Unit 7-2: Industry and Economic Development - AP Outline
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Agglomeration
Occur when firms cluster spatially in order to take advantage of geographic concentrations of skilled labor and industry suppliers, specialized infrastructure, and ease of face-to-face contact with industry participants
Location Economies - shared resources, knowledge spillovers, reduced transportation costs
Urbanization Economies - large consumer market, shared infrastructure, diverse labor pool
Ex. - High technology (Silicon Valley), Music recording (Nashville), Movie/television (Hollywood/Los Angeles), Auto alley (I-65/I-75 corridor)
Comparative Advantage
A country’s ability to produce one product much more efficiently that it can produce other products within its economy
The competitive edge (in the form of lower production costs, cheaper raw materials, etc.) enjoyed by one location over another
Ex. Middle East (Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, UAE) - oil, China/India - cheap labor
Complementarity
Condition that exists when one place has a surplus of a resource or product that is demanded by another place (a deficit). Without this mutual need, there is no economic rationale for movement or trade
When two regions specifically satisfy each other’s needs through exchange of raw materials and/or finished goods
Ex. Saudi Arabia trades oil to U.S. in exchange for transportation equipment and machinery
Economies of Scale
Refers to the cost advantages that a business obtains due to an increase in the size of its output (production). Essentially, as production volume goes up, the average cost per unit of output goes down
Ex. - Automobile manufacturing, global food products (Pepsi, Coca Cola, McDonalds)
Export Processing Zone (EPZ)
Specifically designated, fenced-in area within a country that offers favorable investment and trading conditions to attract foreign (and sometimes domestic) companies to manufacture and process goods exclusively for export (Reduced tariffs and taxes)
Designated area within a country where foreign companies can operate with reduced tariffs and regulations to manufacture goods primarily for export
Located near ports (air/sea/rail)
Ex - China, India, Mexico
Free Trade Zones (FTZs)
Specific designated geographic area within a country where goods can be imported, stored, manufactured, and re-exported without being subject to most customs duties and tariffs
Plays a crucial role in promoting international trade, optimizing global supply chains, and attracting foreign investment
Ex. Located near ports (air/sea/rail) and/or border crossings
Growth Pole
Geographically pinpointed center of economic activity organized around a designated industry, commonly in the high-tech sector
Geographically concentrated area where significant economic development is deliberately fostered, often through targeted investment in key industries, infrastructure, and technology, which then acts as a catalyst for economic growth in surrounding regions
Ex. Silicon Valley, California; Research Triangle, North Carolina, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Industrialization
Began as a result of new technologies and was facilitated by the availability of natural resources
Process by which an economy transforms from primarily an agrarian (farming-based) society to one based on the manufacturing of goods and services
Caused food supplies to grow, allowed workers to migrate to urban areas, and changed class structures
Ex. Began in England/Great Britain/United Kingdom
International Division of Labor
Global distribution of economic activities where different countries specialize in producing specific goods and services based on their comparative advantages
Spatial shift of manufacturing from developed countries (MDC) to developing countries (LDC), including the global scaling of labor markets and industrial sites mainly due to cheaper labor costs
Core - tertiary, semi-periphery - secondary, periphery - primary
International Lending Agency (International Monetary Fund - IMF)
Large-scale, global financial institution that provides monetary support (loans and financial aid) to member nations, primarily developing countries (LDCs), to facilitate economic development, poverty reduction, and financial stability
Provide loans to countries that are so deeply in debt that they cannot get loans from private banks
International Monetary Fund (IMF) - Short-term financial stability and the smooth operation of the international monetary system
World Bank - Long-term economic development and poverty reduction
Just-In-Time Delivery
Manufacturing and logistics strategy where companies receive raw materials, components, or parts from their suppliers only as they are needed in the production process, and not before
Reduces warehousing costs while shortening delivery times between suppliers and manufacturers
Ex. Motor vehicles, food production
Microlending
Strategy for development using small, short-term loans aimed to provide entrepreneurs and small business owners money for investment - mainly in LDCs
Provide financial support to individuals who may not qualify for traditional bank loans due to gender, lack of credit history, or collateral
Multiplier Effects
Economic principle that describes how a new basic industry job or an initial investment in an area creates more than one new non-basic job and generates a greater overall increase in economic activity
Understanding Multiplier Effect
Initial Investment - (Basic Industry) moves to an area
Chain Reaction - (Non-Basic Sector Growth) when new industries open to support factory workers
Ex. Silicon Valley, California; Auto industry, Midwest
Natural Resources
Material or substance found naturally in the environment that humans can utilize for economic gain (water, minerals, forests, fossil fuels)
Play a significant role in shaping economies and influencing political boundaries across the globe
Provides a source of raw materials for manufacturing and energy
Neoliberal Policies
Range of pro-market and antigovernmental positions on the economy, such as reducing government ownership and regulation and promoting privatization and market-based solutions
Refer to a set of economic principles that promote free-market capitalism, advocating for a minimal role for the state (government) in the economy and society
PRO TRADE!!
Ex. Free Trade Agreements and Organizations (EU, World Trade Organization, Mercosur, and OPEC)
Outsourcing
Practice of hiring a third party to complete a company’s work, often in another country - done to cut cost, improve services, or to concentrate on core businesses
Process where a company contracts an external firm to perform a specific business function or service that was previously done internally
Global Drivers of Outsourcing
Labor cost reduction, access to expertise, advances in technology, and neoliberal policies
Ex. Automobile manufacturing/auto parts, Company/call center
Post-Fordist Production
Contemporary economic system that has moved away from the traditional Fordist model of mass production in large factories, instead emphasizing flexible production methods, specialized markets, and smaller, adaptable manufacturing units, often facilitated by advancements in technology and globalization
Characteristics of Post-Fordist Production
Flexible Specialization. Smaller batches of diverse, customized products to meet varied demand
Automation & IT. Computer-aided design (CAD), robotics, and real-time communication
Skilled/Multi-Skilled. Workers often work in teams, capable of performing multiple tasks and problem-solving
Economies of Scope. Cost savings from producing a variety of related products using the same infrastructure
Spatial Fragmentation (NIDL). Different stages of production (R&D, assembly, marketing) are dispersed globally
Ex. Small businesses in Chicagoland providing specialized products
Service Sector
Direct provision of services to either individuals or businesses. These services involve the distribution, consumption, and sale of goods, or the maintenance and enhancement of quality of life.
Examples: Retail (salespeople, cashiers), Hospitality (restaurants, hotels), Transportation (truck drivers, pilots), Personal Services (hairdressers, fitness instructors), and basic Office Clerical work.
Geographic Note: This sector is often heavily tied to population distribution and market size, making it concentrated in urban areas
Involves jobs rather than manufacturing goods, focusing on meeting consumer needs and providing support services.
Part of post-industrial contemporary economic landscape in Core (MDCs)
Tariff
A tax or duty that a country imposes on imported goods or services and are a key concept when studying economic development, globalization, and international trade because they are a form of protectionism that influences the location of production and the flow of global supply chains
Main Goals of Tariffs
Protecting Domestic Industries: By making imported goods more expensive, tariffs reduce the competitive advantage of foreign firms, encouraging domestic consumers to buy local products
Generating Government Revenue: Like any tax, tariffs provide a source of income for the imposing government
National Security: Governments may impose tariffs on certain goods to ensure domestic production of items critical for national defense or public health
Political Leverage/Retaliation: Tariffs can be used as a bargaining chip in trade negotiations or as a retaliatory measure against a country that has allegedly engaged in unfair trade practices
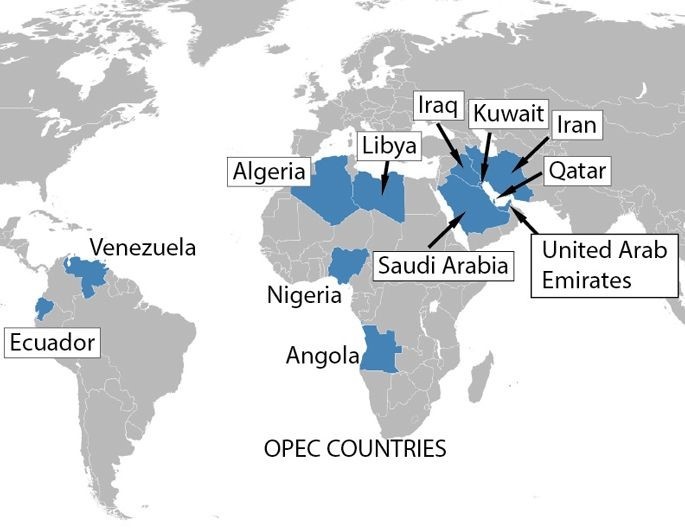
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
International trade agreement composed of major oil-producing nations that work together to coordinate and influence global oil prices by regulating the supply of oil on the market
Intergovernmental organization of major oil-exporting nations that functions as a cartel to coordinate and unify the petroleum policies of its members
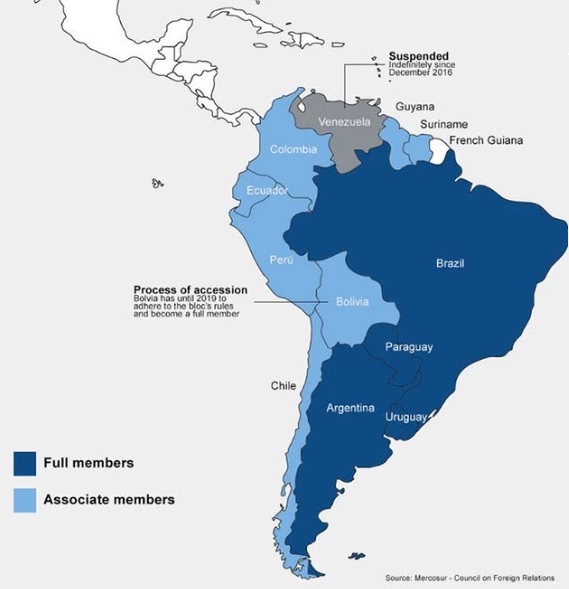
Mercosur (Southern Common Market)
South American trade bloc formed by Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay, which aims to promote free trade and economic integration between its member countries by facilitating the movement of goods, services, capital, and people within the bloc; essentially creating a common market across the region
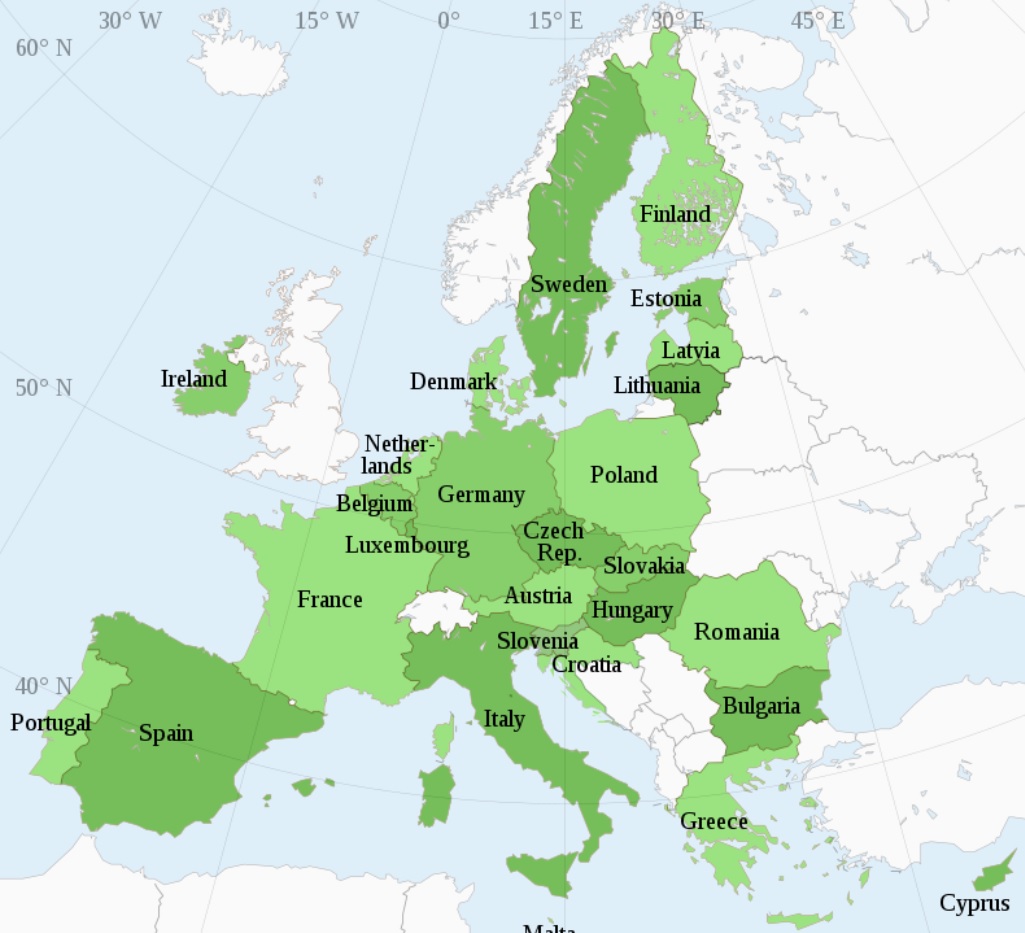
European Union (EU)
Economic alliance of European nations that coordinate trade, immigration and labor policies, making its members one economic unit
Free trade agreement with tariff and non-tariff barriers removed to create a single market
Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
Designated area within a country's national borders where the business and trade laws are different (more favorable) from the rest of the country - primary purpose of an SEZ is to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and promote exports and rapid economic growth
Key Characteristics
Unique Regulations: SEZs operate under liberalized economic regulations
Incentives: Businesses in SEZs are often offered various incentives, including:
Tax breaks or tax holidays (reduced or zero corporate taxes for a period)
Reduced tariffs on imported materials and parts.
Streamlined regulations and simplified customs procedures
Less stringent labor or environmental laws (which can be a point of criticism)
Infrastructure: SEZs typically boast improved infrastructure, such as modern ports, specialized utilities, and transportation networks
Geographically Limited: They are geographically defined, often fenced-in, and managed by a single administrative body
Auto Alley
Refers to the geographical concentration of the North American automotive industry—including vehicle assembly plants, engine plants, and countless parts suppliers—in a distinctive, north-south-oriented corridor
Stretches from Southern Ontario, Canada (near the Great Lakes), through the Midwestern United States (Michigan, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois), and down to the Southeastern United States (Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, South Carolina, Mississippi, and Georgia)
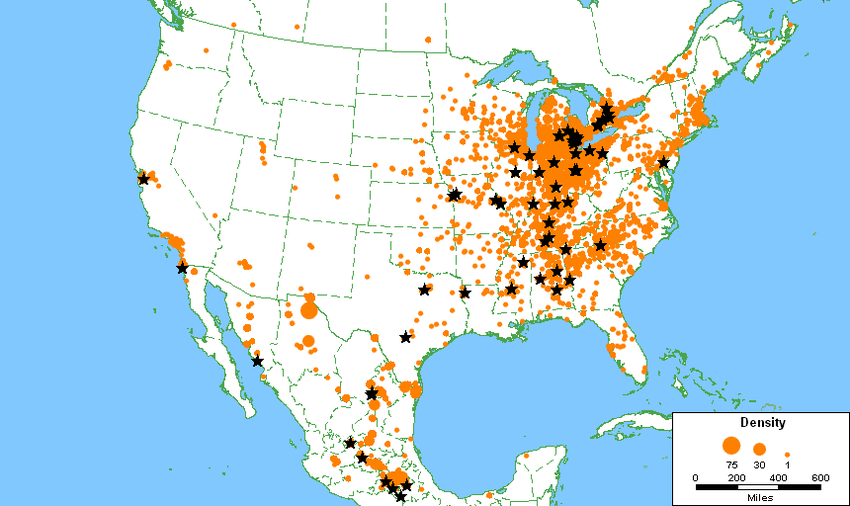
Maquiladora
Manufacturing plant in Mexico, often near the US-Mexico border, where goods are produced primarily for export. Maquiladoras benefit from lower labor costs and tax incentives, facilitating cross-border trade
Vast majority of maquiladoras are concentrated in northern Mexico, particularly in cities directly along the U.S.-Mexico border (e.g., Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, Matamoros). This location is an example of friction of distance being minimized, as it allows for Just-In-Time (JIT) delivery of components from the U.S. and quick transport of finished goods back to the massive U.S. consumer market
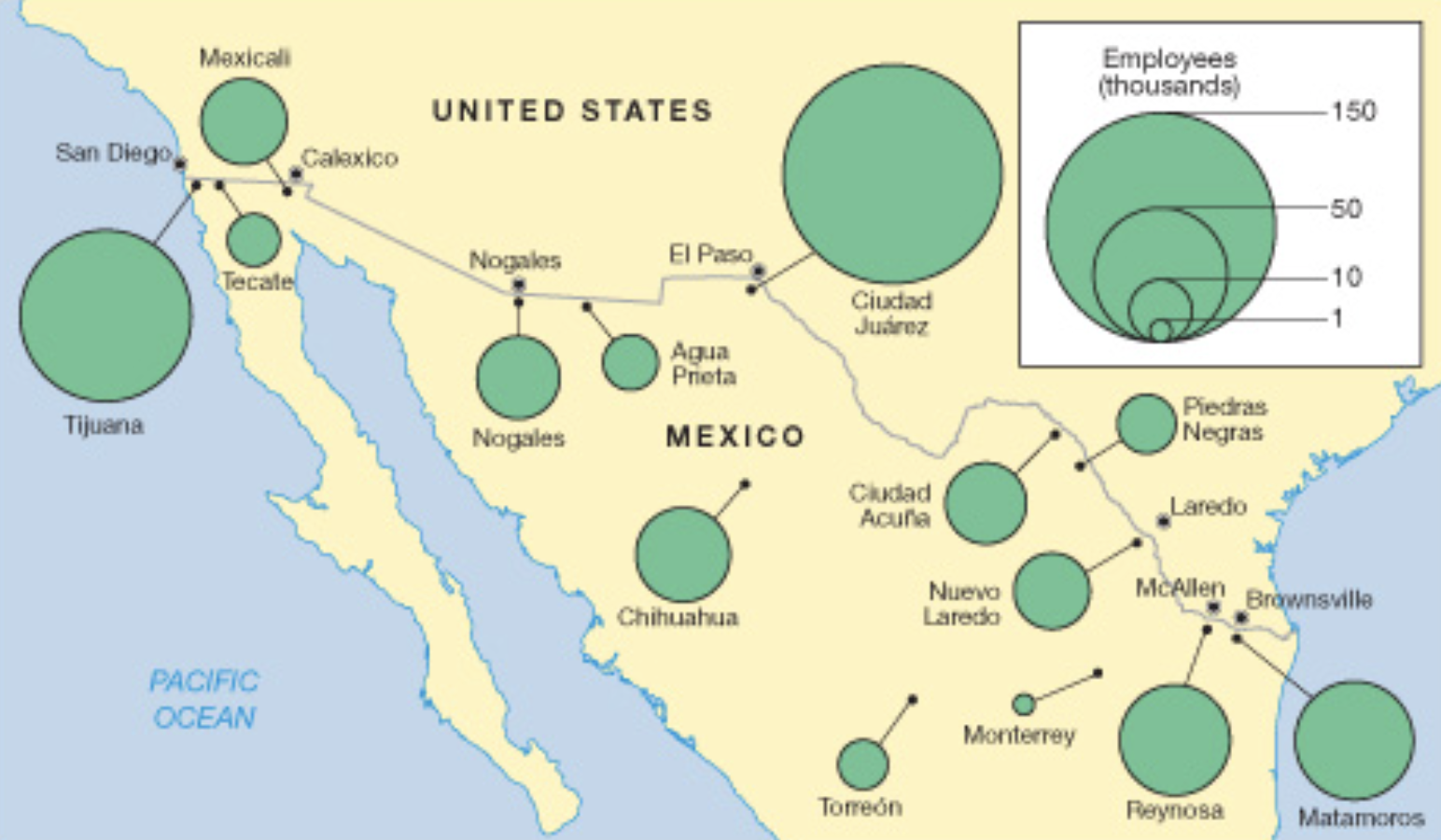
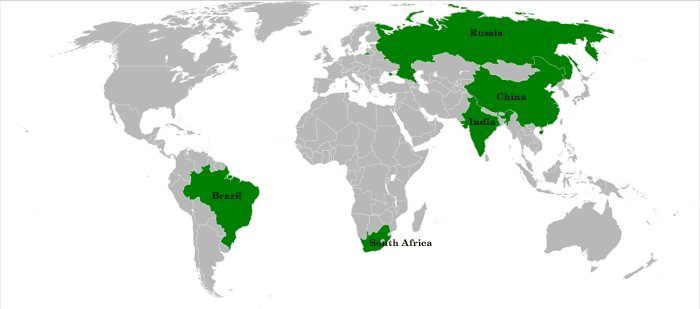
Newly Industrialized Countries
Nation that has moved away from an economy primarily based on agriculture and raw material extraction to one based on manufacturing and industrial production
BRICSM = Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Mexico
Key Characteristics of NICs
Rapid Industrialization: A fundamental shift from the primary sector (agriculture) to the secondary sector (manufacturing)
High Economic Growth: Sustained, rapid growth in Gross Domestic Product (GDP), often faster than highly developed countries
Export-Oriented: A focus on producing manufactured goods for export (e.g., electronics, textiles, vehicles), which attracts Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Rapid Urbanization: Mass migration of people from rural areas to urban centers in search of industrial jobs
Improved Infrastructure: Investment in modern transportation, communication, and energy networks to support industry
Rising Standard of Living: Increases in average income, education, and access to healthcare, though often accompanied by persistent regional and social inequality
Economic Restructuring
Process by which an economy fundamentally changes its structure, moving from a traditional base (like heavy industry or manufacturing) to one dominated by more advanced or service-oriented sectors
Country Type | Restructuring Impact | Economic Role |
Core Countries (e.g., U.S., Germany, Japan) | Experience deindustrialization but gain a massive increase in service sector jobs. | Management, Research, Finance, Consumption (Quaternary & Quinary sectors). |
Semi-Periphery Countries (e.g., China, Mexico, India) | Experience rapid industrialization as they absorb the manufacturing jobs offshored from the Core. | Assembly, Manufacturing, Production (Secondary sector). |
Periphery Countries | Remain largely tied to the Primary sector (resource extraction and agriculture) but may host low-end manufacturing. | Raw Materials and Cheap Labor (Primary and low-end Secondary sectors). |
High Technology Industries
Refers to industries that involve the manufacture of high-value, sophisticated products, and, more importantly, those that engage heavily in Quaternary and Quinary sector activities, such as research, development, and information processing
These industries often include sectors like biotechnology, aerospace, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, characterized by significant investment in innovation and skilled labor
Examples include: Silicon Valley (California), Research Triangle (North Carolina), Route 128 (Massachusetts), Bangalore (India)
Fordist
A production system characterized by mass production and assembly line techniques, emphasizing standardized products and efficient labor practices
Characteristics: assembly line, specialization of labor, standardization, and vertical integration
Global Financial Crises (e.g. Debt Crises)
Period of severe stress in the world's financial markets and banking systems that quickly spreads across national borders, resulting in a widespread loss of confidence, a sharp decline in asset values, and often leading to a global recession
Free Trade Agreement
Treaty between two or more countries that agree to reduce or eliminate barriers to trade, such as tariffs (taxes on imports) and quotas (limits on imports/exports), to facilitate the free flow of goods and services between them
Key Objectives: eliminate tariffs and quotas, attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), and create larger markets
World Trade Organization (WTO)
Intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. It is the primary global institution responsible for setting, monitoring, and enforcing the rules for trade among its member nations
Key Objectives
Lower Trade Barriers
Settlement of Disputes
Non-Discrimination
Trade Blocs
Type of intergovernmental agreement, often part of a regional intergovernmental organization, where member countries agree to reduce or eliminate trade barriers (like tariffs and quotas) among themselves
Primary Economic Sector
- Direct extraction or harvesting of natural resources from the earth - source of raw materials for all other sectors of the economy
Example of Activities - Agriculture, mining, fishing/aquaculture, forestry/logging, quarrying, hunting and gathering
Role in Economic Development
LDCs (periphery) - Large portion of the economy and employs high percentage of the workforce
MDCs - Lower percentage of workforce as tech/mech improves
Secondary Economic Sector
Processing, transforming, and manufacturing of raw materials into finished or semi-finished goods - adds significant value to the raw materials extracted in the primary sector
Characteristics of Secondary
Manufacturing, processing, assembly, construction
Role in Economic Development
Mainly in developing (semi-periphery) countries
Tertiary Economic Sector
Involves activities that provide services rather than producing tangible goods - provides services to consumers, businesses, or government (providing utility rather than a physical product)
Examples of Tertiary Activities
Commercial/Retail - retail stores, restaurants
Professional Services - banking, finance, real estate, accounting, legal services
Personal Services - healthcare, education, entertainment, tourism
Public Services - government administration, defense, police, fire
Transportation - airlines, trucking, telecommunications, postal/delivery services
Role in Economic Development
MDCs - accounts for largest percentage of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employs the majority of the workforce
LDCs - will have some basic services, but mostly focused on primary/secondary
Quaternary Economic Sector
Specialized sub-division of the Tertiary Sector (Service Sector). Specifically concerned with information, knowledge-based processing, research, and high-level technical services
Characteristics of Quaternary
Skill level - Highly skilled, specialized and technically educated
Examples of Quaternary Activities
Information Technology (IT), Finance and Consulting, Research and Development, Government/Education, Media
Role In Economic Development
Largest in core countries (post-industrial)
Drives innovation and is source of highest-paying, value-added jobs in the global economy
Quinary Economic Sector
Highest and most specialized sub-division of the Service Sector (Tertiary) - involve high-level decision-making and top-executive functions that affect the entire economy and society
- CEO/CFO, owners, high government officials, directors of NGOs
- Largest in core countries (post-industrial)
Deindustrialization
Referring to the decline of industrial activity in a region or economy, leading to a shift away from manufacturing and toward a service-oriented economy (the tertiary sector)
Most common example cited in AP Human Geography is the Rust Belt , a region spanning parts of the Northeastern and Midwestern United States (including states like Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Illinois)
Transnational Corporation (Multinational Corporation)
A large company that operates in multiple countries. They manage production, deliver services, and sell products across national borders, typically with a headquarters in one country (usually a More Developed Country/MDC) and subsidiaries or production facilities in many others
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Referring to an investment made by a company or individual in one country (the home country) into business interests in another country (the host country)
Establishes a lasting interest or controlling influence, typically involving at least a 10% ownership stake. It represents a tangible flow of capital and resources across international borders
Non-Base (Basic) Industry
Refers to enterprises that provide goods and services primarily to people and businesses within the local community
Role: These industries are considered city-serving because they recycle the money brought in by the base industries. They grow in response to the needs of the basic workers and their families
Examples: A local dry cleaner, a grocery store, a local hair salon, or a small city hospital (serving only local residents)
Base (Basic) Industry
Refers to an enterprise that brings money into a city or community by exporting its goods or services primarily to consumers outside the settlement
Role: These industries are considered city-forming because they generate the primary wealth (outside money) that flows into the local economy, allowing the city to grow.
Examples: A car manufacturing plant (selling cars nationwide/globally), a university (attracting students who pay tuition and live locally), corporate headquarters (earning revenue globally), or a tourist resort (attracting outside visitors).
Offshoring
Offshoring is the practice of relocating a company's business processes, production, or services to another country
Goal: The primary motivation is usually to reduce costs, mainly by taking advantage of lower labor wages and operational expenses in the destination country. Other reasons include accessing specialized skills, favorable tax regulations, or less stringent environmental rules
The Company's Location: The company that is offshoring still owns the operations, or it might be conducted by a subsidiary/branch of the parent company in the foreign location
Examples:
An American car manufacturer closes a factory in the U.S. and opens a new, wholly-owned factory in Mexico to produce the same goods
A German software firm establishes a customer support call center in India that it directly manages