Anaphylaxis Cornell Video
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Anaphylaxis
Serious, generalized or systemic, allergic or hypersensitivity reaction that can be life threatening or fatal
Pathways that Cause Anaphylaxis
Immunologic IgE-mediated (Classic)
Cross linked IgE (type 1 hypersensitivity reaction)
Insects, food, medications
Previous antigenic stimulation
Immunologic non-IgE-mediated
Immune-aggregates (IgG), complement
Non-immunologic
Physical factors: hot, cold, exercise, opioids
Mediators of Anaphylaxis in the Initiation/Early Phase
Histamine
Tryptase
Heparin/chymase
Mediators of Anaphylaxis in the Mid-Phase
Platelet activating factor (PAF)
Arachidonic acid cascade
Mediators of Anaphylaxis in the Late Phase
Cytokines/inflammatory mediators
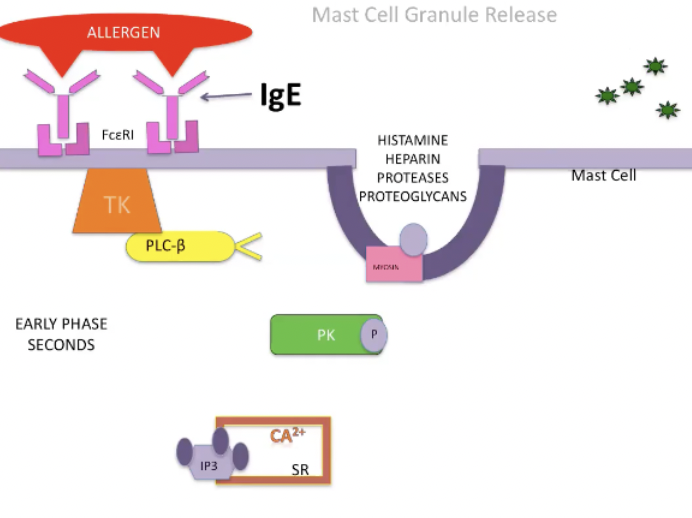
Early Phase of Anaphylaxis
Allergen will crosslink and aggregate IgE molecules bound to high affinity receptors which will stimulate the pathway that involves tyrosine kinase
TK will phosphorylates molecules
When it phosphorylates phospholipase C will chew the phosphate head off of fatty acid tail
IP3 will stimulate release of Ca from SR
Calcium release will stimulate another protein kinase which phosphorylates myosin located on secretory granules which allows the secretory granules to move and merge with mast cell membrane and release their molecules
This happens rapidly, within seconds
Actions of the H1 Receptor
Skin component, dermal angioedema, itchy skin, urticaria
See smooth muscle bronchoconstriction
Causes rhinitis in people
Gq pathway
Some inotropy and chronotropy inhibition which causes the animal to not be able to respond to anaphylaxis
Vasodilation and increased permeability
Actions of the H2 Receptor
Gs pathway
GI tract
Increase in acid production and simultaneously duodenal bicarb secretion is inhibited
Some heart and systemic vasodilation
Actions of the H3 Receptor
Gi pathway
Inhibits release of norepi from the presynaptic portion of the adrenergic system
When we can't release norepi in response to vasodilatory changes we can't have sympathetic nervous system saving us
Actions of the H4 Receptor
Chemotaxis and production of inflammatory cytokines
Anaphylaxis Initiation Phase Mediators
Tryptase
Heparin
Chymase
Anaphylaxis Initiation Phase Mediators - Tryptase
Serine protease, biomarker
Activates: complement, coagulation, kallikrein
Hypotension, angioedema, clot, DIC
Anaphylaxis Initiation Phase Mediators - Heparin
Modulates tryptase activity
Opposes complement, inhibits clots, plasma, kallikrein
Anaphylaxis Initiation Phase Mediators - Chymase
Stimulate AgI to AgII (ACE independent)
Decreases severity of hypotension, causes myocardia ischemia via vasoconstriction
Mid-Phase Anaphylaxis
Same pathway that was initiated by allergen binding FC receptor and same tyrosine kinase will phosphorylate more than one second messenger
Phospholipase A2 will be phosphorylated and stimulated
Will cut up a phospholipid but it cuts off a fatty acid tail and generates arachidonic acid
Also forms a precursor molecule lysoPAF, inactive form of PAF
Arachidonic acid by itself isn't an inflammatory mediator but the byproducts of the arachidonic cascade are key players in inflammation in the body in general and in anaphylaxis
Prostaglandin D2
Comes from the COX pathway
Bronchodilation
Pulmonary/coronary vasoconstriction
Peripheral vasodilation
Leukotrienes
Come from the LOX pathway
1000x more potent than histamine
LTC4, LTD4, LTE4: bronchodilation, increased vascular permeability
LTB4: chemotactic agent
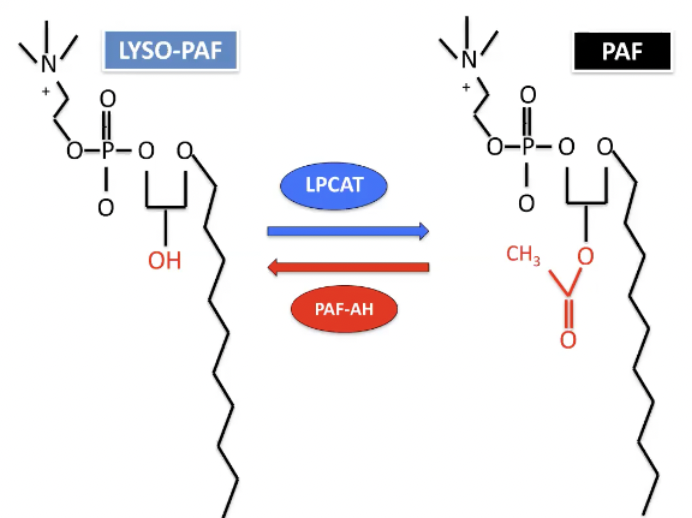
LYSO-PAF and PAF
Lyso-PAF is inactivated form of PAF
Enzyme that adds an acyl group which activates it
Feedback mechanisms that will clear PAF as fast as it is produced as long as you have enough of an enzyme
Enzyme is platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase - breaks off acyl group from PAF and inactivate that
As long as it does that and limits this reaction you won't die from anaphylaxis
Critical Role of PAF
Key mediator of hypotension in anaphylaxis and critical illness
Binds PAFr (GPCR)
GPCR second messenger pathways increase calcium
Also activates PLA2 and PI3K
Stimulates eNOS production of NO → vasodilation
Structurally unique
Vasoactive phospholipid
Target organs - heart, pulmonary vessels, and microcirculation
Promotion of thrombi and second inflammatory mediators
Histamine, kinins, TXA2, leukotrienes, ROS
Nitric Oxide
Formed from L-arginine via NOS
eNOS = endothelial = constitutive
iNOS = inducible
nNOS = neurogenic
NOS production/activation
Pathway: phospholipase C, calcium, and calmodulin
Produced in septic shock states
Due to TNF-a/inflammatory mediators inducing iNOS
Requires hours to occur
NO induces vasodilation via sGC
Forms cGMP that activates protein kinase G
Produces vasodilation
Multiple new pathways discovered involving various factors
VEGF, shear stress, estrogen
PAF (anaphylactic, septic shock)
Inflammatory cytokines (via NFkB pathway)
P53 (tumor cells)
Hypoxemia (HIF-1a inducible factor)
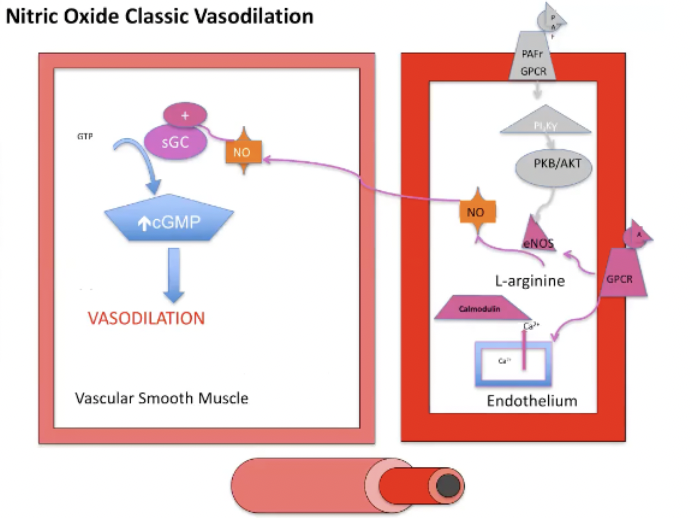
Nitric Oxide Pathway
Binding of PAF to its GPCR via PI3 pathway upregulates the amount of eNOS available
L arginine is converted to NO which diffuses into the adjacent vascular smooth muscle
NO will stimulate sGC which increases cGMP which leads to vasodilation of vascular smooth muscle
Anaphylaxis Mediators of Vascular Permeability
PAF
Histamine
Prostaglandins
Leukotrienes
Vascular Permeability - Capillary Leak Syndrome
Massive fluid shifts
35% of IV volume into extravascular space in 10 mins
Rapid hemodynamic collapse
Capillary leak - endothelial cell contraction via the actin-myosin light chain complex
Ca2+-calmodulin and myosin kinase = pores
Ongoing Ca2+ influx prevents conversion of ATP to cAMP favoring contraction = bigger pores
Reversal requires epinephrine bindings to its B2 receptor (Gs protein) mediated cAMP formation from ATP
Or inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterase
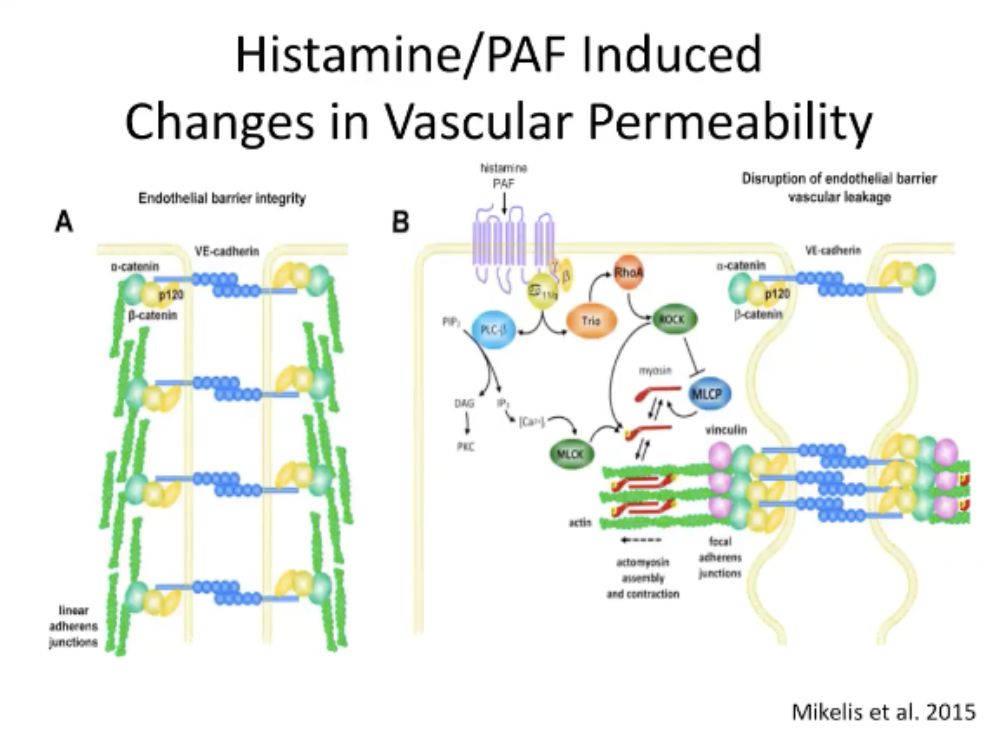
Histamine/PAF Induced Changes in Vascular Permeability
Endothelial barrier integrity is maintained by cadherin molecules
When histamine and PAF bind their receptors the phospholipase C, DAG, IP3 pathway releases Ca
Ca can modulate myosin light chain kinase
Activation of actin and myosin turns on contractile units which cause the endothelial cells to contract and pull away from each other and causes a disruption in the endothelial barrier
PAF Summary
PAF generated from mast cells
PAF binds its receptor PAFr
Initiates and amplifies inflammation and thrombosis
Leads to marked vasodilation and hypotension
Increases vascular permeability contributing to massive fluid shifts
PAF/PI3K pathway increases eNOS and thus increases NO
NO activates soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC)
Leads to marked vasodilation and hypotension
PAF bindings PAFr on systemic mast cells likely responsible for amplification of anaphylaxis
Late Phase Anaphylaxis
2-24 hours after allergen has bound to mast cells
Takes so long because tyrosine kinase pathway has to activate factors within the nucleus of the mast cells, when these factors are activated have to have further transcription and translation of new proteins which takes time
This is the stage that gets manipulated by steroids
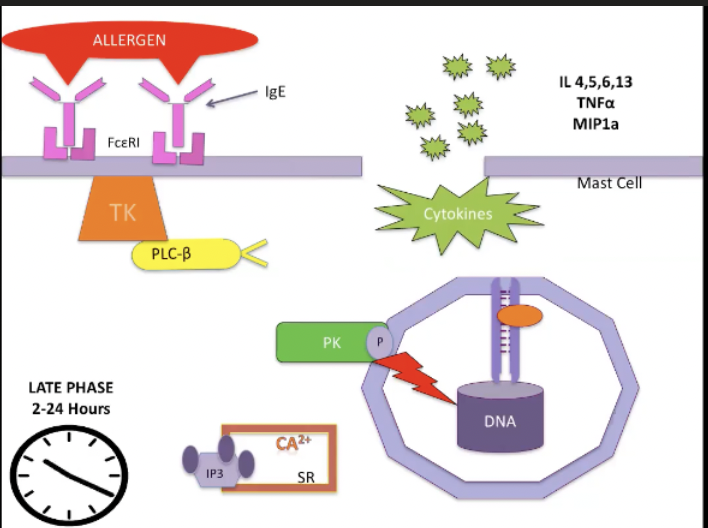
Cytokines and Anaphylaxis
TNFa (late phase)
Activates neutrophils
Recruits effector cells
Increases chemokines
Interleukins
Inflammatory mediators
IL13 antibody generation
IL4 increases cellular responses (3-6x) to mediators
Primary Mediators of Anaphylaxis from Mast Cells
Histamine
Proteases
Heparin
NCFTA
ECTFA
Secondary Mediators of Anaphylaxis from the Arachidonic Acid Cascade
PGE2/PGD2
Prostacyclin
Leukotrienes
Thromboxane A2
PAF
Effects of Histamine in Anaphylaxis
Increased vascular permeability
Increased vasodilation
Increased bronchoconstriction
Increased gastric acid
Effects of Proteases in Anaphylaxis
Increased kinin, activate complement, DIC
Effects of Heparin in Anaphylaxis
Anticoagulant
Urticaria
Immune
Effects of NCFTA in Anaphylaxis
Neutrophil chemotaxis
Effects of ECTFA in Anaphylaxis
Eosinophil chemotaxis
Effects of PGE2/PGD2 in Anaphylaxis
Increased vascular permeability
Increased vasodilation
Increased bronchoconstriction
Effects of Prostacyclin in Anaphylaxis
Increased vasodilation
Platelet aggregation
Effects of Leukotrienes in Anaphylaxis
Increased vascular permeability
Increased vasodilation
Increased bronchoconstriction
Increased WBC
Effects of Thromboxane A2 in Anaphylaxis
Platelet aggregation
SM contraction
Therapeutic Options for Anaphylaxis
Epinephrine (IM then CRI)
Vascular access (IV vs EzIO)
Fluids (colloid/crystalloid)
Vasopressin/vasopressors (Bolus/CRI)
Airway (endotracheal/tracheostomy)
Anti-histamines (H1/H2)
Bronchodilators (Aminophylline)
Steroids - the after thought
Role of Epinephrine in Anaphylaxis
Signaling thorugh the PAFr can be downregulated agents that increase intracellular cAMP levels
Epinephrine acts in part by phosphorylation and inactivation of the PAFr
Early administration
Reduces morbidity and mortality in human anaphylaxis
Delayed administration
Associated with increased mortality
Progressively less effective with time