AP Psychology - History and Approaches
5.0(4)Studied by 76 people
0%Unit 1 Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psychological perspectives and historic psychologists
Last updated 5:06 PM on 4/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Introspection
The psychological method of studying thought by asking people to record what they are thinking.
2
New cards
Structuralism
The belief that the mind operates by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations.
3
New cards
Functionalism
The belief that actual thought processes cannot be studied, so psychologists should only focus on the behavior of people.
4
New cards
Gestalt Psychology
An early field of psychology that examined people’s total experiences and saw how they impacted their perception of things.
5
New cards
Psychoanalysis
A theory that there is an unconscious mind that impacts behavior without conscious thought of it, and that people repress thoughts that create anxiety in their unconscious mind. This theory claims that you have to examine the unconscious mind to truly understand human thought.
6
New cards
Behaviorism
The belief that psychology can only actually study behavior (specifically responses to stimuli), and that other things (like the unconscious mind) can’t be proven.
7
New cards
Humanist Perspective
The perspective that emphasizes that people have individual choice and free will, and that we choose our behavior and that our behavior is influenced by physiological, emotional, and/or spiritual needs.
8
New cards
Psychoanalytic Perspective
A perspecitve that emphasizes that the unconscious mind controls actions and thought, and that people repress certain thoughts in their unconscious mind, so we have to examine that region of the mind through things like dream analysis and word association to fully understand motives behind behavior.
9
New cards
Bio-psychological Perspective (or Neuroscience)
The perspective that claims our behavior is strictly influenced by our biology. For example a person who follows this might believe a person is introverted because their parents gave them genes that promote introversion.
10
New cards
Evolutionary (or Darwinian) Perspective
A perspective that asserts human behaviors exist because of natural selection, and that overtime psychological traits become more common because they are more advantageous for survival.
11
New cards
Behavioral Perspective
A perspective that explains human thought and behavior through conditioning. Adherents believe that you can only study responses to stimuli, not thought.
12
New cards
Cognitive Perspective
A perspective that focuses on how people interpret, process, and remember environmental events.
13
New cards
Sociocultural Perspective
A perspective of psychology that looks at how thoughts and behaviors vary between cultures, and how cultures influence behavior.
14
New cards
Biopsychosocial Perspective
A modern perspective of psychology that looks at biological, psychological, and social factors together to determine causes of thoughts and behaviors.
15
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
The first psychologist to open a psychological lab, who studied subjects with introspection.
16
New cards
William James
The author of *The Principles of Psychology*, the first psychological textbook. He also developed functionalism.
17
New cards
Mary Whiton Calkins
Psychologist who studied with William James and became the first female president of the American Psychological Association.
18
New cards
Margaret Floy Washburn
The first woman to earn a PhD in psychology.
19
New cards
G. Stanley Hall
Psychologist who pioneered the study of child development and became the first president of the American Psychological Organization.
20
New cards
Max Wertheimer
The psychologist who pioneered Gestalt Psychology.
21
New cards
Sigmund Freud
The psychologist who created psychoanalysis.
22
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
A psychologist known for conditioning dogs to salivate when they heard a metronome through frequently ringing a metronome when feeding the dogs.
23
New cards
John B. Watson
A psychologist who believed that for psychology to be a science it had to exclusively focus on observable phenomena. This resulted in behaviorism.
24
New cards
B. F. Skinner
Behaviorist known for observing reinforcement when studying a rat and giving it food every time it pulled a bar.
25
New cards
Abraham Maslow
A founder of humanistic psychology, especially known for creating a hierarchy of needs.
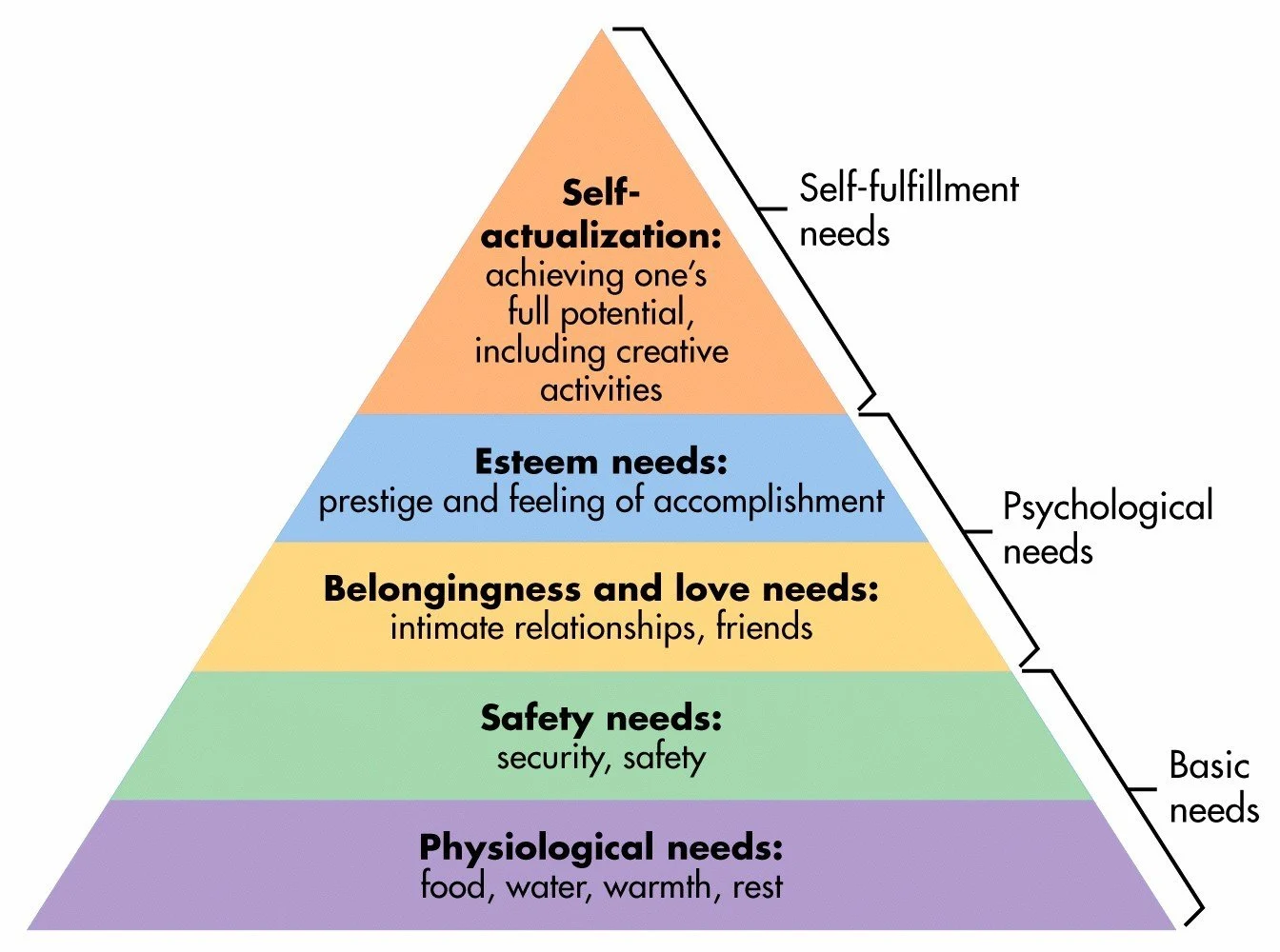
26
New cards
Carl Rogers
A founder of humanistic psychology
27
New cards
Charles Darwin
The person who created the theory of natural selection.
28
New cards
Jean Piaget
Cognitive psychologist who is known for creating the cognitive development theory.