IGCSE BIO 16. reproduction
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
germination
the process whereby seeds or spores sprout and begin to grow
conditions for seed germination
oxygen (for aerobic respiration) / water (to activate enzymes & chemical reactions) / suitable temperature (to activate enzymes)
scrotum
sac covering testes / hang outside the body, to keep testes cool, as sperm cannot withstand temperature above 37C
ovaries
produce ova / progesterone / oestrogen
puberty
the time at whcih sexual maturity is attained
asexual reproduction
a process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring from one parent
sexual reproduction
a process involving fusion of nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote, and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other
fertilisation
fusion of haploid nuclei of gametes to form a diploid zygote
advantages of asexual reproduction
only one parent needed --> so need to find mate / faster mass reproduction / less energy required, as no need to produce big flower or nectaries... / doesn't rely on pollinating agents / if parent well adapts to environment, offspring will also adapt well too
advantages of asexual reproduction, in crops
uniform genetically identical crop (with better yield, disease resistance...etc.) can only be produced
disadvantages of asexual reproduction
absence of genetic variation in offspring --> less ability to survive in different environment (disease resistance..etc.) --> less chance of evolution / overcrowding --> competition for resources
disadvantages of asexual reproduction, in crops
entire crop population can be destroyed by a disease, if they do not have genes of resistance
advantages of sexual reproduction
genetic variation in offspring --> more abilty to survive in different environment --> more possibility of evolution
disadvantages of sexual reproduction
need to find mate --> takes more time (slower) / more energy required, because of need to produce big, colourful flowers and nectaries... / rely on pollinating agents
disadvantages of sexual reproduction, in crops
uniform crop of genetically identical offspring is not possible
sepal
protect the flower, when it is a bud
petal
large and brightly coloured, to attract pollinators
anther
produces pollen grain, which contains male gamete
filament
supports the anther, holds it upright
stamen
another word to call male part of flower = anther + filament
stigma
site of receiving pollen grains
style
connects the stigma to the ovary
ovary
contains ovule, and forms fruit after fertilisation
ovule
contains female gamete (egg cell), and form seeds after fertilisation
carpel
another word to call female part of flower = stigma + style + ovary + ovules
pollination
transfer of pollen grain from anther of one flower to a stigma
!!POLLINATION IS ALWAYS SEXUAL REPRODUCTION!!
self-pollination
transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or different flower on the same plant
cross-pollination
transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower from the anther of a flower to the stigma of flower on a different plant of same species
features of self-pollination
no or little genetic variation / lesser capacity to adapt to change in environment / no reliance on pollinators
features of cross-pollination
genetic variation / more capacity to adapt to change in environment / reliance on pollinators / energy need to be invested in bigger flowers and nectaries etc.
features of insect-pollinated flowers
large, conspicuous, colourful petals / scent & nectaries at the base / anthers & sticky stigma enclosed within petals /less, heavier, spiky pollen
features of wind-pollinated flowers
small, inconspicuous, green petals / no scent & nectaries / large anthers & feathery stigma dangling out of flower / smooth, light, more number of pollen
why self-pollination might be advantagous to a population of plants
prevents extinction / more chance of fertilisation & pollination / no need for pollinators / useful, if plants are isolated / for even smallest variation, pollination as sexual reproduction is better
fertilisation process
pollen grain lands onto the stigma --> pollen forms pollen tube (secretes enzymes to digest a pathway to the ovule through the style) --> male halpoid nuclei in pollen is delivered through pollen tube to the ovule --> fertilisation
types / roles of enzymes in germination
amylase & protease / break down stored food to release energy / diffuse into the embryo --> used for growth / needed in process of respiration
testes
produce sperm & male hormone (testosterone)
sperm ducts (vas deferens)
tube that transports semen from testes to urethra
prostate gland
secrete nutritious alkaline fluid (semen) in which sperm cells are transported / mucus
urethra
carries urine and sperm, but not at the same time : a ring of muscle around the urethra contracts, to prevent urine loss during sexual intercourse
penis
deliver sperm to the vagina for fertilisation / urethra runs down the center of penis
oviduct (fallopian tube)
ovum released from the ovary into the oviduct / site of fertilisation / cilia present, for propulsion of ovum
uterus
site of fetus development / develops spongy wall for embryo implantation, in case of pregnancy
cervix
narrow opening, which separates vagina from uterus
vagina
muscular tube opening outisde the body / receives male penis during the sexual intercouse / site of sperm deposition
adaptive features of sperm cells
acrosome : vesicle containing enzymes, which dissolves way through the jelly surrounding the egg cell / middle piece containing mitochondria to release energy for swimming / flagellum : allows swimming movements
adaptive features of ova
thick cytoplasm, containing lots of food stores / jelly coat : hardens after ferilization, to prevent entry of other sperms (NOT PROTECTIVE IN FUNCTION)
movement of spem cell / ova?
sperm cell : mobile / egg cell : motile (does not move by itself, move along by cilia and peristalsis)
food store in sperm cell / ova?
very little in sperm cells, as they respires the sugar in seminal fluid / ova has enough to last till implantation
number of sperm cells / ova produced?
sperm cells in millions constantly / ova one released per month
how ova is produced from ovary?
by meiosis
ovulation
release of mature ovum from ovary
embryo
ball of cells, which is the result of mitosis of zygote along the way through oviduct to uterus
another name of uterine lining
endometrium
placenta
disc-like structure formed from cells of embryo, soon after implantation
function of placenta
exchange of substances (oxygen, nutrients, excretory products.../ through diffusion / blood vessels close to each other)
placental barrier (prevents mixing of maternal and fetal blood, bursting of fetal vessels due to high pressure of maternal blood / prevents entry of pathogens from mother to fetus)
endocrine functions (secrete oestrogen & progesterone)
umbilical cord
connects endometrium to embryo / contains blood vessels from fetus
amniotic sac
a fluid-filled sac that cushions and protects a developing embryo and fetus in the uterus
amniotic fluid
fluid within the amniotic sac that surrounds and protects the fetus
functions of amniotic fluid
supports fetus / protects fetus against damage / provides constant temperature / allows movement of fetus / needs for bone & muscle & lung & gut development / needed for excretion / provides sterile environment
secondary sexual characteristics of male
enlargement of testes & penis / deepening of voice / broadening of shoulders / growth of hair in the pubir region, armpits, face, chest / rapid increase in growth rate
secondary sexual characteristics of female
increase in size and uterus & vagina / growth of breasts / widening of hips / growth of hair in the pubic region, armpits / rapid increase in growth rate
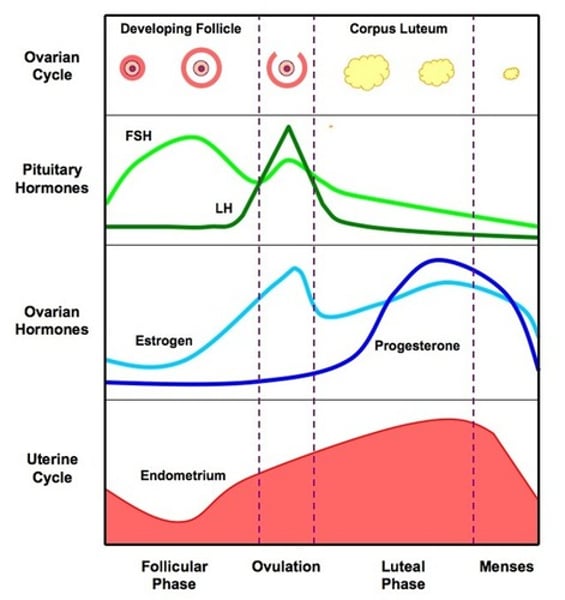
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
produced by pituitary gland / makes egg mature in the ovary / stimulates production of oestrogen from ovary
LH (luteinizing hormone)
produced by pituitary gland / causes ovulation
oestrogen
produced by ovaries / stimulates the thickening of uterus wall / inhibits the production of FSH / stimulates pituitary gland to make LH
progesterone
produced by ovary --> placenta / prevents menstruation (maintains the thick uterus lining) / increases the thickening of lining of uterus
corpus luteum
structure in ovary that forms from follicle left after ovulation / produces progesterone
day 0-5 of menstrual cycle
menstruation (shedding of uterus lining for last egg + unfertilized egg)
day 0-12 of menstrual cycle
new egg mature in ovary (FSH produced --> oestrogen produced from ovary --> FSH level drops)
day 12-16 of menstrual cycle
ovulation (release of one mature egg from one ovary) (LH (with FSH slightly) released and drop)
day 16-23 of menstrual cycle
egg travels through oviduct to uterus / fertilisation can happen
day 23 - 28 of menstrual cycle
if fertilized : implanted in uterus wall (progesterone & oestrogen level remains high)
if not fertilized : uterine lining starts to wear away (progesterone level drops due to dying of corpus luteum)
hormone graph of menstrual cycle
sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
infection that is transmitted via body fluids, through sexual contact
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
virus that makes the immune system so weak
AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
collection of diseases due to weak immune system by action of HIV
how HIV is transmitted
in blood (not insects) / in semen & unprotected sex / contaminated hypodermic needles / blood transfusion / at birth (when two blood vessels are closely in contact) / via breast milk / NOT SALIVA & BLOOD SUCKING INSECTS
prevention of HIV
use of condoms / antiviral drugs / reduction of shared needle usage by drug users