Lecture 21a: The Pharmacy Workforce | Primary Care Pharmacy (GP Practice)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Primary Care
NHS long term plan - collaborative working
First point of contact for patients in healthcare system
Main contact is GP. Also, community pharmacy, urgent care centres, dentists, opticians
Primary Care Networks (PCNs)
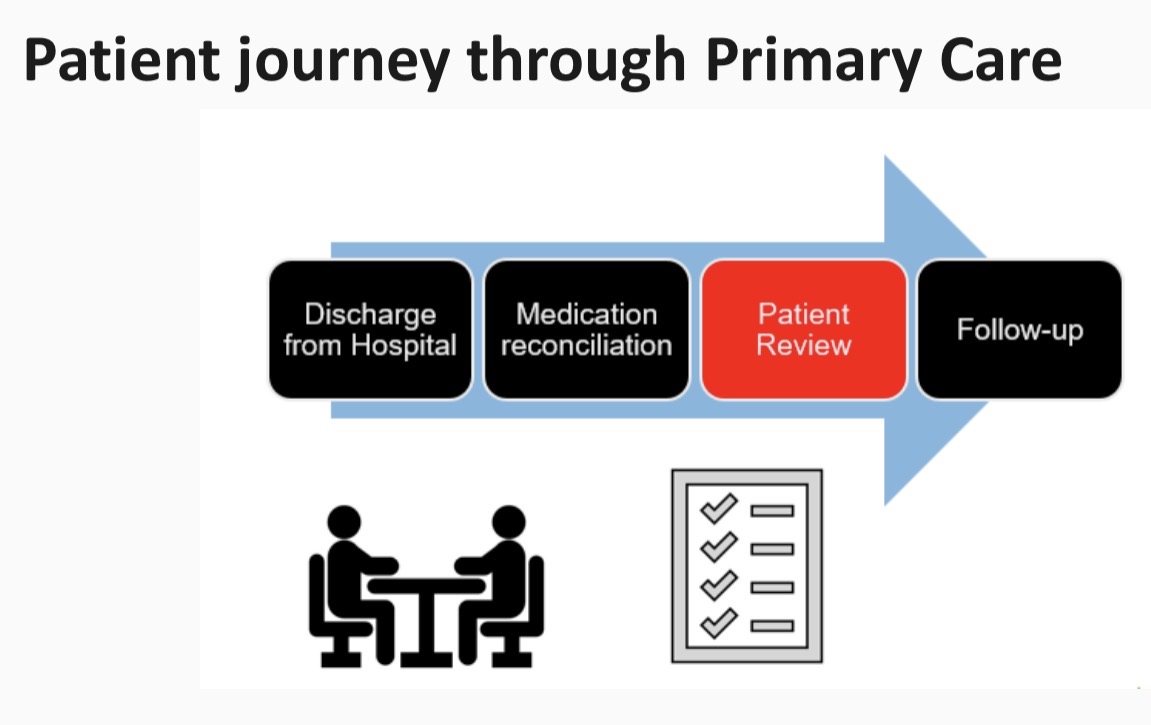
Primary Care - General Practice
GP practice roles (ARRS)
Multidisciplinary Team working (MDT)
Management:
Acute conditions
Long term conditions
Medication reviews
Referrals
Public health
Support services
Quality Outcomes Framework (QOF)
Voluntary annual incentive and reward programme
Various domains to support patient care
Clinical domain (437 points)
Public Health domain (127 points)
Quality improvement domain - now retired (April 2025)
General Practice Pharmacy
Network Contact DES Specification
Additional Roles Reimbursement Scheme - Clinical Pharmacist
Must be enrolled in or have qualified from an accredited training pathway that equips the pharmacist to be able to practice and prescribe safely and effectively in a Primary Care setting
CPPE Primary Care Pharmacy Education Pathway (PCPEP)
Responsibilities
Medicines optimisation - doses, prescribing/deprescribing (SMRs)
Medication reviews
Long term conditions management
Advice - patients and other HCPs
Drug monitoring
Medication safety
Counselling
Audit
Medicines reconciliation
Guidelines
Medicines management (EBM)
Cross-sector communication/collaboration
Independent prescribing
Prescribing now embedded into MPharm
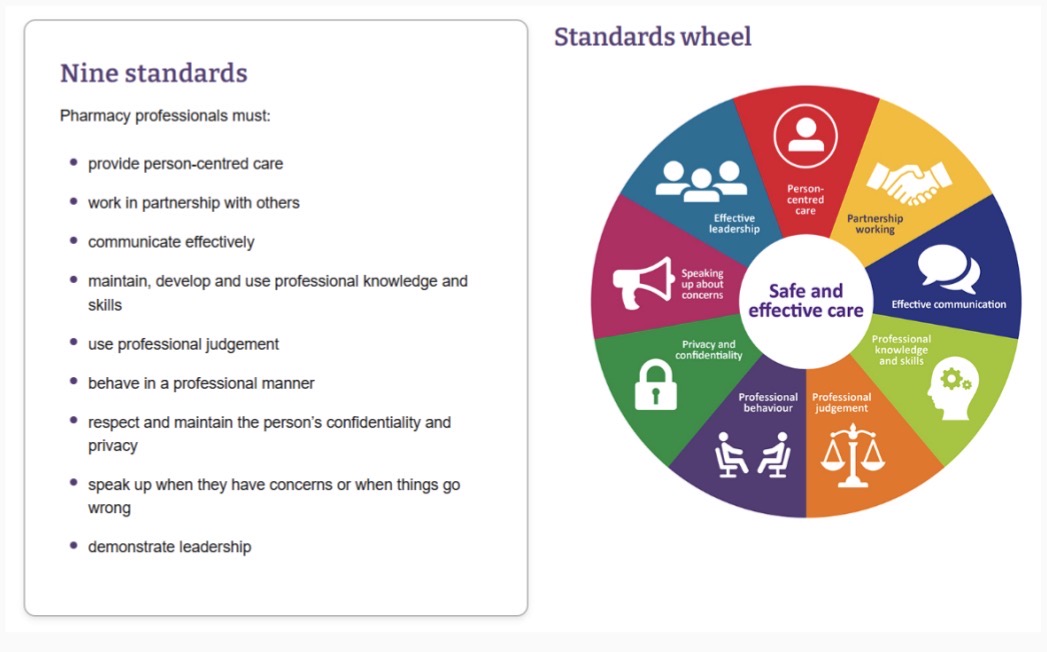
GPhC professional standards
Autonomy
Within scope of practice - boundaries of clinical practice
Indemnity insurance
GPhC standards
Local formulary

Typical day
Structured Medication Reviews (SMR)
An evidence-based and comprehensive review of a patient’s medication, that would normally be carried out by a clinical pharmacist or doctor, taking into account all aspects of the patient’s health
Medicines optimisation strategies for reducing polypharmacy, minimising risk of prescribing harm, reducing over-prescribing and managing risk of dependency on prescription drugs
PCNs to use SMRs for high-risk cohorts
SMR outcomes
Medicines optimisation
Reduce hospital admissions related to medications
Reduce medicines wastage
Patient education
Cost savings
Hypertension clinic
Initiation clinic
Dose optimisation
Monitoring:
Blood pressure
Bloods
Questions/infomation
Follow up
Escalation/referral
Care home ward round
Weekly care home visit
MDT - GP, pharmacist, paramedic, nurse, HCA, care co-ordinator
Shared decision-making:
Patient
Parent/carers
Nurses
Best interest - mental capacity assessment
Diabetes MDT
Monthly review of diabetes patients in care homes
Clinical pharmacist and diabetes specialist nurse
Consistent prescribe (particularly insulin)
Regular monitoring (including QOF)
Escalation to GP if needed
Tasks
Medicines reconciliation - Docman
Pharmacists advice - EMIS:
Alternatives
Interactions
Calculations
Formulation changes
Prescribing decisions
Dose adjustments
Drug warnings
Product recalls
Future
Specialist in medication
Patient centred care
Shared decision making
Holistic approach
Improves patient access