anatomy and physiology UWEC BIOL 214 Exam 1 Answers
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
carbohydrates
primary components of bread and candy
lipids
organic compound that includes cholesterol
protein
inlcudes enzymes
ATP
the energy currency of the cell and is made from glucose
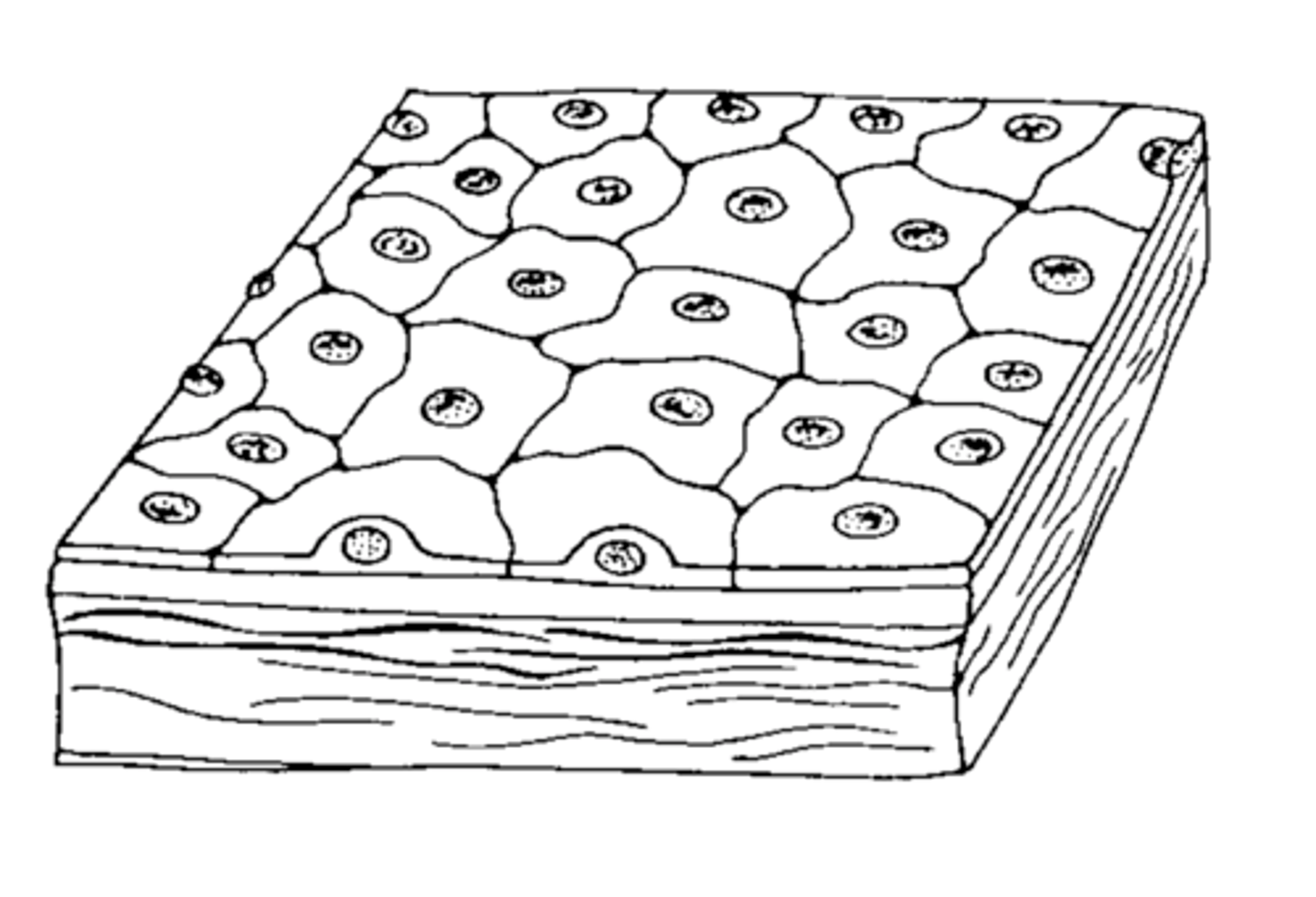
cell shape: squamous
thin, flat, scaly
cell shape: discoid
disc-shaped
egg cells
very large, 100 um diameter
__% of membrane molecules are lipids
98
glycolipids
-5% of the membrane lipids
-phospholipids with short carb chains on extracellular face
-contributes to glycocalyx (carb coating on cell surface)
-COMPLEX CARB STUCK ONTO A LIPID
where is a proton found and what is its charge?
the nucleus +1
where is a neutron found and what is its electrical charge?
the nucleus 0
where is an electron found and what is its charge?
orbitals -1
proton defintion
positively charged particles in the nucleus of atoms
atom definiton
smallest piece of an element with the chemical and physical properties of the element
energy defintion
puts matter in motion
electron definition
negatively charged particle with a very small mass
ion
charged atoms that hace either lost or gained electrons
matter
examples are solids, liquids, and gases
element
made up of atoms and have the same atomic number
molecule
two or more atoms that are bonded together by covalent bonds
neutrons
particles in the nucleus with a mass of 1 AMU and no charge
valence
electrons in the other energy levels of atoms, involved in bonding
glucose
building blocks of carbs
steroids
a lipid that includes sex hormones
amino acids
building blocks of a protein
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA are examples
carbohydrates (glucose)
the single most important fuel source for body cells
lipids
used to insulate the body and found in all cell membranes
proteins
primary components of meat and cheese
RNA
is single-stranded and found in the cytoplasm of cells
DNA
is double-stranded and found in the nucleus of cells
cell theory (4 parts)
-all organisms are composed of cells and cell products
-an organisms structure AND function are due to activities of the cell
-cells only come from pre-existing cells
-cells of all species exhibit biochemical similarities
cell definition
simplest structural and functional unit of life
cell shape: cuboidal
squarish-looking

cell shape: columnar
taller than wide
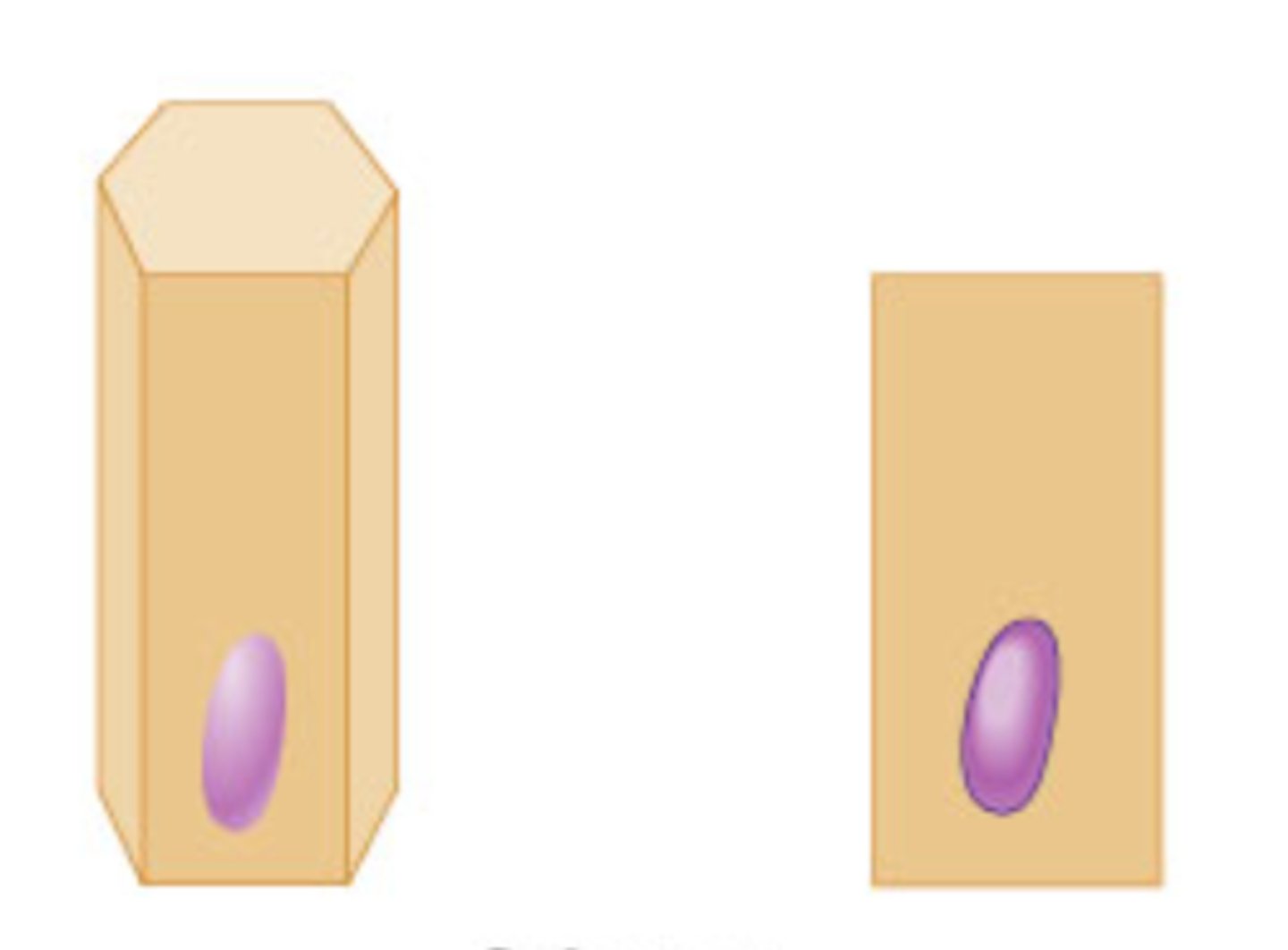
how can a cell shape appear differently?
if it is viewed in a different type of section (longitudinal vs. cross section)
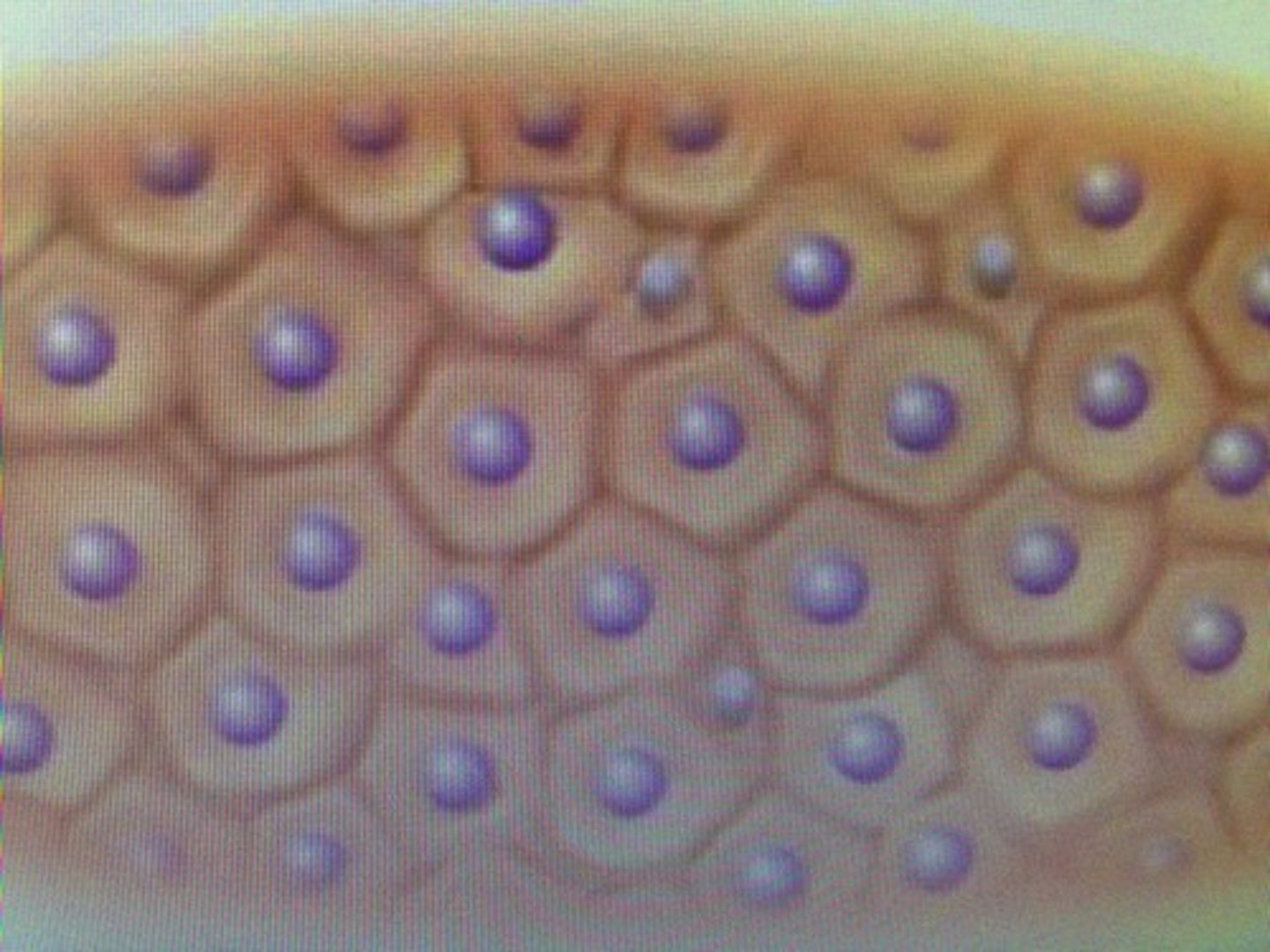
cell shape: polygonal
irregular angular shapes, multiple sides
cell shape: stellate
star-like
cell shape: spheroid to ovoid
round to oval
cell shape: fusiform
thick in the middle, thin at ends
cell shape: fibrous
thread-like
length of nerve cells
very long, can be over 1 meter long
limit of cell size
an overly large cell cannot support itself, it may rupture
for a given increase in diameter, ___ increases more than ___ ___
for a given increase in diameter, volume increases more than surface area
volume is proportional to...
cube of diameter
surface area is proportional to...
square of diameter
light microscope
shows plasma membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm
+BACKBONE OF HISTOLGY

transmission electron microscope (TEM)
improved resolution
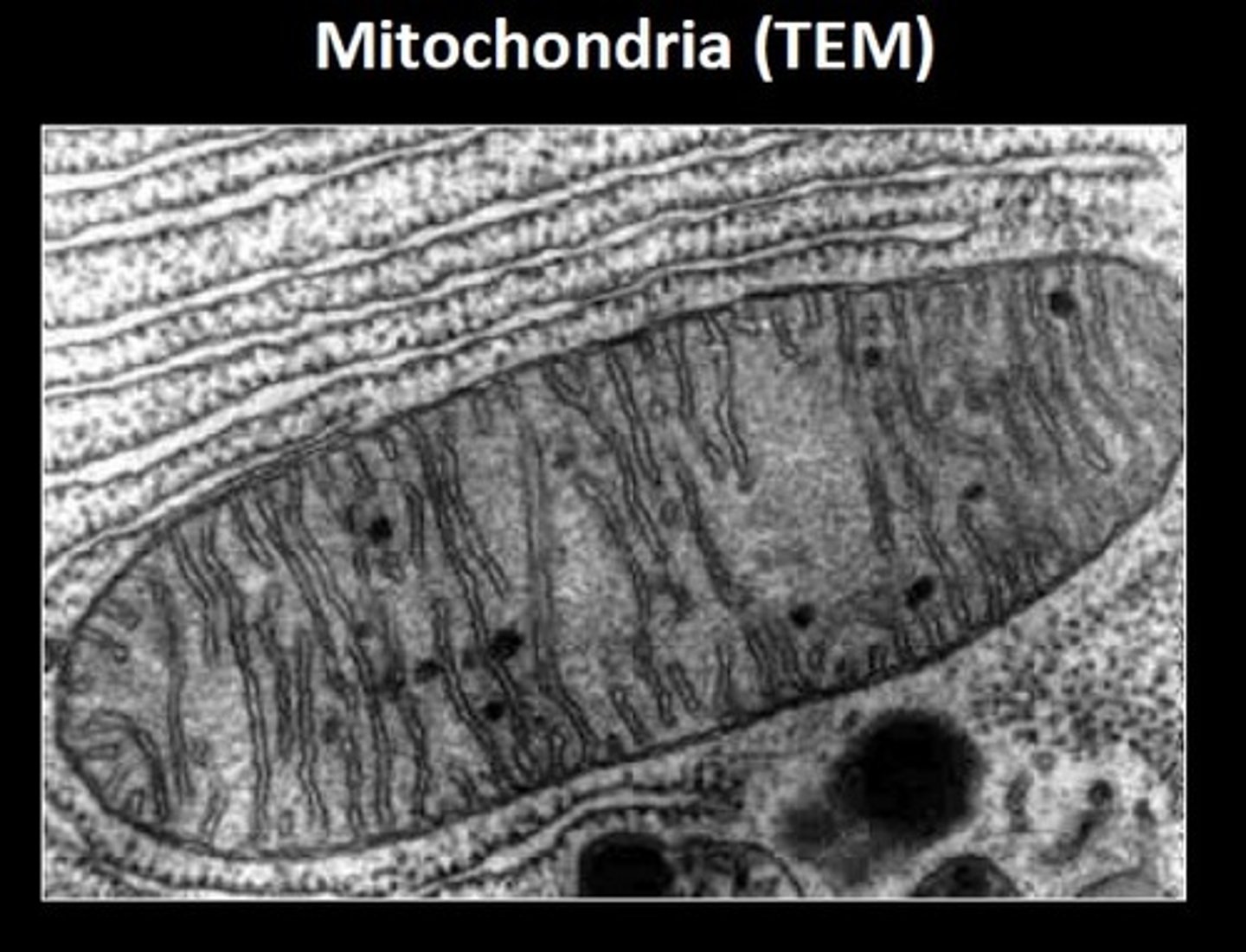
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
improved resolution further than TEM, but only for surface features

plasma membrane
-surrounds cell and defines boundaries
-made of proteins and lipids
-governs interactions with other cells
-controls passage of materials in and out of cell
-has intracellular and extracellular faces
cytoplasm
interior of a cell
(organelles, nucleus, cytoskeleton, inclusions, and cytosol)
extracellular fluid (ECF)
fluid outside of cells includes tissue (interstitial fluid)
phospholipids
-amphipathic molecules arranged in a bilayer
-hydrophilic phosphate heads face water on each side of membrane
-drift laterally, keeping membrane fluid
cholesterol
-20% of the membrane lipids
-holds phospholipids still and can stiffen membrane
membrane proteins
-2% of the molecules but 50% of the weight of the membrane
integral proteins
-penetrate membrane
-transmembrane proteins pass completely through
-hydrophilic regions contact cytoplasm, extracellular fluid
-hydrophobic regions pass through lipid of the membrane
-some drift in the membrane, others are anchored to the cytoplasm
peripheral proteins
-adhere to one face of the membrane (do not penetrate it)
-usually tethered to the cytoskeleton
function of membrane proteins
-receptors
-second-messenger systems
-enzymes
-channels
-carriers
-cell-identity markers
-cell-adhesion molecules
membrane protein
receptors
bind chemical signals
membrane protein
second messenger systems
communication within the cell
-receiving chemical message
membrane protein
enzymes
catalyze reactions including digestion of molecules, production of second messengers
channel proteins
allow hydrophilic solutes and water to pass through membrane
-some are always open, some are gated
channel proteins
ligand-gated channels
respond to chemical messengers
channel proteins
voltage-gated channels
respond to charge changes
channel proteins
mechanically-gated channels
respond to physical stress on cell
ex: inner ear cells
carriers
bind solutes and transfer them across the membrane
-pumps-carriers that consume ATP
membrane proteins
cell-identity markers
gylcoproteins acting as identification tags
membrane proteins
cell-adhesion molecules
mechanically link to cell to extracellular material
G-proteins
-take a small extracellular signal and amplify it intracellularly
-chemical first messenger (epinephrine) binds to a surface receptor
-surface receptor changes shape and initials chemical reactions inside of cell
2 common secondary messengers
-cAMP
-Ca2+
up to __% of drugs work through G proteins and second messengers
60
if there is a weak signal stuck on the outside of the cell, there will be a _____ _____ on the inside
strong signal
when something changes shape....
it changes function
glycocalyx
fuzzy coat external to plasma membrane
-carb moieties of glycoproteins and glycolipids
-unique in everyone BUT identical twins
functions of glycocalyx
-protection
-immunity to infection
-defense against cancer
-transplant compatibility
-cell adhesion
-fertilization
-embryonic development
microvilli
extensions of membrane (1-2um)
-GIVES 15-40 TIMES MORE SURFACE AREA
-specializes cells absorption
how do microvilli appear on some absorptive cells?
a brush border, very dense
what do some microvilli contain?
actin filaments that are tugged towards the center of the cell to get more contents into the cell
with faster transport, you can absorb more ____ quicker
nutrients
motile cilia
beat in waves sweeping material across a surface in one direction
-50-200 on each cell
-beat freely within a saline layer at cell surface
Cl pumps pump Cl- into ECF
Na+ and H2O follow
-mucus floats on top of saline layer
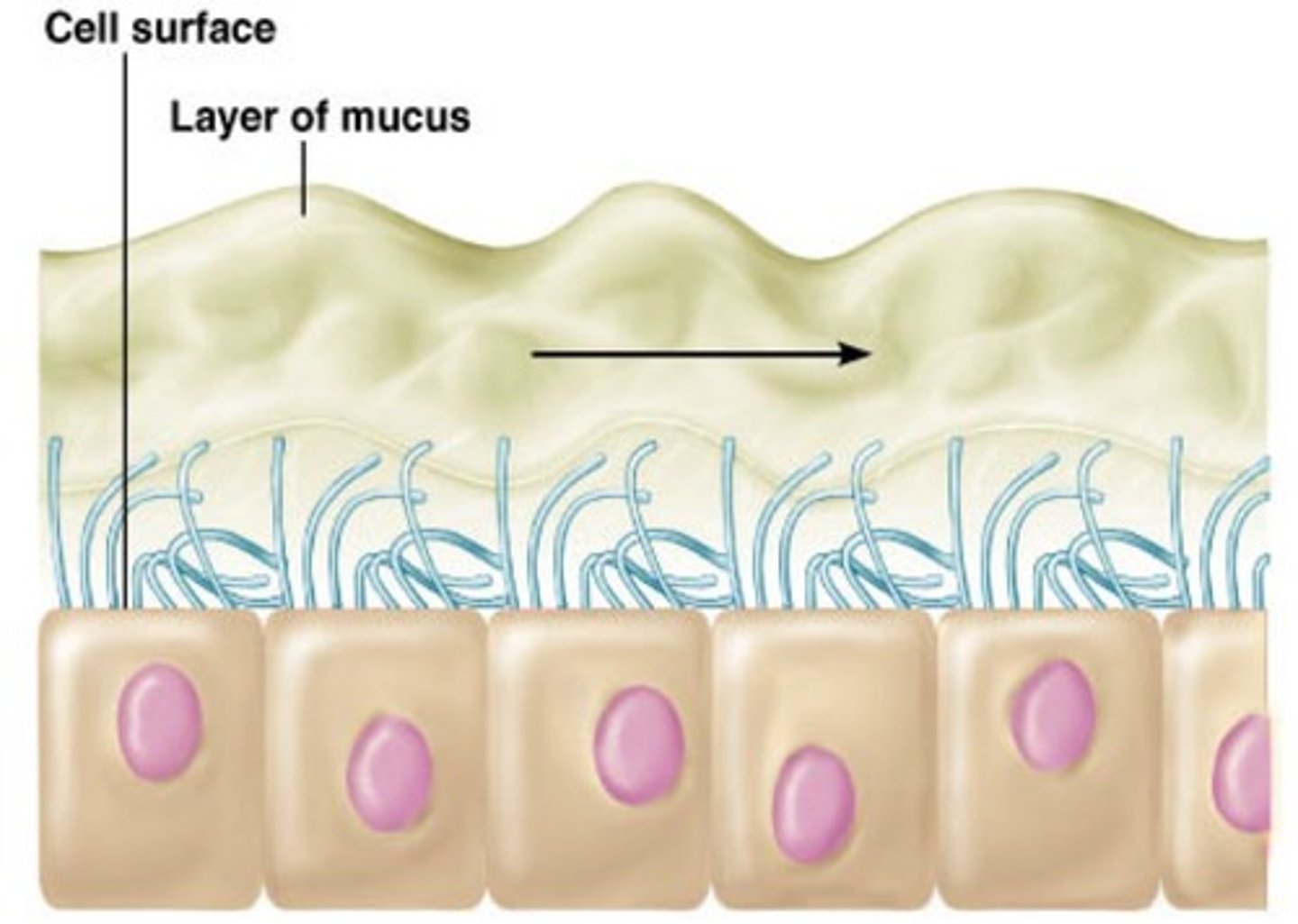
where can you find cilia?
respiratory tract, uterine tubes, ventricles of brain, ducts of testes
cystic fibrosis
heredity disease in which cells make chlorine pumps, but fail to install them in the plasma membrane
-chlorine pumps fail to create adequate saline layer on cell surface
-instead of recycling mucus, they keep the bacteria filled mucus
-HIGH RISK OF PNEUMONIA
what causes cystic fibrosis?
thick mucous plugs pancreatic ducts and respiratory tract
what are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis
-inadequate digestion of nutrients and absorption of oxygen
-chronic respiratory infections
-life expectancy of 30
flagella
tail of sperm, only functional flagellum in humans
-whip-like structure with axoheme identical to cilium's
-much longer than cilium
-stiffened by coarse fibers that support the tail
-movement is snail-like
-no power stroke or recovery strokes
Pseudopods
continually changing extensions of the cell that vary in shape and size
-can be used for cellular locomotion, capturing foreign particles
*temporary extension of a cell
Pseudo=
fake/false
Do passive mechanisms require ATP?
no!
where does the energy come from for passive mechanisms?
random molecular motion of particles provide necessary energy
examples of passive mechanisms
filtration, diffusions, osmosis
carrier-mediated machanisms
use a membrane protein to transport substances across membrane
filtration
particles are driven through membrane by physical pressure
ex:
-filtration of water and small solutes through gaps in capillary walls
-allows delivery of water and nutrients to tissues
-allows removal of waste from capillaries in kidneys
simple diffusion
net movement of particles from place of a high concentration to a lower
-doesn't require a membrane
-substances can diffuse through a membrane if the membrane is permeable to the substance
what causes simple diffusion?
constant, spontaneous molecular motion (molecules collide and bounce off each other)
what factors affect diffusion rate?
1- temp (higher temp=faster diffusion)
2- molecular weight (bigger=slower)
3- steepness of concentration gradient
4- membrane surface area (more surface area, the faster)
5- membrane permeability (higher permeability, faster diffusion)
osmosis
net flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane (water moves from a more concentrated area to a side where its less concentrated)
what does solute particles do when they can't pass through the membrane?
they draw water from the other side
what is crucial consideration for I.V. fluids?
osmosis... osmotic imblances underlie diarrhea, costipation, and edema
aquaporins
channel proteins in membrane specialized for water passage
(water can diffuse thru phospolipid bilayers, but osmosis is enhanced by these)
CELLS CAN SPEED OSMOSIS BY INSTALLING MORE AQUAPORINS
osmotic pressure
the pulling force, it increases as the amount of nonpermeating solute rises (ex: salt or protein)