Lecture 2 Good Compounding Practices, Solubility, Ionic Equilibria, and Partition Coefficient
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Compounding
- Preparation of drugs or devices in anticipation of prescription drug orders based on routine, regularly observed prescribing patterns.
- Reconstitution or manipulation of commercial products that may require the addition of one or more ingredients as a result of a licensed practitioner's prescription drug order.
- Preparation of drugs or devices for the purposes of, or as an incident to, research, teaching, or chemical analysis
Compounding Category 1
Nonsterile (Simple): The mixing of two or more commercial products
Compounding Category 2
Nonsterile (Complex): Compounding with the bulk drug substances or when calculations are required
Compounding Category 3
Sterile: Risk level 1
Compounding Category 4
Sterile: Risk level 2
Compounding Category 5
Sterile: Risk level 3
Compounding Category 6
The preparation of radiopharmaceuticals
Compounding Category 7
The preparation of veterinary pharmaceuticals
Responsibilities of the Compounder (Part 1)
- To be proficient in compounding and continually expand compounding knowledge by studying appropriate literature/participating in seminars
- To be familiar with nonsterile preparations 795, sterile preparations 797, pharmaceutical calculation in prescription compounding 1160, and other applicable guidelines/laws
- Must ensure personnel engaged in compounding wear clean clothing appropriate to the type of compounding performed
- Implement procedures to prevent cross-contamination when compounding drugs that require special precautions to prevent cross-contamination
Responsibilities of the Compounder (Part 2)
- Certifying all prescription orders
- Approving or rejecting all components, drug product containers, closures, in-process materials, and labeling
- Preparing and reviewing all compounding records to ensure that errors have not occurred in the compounding process
- Assuring the proper maintenance, cleanliness, and use of all equipment used in a prescription compounding practice
- Assuring that only authorized personnel shall be in the immediate vicinity of the drug compounding operations
- Assuring that the drug product and components of drug products are not on the list of federally recognized drug products that have been withdrawn or removed from the market for public health reasons
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
Developed for the following:
- Facility
- Equipment
- Personnel
- Preparation, packaging, and storage of compounded preparations
- Ensure accountability, accuracy, quality, safety, and uniformity in compounding
Documentation
Enables a compounder, whenever necessary, to systematically trace, evaluate, and replicate the steps included throughout the preparation process of a compounded preparation
Facilities
- An adequate space that is specifically designated for the compounding of prescriptions
- Sterile processes are conducted separately from non-sterile processes
- Area shall be maintained in proper conditions
- Maintained in a good state of repair
- Potable water shall be supplied continuously in positive pressure
- Area should have adequate lighting and ventilation
- Area shall be free of infestation
- Sewage and other refuse are disposed of in safe and sanitary manners
- Any materials used in the compounding of drugs must be stored as directed by the manufacturer in a clean, dry area, under appropriate temperature conditions
Equipment
- Equipment should be stored such as to protect it from contamination
- Equipment should be of suitable composition
- Equipment should be routinely inspected, calibrated as necessary
- Before using the equipment, it should be inspected to determine its suitability for use
- After use, the equipment should be appropriately cleaned
Food and Drug Modernization Act of 1997
Ensures that patients have access to individualized drug therapy
Container
That which holds the article
Immediate Container
that which is in direct contact with the article at all times
Closure
A part of the container
Tight Containers
- Protects the contents from contamination by liquids, solids, or vapors
- Protects from loss of article
- Protects the contents from efflorescence, deliquescence, or evaporation
under the ordinary or customary conditions of handling, shipment, storage, and distribution, and is capable of tight re-closure
Well-Closed Containers
- Protects the contents from extraneous solids
- Protects the contents from loss of the article
under the ordinary or customary conditions of handling, shipment, storage, and distribution
Light-Resistant Containers
Protects the contents from the effects of light because of the specific properties of the materials in which the contents are made, including any coating applied to it
Hermetic Containers
Containers that do not allow air or any other gas under ordinary conditions
Tamper-Resistant Containers
Containers that are so sealed that the contents cannot be used without obvious destruction of the seal
Other Types of Containers
- Single Unit
- Multiple Unit
- Single Dose (Ex. Ampul)
- Multiple Dose (Ex. Vial)
- Unit Dose
Polyethylene Plastic
- Good water barrier
- Poor oxygen barrier
- Not too clear
- Odors, flavors, gases permeate

Polypropylene Plastic
- Excellent barrier to water and gases
- Not too clear
Polyvinyl Chloride Plastic
- Clear, Rigid
- Good oxygen barrier
- Permeable to water
- Yellows when exposed to heat or UV light
- Used for parenteral solutions

Polystyrene Plastic
- Rigid
- Crystal clear
- Used for solid dosage forms

Polycarbonate Plastic
- Clear and transparent
- Rigid
- Possible replacement for glass
- Expensive

Compliance Packaging
Includes the following:
- Educational techniques
- Reminder aids
- compliance packages
- Devices to assist patients in taking their medications on schedule
Manufacturer's Label
Contains the following:
- FDA approved for prescription drugs
- Controlled by the FDA
Prescription Label
Contains the following:
- Controlled by the State Board of Pharmacy
- Must also meet federal requirements (FDA, DEA, etc.)
Over-the-Counter Label
Includes the following:
- Drug Facts box
- Standardized headings and subheadings
- Standard order of presentation
- Standard type style
- Simpler labeling language that is more easily understood by the consumer
Storage Information
- Expiration and Beyond-Use Dating
- Temperature Effects
- Storage Temperatures
- Reasons to Protect from Freezing
Temperature Effects
Increases the rate of chemical reactions
High Temperatures
- Sublimation (solid)
- Solvent loss (liquid)
- Chemical decomposition of dyes (color fading)
- Phase separation (emulsions)
- Increased sedimentation (suspensions)
- Increased disintegration times (tablets)
Low Temperatures
- Crystal formation in solutions
- Phase separation (emulsions)
- Increased sedimentation (suspensions)
- Cracking of sugar-coated tablets
Controlled Room Temperature
A temperature maintained thermostatically that encompasses the usual and customary working environment of 20°C to 25°C
Reasons to Protect from Freezing
- Risk of container breakage
- Loss of strength or potency
- Destructive alteration of dosage form
Records and Reports
- The compounder shall maintain records (including formulation and compounding records)
- The compounder shall keep adequate records of controlled drug substances (scheduled drugs) used in compounding
- All records of all compounded preparations shall be kept for a period of time as set forth in the federal and state laws or regulations
- The compounding records shall include the manufacturer and lot number of all ingredients
Compounding for a Prescriber's Office Use
- Compounders may prepare compounded drug preparations for a prescriber's office use only, where permitted by federal and state requirements
- An order by the prescriber indicating the formula and quantity ordered may be filled in the compounder's facility
- Shall compound the preparation for the sole purpose of administration by or for the prescriber
- A record of the compounding process shall be maintained
- A label must be generated, and a number may be assigned
Compounding Veterinarian Products
- Compounders shall compound prescriptions for animals on the basis of prescription orders
- These prescriptions shall be handled and filled according to the guidelines available for compounding of veterinarian products
Solubility and pH
As the pH of the solution increases, the quantity of drug in solution increases because the water-soluble ionizable salt is formed.
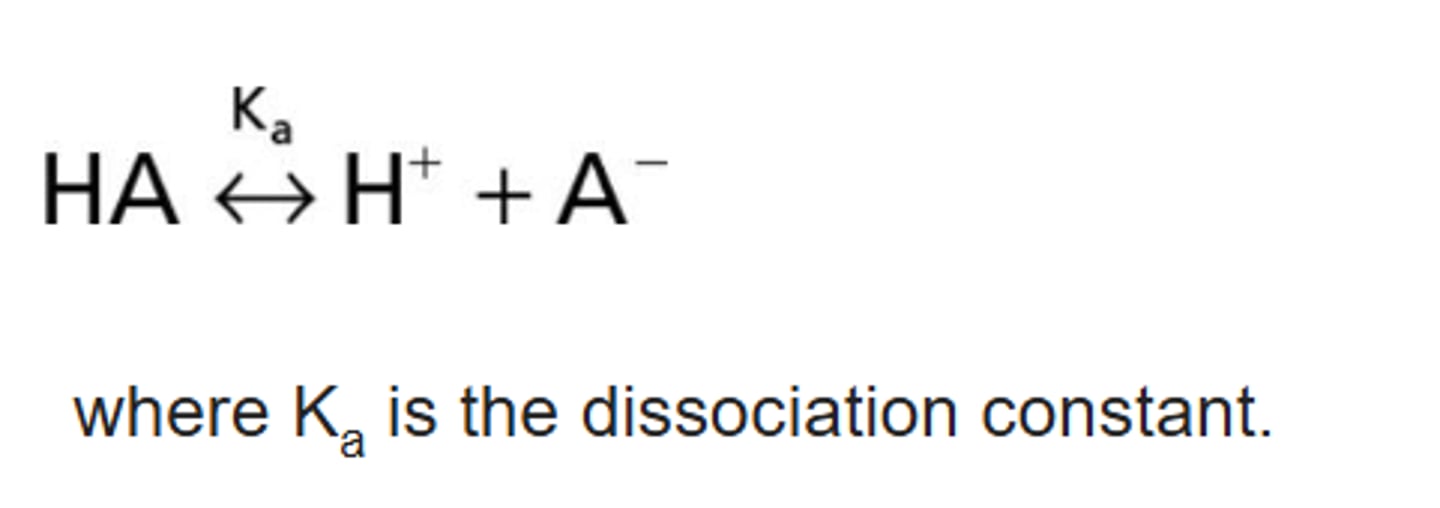
Partition Coefficient
- If a solute is added to a mixture of two immiscible liquids, it will distribute between the two phases and reach an equilibrium at a constant temperature
- The distribution of the solute between the two immiscible layers is the partition coefficient
Octanol is the oil phase

pKa/Dissociation Constants
- The extent of dissociation or ionization in many cases is highly dependent on the pH of the medium containing the drug. It also has a strong effect on the extent of a drug's absorption, distribution, and elimination.
- The dissociation constant is usually determined by potentiometric titration
Hygroscopic Powders
Tend to absorb moisture from the air
Deliquescent Powders
Absorb moisture from the air and even liquefy
Efflorescent Powders
May give up their water of crystallization and may even become damp and pasty