Nucleic Acid Structure
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1) Adenine
2) N-9
1) ID
2) Where does the sugar attach?
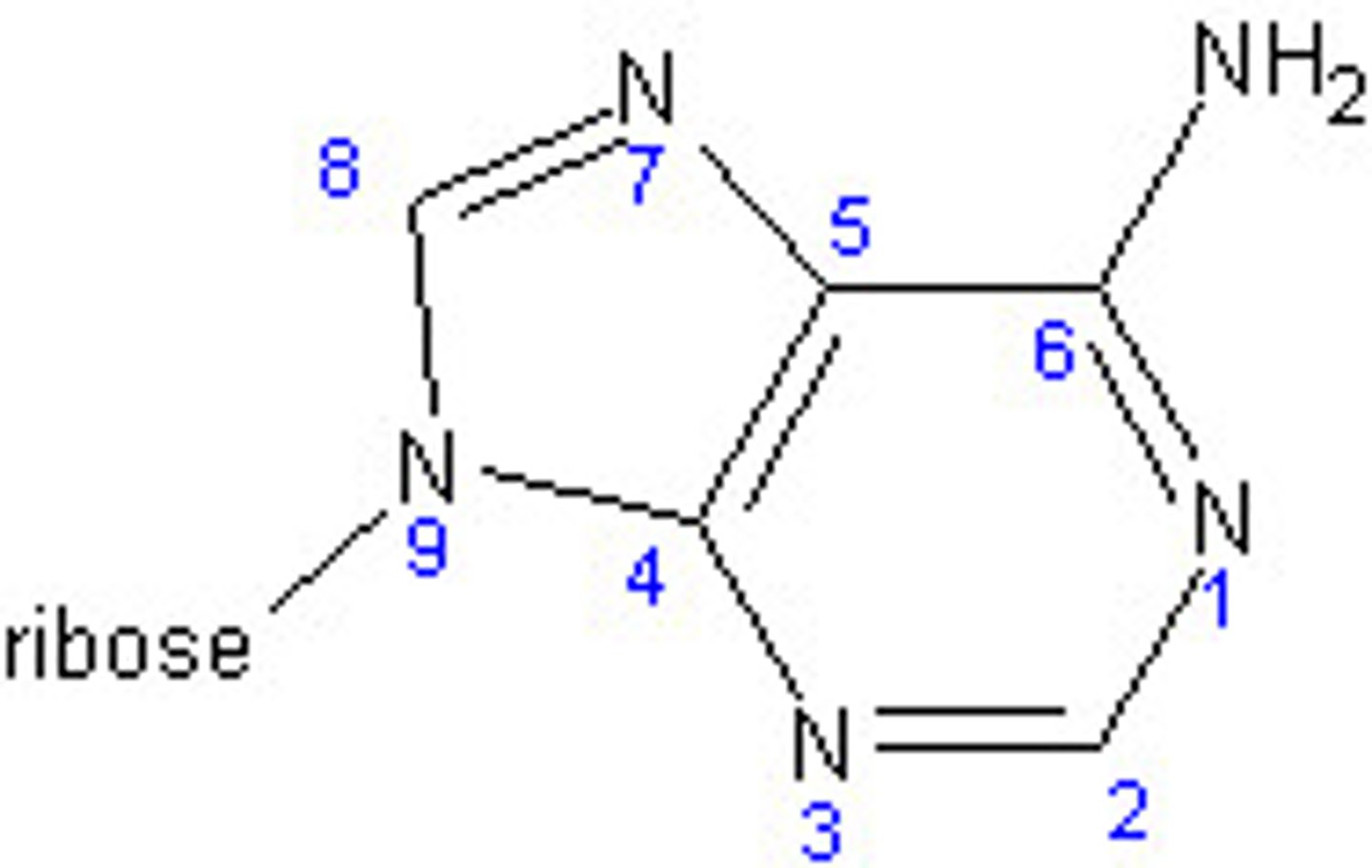
1) Guanine
2) N-9
1) ID
2) Where does the sugar attach?
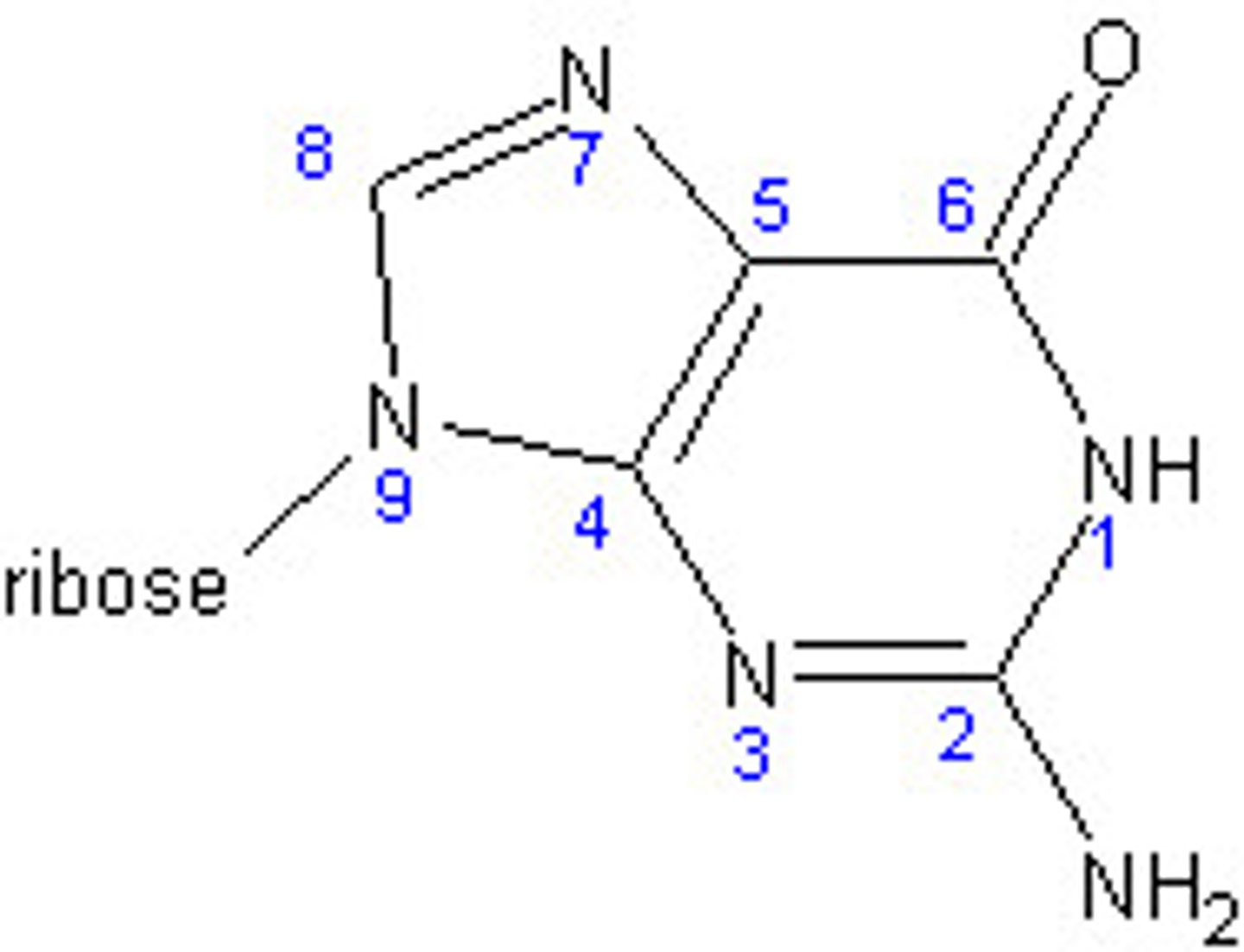
1) Cytosine
2) N-1
1) ID
2) Where does the sugar attach?
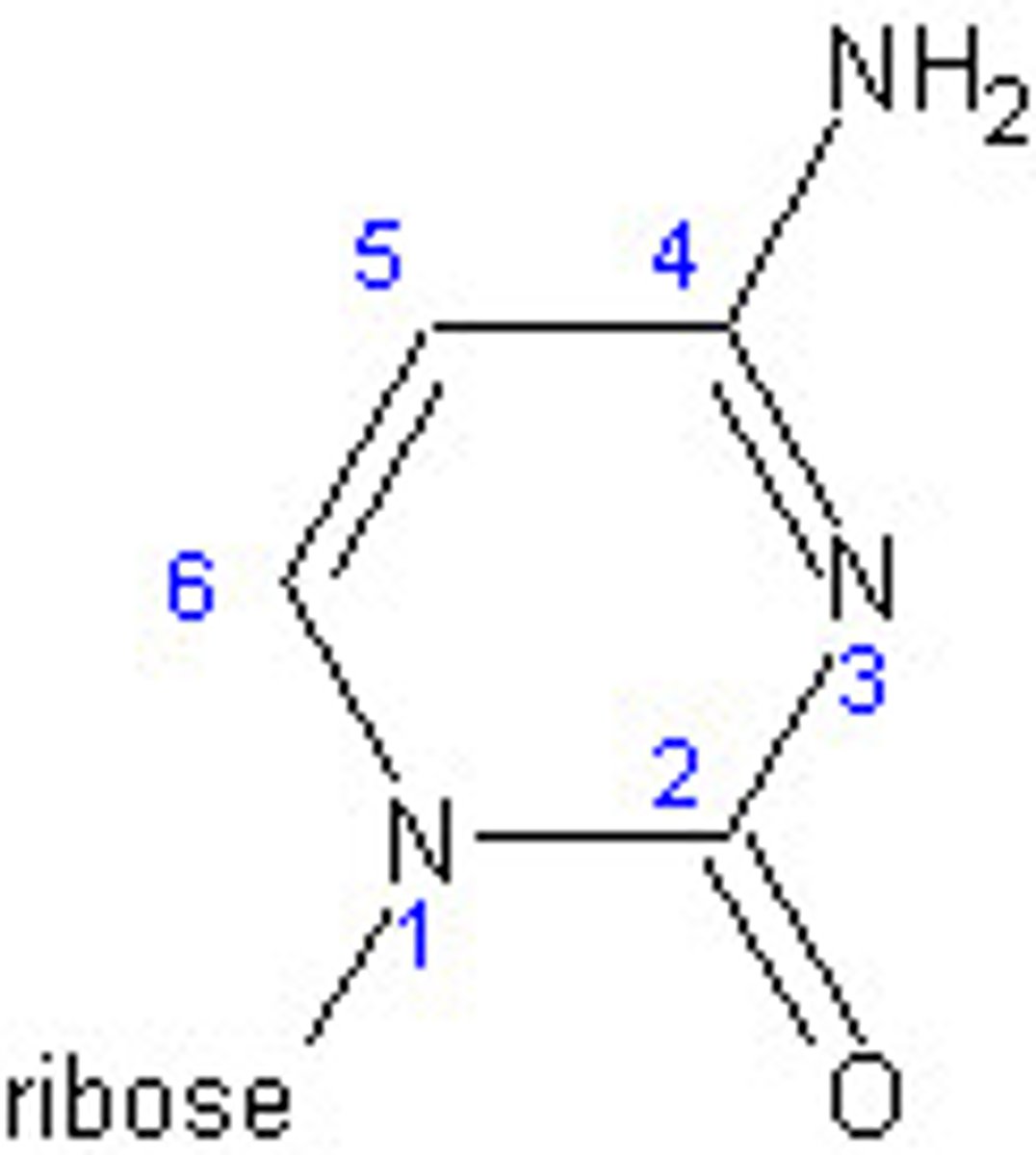
1) Thymine
2) N-1
3) Methyl group on C-5
1) ID
2) Where does the sugar attach?
3) To obtain uracil, you would remove _______.
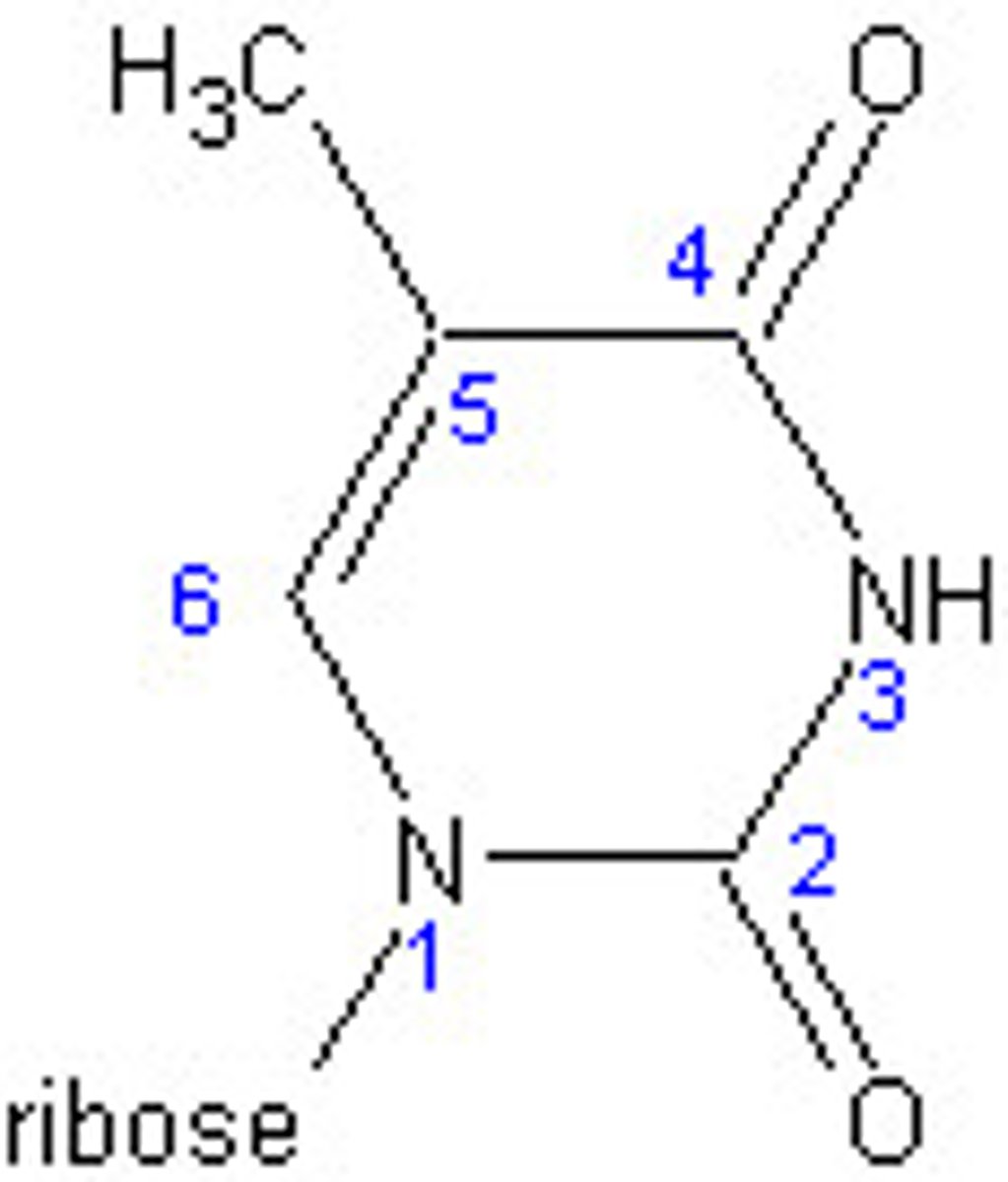
1) base
2) nucleoside
3) nucleotide
A ____ is simply the pyrimidine or purine of nucleic acids. The __(a)__ is the base with a sugar attached, either ribose or 2-deoxyribose. A ____ is a __(a)__ which has a phosphoryl group esterified to the C5 of the sugar. Nucleotides can be mono-, di-, and tri-phosphorylated.
Adenosine
Guanosine
Cytidine
Thymidine
Uridine
Nitrogenous base Nucleoside
Adenine _______
Guanine _______
Cytosine _______
Thymine _______
Uracil _______
1) thymidine
2) ribose
3) deoxyribose
For all nucleosides except ____, the sugar attached is ____. For __(a)__, the sugar is ____.
Phosphodiester bond
The bond(s) linking 5'-ribose through phosphate to another 3'-ribose. This forms the backbone of the polynucleotide structure.
1) cytidine
2) thymidine; uridine
3) base pairing
Through hydrophobic interaction, the planar bases of polynucleotides stack, through hydrogen bonding of complementary structures guanosine pairs with ____ and adenosine pairs with ____ (or ____). This phenomenon is known as ____.
Hydrogen Bond
The stabilizing factor for base pairing.
1) hydrophilic
2) hydrophobic
The ribose and phosphate parts of nucleotides are ____, the nitrogenous bases are ____, and these interactions stabilize the bases in a stacked formation.
1) Hydrogen bonds
2) antiparallel
Ribose molecules of polynucleotides are connected serially, from the 5'>3' direction. Two strands (leading and lagging), which are held together by ____, have backbones that are oriented in opposite directions. This is described as ____.
1) major grooves
2) minor grooves
In the polynucleotide sequence, __(a)__ occur where the backbones are far apart and ____ occur where they are closer together. DNA binding proteins (that may alter structure or regulate processes) will more likely interact with bases at the __(a)__.
B-DNA
____ is the most predominant form of DNA, described as having a right handed double helical structure, the typical one.
A-DNA
____ is similar to B-DNA, in that it also has the right-handed turn and major and minor grooves. However, it is more compact and has a tighter coil.
Z-DNA
The ____ form is named for the zig-zag pattern the ribose/phosphate takes in the left handed turn. It has a looser coil and bases are more positioned to the periphery than B-DNA.
Alkali and heat
Under which two conditions can nucleic acids be denatured?
1) prokaryotic
2) plasmids
3) eukaryotic
The ____ genome is described as having one large circular piece of DNA. Some also have extra DNA held on small circular structures called ____ which can be swapped between neighbors and across bacterial species. Also, there are no intron regions and very few repeated sequences. This differs from ____ genome which has the DNA on linear chromosomes. Also, there are introns in the genes, a greater space between genes, and wide repeating sequences.
Tm
3
2
The temperature at which half of the bases in a given DNA are denatured (melted) is the ____. It is related to the G-C content of the DNA because breaking of ____ hydrogen bonds takes more energy than breaking of ____ bonds.
supercoiling
topoisomerases
I
II
Bacterial and mitochondrial DNA are packaged by ____. Supercoiled DNA is circular DNA that is twisted around itself to form a more compact structure. Supercoiling is produced by the action of enzymes called ____. Type ____ cleaves only one strand of DNA and can only relieve stress in the DNA molecule (removes supercoils). Type ____ cleaves both strands of the DNA and can use the energy from ATP hydrolysis to either make or remove supercoils.
Histones
chromatin
nucleosomes
____ are small basic proteins containing large amounts of arginine and lysine involved in the packaging of eukaryotic DNA. The complex of DNA and proteins is called ____. Further compaction occurs as the strings of ____ wind into helical, tubular coils called solenoid structures.
gene expression
heterochromatin
euchromatin
Chromatin structure plays a large role in the regulation of ____. ____ is defined as regions of chromatin that are always highly condensed. It is visualized in micrographs as the dense, darkly staining portion of the nuclear DNA. More importantly, it is found on the periphery of the nucleus and represses transcription. The ____ is much less dense, contains active genes and is found primarily in the more central part of the nucleus.
RNA; DNA
C2; C5
single; double
ribozyme
____ differs from ____ in that it contains the base uracil in place of thymine. The ribose sugar has a hydroxyl group on C__ rather than C__. In addition, it is usually ____ stranded (rather than ____ stranded) and its secondary structure is irregular, but can be extensive. A ____ is a RNA molecule that catalyzes a reaction that changes itself; therefore it is not a true catalyst. The reaction is usually a removal of an internal segment and splicing together.
mRNA ('messenger')
guanosine 5'-cap
leader
trailer
poly(A) tail
____ is the RNA formed from transcription of DNA genes that will be translated into the amino acids sequence of a polypeptide. The structure generally involves a ____ at the 5' end (added posttranscriptionally), followed by a non-coding sequence (____ sequence), followed by a start codon, protein coding sequence, and a stop codon, followed by another non-coding sequence (____ sequence), and finally a ____ at the 3' end (added posttranscriptionally).
polycistronic message
5' untranslated region (UTR)
3' UTR
In bacteria, but not in humans, a single messenger may code for more than one protein (____). In eukaryotes, there are usually a large number of nucleotides located in the leader sequence, this region is known as ____. A similar region exists at the trailer sequence known as ____.
rRNA
Ribosomes
____ contains many loops with extensive base pairing. ____ are ribonucleoprotein complexes which function in protein synthesis.
larger
prokaryotic
Cytoplasmic ribosomes are generally ____ than prokaryotic ribosomes. Mitochondrial ribosomes have similar properties to ____ ribosomes yet are a bit smaller in size.
small
cloverleaf
10-20% of the nucleotides of tRNA are modified. They are relatively ____ in size when compared to rRNA and mRNA. They typically form a secondary structure that resembles a ____. They contain an amino acid attachment site and an anticodon.