Soil Stuff
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What is ecology?
study of relationships between living organisms and their physical environment
autecology
individual organisms of single species in relation to environment
synecology
homogenous/heterogenous groups of organisms in relation to their environment
What are the six important scales in ecology?
genes & traits, individuals, populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes
biogeography
study of geographic distribution of life - biodiversity over space and time
climax vegetation
balanced ecosystem
What is the role of chance regarding island biography?
chance of species reaching larger island greater than small island; higher extinction rates in smaller populations bc of low genetic diversity and vulnerability to stochastic events
stochastic events
random occurrence or process driven by probability
What are some facts about heterogeneity (diversity) in islands?
heterogeneity higher on larger islands, more variation in conditions and resources
What are five theories of island biogeography?
#species on island eventually constant; #species determined by balance of extinctions and immigration; large islands have more species; #species declines with distance to mainland; no difference between real & mainland islands
What is Natura 2000?
network of nature protection areas in EU
Succession
directional change in species populations, community, and ecosystem at a site following a disturbance
What the difference between primary succession and secondary succession?
primary - on new land that was previously occupied; secondary - after disturbances (faster than primary)
seed bank
dormant collection of seeds residing in the soil, leaf litter, or on surface
rhizomes
horizontal underground plant stems that sends out roots from the nodes
plagioclimax
human-induced climax to succession
What are the four theories on succession?
monoclimax, polyclimax, mosaic, cyclical climax
What is the monoclimax theory, and who theorized it?
Clements; all successions lead to a single climax community
What is the polyclimax theory, and who theorized it?
Tansley; a single climax community can lead to multiple climax communities
What is the mosaic theory, and who theorized it?
Whittaker; climax communities are a result of both biotic & abiotic environment
biotic
all living components in an ecosystem
abiotic
non-living components in an ecosystem
pioneer species
first hardy organisms to colonize barren or disturbed land
allelopathy
one organism produces biochemicals (allelochemicals) that affect other organisms growth
What are the five components of the cyclical succession in nature conservation?
health-lands, pioneer stage, culturally-valued landscapes, natural succession, regular reset of succession
What is the cyclical climax theory, and who theorized it?
Aubreville; species become established only in association with other species
plant-soil feedback
plants alter soil properties that influence performance of seedlings
monoculture
cultivation of a single crop
trophic cascade
indirect interactions that control ecosystems
What group of a food web regulates the ecosystem with a bottom-up control?
resources
What group of a food web regulates the ecosystem with top-down control?
predators
What is the ecology of fear?
risk or perception of predators that changes prey behavior and physiology
What is Net Primary Productivity (NPP)?
Gross Primary Productivity - Respiration
What is Liebig’s Law of the Minimum
limiting resource determines maximum growth
fundamental niche
species can exist based on combination of tolerance ranges for all conditions
What is Shelford’s Law of Tolerance
every species has a max, min, and optimum amount of resources for optimal growth
What is exploitative competition?
indirect competition over resource
What is contest competition?
direct conflict between animals
What is Intraspecific Competition, and what are the two kinds?
competition between animals within a species; exploitative & contest
What is Interspecific Competition?
competition between animals of different species
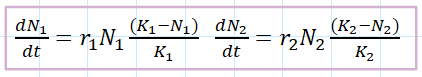
What is the competition coefficient in the Lotka-Volterra competition model?
ratio between competitive effects of both species
What is Gause’s Principle?
species with identical ecological requirements cannot coexist in same environments
What is niche differentiation?
competing species adjust resource use/behavior to minimize competition
niche shifts
replace niche space
niche contractions/expansions
reduce/increase niche breadth
What are the three diversity classifications (related to distance of diversity)?
alpha - local diversity; beta - two habitats or same environmental gradient; gamma - regional diversity
evenness
distribution of # of individuals over # of species compared to when evenness would be maximal
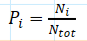
What does the Shaonnon Wiener Index help us find, and what are the individual components of it?
proportions of individuals of a species; s = species #, Ni = # individuals of species i, Ntot = # of individuals of all species
What is the Simpson’s Index?
probability that two individuals at random are same species
What are some reasons for biodiversity of the tropics?
tropics have more solar energy, more rainfall, less seasonal variation, undisturbed during glaciation periods, resource rich
What is the Old, Climatically Buffered, Infertile Landscapes (OBCIL) theory, and who theorized it?
Hopper; ecosystems will reach a stable environment given enough time
What is the Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis, and who theorized it?
Connell; intermediate disturbance → support both species that require disturbance to propagate and species that persist through disturbance; high disturbance → pioneer species flourish; low disturbance → climax species flourish
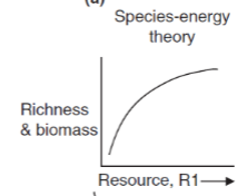
What is the Species Energy Theory, and who theorized it?
Wright; large amount of resources relaxes competition
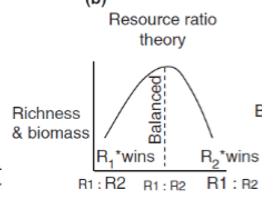
What is the Resource Ratio Theory, and who theorized it?
Tilman; availability of any one resource increases then other resource is likely limiting
What is the Multidimensional Niche Hypothesis, and who theorized it?
Harpole & Tilman; number of added resources remains significant predictor of diversity loss
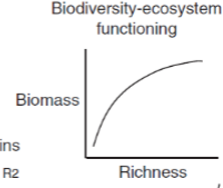
What is the Biodiversity-Ecosystem Functioning Theory?
productivity is result of species diversity, not the driver of it
What is soil?
a living, natural body comprised of solids, liquids, and gases that occur on land surface
What is the static view of soil?
soil is an object, resulting from various processes that have altered the original bedrock or sediment
What is the dynamic view of soil?
environmental compartment in which input and output of mass and energy determine characteristics
What are some physical soil properties?
density, texture & structure, stability, porosity, hydraulic conductivity
What are some chemical soil properties?
C, N, nutrients, electrical conductivity, cation exchange capacity, carbonates
What are some biological soil properties?
microbial biomass, microbial respiration, microbial community composition, enzymatic activity, earthworms & nematodes
pedogenesis
complex phenomenon leading to soil formation from mineral and organic parent material
What are the three rock types?
igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
How are igneous rocks formed?
cooling & solidification of magma/lava
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
accumulation and lithification of sediments or organic material
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
igneous or sedimentary rocks are changed by extreme heat/pressure
How do fauna influence soil?
move organic material & minerals around
How are flora influenced by soil?
determines growth; main source of organic material; influence microclimate & hydrology
Explain the transformation of rock via unloading
breaking up when erosion removes pressure on underlying rocks
Explain the transformation of rock via thermal weathering (thermoclasty)
results from variable thermal conductivity of minerals & rocks
Explain the transformation of rock via gelifraction
caused by ice formation → freezing water breaks rocks
Explain the transformation of rock via leaching
removal of solutes by soil water after dissolution
Explain the transformation of rock via hydrolysis
breaking due to reaction with water
Explain the transformation of rock via ocidation/reduction
electron exchanges cause creation of minerals
mottles
irregular arrangement of spots of color in soil
How are materials transferred within a soil?
bioturbation, pedoturbation, eluviation
bioturbation
mixing materials in soil by animals
pedoturbation
mixing materials within soil by alterations of wet and dry periods
eluviation
mixing of materials in soil by transporting within the solution
cheluvation
formation between soluble organic compounds and normally insoluble metal cations enable transport by percolating water
podzolization
acidic water leaches iron, aluminum, organic matter from surface to lower layer
lessivage
transport of clay in suspension (without chemical alteration)
What is the Mechanical Sieve effect?
chemical changes lead to lower solubility or suspension → dependent on size of transported material and pore sizes in deeper parts of soil
What happens during extreme accumulation duricrusts?
solid layers originate from transport and precipitation of weathered material
gleying
seasonal dynamics in soil water saturation cause mottles
What are the possible ways soil can be transformed?
chemical weathering, hydrolysis, hydration, oxidation/reduction
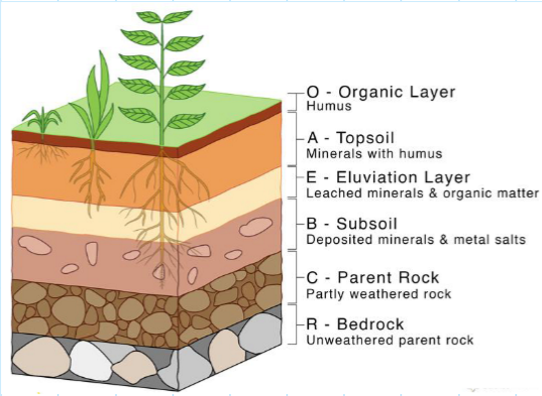
What are the five layers of soil, and name their corresponding letter?
O - organic layer; A - topsoil; E - eluviation layer; B - subsoil; C - parent rock; R - bedrock
What describes the physical quality of soil?
soil porosity, soil water content
What describes the chemical quality of soil?
nutrient content, concentration of heavy metals
What describes the biological quality of soil?
biodiversity, soil organisms, soil microbial biomass
What are the four types of soil degradation, and list an example of each?
physical - erosion; biological - loss of biodiversity; ecological - loss of nutrients; chemical - nutrient imbalance
salinization
presence of high salt concentrations in topsoil
sodication
saturation of soil with sodium
What happens to plants when the soil is salinized?
reduced water uptake, ion toxicity, reduced nutrient uptake
What are the three types of weathering?
physical, chemical, biological
What are the primary crystalline minerals, and how are they formed?
feldspar, micas, quartz; derived from igneous & metamorphic rock
What are the secondary crystalline minerals, and how are they formed?
silicates, hydroxides of aluminum & iron; formed at low temperatures during chemical & biological weathering
What is the tetra:octo ratio of kaolinite?
1:1
What is the tetra:octo ratio of illite?
2:1