Ch. 16: The Endocrine System
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
WHere do endocrine glands secrete their substance
ENDO: directly into the blood
where do exocrine glands secrete their stubstances
EXO: sercrete external secretions into body cavities or onto body surface via ducts (tears, sweat, saliva)

E.
what makes a cell the target of a hormone
target cells have receptors specific for each hormone
memorize ts on notability
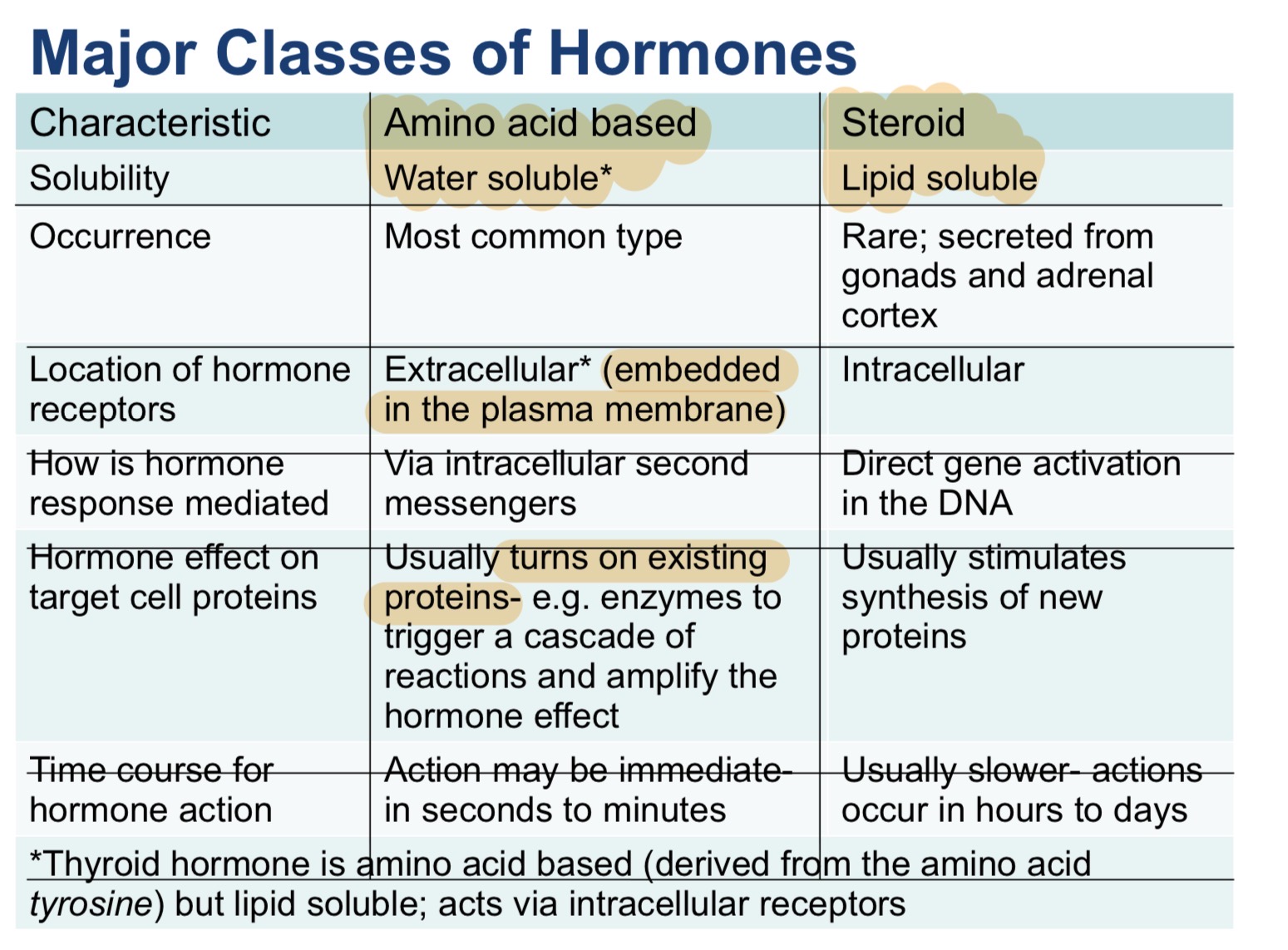
what are three most comon types of amino acid based hormones
proteins (insulin and glucagon)
peptides (ADH and oxytocin)
derivatives of amino acids (thyroid hormones)
what are the 4 steps of amino acid based hormones
bind to extracellular receptors
activate a 2nd messenger such as cAMP
cAMP activates kinase enzymes that turn on other enzymes
turns on existing proteins and what not
When insulin binds to receptors on its target cells, it quickly turns on glucose transporters. Glucose is taken into the target cells by ___ ___ ___ ___
carrier mediated facilitated diffusion
“Insulin lowers blood glucose levels” means that
_______________.
A. Insulin signals target cells to increase uptake of
glucose molecules from the blood
B. Insulin binds to glucose molecules and removes
them from the blood
C. Insulin transports glucose molecules into cells by
carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion
D. Insulin breaks down glucose molecules by
glycolysis
A. insulin signals target cells to increase uptake of glucose molecules from the blood
steroid hormones are ____ soluble derived from ___
lipid; cholesterol
steroid hormones are synthesized by two things…what are they
gonads: testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
adrenal cortex: aldosterone, cortisol, cortisone, etc.
why do steroid hormones and thyroid hormones bind to intracellular receptors
closer to DNA
explain the process of steroid and thyroid hormones
hormone forms a complex with the receptor and enters the nucleus
receptor hormone complex activates genes in the DNA
results in synthesis of new proteins
glucagon _____ blood sugar while insulin ____ levels
glucagon raises levels while insulin lowers levels
Gluvagon and insulin are secreted from Islets of Langerhans cells in the pancreas. Beta and alpha cells secrete what?
Alpha cells secrete gluvagon
beta cells secrete insulin
where would you predict the hormone receptors for insulin and glucagon be located on their target cells…why?
embedded on the cell membrane
Amino Acid hormones do not cross the cell membrane
this molecule is used to store glucose in the liver
glycogen
where is glycogen stored
liver
what is glycogenolysis in the liver
the release of free glucose into the blood to maintain normal blood glucose levels
what is the cause of type 1 diabetes
autoimmune disease. Body creates antibodies that attack the insulin producing beta cells in the pancreas
a person who has type 1 diabetes will not be able to…
produce insulin and is permanent
this type of diabetes…
autoimmune response(bodys immune system attacks the insulin producing cells of the pancreas)
type 1
this type of diabetes…
typically 90% of all cases of DM
typically seen in overweight adults after the age of 40
strong hereditary link
type 2
what is the cause of type 2
unable to secrete insulin or unable to effectively use insulin
which type of diabetes is this…
abnormal or missing insulin receptors
abnormal glucose transporters
diet and exercise seen to help
any abnormality that does not allow effective usage of insulin
type 2
what is hyperglycemia and what can cause hyperglycemia
too much sugar
cause: type ½ diabetes
what bony feature of the skull encloses and protects the pituitary gland
sella turcica
what are some characteristics of the POSTERIOR pituitary gland and what hormones would be secreted from here?
neural tissue
developed from a downward projection of the hypothalamus
composed of axons and axon terminals
oxytocin and ADH
what are some characteristics of the ANTERIOR pituitary gland
developed from an UPWARD projection from the roof of the mouth
the hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus are transported to the posterior pituitary gland by the ___ ___ ___
hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract
what does ADH promote
water conservation by preventing diuresis (large loss of water in the urine)
What does a HYPOsecretion of ADH cause
diabetes insipidus; huge output of dilute urine and intense thirst (different from diabetes mellitus)
explain how adh and dehydration are related
Dehydration stimulates the hypothalamus to produce antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which is released from the posterior pituitary gland. ADH then acts on the kidneys to increase water reabsorption back into the bloodstream, helping restore fluid balance and reduce dehydration.
how can a head injury cause diabetes insipidus
head injury may damage the hypothalamic neurons that synthesize ADH or posterior pituitary that secretes ADH
OXYTOCIN and ADH are neurohormones, synthesized by the ____, transported in the ___-___ ___, and is secreted from axon terminals in the ___ ___
synthesized by the hypothalamus; transported in the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract; secreted from axon terminals in the posterior pituitary
what hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland
GH
PRL
FSH
LH
TSH
ACTH
what 4 hormones secreted by the Anterior pituitary gland are tropic hormones, what does tropic mean
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
LH (luteinizing hormone
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
tropic: a hormone that targets and stimulates other endocrine glands to grow and secrete their own hormones
how do the hormones secreting in th hypothalamus get tp the anterior pituitary gland
hypothalamic hormones travel in blood vessles leading to the anterior pituitary
what hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland are NOT tropic hormones
Growth hormone and prolactin
what does the mnemonic device GPA refer to
G: Growth Hormone
P: Prolactin
A: acidophils
growth hormone and prolactin are produced and secreted by acidophils (they also stain well with acid dyes)
GH secretion is controlled by which two hypothalamic neurohormones
GHRH
GHIH
what are direct effects of GH
METABOLISM
makes fuels such as fatty acids and glucose more available for cellular growth
How does GH promote indirect growth
IGF (insulin like growth factor) stimulate body cells to enlarge and divide
long bones grow to adult size by ____ ____
endochondral ossification
Hypersecretion of GH is often caused by an anterior pituitary tumor. What does hypersecretion of GH cause?
CHILDREN
Gigantism: excessive lengthening of long bones; extreme height (8 feet or more)
ADULTS
Acromegaly: bones in the face and feet, hands continue to grow.
Hyposecretion of GH causes what?
CHIlDREN
pituitary dwarfim: abnormally short height (2-4ft) but fairly normal body proportions
ADULTS
rare, fat mass and decrease in muscle mass, decreased energy and quality of life
what is the function of prolactin
Prolactin is a peptide hormone, primarily produced by the pituitary gland, essential for initiating and maintaining lactation, developing breast tissue, and regulating reproductive functions
why is the anterior pituitary not a master gland
it is under the influence of the hypothalamus, so the hypothalamus should be considered the master gland
what does the mneumonic device BFLAT stand for
Basophils produce and secrete FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH
the tropic hormones are… and they are secreted by…
TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH
secreted by basophils
what teo hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gand are gonadotropins
FSH and LH
What hormones are considered to be gonadotropins and what is their function
FSH and LH
target the ovaries and testes
cause secretion of the steroid sex hormones and development of sex cells
this gland…
H-shaped butterfly located in the anterior aspect of the neck
thyroid gland
In the thyroid gland has lobes which are composed of hollow spherical follicles. What do these