IED EoC Study
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
6 steps of design process
define the problem
generate concepts
more just research
NVM use decision matrix here
develop solution
, drawing
construct / test prototype
evaluate solution
reflect and improve from testing
present solution
design brief
This concise document (no more than one page) identifies the client, clearly states his/her problem or need, details the degree to which the engineer will carry out the solution, and lists the rules and limits within which the engineer must perform.
deliverables
Project deliverables are the output you expect to have at the end of your project. Deliverables can be anything—a new product, marketing campaign, feature update, sales deck, a decrease in churn, or an increase in NPS.
project portfolio
Used to document the project and given to the people who offered the Design Brief (problem)
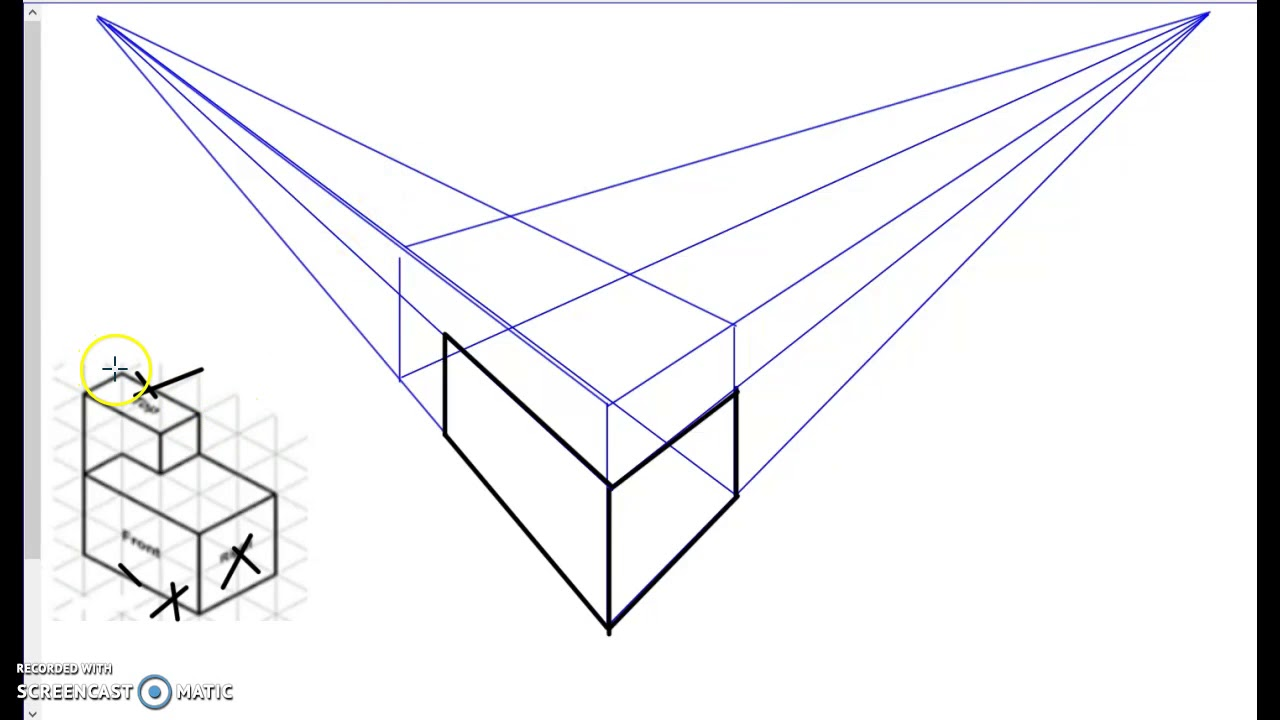
perspective sketch
A type of pictorial drawing in which vanishing points are used to provide the depth and distortion that is seen with the human eye.
natural looking and no distortion
oblique drawings
▪start with a straight-on view of the one of the object's faces, which is often the front face
▪angled, parallel lines are drawn to one side to represent the object's depth. common oblique angles include 30°, 45°, and 60°
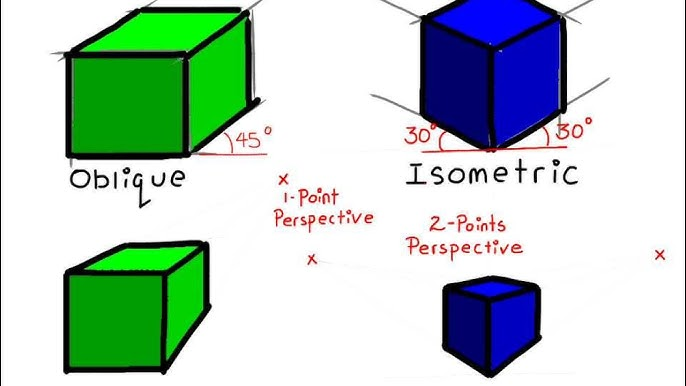
pictoral sketch
▪2D illustrations of a 3D object
▪shows 3 faces of an object in one view
▪3 types:
-isometric
-obliques
-perspective
dimensioning rules
dimensions are actual size not scaled size
overall dimensions: width, height, depth
Include all dimensions necessary to produce or inspect the part.
Do not include unnecessary dimensions
Dimensions should be attached to the view that best shows the contour of the feature to be dimensioned. (usually front view)
A dimension should be attached to only one view; for example, extension lines should not connect two views.
Whenever possible, locate dimensions between adjacent views.
don’t dimension hidden lines
don’t place inside object
don’t cross dimension line with another dimension line or extension line
don’t cross with leader lines
leader lines cant be straight and must point to center
dimension values should be centered but staggered when stacked dimensions
a circle is dimensioned by its diameter and an arc by its radius
holes should be located and sized in the view that shows a circle
holes are located by their centerlines which may be extended and used as extension lines
types of lines
object
Lines are thick and dark
used to define the object
Construction
Very lightly drawn lines
used as guides to help draw all other lines and shapes properly.
hidden line
dashed
used to show interior detail that is not visible from the outside of the part.
center line
Lines that define the center of arcs, circles, or Symmetrical parts. They are half as thick as an object line.
section line / break line
Lines are used to define where there is material after a part of the object is cut away.
extension lines
Lines used to show where a dimension starts and stops on an object.
leader lines
Leader lines are used to show dimensions of arcs, circles and to help show detail.
ribbon
browser
geometric constraints
perpendicular
parallel
tangent
smooth
makes continuous curvature between curves
coincident
constrains geometries together
concentric
makes have same center point
collinear
makes lie on same line
horizontal
vertical
equal
makes have same radius or samelength
fix
fixes in position
symmetry
place features symmetrically on part
precedence of lines
Object lines take precedence over hidden and center lines.
Hidden lines take precedence over center lines.
Cutting plane lines take precedence over all others.
hole types
clearance
Hole large enough to allow screw head (and driver) to pass through
blind
Hole does not cut through entire thickness
countersink
Conical-shaped recess around hole at surface
Often used to accept tapered screw
counterbore
Cylindrical recess around hole at surface
Often used to receive a bolt head or nut
tapped
hole has internal threads
