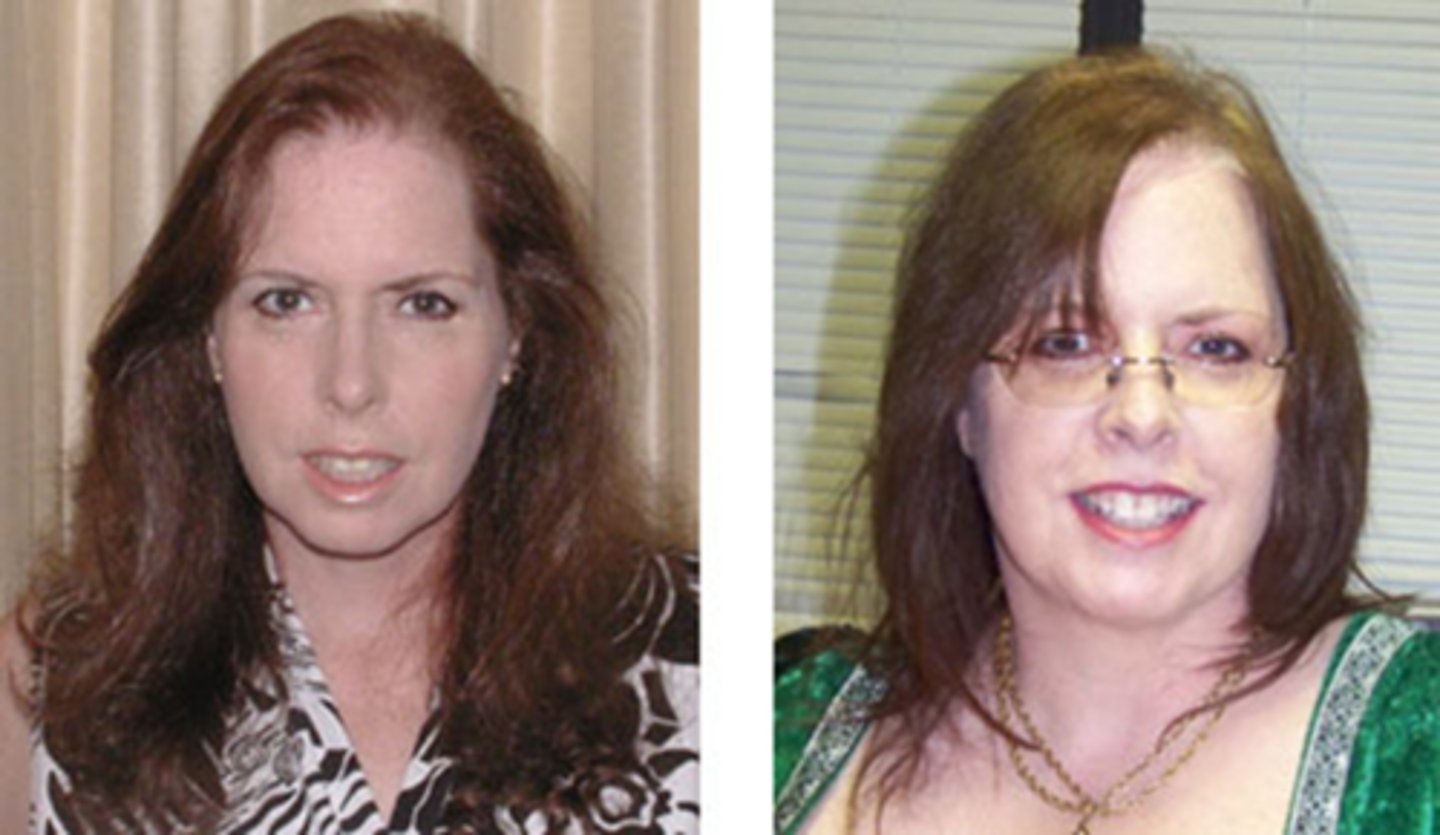

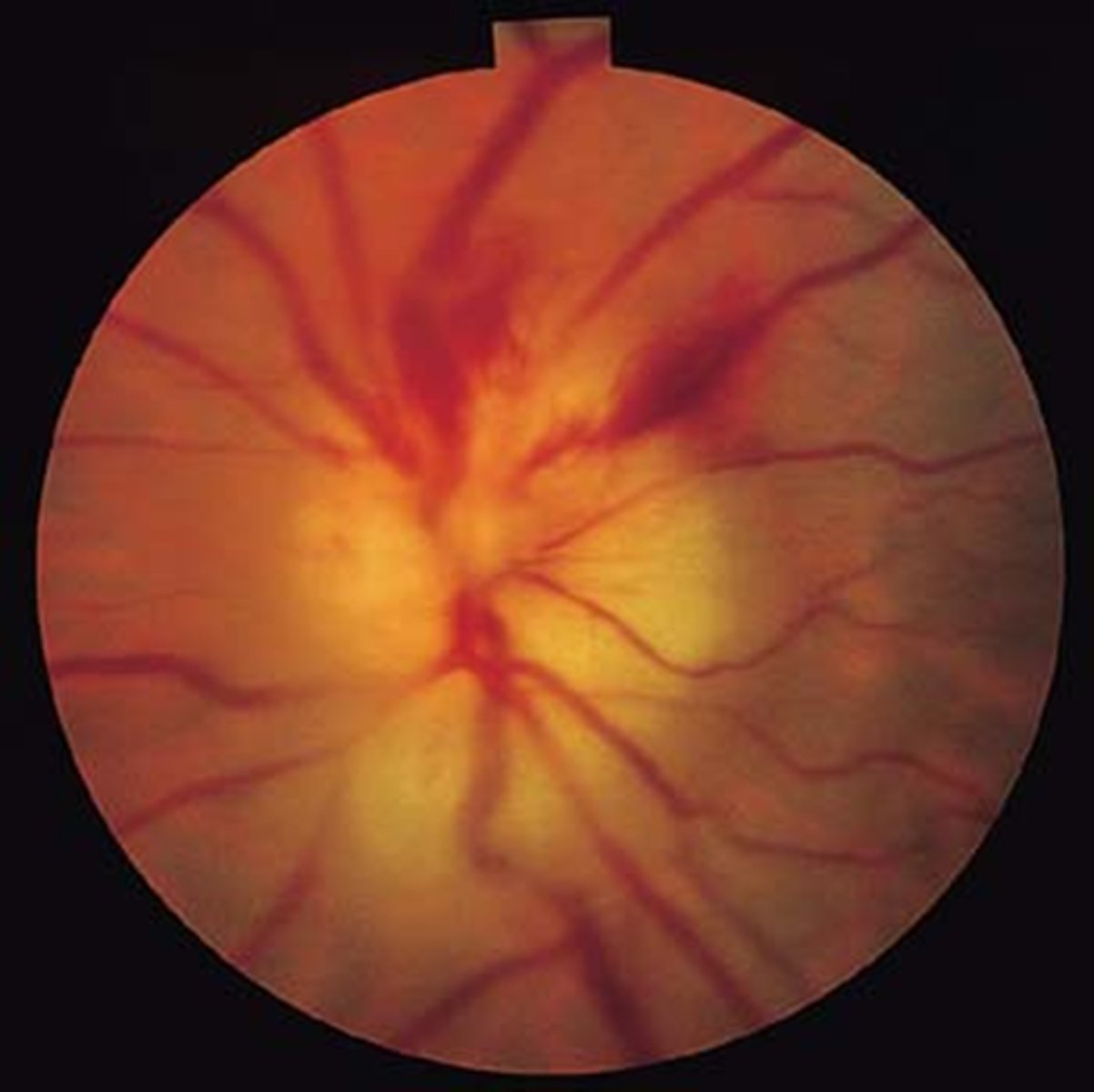
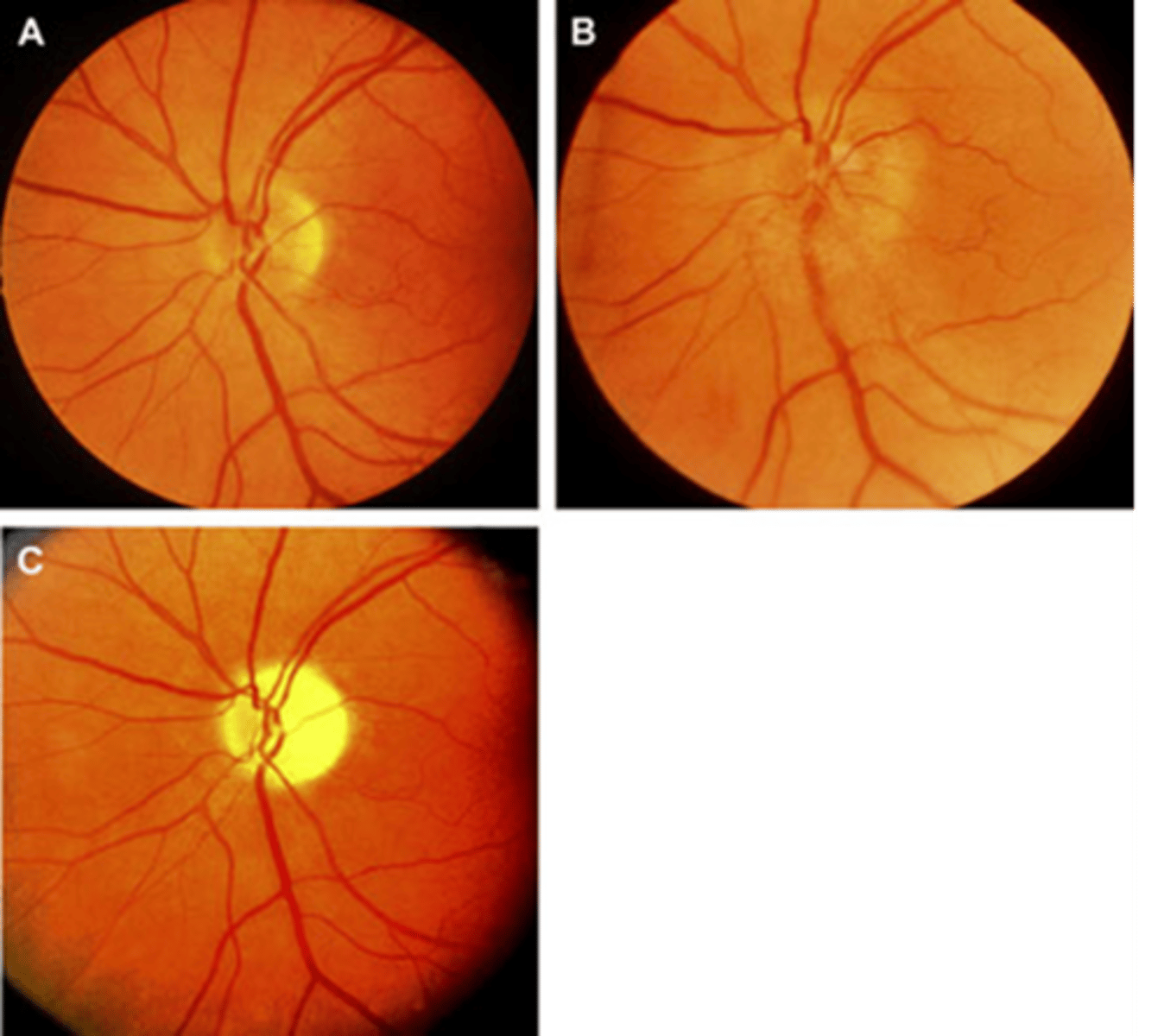
pale due to optic atrophy (C)
Acutely, a nerve in GCA and AAION will appear as swollen +/- hemes (B). How does it appear long term?
prevent involvement of the fellow eye in the coming hours or days = occurs in 25% of pt's
While we cannot recover vision in the affected eye, why do we tx GCA?
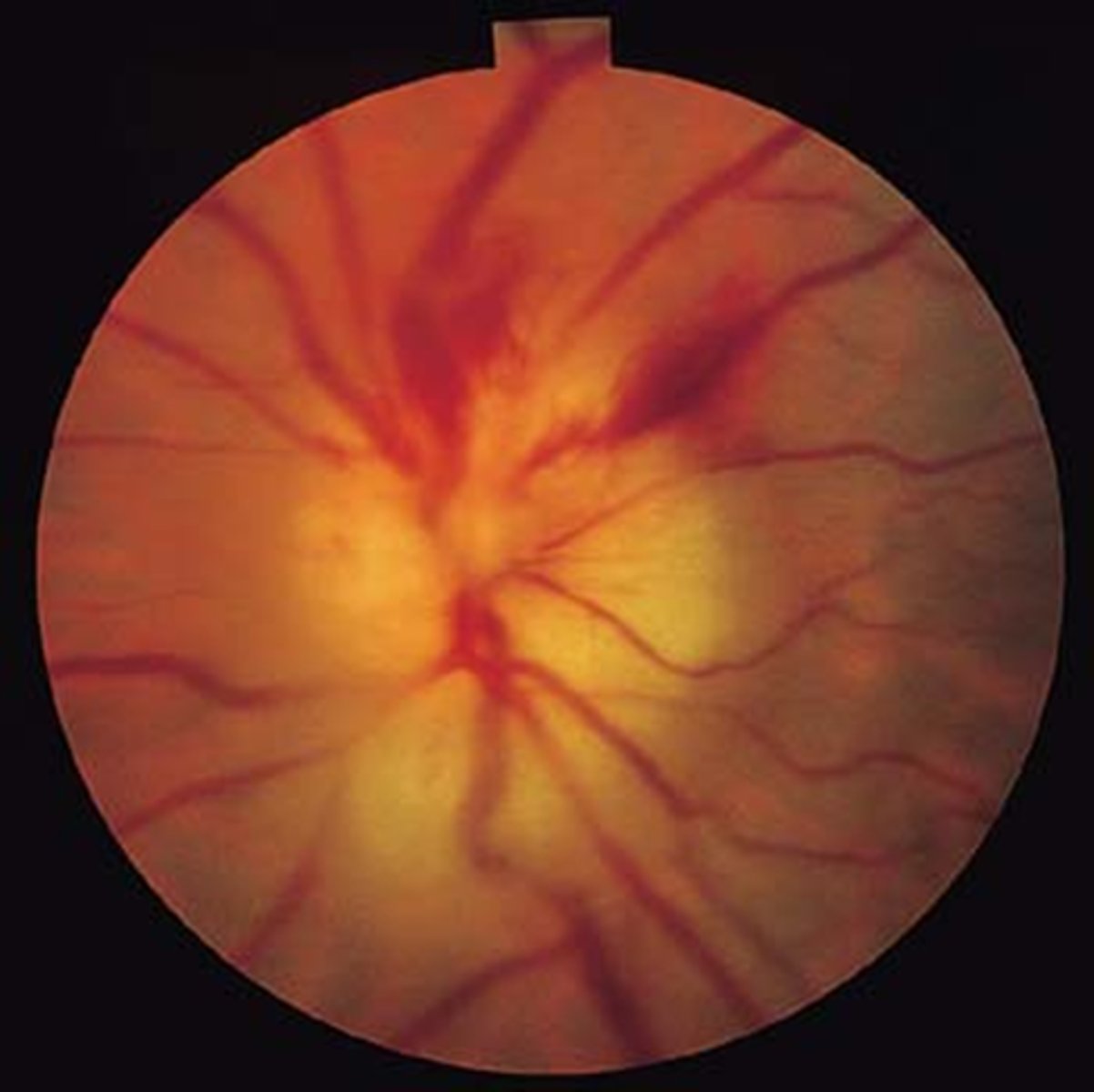
NORMAL
How does migraine typically occur on physical exam?

classic = pt has a visual prodrome, then the HA
common = HA and nausea but not prodrome
complicated = focal neuro deficit with the HA
What are 3 presentations of migraine?

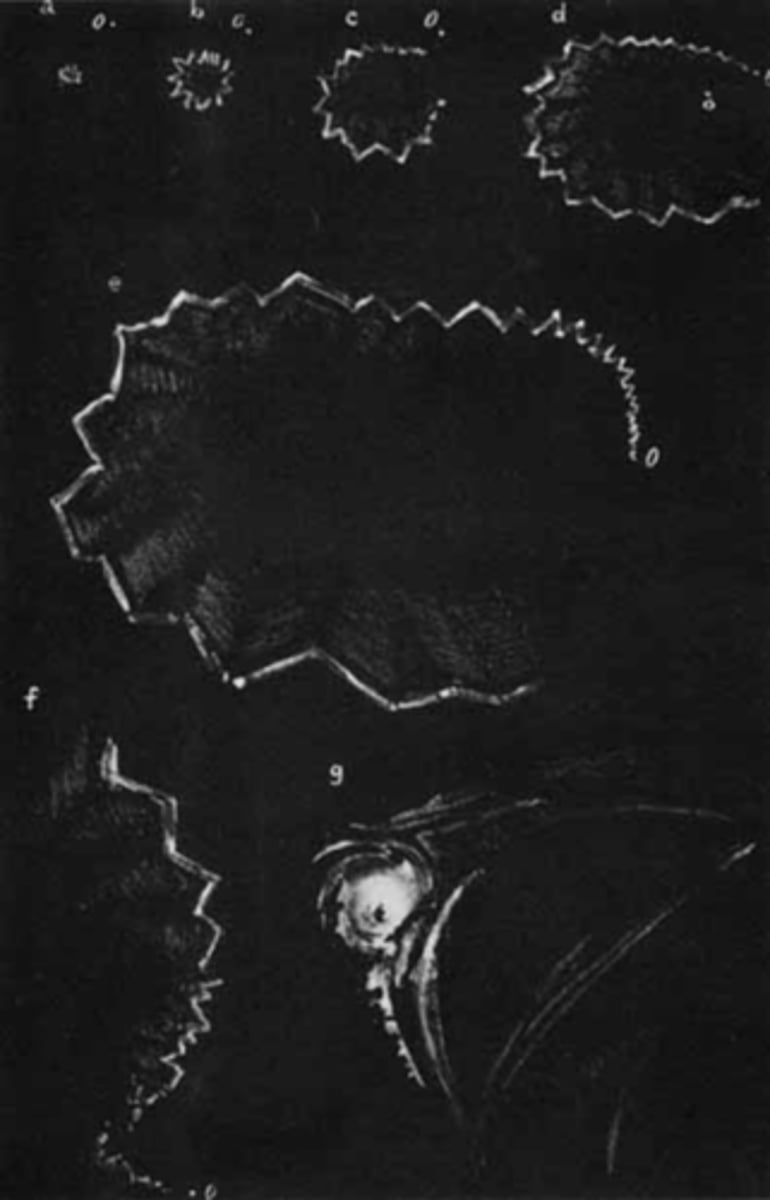
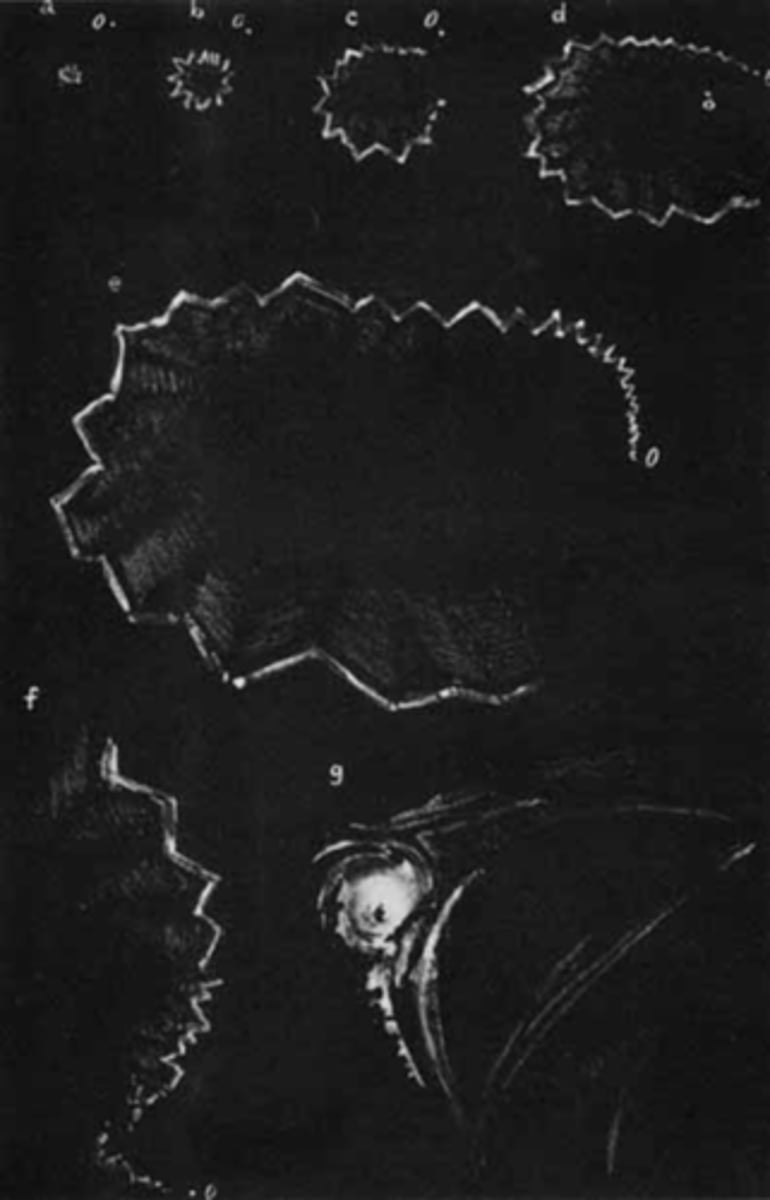
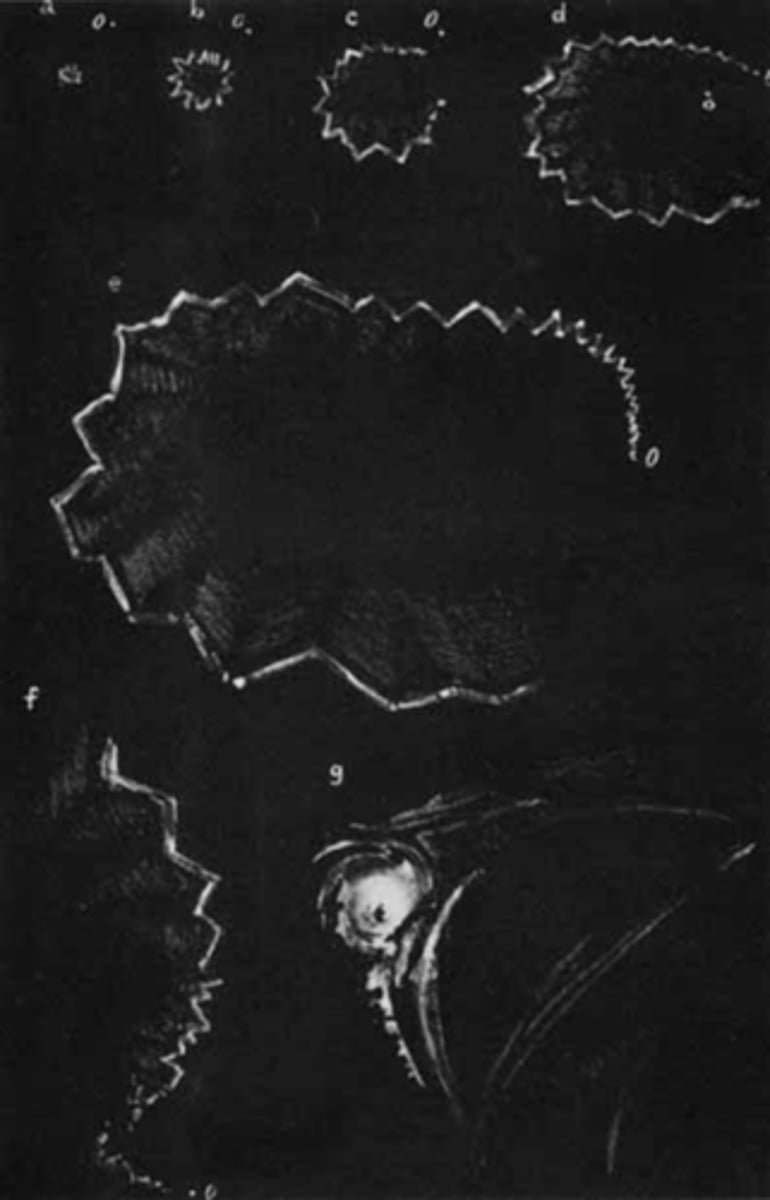
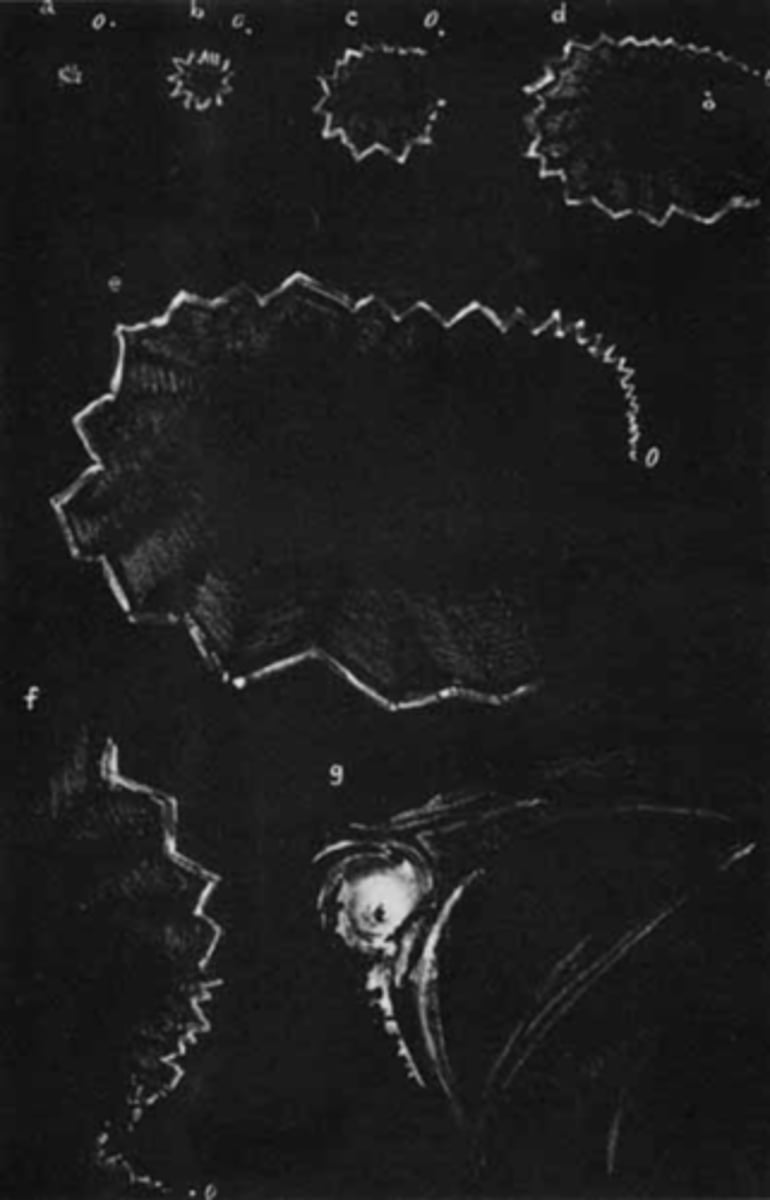
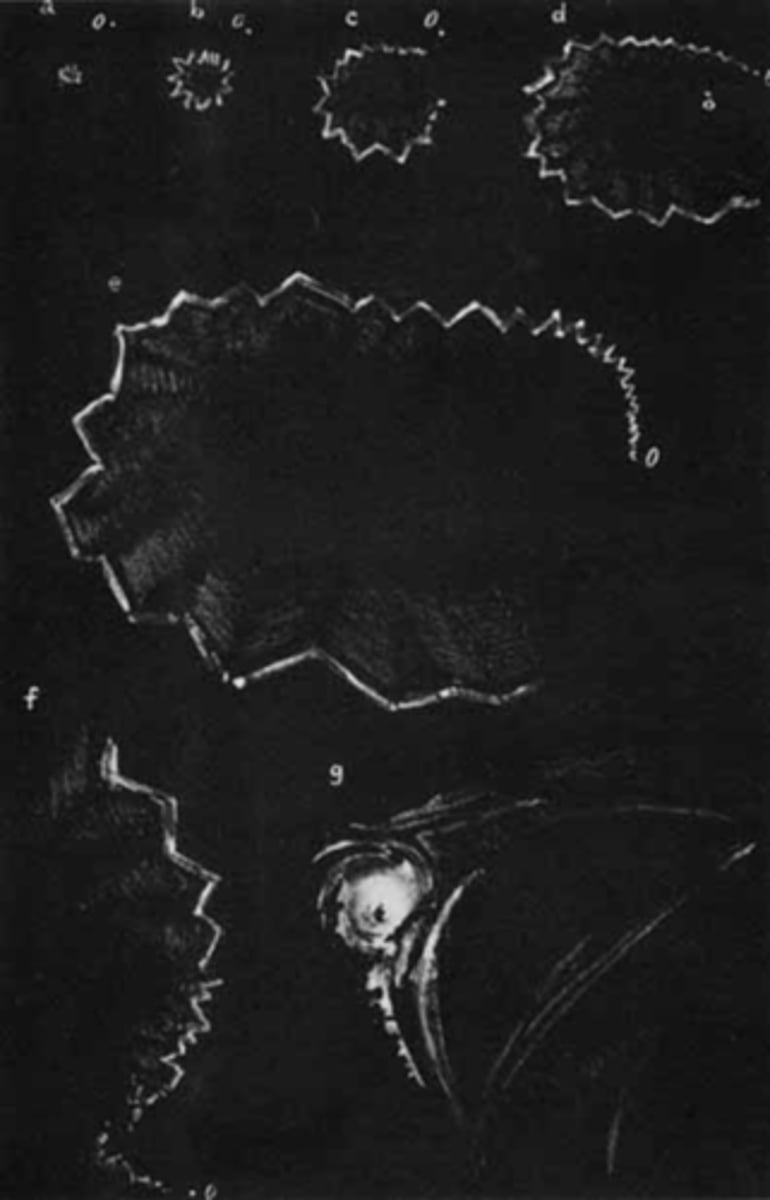
bilateral flashing lights or teichopsias/jagged saw-tooth lines (positive scotoma) that starts in periphery then expands
then a negative scotoma (homo hemianopsia)
Describe the visual prodrome that pt's have during migraine.

20min
How long does the migraine prodrome occur for?

abortive migraine meds like ergotamine
pregnancy or menopause can make the pain go away
pt may forget HA if they are distracted by the photopsias
elderly pt
What are 4 situations in which a pt may have a prodrome without a HA?

< age 40
female >>> male
FHx of migraines
type A perfectionist
stress and major life events
Which demographics are most often affected by migraine?

< age 20 (esp onset of menarche) = classic migraine
age 20-40 = common migraine
age 40+ = simple HA
How does migraine presentation differ based on age?

homonymous hemianopsia opposite to the side of the HA
What VF defect is present DURING a migraine attack?
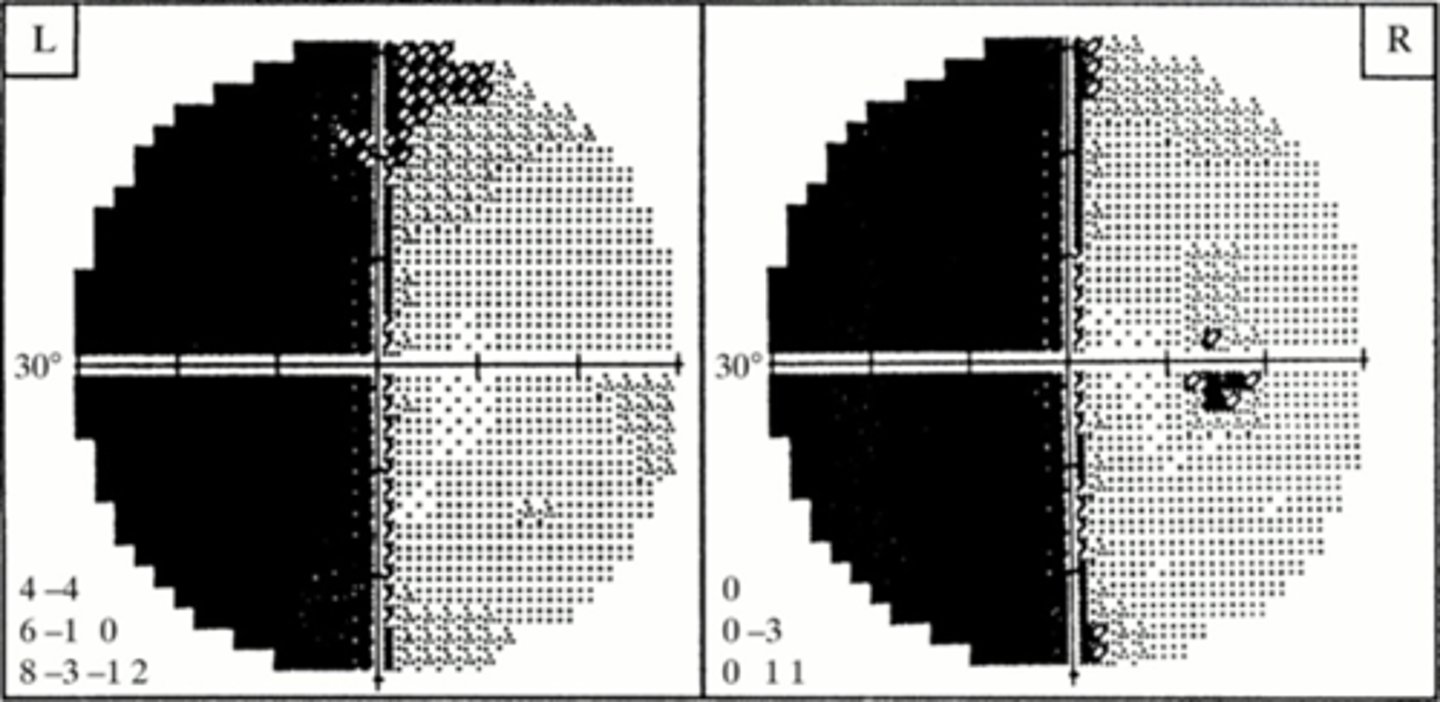
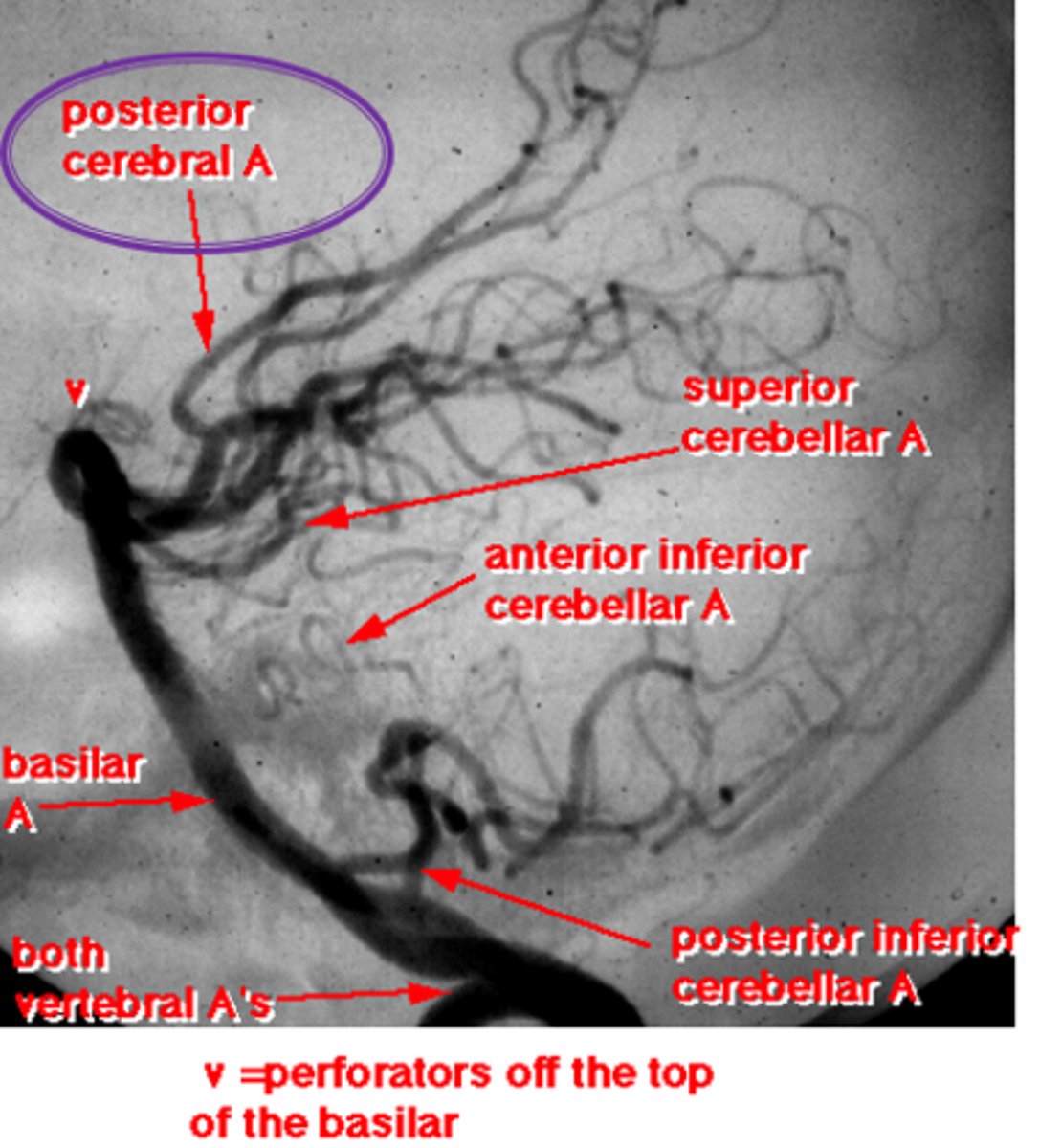
vasoconstriction = ischemia along the post cerebral arteries
What is the pathophysiology of migraine?
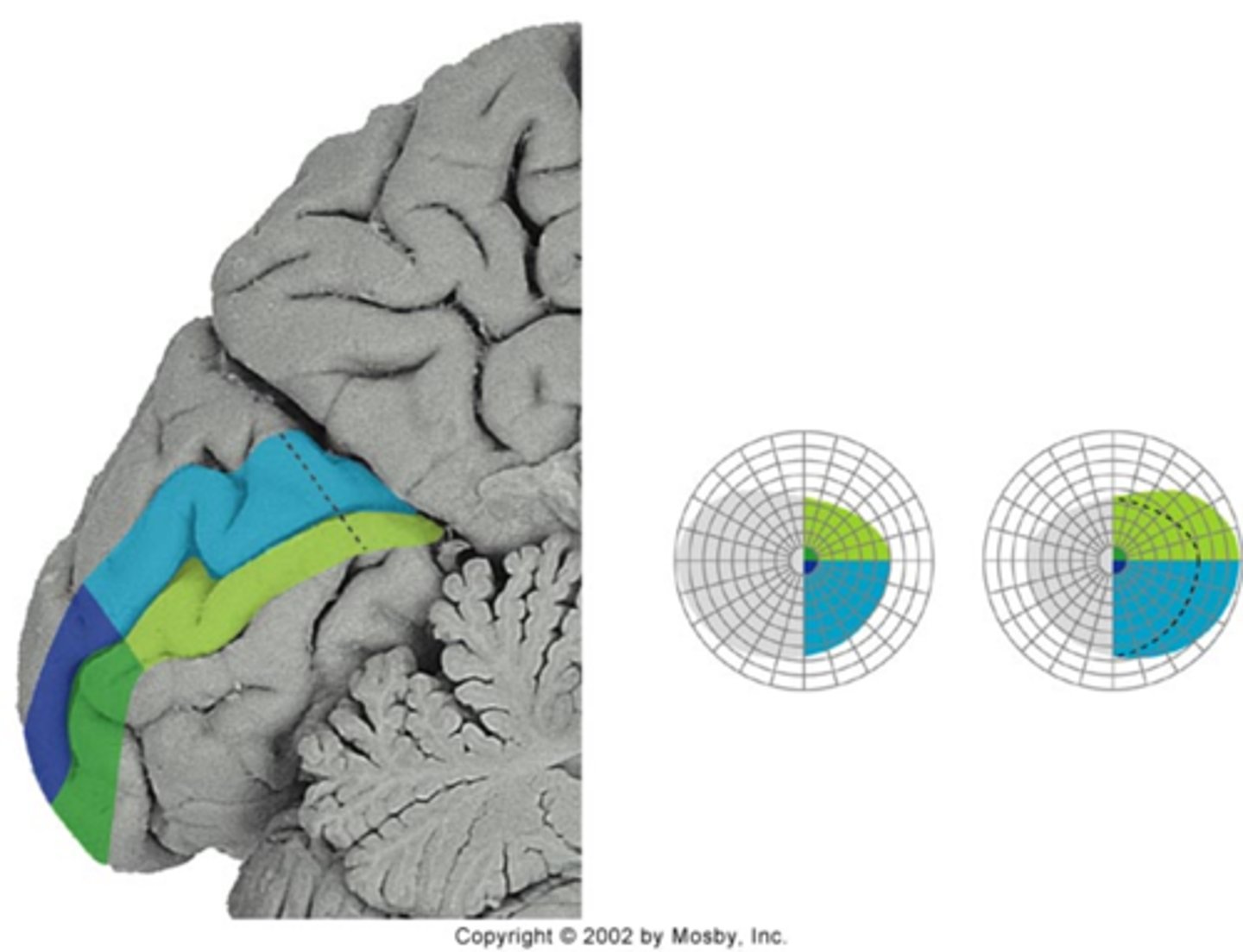
1/2 of the visual cortex is devoted to macula = 1/2 of the photopsia episode time (10min) occurs in central vision
How does the pattern of migraine prodrome correlated to occipital lobe anatomy?
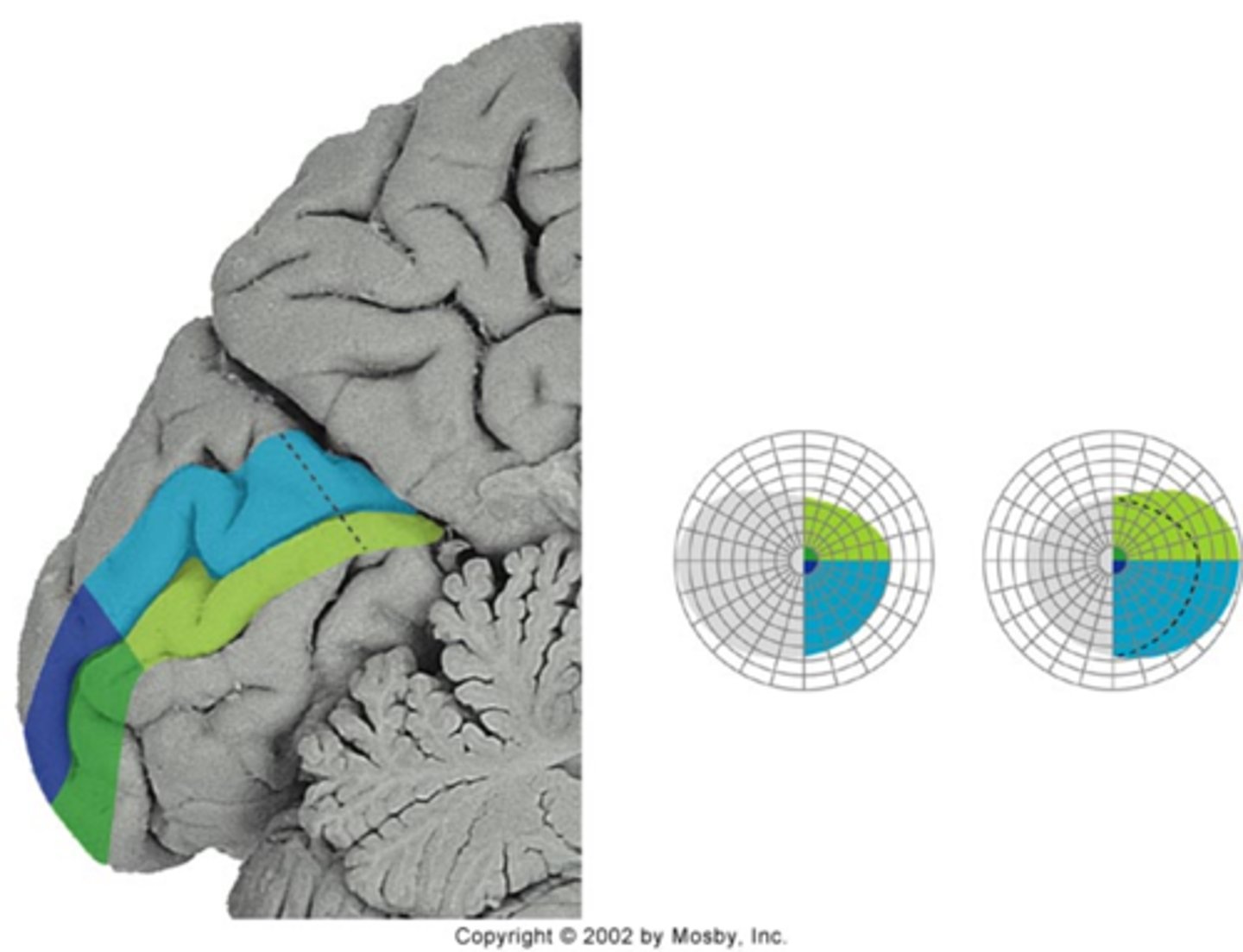
ischemic process is traveling across remaining 50% of visual cortex
Why does the migraine prodrome appear to speed up in the periphery?
abortive tx (oral, injection, nasal sprays) = prevent migraine or stop it once it starts
prophylactic tx to prevent frequent migraines
surgery = peripheral nerve decompression for pt's who can identify a specific locus
What is the main tx for migraine?

triptans = target serotonin = sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, rizatriptan
ergotamine tartrate (cafergot)
anti-nausea medications = prochlorperazine, promethazine
weak narcotics for pain = butalbitol, acetaminophen with codein
OTC = aspirin, acetaminophen, ibuprofen; with caffeine
CGRP antagonists = blocks CGRP (often high in migraineur blood) = less vasodilation
5HT agonists = increase serotonin affinity without vasoconstriction (safe in cardio dz)
What are some examples of abortive tx for migraine?

beta-blockers = propranolol, timolol
Ca-channel blockers = verapamil
anti-depressants = amitriptyline
anti-seizure meds = gabapentin, topiramate, valproic acid
antihistamines and anti-allergy drugs = diphenhydramine
botox
CGRP anatognists
What are some examples of prophylactic tx for migraine?
