CARIOLOGY
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
SHAFER (1993)
Define caries as irreversible ⎯ Microbial disease of hard calcified tissue of the tooth
Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry 2012
Infectious, microbial disease of teeth that result in localized dissolution of calcified tissue
2017
Plaque(ON)/biofilm (NN) ⎯ Sugar driven ⎯ Multifactorial ⎯ Dynamic o Disease that results in the phasic demineralization and remineralization of dental hard tissues
2020
⎯ Biofilm mediated ⎯ Diet-modulated ⎯ Multifactorial ⎯ Dynamic ⎯ Noncommunicable o Disease resulting in net mineral loss of dental hard tissue.
▪ Dental Caries
⎯ Name of the disease.
▪ Cavitation of caries lesion
⎯ symptom of disease
▪ Incipient Lesion
⎯ or white spots ⎯ can be reversed or arrested
Ø Tooth level
Ø Person level
Ø Community level
Caries is a complex disease prevention and management should be done at the :
Dental Caries
Multifactorial oral disease
Caused primarily by complex interaction of cariogenic oral flora with fermentable dietary carbohydrates on the tooth surface over time.
Greene Vardiman Black
Who is considered one of the founders of modern dentistry in the United States?
DENTAL PLAQUE
A term historically used to describe the gelatinous (soft, translucent, tenaciously adhering) mass of bacteria adhering to the tooth surface.
Biofilm
An aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other and/ or to a solid substrate exposed to an aqueous surface
Polysacharides
Which substance produced by oral bacteria holds biofilms together
extracellular polysaccharides (EPS).
What is the gel-like matrix in dental biofilm mainly composed of
90%
What percentage of biofilm volume is comprised of a gel-like intermicrobial matrix
Formation of Pellicle
initial attachment
irreversible attachment
early maturation
late maturation
dispersion
Stages of BIOFILM Development
Streptococcus sanguinis
early colonizers of the teeth,normal inhabitants on the mouth
– Weak and reversible van der Waals forces.
What type of forces mediate the initial attachment of early colonizers?
van der Waals forces
(distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules
Materia alba
⎯ Soft accumulation of bacteria, salivary proteins , food debris and tissue cells. ⎯ Lacks the organized structure of dental plaque ⎯ Easily displaced with a water spray.
Calculus (tartar)
⎯ This is formed over time, if plaque isn't removed on a regular basis, minerals from your saliva are deposited into the plaque biofilm causing it to harden within 24 to 72 hours ⎯ Mineralized dental plaque - Or TARTAR, CALCULAR DEPOSITS
Pathological factors
Protective factors
Factors influencing initiation and progression of caries (2017 definition)
Tooth/Lesion level
Person level
Community level
Three levels of caries management
Fluoride
Sealants
Salivary stimulation
Protective factors against caries
Acidogenic
→ produce acids
Aciduric
→ thrive in acidic environment
Willoughby Dayton Miller
The American dentist considered the first oral microbiologist who proposed the chemo-parasitic theory of caries.
Streptococcus mutans & Lactobacilli
The bacterial group primarily responsible for lactic acid production in caries.
Demineralization
The process by which enamel minerals dissolve when pH falls below 5.5.
Remineralization
The process where minerals are redeposited in enamel when pH rises above 5.5.
BUFFER
⎯ A solution (or substance) that has the ability to maintain pH and bring it back to its optimal value by addition or removal of hydrogen ions
▪ S. mutans (or MS) ▪ Lactobacilli
aciduric and acidogenic microorganisms:
SOLUBILITY
⎯ Is the measure of the concentration of dissolved solid in a saturated solution
UNDERSATURATED
⎯ When the solution contains less than the equilibrium concentration of dissolved solid
SUPERSATURATED
⎯ when the concentration of dissolved solid in solution is greater than at equilibrium
GV Black
organized 'Black's Classification of Caries Lesions' which is still in use today
Ecological Shift
What is the term for the process where the pH in dental plaque becomes acidic due to sugar metabolism by acidogenic bacteria?
subsurface lesion.
This is seen as a white spot lesion. The first clinical sign of incipient caries.
"disturbance in the mineral homeostasis"
More minerals in saliva will enter the plaque in an attempt to neutralize or buffer the acidic plaque. The entry of more minerals into the biofilm makes the saliva undersaturated(of minerals) compared to the minerals on the tooth surface. This is called
Demineralization
To restore the mineral levels of saliva, the hydroxyapatite of enamel will dissolve and release calcium and phosphates. This is called ?and this happens at a pH of <5.5 in the absence of flouride.
Remineralization
The mineral level in saliva is now higher compared to the mineral level in enamel. The higher levels in saliva will cause reprecipitation of minerals in enamel. This is called ??. This happens at a pH pf> 5.5
lactic acid and extracellular polysaccharide like glucan.
Acidogenic bacteria will metabolize sugar and produce
Black's Classification of Caries Lesions
GV Black organized
CLASS I
Occlusal of posterior teeth
or lingual pit near cingulum
in maxillary incisors
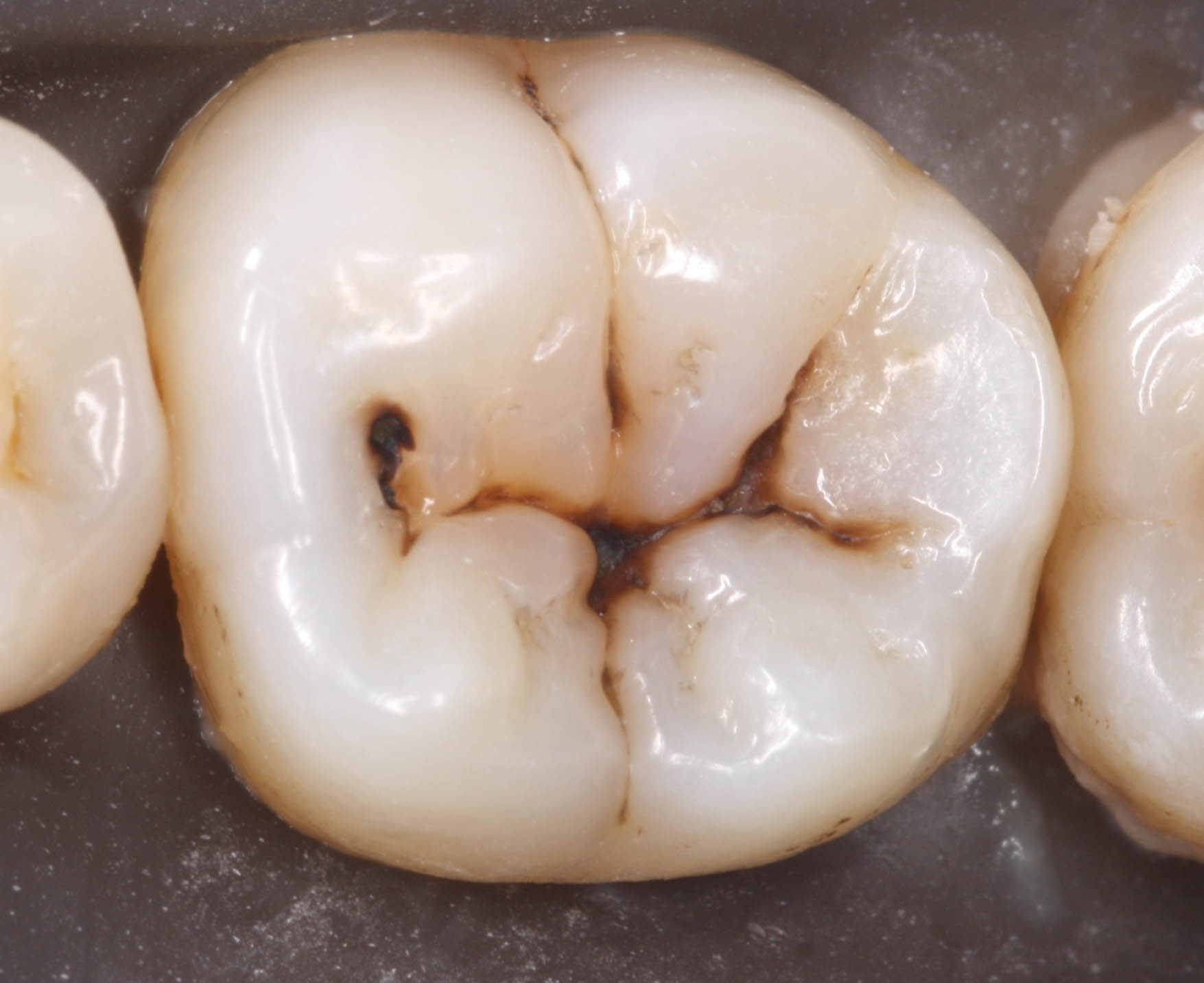
CLASS 2
Proximal
surfaces of
posterior teeth
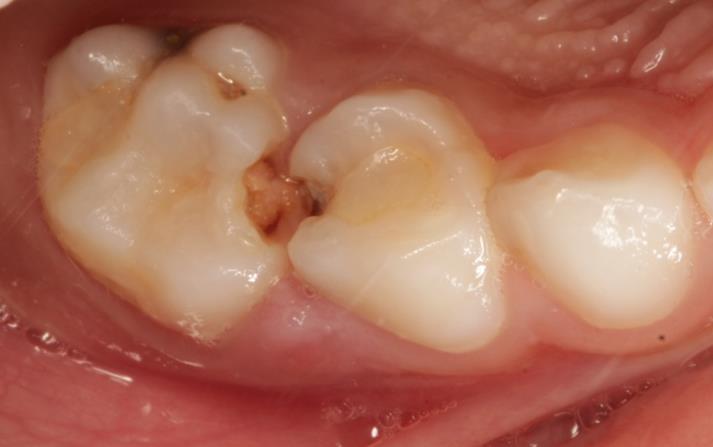
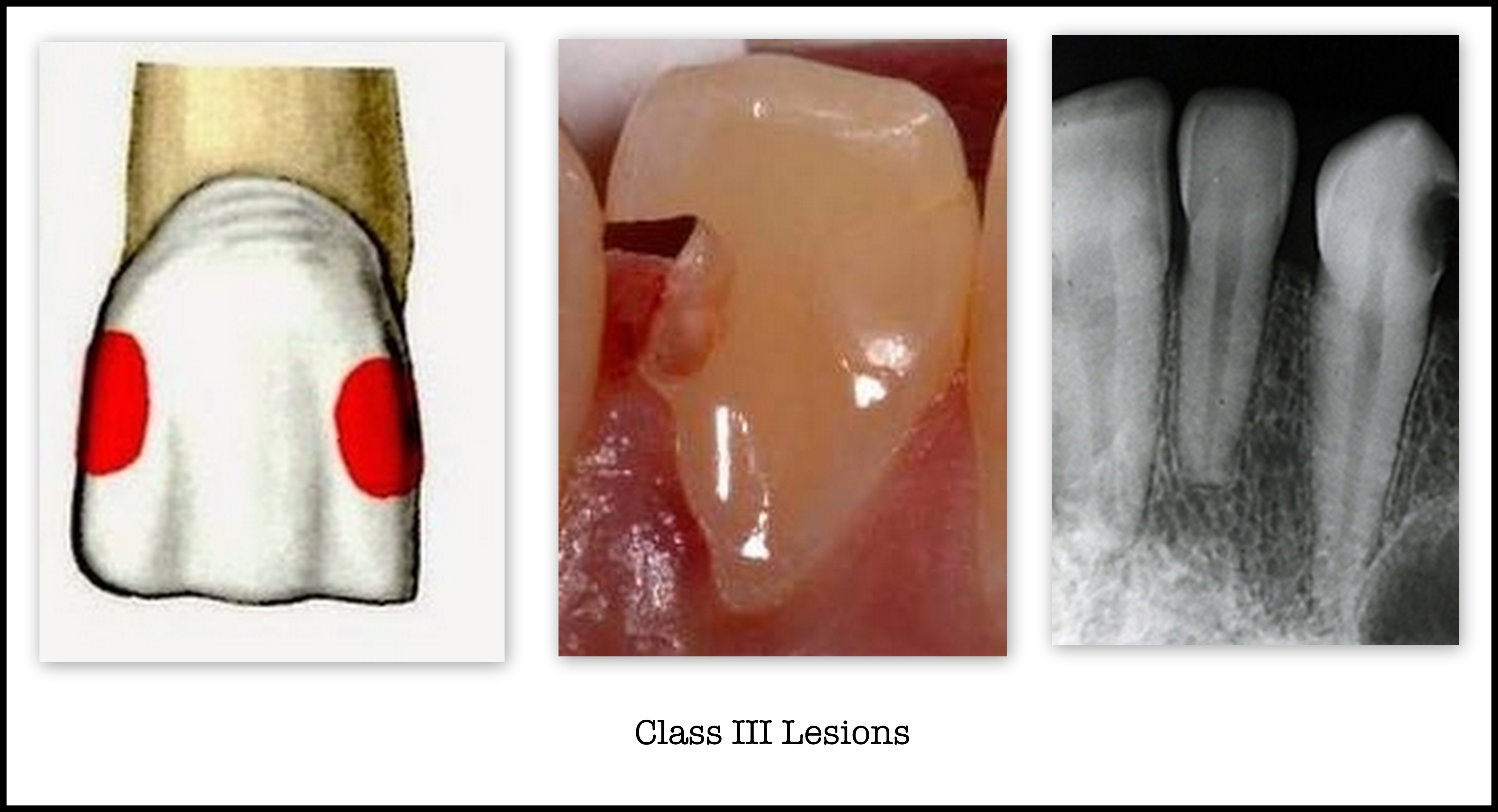
CLASS 3
Interproximal surfaces
of anterior teeth without
Incisal edge involevement
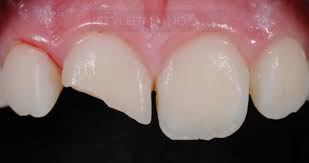
CLASS 4
Interproximal surfaces
of anterior teeth with Incisal
edge involevement
CLASS V
Cervical third of
facial or lingual
surfaces of teeth
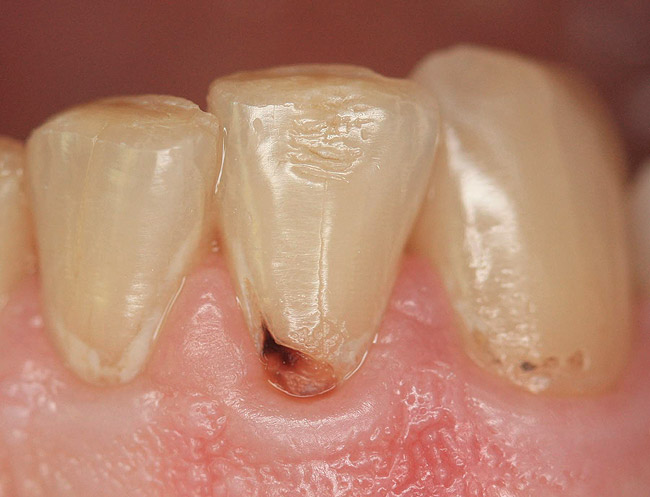
CLASS VI
affect the cusp tips of posterior teeth and the incisal edges of anterior teeth, often resulting from abrasion, erosion, or attrition.
DENTAL PLAQUE
Cannot be seen by the naked eye o but can often feel significant build-ups by running the tongue across the surface of the teeth due to its sticky properties.
DENTAL PLAQUE
More recently referred to as the dental biofilm or simply the biofilm, which is a more complete and accurate description
Plaque
- is an invisible layer of film made up of millions of bacteria and protein from saliva
BIOFILM
Provides the environment for bacteria to form acid
BIOFILM
Form via an ordered sequence of events resulting in a structurally and functionally organized,species-rich microbial film
salivary glycoprotein, phosphoproteins, and lipids
Composition of pellicle
“Streptococcus sanguinis”
form an initial attachment to the pellicle by weak and reversible van der Waals forces
Van der Waals forces
Which type of force allows early colonizers like Streptococcus sanguinis to make a weak and reversible initial attachment to the tooth pellicle?
Specific adhesion–receptor interaction
Organisms that were unable to attach to the pellicle begin to adhere to the first layer of colonizer with irreversible attachment via what process?
dispersin B
allow some bacteria to detach themselves from the biofilm
MATERIA ALBA
Lacks the organized structure of dental plaque
MATERIA ALBA
Easily displaced with a water spray
24 to 72 hours
How many hours does it take for minerals from saliva to harden dental plaque into calculus?
Theory
⎯ a system of ideas intended to explain something
⎯ hypothesis
⎯ assumption
⎯ proposition
synonyms: of theory
Etiology
⎯ the cause, set of causes, or manner of causation of a disease or condition
1. Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis
2. Specific Plaque Hypothesis
3. Ecological Plaque Hypothesis (1991)
Theories on Etiology of Dental Caries
Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis (NSPH)
Which plaque hypothesis, proposed by Loesche in 1976 and based on the works of Black (1884) and Miller (1890), states that all plaques are pathogenic and that caries result from the combined action of all oral organisms?
Loesche
Who proposed the Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis in 1976?
Black and Miller
Which two researchers’ works (from 1884 and 1890) formed the basis of the Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis?
Willoughby Dayton Miller
Who is considered the first Oral Microbiologist?
1976
In what year did Loesche propose the Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis?
1884
In what year did Black contribute work that later supported the Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis?
1890
In what year did Miller contribute research related to the Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis?
1970s
In what decade was the Specific Plaque Hypothesis proposed?
Specific Plaque Hypothesis
In the 1970s, culture-based techniques and microscopy allowed discrimination of specific bacterial species and opened the hunt for disease-related microorganisms. This led to which theory?
Ecological Plaque Hypothesis
In 1991, a change in the environment of the residential flora that gives pathogenicity to specific species and produces disease only at specific sites is explained by which hypothesis?
Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis
All plaques are pathogenic, and caries is the result of the combined action of all oral organisms. This describes which hypothesis?
Specific Plaque Hypothesis (SPH)
Caries is caused by infection with specific bacteria found in dental plaque.
Ecological Plaque Hypothesis (EPH)
Changes in the oral environment disturb the balance of bacteria, giving certain species the chance to cause disease at specific sites.
▪ Streptococcus oralis
▪ Streptococcus mitis
▪ Streptococcus sanguis
First to colonize biofilm are
30–60 minutes
How long after an acid attack can buffers in saliva increase the pH?
BUFFER
⎯ A solution (or substance) that has the ability to maintain pH and bring it back to its optimal value by addition or removal of hydrogen ions
MS (Mutans Streptococci) & Lactobacilli
Which bacteria produce lactic acid, extracellular polysaccharide (glucan), and intracellular polysaccharide that can be used for energy and contribute to the plaque matrix?
Crystal dissolution & precipitation
The processes underlying demineralization and remineralization in caries are?
intracellular polysaccharide
(can be used for energy production and converted to acid when sugars are not available)
Dissolution and crystal growth
are both surface- related processes
Saturated
When the rates of these processes are equal, the solid is in equilibrium with the solution and no net dissolution or crystal growth will occur. In this situation, the solution is said to be "_________" with respect to that particular solid.
Below 5.5
At what pH do tooth minerals (hydroxyapatite) start to dissolve?
Crystal growth / remineralization
What happens when the oral fluids become supersaturated with calcium and phosphate?
> 4.5
At what pH in the presence of fluoride does re-precipitation of hydroxyapatite occur?
Elimination or modification of etiological factors (dietary, microbial) and/or by enhancing protective factors (fluoride, sealants and salivary stimulation)
The early stages of dental caries can be prevented, reversed or arrested, primarily through what?
▪ Phosphate ▪ Calcium
When pH goes up ▲ the oral fluids become supersaturated with
(fluoride, sealants and salivary stimulation).
protective factors
(dietary, microbial)
etiological factors
Cell-free protein-rich layer (pellicle)
What layer forms on enamel soon after brushing?