Exam 2 Not complete doe
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Perioperative Nursing Responsibilities
Collect Health Data
Working with patients to ensure documents are signed
Coordinate care & delivery
Evaluating patient condition pre-op, intra-op, post-op
Educating the patient on best practices for patient recovery
Pre-Op Terms
Pre-Op Phases
Pre-op
Operative
Post-Op (PACU)
Types of Surgeries
Inpatient vs. Outpatient (ambulatory)
Major vs. Minor
Elective, Urgent, Emergent
Laparoscopic
Why rates of ceseran in US is high
Fewer midwives in the US
Hospital scheduling and inconvenience
More medical interventions being used (epidural, inductions)
Repeat C-sections
Patient preference
Ceserean Indications
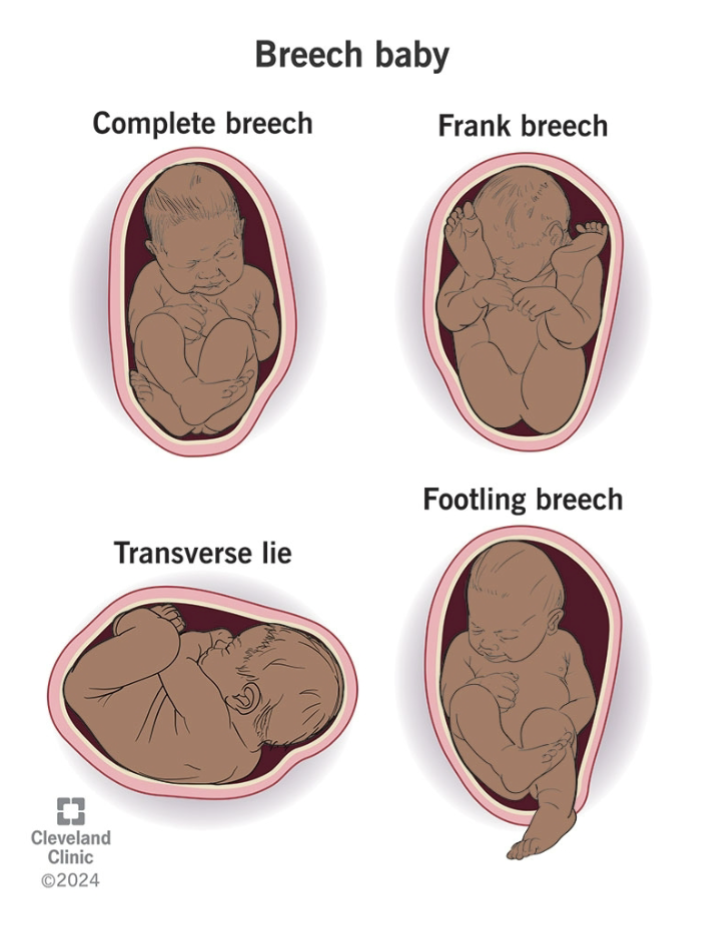
Breeching
Repeat/previous C-section
Non-reassuring fetal status (ex: poor heart rate, contractions, accelerations)
Active herpes lesions
Placenta previa and abruption
Stalled labor
myomectemy
Specific cardiac disorder (maternal0
Elective
Breech babies are born via c-section since
Head entrapment may occur and birth injuries and oxygen deprivation is more common
Exception being a second twin
External Cephalic Version
External manipulation done by provider to get fetus from breech or transverse to cephalic
Provider may use an epidural or terbutaline to relax the uterus
Types of Ceserean Sections
Scheduled
Unplanned
Failed progression of labor or fetal intolerance
Emergent
Same with unplanned except indicators of fetal or maternal distress that was measured for immediate delivery
Types of Anesthesia
General Anesthesia
IV and inhalation drugs
Loss of consciousness, analgesia, amnesia, relaxed skeletal muscles and depressed reflexes
Risk: Respiratory, depression, low blood pressure
Moderate Sedation
Minimal invasive procedures
IVV sedative or analgesics
Regional Anesthesia
Inject near nerve pathaway; stop sensory stimuli
Awake, less sensation in certain area
Spinal Anesthesia
Similar to an epidural
Needle is inserted into spinal space
Usually a 1 time injection
Effect is more immediate (lasts 1-2 hours)
Removes sensation and motor function
Side effects: hypertension, severe headache postpartum
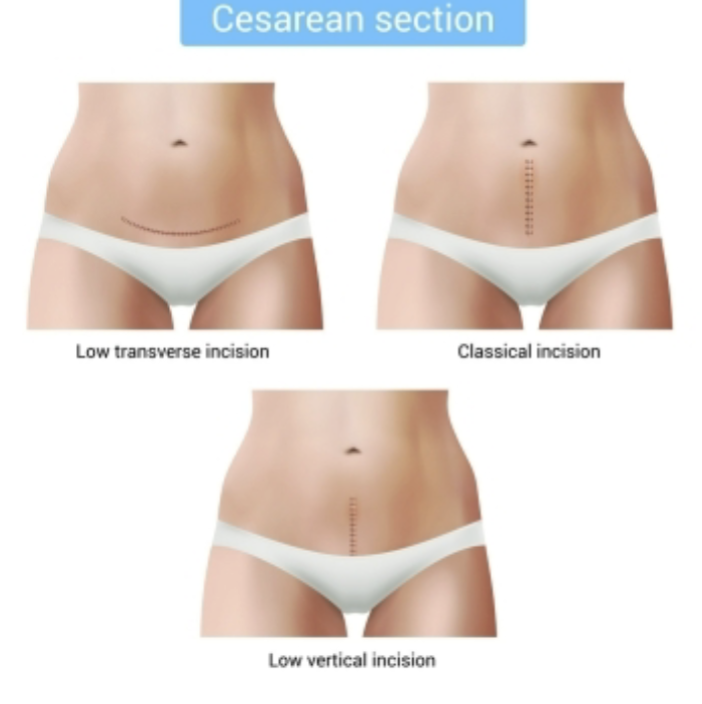
Inscions on Ceserean Section
Skin incision:
Vertical
Transverse
Uterine incision types:
Vertical- low or classical
Transverse
Pre-operative care
Signed consents
Blood work
Maternal VS
NST
Peripheral IV start and at least 1L of Fluids
Need to stop hypotension (low BP), because they may lose lots of blood
Informed Consent
18 years old or emancipated minor
Parent signs for a dependent child
Competent to sign
Alert and oriented
Considered if narcotics or was sedated
Not necessary if patient is under a life threatening situation or legally authorized person cannot sign
2 physicians must sign
Nurses role
Advocate for patient understanding
Witness appropiate person signs
RN Roles in C-section
Circulator
Passes instruments and laps, helps with prep
Recorder/second RN
Recording events in surgery, such as people coming in and out.
Baby RN (Nicu)
Stabilizing baby
Adverse Events
Never Event
Medical error that should not occur
Preventable but devastating
Example: Leaving tools in patients, breaking sterility during surgery
Sentinel Event
Not foreseeable, or preventable if it occurs
Example: Technology shut down, power is off etc.
Use surgical counts, checklists, and define roles for never events.
C-section Medication
Cephazolin
Indication: Antibiotic given to decrease risk of possible infection
Sodium Citrate(Bicitra)
Indication: Neutralizes stomach acids, given before preop. Reduces chance of throwing up in surgery and decrease infection
Ephedrine/Phenylephrine
Indication: Increases blood pressure since sedations are used and may affect heart.
Ondasteron
Interop or post op, prevents nausea and vomitting
Acetominophen (tylenol)
Pain reducer, anti-inflammatory like NSAIDS
Ketorolac
NSAID, short-term moderate to severe pain reduces pain and inflammation.
Fentanyl
Severe pain management, used in short procedures, pain med opiod. IV. Used for post Op.
Hydromorphone (Dilaudad)
Narcotic, administered IV. Used for pain often for post op or chronic pain
Spinal Morphine (D
Given post op/intra op, provides extended pain control for c-sections.Monitor sedation and respiratory levels
Endometriosis
Growth of endometrial tissue where tissues grows outside the uterus. Thickens in menstural cycle, estrogen thickens, breaks it down, and bleeds.
Symptoms: Pelvic pain, dyspareunia (painful sex), dysmenorrhea (mensutration cramps), abnormal vaginal bleeding, painful urination/bowel movemnet
Pharamcologic
Anovulation, amenorrhea, decreased pain, interruption of lesion development
Risks: medicually induced menopause
Oral contraceptives
NSAIDS for pain managment
Suppress ovulation/ menstruation
Menopause
Absence of period for a year
Symptoms: Irregular periods, vaginal dryness, urinary incontinence, recurring UTI’s, pain with sex, hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings
Risks: Osteoperosis, and Heart Disease
Pharamcologic Managment
Recommended for women <60 years.
Hormone therapy: progesteron-estrogen therapy
Administration options: oral, topical, transdermal, suppositories, vaginal rings
Side effects: Swelling, weight gain, breast soreness, brown spots on skin, eye dryness, depression
Long term: blood clots, hypertension, stroke
Erectile Dysfunction
Persistent inability to achieve or maintain erection
Causes
Neurlogic: spinal cord injury, stroke, parkinson
Hormona: endocrine disorder, aging,
Vascular: atrophy, fibrosis of smooth muscle
Drug induced: antidepressants, antipsychotics, etc.
Sildenafil (Viagra)
Smooth muscle relaxant to increase blood flow into the corpus cavernosa
Cant be used with nitrates (such as treating angina), dilate blood vessels.
Side effects: Flushing, hypotension, dizziness
Other options include vacumn devices, psychosexual therapy, IC injections.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of prostate
Obstructive to nearby organs such as: prostate, urethra, bladder, penis
TURP( Transurethral Resection of the Prostate)
Surgical restriction to carve out the tissue blockage
Pharmacologic Treatment
Prazosin, Tamsulosin
Relaxes smooth muscle of bladder neck and prostate - Better Urine Flow
Finasteride
Prevents testosterone conversion> decreases prostate size> urine flow
Side effects: sexual dysfunction
STI’s
Transmission Routes
Sex, needles, fluid exchange, skin-to-skin, blood-to-blood, oral transmission
3 Types of Virals
Viral
Bacterial
Parasitic
5 P’s
Partners: gender/partner
Practices: What kind of sex?
Protection: Methods use to protect? Have you talked with your partner to prevent/protect?
Past History: Have you or your partners been tested/diagnosed for STI in the past, have you and partner injected drugs?
Pregnancy: How important is it for you to pregnancy are you using form of birth control
STI Bacterial’s
Chlamydia & Gonorrhea
Transmitted via sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal)
Symptoms: asymptomatic, abnormal discharge, burning urination, bleeding, burning with urination
Treatment: antibiotics
Syphilis
Transmission: Sexual contact, congenital (mother to fetus)
Symptoms: Painless sores (chancres) on genitalia, rectum, or mouth. Rash on palms, sores, fever, fatigue
Treatment: antibiotics, penicillin G
STI Virals
Hepatitis A
Transmitted orally, can be food transmission, fecal-oral exchange
Symptoms: flu-like, Malaise, fatigue, anorexia, nausea, itching, fever, RUQ pain
Treatment: Vaccine, anti-viral treatment
Hepatitis B & C
Transmitted as blood borne virus (IV, needles, blood-to-blood)
Symptoms: Silent infection/asymptomatic, jaundice, dark urine, clay stools
Treatment: Hep B Vaccine
Herpes Simplex Virus
Transmitted via skin-to-skin, asymptomatic
Symptoms: Painful, recurrent ulcers on genitals, rectum or mouth, fever, chills, malaise, severe dysuria
Treatment: Antiviral medications
Active lesions on genitalia indicate C-section
HIV
Transmission: sexual contact, blood borne, mother-to-child
Symptoms: Flu-like illness, fever, night sweats, malaise
Treatment: Antiretroviral therapy, controls virus, imprvoes immune function
HPV
Transmission: Sexual Contact
Symptoms: Genital Warts, asymptomatic, cervical abnormalities
Treatment: HPV topical, surgery removal, Gardasil, vaccination
STI Parasitic
Trichomoniasis
Transmitted skin to skin, unprotected sex
Symptoms: Foul smelling discharge (yellow, white, frothy). inflammation of vagina/vulva, itching, painful urination
Treatment: Antibiotics
Pubic Lice
Transmitted: bedding or clothing that has lice
Symptoms: Visible crawling, attached to hair itching
Treatment: Shave and anti-parasitic cream
Bacterial Vaginosis
Vaginal infection, overgrowth of NL flora of vagina
Potential cause: use of antibiotics, sexual activity on new partners
Symptoms: thin, white/grey vaginal discharge, fishy odor, itching/irritation, painful urination/sex
Treatment: antibiotics
Prevention Practices
Education about safe sex
Condoms, etc,
STI education
Inspecting genatalia
Tested regularly
Vaccines: Hep B, Hep A, HPV
Condoms, male or female, topical spermicides
STI Risks and Pregnancy on Maternal and Neonate
Maternal
Preterm Labor
Pre rupture of membrane
SAB
C-section delivery
Neonatal
Sepsis
Eye infections
Fetal/Neonatal Death
Birth Defects
Chronic carrier/infection with Hep B
APGAR
Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity, Respiratory
Score must be >7, 8 is considered Normal. Anything less than 7 (less than or equal to 6 is abnormal!!)
Purpose: Baby is transitioning and using organs, supports resuscitation
“Golden Hour”
1st hour of babies life
Benefits:
Promotes bonding (mother rewleases oxytocin hormone)
Latches easier for long term breast feeding
Stabilizing heart and breathing rate
Abnormal Apgar Score
Bring baby to radiant warmer
For Airway and Color
Obstruction: Bulk suction or manual suction (at warmer)
Breathing issues: positive pressure ventilation (PPV) to open alveoli
For circulation
Same as airway and color, except assess HR within 15-30 seconds
Ideal 100 BPM>
Delayed Cord Clamping
Waiting to clamp cord 30-60 seconds
Benefits:
Increased Hgb
Increased Iron Stores
Preterm infants: higher blood volume
Lotus birth
Leave cord attached to baby & placenta until cord naturally falls off
Respiratory in Babies
Stethoscope
Normal findings in babies
BPM 30-60 per minute
Quiet and effortless
Iregular pattern or short pauses
Pinkish color)
Abnormal Findings
Grunting
Retractions
Nasal Flaring
Crackles
Cardiovascular
Assess via: temperature, capillary refill, listening for heart rate
Normal findings:
HR 110-160 BPM
Regular rhythm (no sounds)
cap refill < 3 seconds
no murmurs
Abnormal findings:
Arcoyanosis, irregular HR, mumurs beyond 24 hrs
Central cyanosis
Hypothermia
Temperature less than 36.5 * C
Method of heat loss and intervention to prevent
Evaporation
Immediately dry newborn
Convection
Conduction
Radiation
Hyperthermia
Temperature >37.5 (99.9 F)
Causes: Sepsis, inappropriate use of external heat sources
Large surface area and lack of sweat glands
Symptoms: skin is flushed, red, warm to touch
Extension
Risks
Seizures,
Reflexes
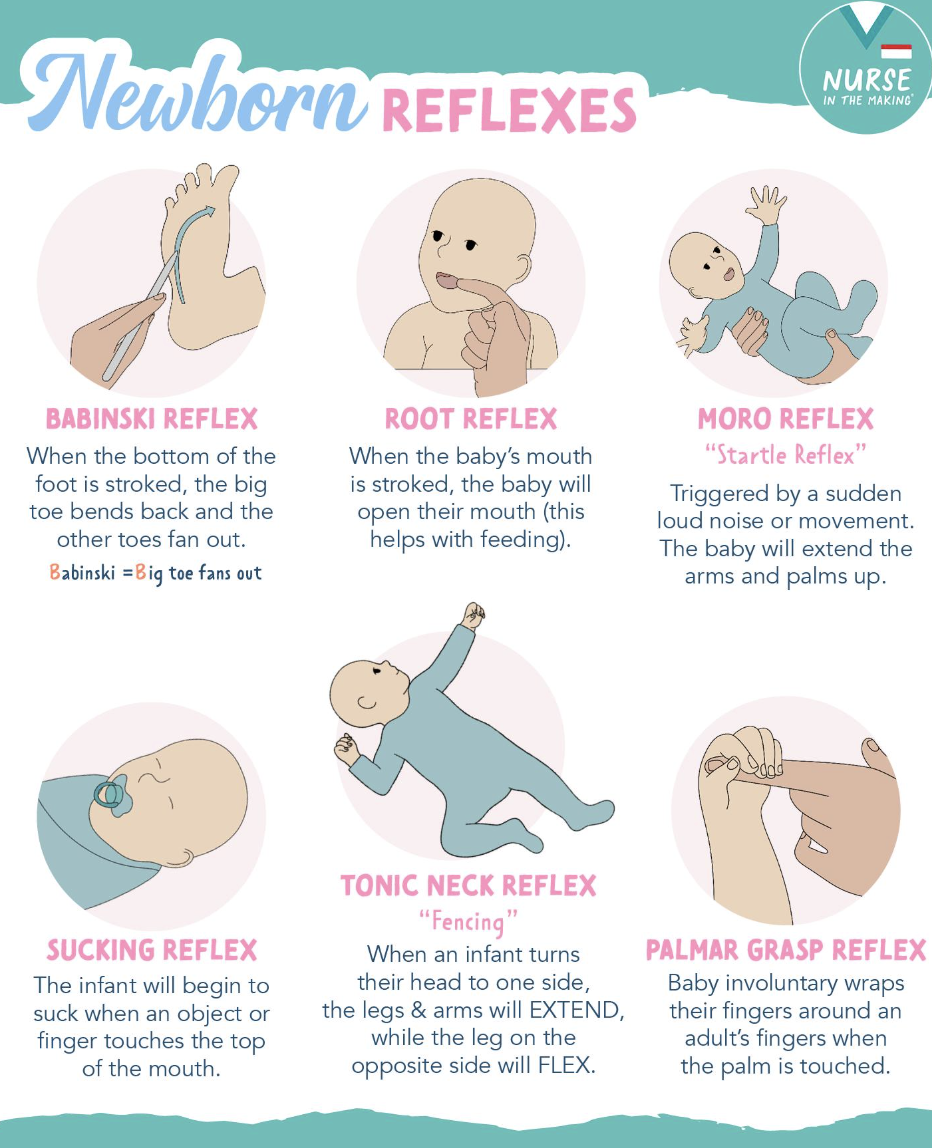
Babinski Reflex
Bottom of foot is stroked, big toe bends
Root reflex
Baby's mouth is stroked, baby will open their mouth
Moro Reflex
Triggered by a sudden loud noise or movement. Baby extends the arm and palms up
Sucking Reflex
Infant will begin to suck when an object or finger touches the top of the mouth
Tonic Neck Reflex
Infant turns their head one side, legs and arms will extend while other leg will flex
Palmar Grasp
Grasps my fucking finger around adults finger when palm is touched.