CAP4770 Exam 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
T/F - Hierarchical clustering requires a predetermined number of clusters.
False
T/F - Normalization is essential in clustering to ensure all variables contribute equally to the distance measures.
True
T/F - K-means clustering assigns records to clusters based on probabilities.
False
T/F - Binary similarity measures are preferred when working with continuous data.
False
Which of the following is an unsupervised learning task?
Clustering
Regression
Classification
Reinforcement learning
Clustering
Which distance measure is most commonly used in clustering but has limitations such as sensitivity to outliers?
Cosine similarity
Manhattan distance
Euclidean distance
Jaccard similarity
Euclidean distance
In clustering, normalization of numerical variables ensures that:
Larger variables dominate the clustering process
All variables contribute equally to the distance measures
Only important variables contribute to distance measures
Clustering becomes faster
All variables contribute equally to the distance measures
In k-means clustering, the number of clusters is:
Randomly chosen after clustering
Automatically determined by the algorithm
Predefined before running the algorithm
Predefined before running the algorithm
What does hierarchical clustering require that can make it computationally expensive?
An n x n distance matrix
A small dataset
A random seed
A predetermined number of clusters
An n x n distance matrix
T/F - The k-means algorithm always guarantees the globally optimal clustering solution.
False
T/F - K-means clustering is best suited for datasets with spherical clusters.
True
T/F - K-means is more sensitive to outliers compared to K-medoids clustering.
True
T/F - In centroid linkage clustering, the distance between clusters is calculated by averaging the distances between all points in the two clusters.
False
T/F - The sum of squared errors (SSE) decreases as the number of clusters (k) increases in k-means clustering.
True
T/F - The “elbow method” is used to determine the most appropriate number of clusters in k-means clustering.
True
T/F - K-means clustering can be applied to both continuous and categorical data without modification.
False
What is the main goal of k-means clustering?
Minimize between-cluster variance
Maximize between-cluster variance
Minimize within-cluster variance
Maximize within-cluster variance
Minimize within-cluster variance
Which of the following statements about K-medoids is true?
It only uses squared Euclidean distance to calculate distances
It is less sensitive to outliers compared to k-means
It uses centroids to define clusters
It assumes clusters are spherical
It is less sensitive to outliers compared to k-means
In k-means clustering, what is the purpose of the “elbow method”?
To determine the optimal number of clusters
To minimize outliers
To increase the number of centroids
To reduce the within-cluster variance
To determine the optimal number of clusters
Maximum Coordinate Distance is the same as _________. Both refer to the distance between two points where only the maximum absolute difference across any of the dimensions is considered.
Euclidean distance
Manhattan distance
Chebyshev distance
City block distance
Chebyshev distance
T/F - In agglomerative hierarchical clustering, the clustering process starts with each instance as an individual cluster.
True
T/F - Divisive clustering is a bottom-up approach to hierarchical clustering.
False
T/F - Single linkage clustering calculates the maximum distance between points in two clusters.
False
T/F - Ward’s method minimizes the loss of information at each step by using Error Sum of Squares (ESS).
True
T/F - Dendrograms are tree-like diagrams used to show the order of clustering and the distance between clusters.
True
In complete linkage clustering, how is the distance between two clusters measured?
By the average distance between all pairs of points
By the distance between the farthest points
By the distance between centroids
By the distance between the closest points
By the distance between the farthest points
What characteristic is commonly associated with single linkage clustering?
Spherical clusters
Large compact clusters
Globular clusters
Elongated, chain-like clusters
Elongated, chain-like clusters
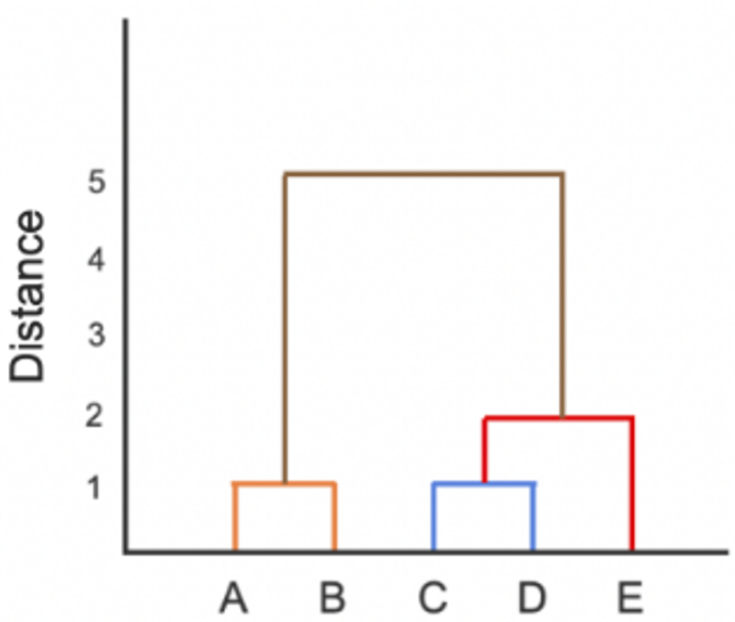
Which of the following instances is most similar to A?
B
C
D
E
B
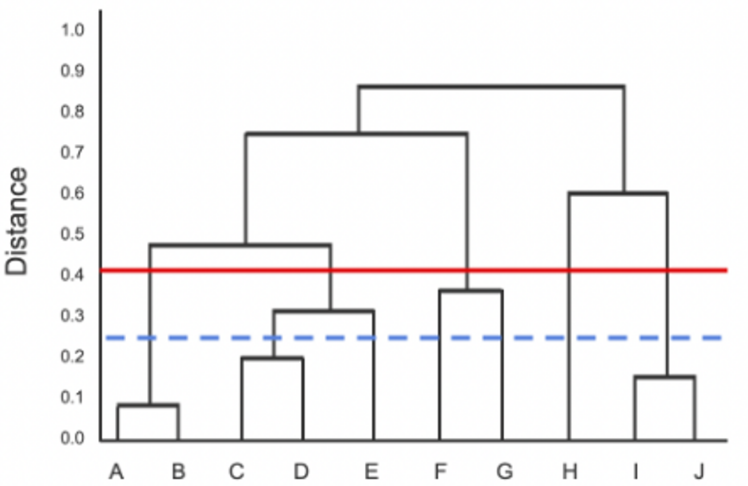
In the figure, two thresholds are represented by a solid red line and a dotted clue line. How many clusters would be formed at the solid red line threshold and at the dotted blue line threshold, respectively?
5, 5
5, 7
6, 11
7, 7
5, 7
Which of the following is NOT a feature of DBSCAN?
Handles noise and outliers
Discover clusters of arbitrary shapes
Sensitive to initial cluster centroids
Does not require you to pre-specify the number of clusters
Sensitive to initial cluster centroids
In DBSCAN, a point is classified as a core point if:
It has at least a specified number of points within the epsilon radius
It is on the boundary of the cluster
It does not belong to any cluster
It has a large distance to its nearest neighbors
It has at least a specified number of points within the epsilon
What is the main parameter that defines the neighborhood of a point in DBSCAN?
Variance
Eps (epsilon)
k-nearest neighbords
Number of clusters
Epsilon
Which of the following methods does DBSCAN use to form clusters?
Identifying regions of high data density
Maximizing intra-cluster similarity
Minimizing distances to centroids
Dividing data into equal partitions
Identifying regions of high data density
T/F - In DBSCAN, all border points have more than MinPts neighbors within the Eps radius.
False
T/F - DBSCAN can find clusters of arbitrary shapes, unlike k-means, which assumes spherical clusters.
True
T/F - DBSCAN requires the number of clusters to be specified before clustering begins.
False
T/F - The elbow method helps in determining the optimal number of clusters for k-means clustering.
True
T/F - External indices require ground truth labels to evaluate clustering results.
True
T/F - A higher Dunn Index indicates poor clustering quality.
False
In a GMM, the “soft clustering: property means that:
Each data point is assigned a probability of belonging to each cluster
Each data point is assigned to exactly one cluster
Each data point is assigned a probability of belonging to each cluster
T/F - the Silhouette Score ranges from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates the worst clustering quality.
False
What does the Dunn Index measure?
Cohesion and dispersion
Silhouette coefficient
Intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster separation
Cluster variance
Intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster separation
Which of the following is an internal index for cluster evaluation?
Precision
Purity
Accuracy
Silhouette Index
Silhouette Index
What does a high Silhouette Score indicate about clusters?
Clusters overlap significantly
Clusters are well-separated and cohesive
Clusters are poorly defined
Clusters are compact but not well-separated
Clusters are well-separated and cohesive
Which of the following best describes the purpose of a Gaussian Mixture Model?
To perform hierarchical clustering by combining clusters in a tree-like cluster
To separate data into clusters using a distance-based metric
To model data with a single Gaussian distribution
To model data with overlapping clusters by representing each cluster as a Gaussian distribution
To model data with overlapping clusters by representing each cluster as a Gaussian distribution