4.4, 4.5, 4.6, 4.7 Cell Cycle and Cancer | AP Biology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
Mitosis (M phase)
Cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes; Includes prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Centrosome
A structure in animal cells containing centrioles from which the spindle fibers develop.
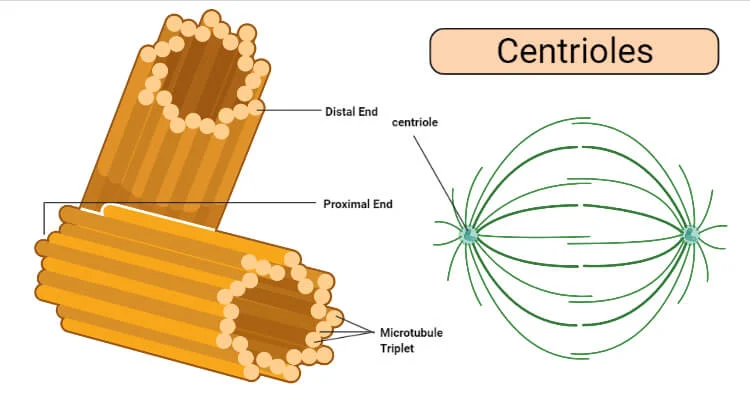
Centrioles
Located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible (chromatin condenses), nuclear envelope dissolves, spindle fibers form (Mitotic spindle apparatus)
Metaphase
Spindle fibers attach, Chromosomes line up in the middle (equatorial plate) of the cell
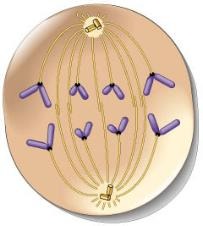
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell + spindle fibers contract
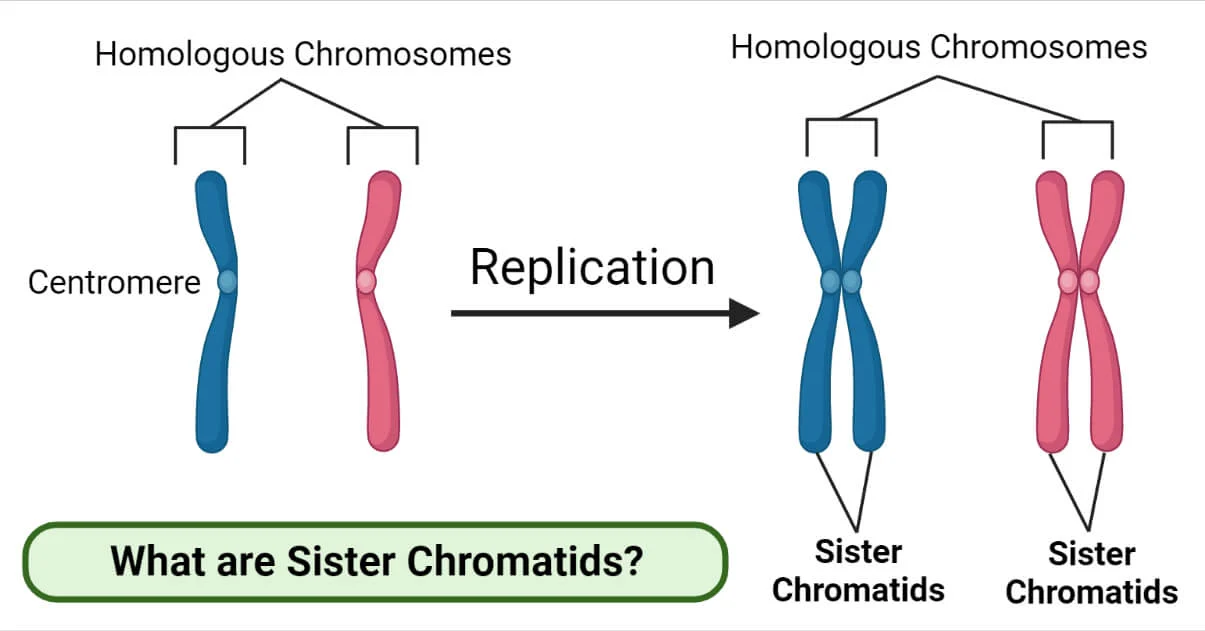
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase. — Halves of a Chromosome
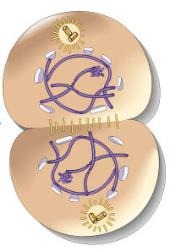
Telophase
Phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin (nucleus reforms, DNA decondenses, cell membrane starts pinching in)
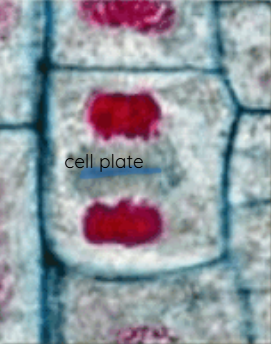
Cell plate
Plant cells: The precursor of a new plant cell wall that forms during cell division and divides a cell into two
Cleavage Furrow
Animal cells: The area of the cell membrane that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell
Cancer
Disease in which some of the body's cells lose the ability to control growth (cell doesn’t signal for apoptosis even with DNA errors, and mutations in cells that hide them from the immune system)
Metastasize
The process by which cancer spreads from one place to another (malignant tumors)
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Cyclin Dependent Kinase (CDK)
A protein that binds with a cyclin to activate it, which regulates a step/checkpoint (3 checkpoints!) in the cell cycle
G1 (Growth 1)
Cell grows; produces more VIP molecules (nucleotides, enzymes, etc.) and structures. Checkpoint to make sure cell is big enough and has proteins for division (if not, cell may enter G0).
G0
Resting Phase: Non-dividing cells (most neurons) enter & leave cell cycle due to environmental pressures
G2 (Growth 2)
Final preparation phase; finish growing/DNA replication/repair. Cell checks for DNA errors and begins to form centrosomes. (Prepares for Mitosis).
S-phase
DNA is replicated
Cyclins
A group of proteins whose function is to regulate the progression of a cell through the cell cycle and whose concentrations rise and fall throughout the cell cycle
How do gene mutations affect the cell response?
Mutations lead to change in shape/chemical affinity in ligands, receptors, and proteins in transduction, changing/stopping the response
Positive Feedback
A type of regulation that responds to a change in conditions by initiating responses that will amplify the change/response. Takes organism away from a steady state (initiate/amplify biological processes).
Negative Feedback
Most common type of feedback: Responds to a change in conditions by initiating responses that will counteract the change (doing opposite of stimulus). Maintains a steady state (homeostasis).
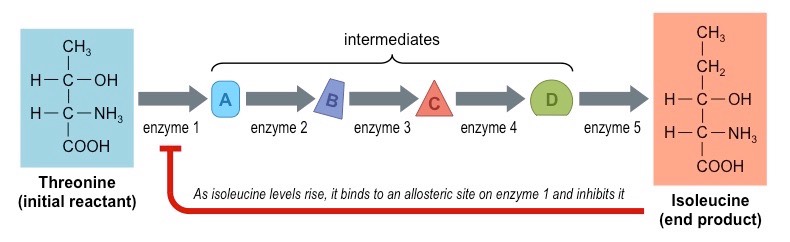
What would happen to the concentrations of the intermediates if enzyme 3 were inhibited?
Substrate B would build up in the cell since it isn’t converted into intermediate C by enzyme 3.
All cells divide at the same rate.
False
How long (out of 24 hours) does interphase usually occur?
23 out of 24 hours
Why do developing organisms go through the cell cycle?
Require new cell production, each containing a genome (DNA copied from parents) needed to grow
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides, cell membrane pinches in = 2 genetically identical daughter cell
How do cells know to move to the next step of the cell cycle?
Growht factor signals to produce cyclin proteins, which builds up in the cell. At high concentrations, cyclin binds to specific CDKs, and CDK starts phosphorylation cascade to allow cell to pass checkpoint. Phase-specific cyclin is broken down (prevent wrong signaling).
What are the cell cycle’s 3 checkpoints (Not just interphase)?
G1, M, G2
How do damaged/mutated cells enter cell cycle arrest?
The cell produces inhibitors of cyclin proteins to prevent progression through the cell cycle.
Repairable Damage
Damaged DNA = repaired and goes through 3 checkpoints (completion) of cell cycle to produce 2 identical daughter cells.
Irrepairable Damage
Cell goes through apoptosis, no cells are produced; Diseases like cancer are prevented
What is cancer?
Uncontrolled cell growth leading to tumors
How do cancer cells develop?
Accumalation of mutations in genes to prevent apoptosis and allows cancer cells to grow/divide
Which of the following is NOT a purpose of Mitosis?
To divide inhibitors so that they cannot inhibit enzymes within the signal transduction pathway
Which is the proper order for the cell cycle?
Interphase, Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
Chromatin
Interphase: Uncoiled versions of DNA/chromosomes
Centromere
Region of chromosome that is the attachment point between sister chromatids.
Does mitosis occur in body cells (somatic) or sex cells (gametes)?
Somatic
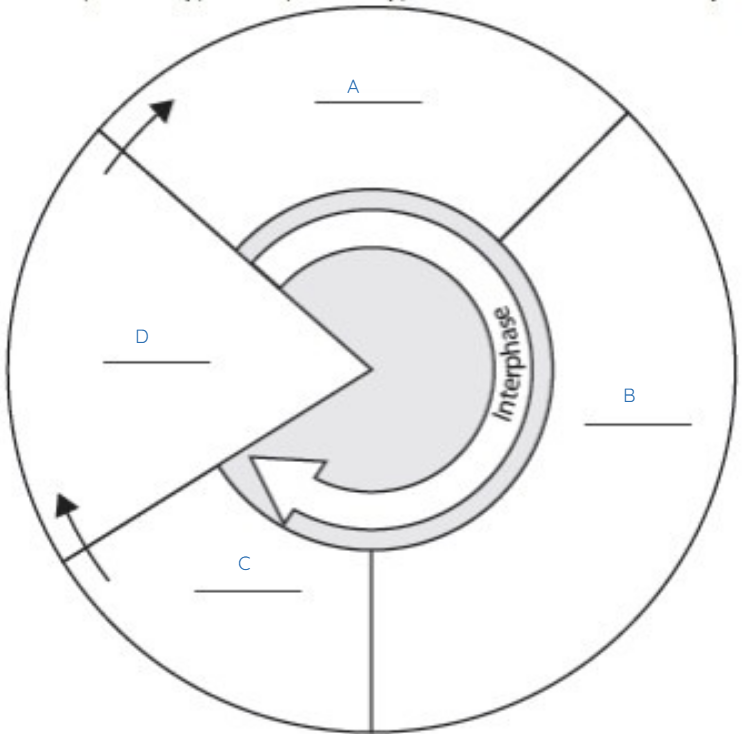
What does A represent?
G1
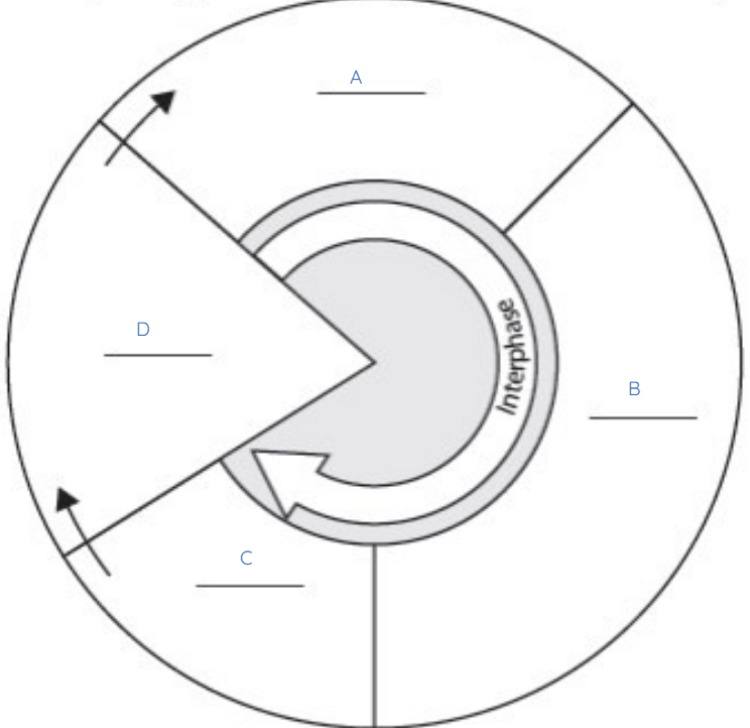
What does B represent?
S
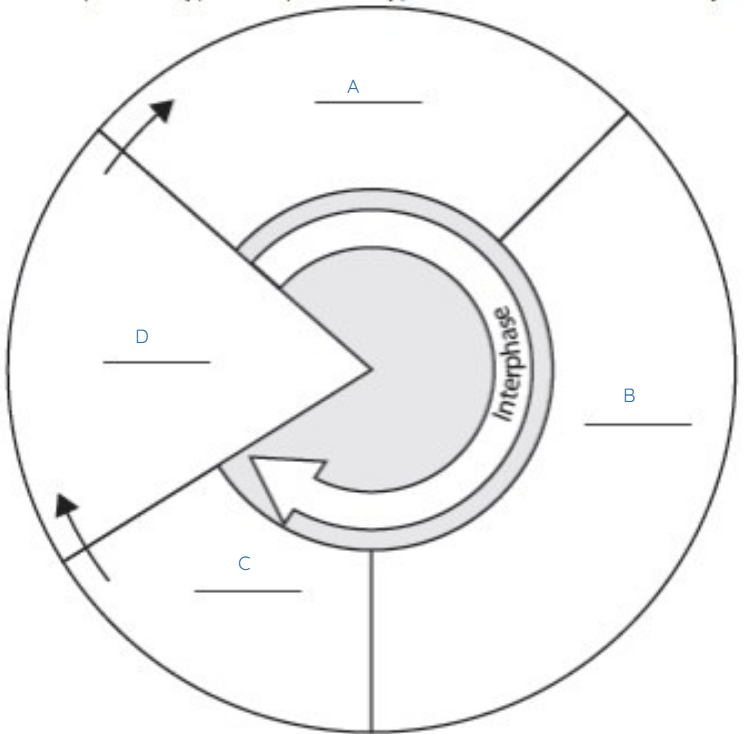
What does C represent?
G2
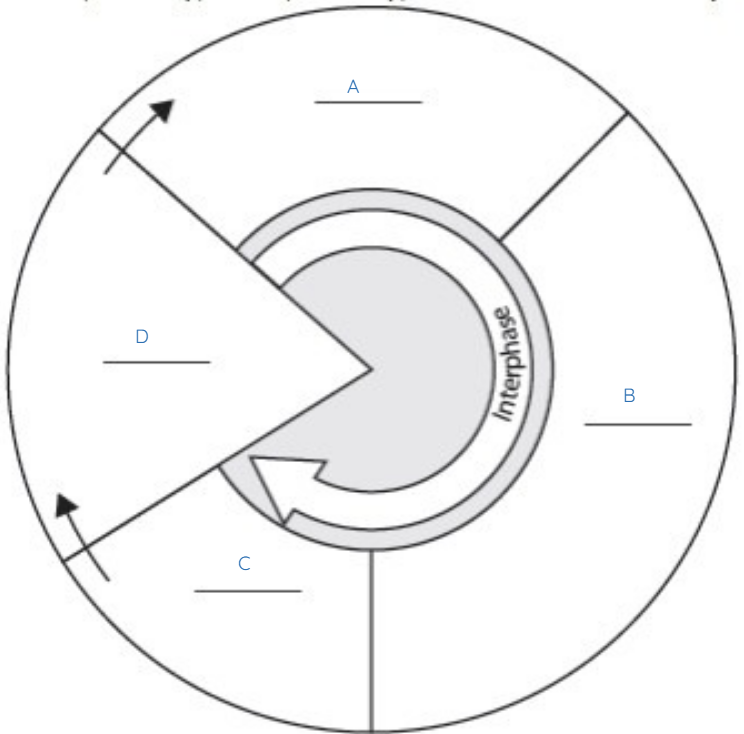
What does D represent?
M
Thermoregulation: Sweating when you’re hot, shivering when you’re cold.
+ Maintaining blood glucose, water balance (osmoregulation), blood pH, etc.
Which type of feedback?
Negative Feedback
Ethylene gas ripening fruit: Gas signals fruit to ripen, increases amount of ethylene gas produced (Hint: original stimulus amplified!)
+ Lactation, blood clotting, labor
Which type of feedback?
Positive Feedback
In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes consist of one long, linear strand of DNA that is wound up around proteins called ____.
Histones
Diploid
A somatic cell with two copies of each chromosome
Gametes
Haploid Reproductive cells (sperm, egg) with one copy of each chromosome (half the number of chromosomes as somatic)
Centrosome vs. Centrioles?
Centrosomes is a structure including 2 centrioles and PCM (not required to know)
Benign Tumors
Tumors that remain only in their original site — not considered cancerous
Malignant Tumors
Tumors with genetic mutations (from Mutagens [or carcinogens which are mutagens that disrupt the cell cycle]) that allow them to spread to new tissues/regions of the body — considered cancerous
Proto-oncogenes
Class of genes that code for proteins that stimulate the cell cycle and promote cell growth
Tumor suppressor genes
Class of genes that code for proteins that suppress the cell cycle and promote apoptosis.
Ex: p53, which slows down the cell cycle by inhibiting CDK, pausing a cell in G1 if damage to DNA is detected. 50% of all cancers will have mutations in genes for p53 protein.
Kinetochore
Spindle microtubules (fibers) attach to this part of the centromere (which is the center of the chromosome).