bsc2085 lesson 15/16
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Midbrain
- brain region that develops from embryonic mesenecephalon
anatomical features of midbrain
- cerebral aqueduct
- motor nuclei of 2 cranial nerves
- tectum
- tegmentum
- substantia nigra
cerebral aqueduct is surround by
central gray substance (periaqueductal) involved in pain awareness
Motor nuclei in midbrain
CN III (oculomotor) and CN IV (trochlear)
Tectum
- roof-life part of the midbrain posterior to cerebral aqueduct
- 4 bulges- two superior colliculi, and two inferior
superior colliculi
visual attention, tracking moving objects, and visual reflexes
inferior colliculi
relays signals from inner ear to thalamus and other parts of the brain, auditory reflexes
tegmentum
connections go to and from cerebellum for motor control
Substantia nigra
- dark nucleus pigmented with melanin
- motor center that relays inhibitory signals to thalamus and basal nuclei, suppressing unwanted body movement
- degeneration of neurons leads to tremors of Parkinson's
Reticular activating system (RAS)
- component of the reticular formation in midbrain important for alertness and attentiveness
- habituation
- pain modulation
- sleep and consciousness → damage will lead to irreversible coma
cerebellum
largest part of hindbrain, second-largest part of brain as a whole, and contains more than half of all brain neurons
cerebellum components
- granule cells
- purkinje cells
- right and left hemispheres connected by vermis
- folia and branching arbor vitae
vermis
connects right and left cerebellar hemispheres
folia
superficial cortex of gray matter with folds
Functions of cerebellum
- Motor coordination and locomotor ability
- Sensory, linguistic, emotional, and other non-motor functions
Sensory, linguistic, emotional, and other non motor functions of cerebellum
- comparing textures of objects
- perceiving space
- recognizign objects from different views
- keeping judge of elapsed time and maintaining tapping rhythm
- directing eye movements to compensate for head movement
- judging pitch of tones distinguishing between spoken words
- helping in verbal association tasks
- planning, scheduling, and emotion control
ataxia
clumsy awkward gait from lesions in cerebellum
2 part of forebrain
diencephalon and telencephalon
diencephalon
encloses 3rd ventricle; most rostral part of brainstem
telencephalon
develops chiefly into cerebrum
3 major components of diencephalon
- thalamus
- hypothalamus
- epithalamus
thalamus
- mass on each side of brain
- 4/5 of diencephalon
- synchronizes electrical activity between 2 hemispheres of cerebrum
- gateway to cerebral cortex
- plays key role in motor control
- involved in memory and emotion
desynchronization
damage to thalamus can cause ____ between hemispheres; leads to epilepsy and seizures
treatment can be to cut corpus callosum
anterior group of thalamic nuclei
part of limbic system; memory and emotion
medial group of thalamus
emotional output to prefrontal cortex; awareness of emotions
Ventral group of thalamus
Somatosensory output to postcentral gyrus; signals from cerebellum and basal nuclei to motor areas of cortex
Lateral group of thalamus
Somatosensory output to association areas of cortex; contributes to emotional function of limbic system
Posterior group of thalamus
Relay of visual signals to occipital lobe and auditory signals to temporal lobe
thalamus as the gateway to cerebral cortex
- processes info on way to cerebral cortex
- not all is passed, it screens out most it receives
thalamus in motor control
- relays signals from cerebellum to cerebrum
- provides feedback loops between cerebral cortex and basal nuclei
hypothalamus
- extends anteriorly to optic chiasm and extends posteriorly to mammillary bodies
- process olfactory and other sensory information and controls reflex eating movements
Attachment of hypothalamus to pituitary gland
Through a stalk-like structure called the infundibulum
Hypothalamus components and functions
- contains many nuclei with a wide variety of visceral, emotional, and behavioral functions
- homeostatic regulation of all systems
- major control center of autonomic nervous system, endocrine systme
functions of hypothalamic nuclei
- hormone secretion
- autonomic effects
- thermoregulation
- food and water intake
- sleep and circadian rhythms
- memory
- emotional behavior and sexual response
hormone secretion of hypothalamic nuclei
- controls anterior pituitary; regulates growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response
- produces posterior pituitary hormones for labor contractions, lactation, and water conservation
autonomic effects of hypothalamic nuclei
- major integrating center for autonomic nervous system
- influences heart rate, blood pressure, gastrointestinal secretions, motility
thermoregulation of hypothalamic nuclei
- hypothalamic thermostat monitors body temperature, activates, mechanisms to adjust temp if necessary
food and water intake of hypothalamic nuclei
- regulates hunger and satiety; responds to hormones influencing hunger, energy expenditure, and long-term control of body mass
- osmoreceptors monitor osmolarity of blood, can stimulate production of ADH to help conserve water
sleep and circadian rhythms of hypothalamic nuclei
Suprachiasmatic nucleus controls 24-hour (circadian) rhythm
memory of hypothalamic nuclei
Mammillary nuclei relay signals from hippocampus to thalamus
emotional behavior and sexual response of hypothalamic nuclei
anger, aggression, fear, pleasure, contentment, sex drive
pineal gland
- located in epithalamus
- produces melatonin hormone, helps with circadian rhythm and reproduction function
cerebrum
- develops from the telencephalon and is the largest, most conspicuous part of human brain
- seat of sensory perception, memory, thought, judgment, and voluntary motor actions
3 functional principles of the cerebrum
each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from, and sends motor commands to, the opposite side of the body
the 2 hemispheres have different functions, although their structures are alike
correspondence between a specific function and specific region of cerebral cortex is not precise
Frontal lobe
Voluntary motor functions, motivation, foresight, planning, memory, mood, emotion, social judgment, and aggression
Prefrontal cortex
- Integrates information from sensory areas
- allows us to perform abstract intellectual activities
- damage affects temporal relationships between events
Parietal lobe
- Integrates general senses, taste, and visual info
Occipital lobe
- Primary visual center
Temporal lobe
- Hearing, smell, learning, memory, and some aspects of vision and emotion
Insula
- Helps in understanding spoken language, taste, and integrating info from visceral receptors
White matter
- Makes up most of the volume of the cerebrum
- Form from glia and myelinated nerve fibers
Tracts
Bundles of nerve fibers in CNS
Projection tracts
Extend vertically between cerebrum and lower brain and spinal cord centers
Commissural tracts
Cross from one cerebral hemisphere to the other allowing communication between the two sides
Most commissural tracts pass thru
corpus callosum
Disconnection syndrome
- caused by cutting corpus callosum
- hemispheres are unaware of each other
Association tracts
- Connect different regions within the same cerebral hemisphere
- long fibers connect different lobes; short fibers connect gyri within a lobe
Cerebral cortex
- 40% of brain mass
- Layer of gray matter covering surface of hemispheres
- 90% of it is neocortex
Neocortex
6 layered tissue that has relatively recent evolutionary origin
Limbic system
- Important center of emotion and learning
- Consists of regions of cerebrum and diencephalon
- memory storage and retrieval
- establishes emotional states
Primary somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus)
- Site where sensory input is first received and one becomes conscious of the stimulus
- Exhibits somatotopy
Primary sensory areas have ______ to process and interpret the sensory info
Association areas
Somatotopy
Point to point correspondence between an area of the body and an area of the CNS; reflected in sensory homunculus in post central gyrus
Sensory homunculus
- Diagram of sensory inputs to the primary somatosensory cortex in parietal lobe
- Resembles upside down sensory map of contralateral side of body
- Areas with lots of receptors take up a larger amount of space in it
Primary visual cortex
Posterior region of occipital lobe; receives visual signals from the eyes
Primary auditory cortex
Superior region of temporal lobe; receives auditory signals
Auditory association cortex
Inferior to primary auditory cortex; recognize spoken words, music, voices
Primary gustatory cortex
inferior end of postcentral gyrus, taste and smell
Primary olfactory cortex
medial cortex of temporal lobe, taste and smell
Voluntary motor commands are transmitted to neurons of the
precentral gyrus (primary motor area)
Primary motor area
Send signals to brainstem and spinal cord leading ultimately to muscle contractions
Precentral gyrus
Exhibits somatotopy diagrammed as motor homunculus
Motor homunculus
- looks distorted because the amount of cortex devoted is proportional to motor units, not region size
- boundaries of cortical areas overlap
Wernicke area
- posterior to lateral sulcus, usually in left hemisphere
- recognition of spoken and written language
Broca area
- inferior prefrontal cortex, left hemisphere
- generates motor program for muscles of larynx, tongue, cheeks, and lips for speaking and for hands when signing
- motor language area
When we try to speak
- Wernicke formulas phrases and transmits plan of speech to Broca
- Broca transmits to primary motor cortex for commands to lower motor neurons that supply relevant muscles
affective language area
usually in right hemisphere, controls emotional aspect language
Aprosody
Flat, emotionless speech produced by legions in affective language area
Aphasia
- Any language deficit from lesions in Wernicke or Broca areas
nonfluent/broca aphasia
slow speech, difficult choosing words that approximate the correct words
fluent/wernicke aphasia
use jargon/made up words
Cerebral lateralization
- Difference in structure, function between 2 hemispheres
- Neither is dominant but each is specialized
- Used equally
Categorical hemisphere (left)
- specialized for spoken/written language
- analytical reasoning (math/science)
- breaks info in fragments and analyzes
Representational hemisphere (right)
- more integrated perception
- imagination and insight
- musical and artistic skill
- patterns and spatial relationships
- comparison of sights, sounds, smells, and taste
____ exhibit more lateralization than ____ and suffer more functional loss when one hemisphere is damaged
Men; women
Lateralization develops with age
Children more resilient to lesions on one side
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Recording of brain waves, rhythmic voltage changes in surface layers of cortex
- Useful for studying normal brain functions as sleep and consciousness
Lack of brain waves
Common criterion for brain death
4 types of brain waves
alpha, beta, theta, delta
Alpha waves
- 8-13 Hz
- Awake and resting with eyes closed and mind wandering
- Suppressed when eyes open or performing a mental task, absent during sleep
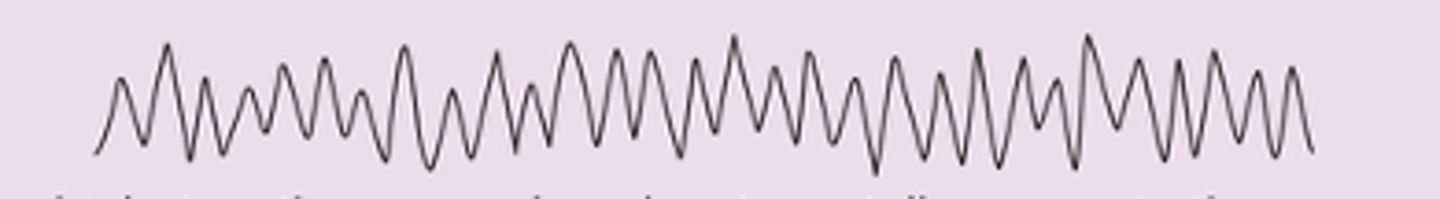
Beta waves
- 14 to 30 Hz
- Accentuated during mental activity and sensory stimulation
- Appear when awake and concentrating on something/performing a task

Theta waves
- 4 to 7 Hz
- Found normally in children or in intensely frustrated, stressed, drowsy, or sleeping adult
- May indicate a brain disorder or brain tumor in other adults

Delta waves
- less than 3Hz
- High amplitude
- found in adults in deep sleep, adult with brain damage