PHR912: LIPID METABOLISM 1
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BLOCK 4 WEEK 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
TB and Bacterial Lipid Metabolism:
Large fatty acids play a unique role in the encasulation process of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Lipids:
Family of biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents but not water
Esters of fatty acids:
Triacylglycerols, phospholipids
Steroids:
consist of 4 fused carbon rings.
three 6 membered rings + one 5 membered ring
Can steroids be broken down?
no
Esters of fatty acids examples:
Triacylglycerols
phospholipids (glycerophospholipids)
sphingolipids
oils, waxes, fats
Steroid molecules:
Cholesterol
Steroid hormones
Bile acids
Special lipids:
Eicosanoids
fat soluble vitamins
functions of lipids:
store energy (triglycerides)
major components of cell membranes (phospholipids)
serve as chemical messengers (hormones)
help digestion (bile acids)
anchor proteins to membranes (lipoprotein receptors)
Insulate nerves and protect internal organs
Short chain fatty acids:
2-4 carbons
Medium chain fatty acids:
4-12 carbons
Long chain fatty acids:
12-20 carbons
Very long chain:
>20 carbons
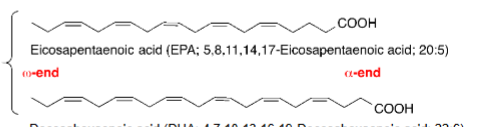
What molecule is this
omega 3
Fatty acids are:
Major source of energy for ATP synthesis
What cells cannot use fatty acids as fuels:
red blood cells and brain
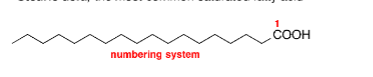
What is the most common saturated fatty acid?
Stearic acid
Unsaturated fatty acids are what and contain what?
Not linear and contain kinks due to double bonds
Multi-unsaturated fatty acids are what to our body?
Essential, thus are like vitamins
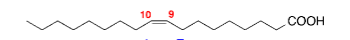
What fatty acid is this
oleic acid
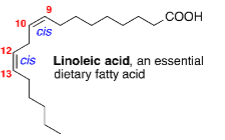
what fatty acid is this
linoleic acid
What kind of bond connects the glycerol backbone to the fatty acid?
Ester bond
Triacylglycerols are:
Triesters of glycerol and three fatty acids
Glycerophospholipids:
Similar to triaclglycerols, but one of the hydroxyl groups of glycerol is esterified with a phosphoric acid aminoalcohol ester
Consists of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid residues, a phosphate and a polar head group.
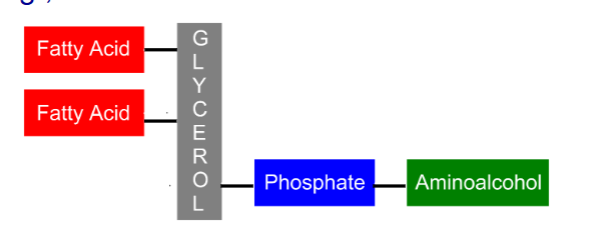
what molecule is this
glycerophospholipid
Glycerophospholipids contain what kind of tail and head
Lipophilic tail and hydrophilic head
Phospholipids are the
Backbone of cell membrane
Liposomes are:
Vehicles for drug delivery
Single bilayer
Lecithin is an important what:
Glycerophospholipid
Sphinoglipids are the only:
Membrane phospholipids not dervied from glycerol
What is the backbone of a sphingolipid?
Sphingosine
Eicosanoids:
Hormone-like substances produced from the C20 -fatty acid arachidonic acid (AA)
‘local hormones’
Where are eicosanoids needed?
produced in low amounts at the location in the body where they are needed and broken down rapidly
What do eicosandoids do
Regulate blood pressure, contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle, inflammation, pain, fever, blood coagulation, reproduction, and bronchoconstriction, regulates cellular metabolism
MOA: NSAIDS:
blocks PGH2 synthase (COX), the enzyme that converts AA to prostaglandins
Vitamin A supports what:
vision, growth, and differentiation
Vitamin K supports what:
Blood clotting
Vitamin E supports what
antioxidants
vitamin d supports what
calcium metabolism regulator
immune system modulator
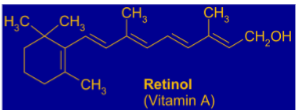
Which vitamin is this
retinol
vitamin A
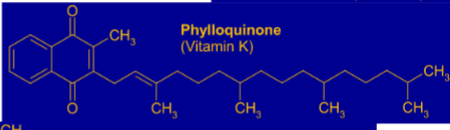
which vitamin is this
vitamin k
phylloquinone
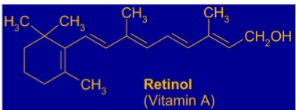
which vitamin is this
vitamin a
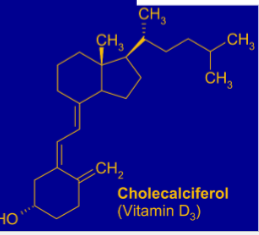
Which vitamin is this
vitamin D
Cholecalciferol
Steroids:
Cholesterol
Steroid hormones
bile acids
Purpose of cholesterol:
Membrane stability
Precursor for steroid hormones and bile acids
Important in membranes, liver, and skin
a late precursor of cholesterol is also a precurosr for vitamin D3
What do steroid hormones do:
Regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction
What do bile acids do
Are involved in lipid digestion and absorption
Steroid structure:
Backbone is a tetracyclic C17-alkane consisting of three 6-membered and one 5-membered ring (sterane)
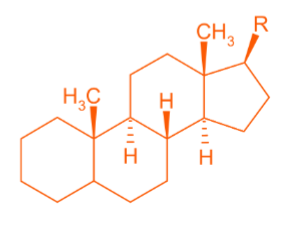
What is this molecule
steroid
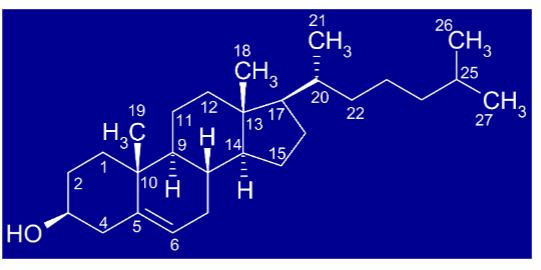
what molecule is this
cholesterol
Hormones:
Chemical messengers that provide communication from one part of the body to another
Corticoadrenal hormones:
Corticoids: downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines
Where are triacylglycerols (TG) mainly digested
in the intestine
What enzyme breaks down triacylglycerols in the intestine
Pancreatic lipase
Products of the breakdown of triacylglycerols
2 fatty acids and a 2-monoacyl-glycerol
Fatty acids of 12 carbons or less are digested:
Hydrolyzed by lipases from the mouth or stomach
what ester bonds get cleaved by the lipase during the first step of lipid degradation?
1 and 3 ester
Monoacylglycerol is used to:
Resynthesize a triacylglycerol
Fatty acids are degraded through:
Beta-oxidation and acetyl-CoA
Glycerol can be converted to what via what
Glucose via gluconeogenesis
Bile acids:
Emulsify dietary fats in the intestine- necessary for digestion to occur
Essential for the absorption of the digestion products of lipids
Recycled
Amphipathic-detergent like molecules
Cholesterol derivatives
Glycine or taurine conjugates
Structure of bile acids:
Cholesterol derivatives with 2 variable residues
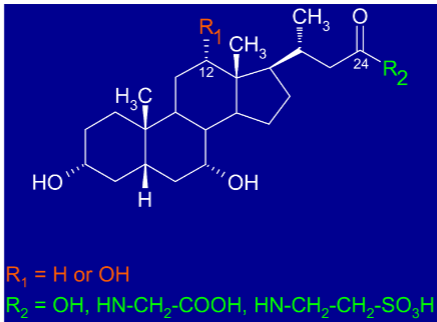
Lipases are:
Special esterases
Pancreatic lipase:
A triacylglycerol lipase
Responsible for the digestion of triacylglycerols in the intestine, operating at pH 6
What is secreted along with pancreatic lipase
colipase and bicarbonate for neutralizing stomach acid until pH 6 is reached
Colipase:
binds to both the fats and the triacylglycerol lipase
ex: pancreatic lipase, making it more active
What does pancreatic lipase hydrolyze?
fatty acids from positions 1 and 3 of the glycerol backbone
Phospholipases:
Digest phospholipids
Free fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerols are packaged:
Into micells with other dietary lipids, and emulsified by bile acids
Where do the micelles go after fatty acids and 2-monoacylglycerols are packaged into them?
Travel to the surface of intestinal epithelial cells, where everything MINUS the bile acids are absorbed
Where do bile acids get absorbed?
In the ileum via recycling
do short and medium length fatty acids (4-12 carbons) require bile acids for absorption?
NO
Micelle structure:
Monolayer membrane
outside: water
inside: lipid
Small
Lipsome structure:
Bilayer membrane
outside: water
Inside: water
relatively large
How are triacylglycerols recycled?
Within epithelial cells (enterocytes)
Fatty acids activated by acetyl CoA
Recombined with 2-monoacylglycerol
Forming triacylglycerols in the smooth ER
Dietary lipids are packaged into what for transport?
Chylomicrons in intestinal epithelial cells
Lipids can also be synthesized from:
Carbohydrates in the liver
Lipids who were synthesized in the LIVER travel via how?
Packaged into VLDLs (very low density lipoprotein)
Why are lipoproteins like chylomicrons and VLDLS necessary
Transport of lipids to prevent the accumulation of insoluble fat droplets in the blood
What increases the water solubility of lipoproteins?
amphipathic phospholipids on the surface of the lipoprotein
What is the major apoprotein of chylomicron
B-48
What is the major apoprotein of VLDL
B-100
Where are the protein components of a lipoprotein synthesized in
rough ER
Where does synthesis of TGs occur:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Where does apoprotein synthesis occur
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Assembly of chylomicrons occurs where
Golgi complex
TG + Apoprotein =
Chylomicron
Finished chylomicron enters what
lymph through exocytosis
Chylomicron retention:
Inhereited disorder impairing the normal absorption of fats, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins
Begins in infancy or early childhood
Symptoms of chylomicron retention
slow growth
slow weight gain
requent and chronic diarrhea
steatorrhea (fat in stool)
What gene is affected in Chylomiron retention
SAR1B whose product promotes the transport of pre-chylomicrons in micelles
Mutations cause retention of chylomicrons within endothelial cells and prevent release into bloostream- lipid droplets accumulate
Chylomicrons are secreted by:
Exocytosis into the lymphatic system, and then to the blood via the thoracic duct
Chylomicrons require what to become “mature”
HDL
apoE:
Recognized by membrane receptors
apoCII
Activator of LPL (lipoprotein lipase)
What digests the triacylglycerols of the chylomicrons?
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) attached to the proteoglycans of capillary epithelial cells
When the triacylglylcerols of the chylomicrons are broken down:
Resuliting fatty acids are taken up by adipose (most often) and muscle (less often) and stored in the adipose or beta-oxidized for energy (within muscle)
Glycerol is recycled in the liver during:
Fed state
Glycerol is used for gluconeogenesis in:
Fasting state
Cylomicron remnants are taken up and recycled by what:
Liver