General Chemistry 16.5 (Titration and pH Changes)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What does a titration do?
It shows how pH changes when you add an acid to a base or a base to an acid.
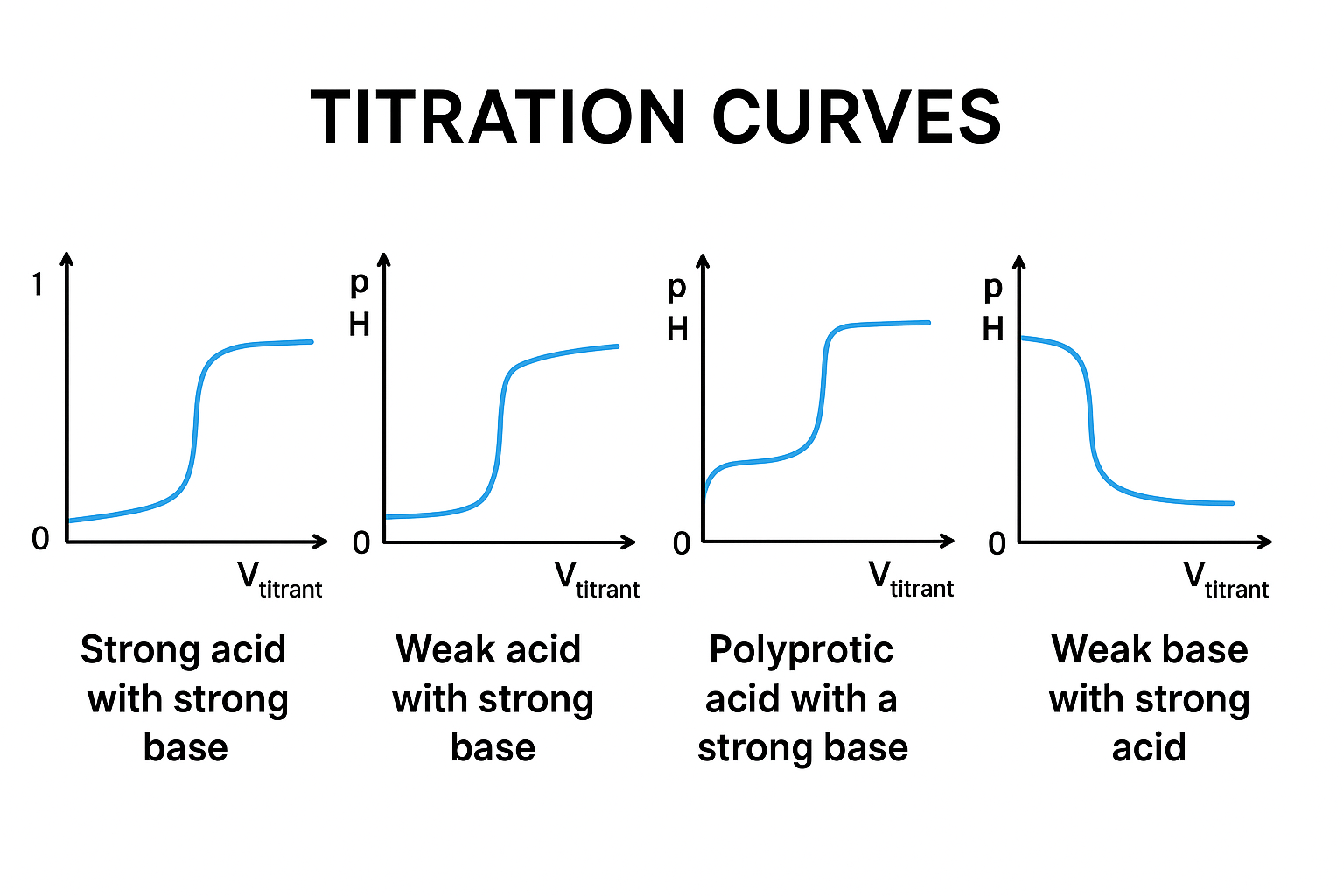
What does the curve look like for a weak acid + strong base?
The pH rises slowly at first (because of a buffer), then jumps sharply near the equivalence point.
Why is the equivalence pH > 7?
Because the weak acid turns into a conjugate base, which is slightly basic.
What happens at the very beginning?
Only the weak acid is present, so the pH is mildly acidic.
What is happening before equivalence?
Some acid has turned into its conjugate base, making a buffer that resists pH change.
What is special about the half-equivalence point?
Acid = conjugate base.
At this point, pH = pKa.
What happens at the equivalence point for a weak acid?
All acid has turned into conjugate base.
This conjugate base makes the pH slightly basic.
What determines pH after equivalence?
The extra strong base added.
What does “polyprotic acid” mean?
An acid that has more than one H⁺ to give away.
Why do their titration curves show multiple big jumps?
Because each H⁺ comes off in a separate step, and each step has its own equivalence point.
What does the first half-equivalence point show?
The pH equals pKa₁.
What does the second half-equivalence point show?
The pH equals pKa₂.
What happens if you switch and add acid to a base?
The curve flips upside-down: it starts high in pH and drops as acid is added.
What does the curve of a strong base titrated with strong acid look like?
The pH stays very high until close to the equivalence point, then falls sharply.
What does the curve of a weak base titrated with strong acid look like?
The pH drops slowly at first (buffer zone), then drops sharply at the equivalence point.
What does pH equal at the half-equivalence point for a weak base?
pH = pKb.
What are polybasic substances?
Bases that can accept more than one H⁺.
They have multiple equivalence points, just like polyprotic acids.
What are the 4 main types of titration curve shapes?