Summary of Chapter 1: Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the four major categories of materials based on chemical composition and atomic structure?
Metals- Valence electrons are detached from atoms and spread in an “electron sea” that “glues” the ions together, Good conductors of heat and electricity
Ceramics-Atoms behave like either positive or negative ions and bond by Coulomb forces, insulator of heat and electricity, hard but very brittle.
Polymers- Large organic molecules based on carbon and hydrogen, other non-metallic elements, soft and flexible, insulator of heat and electricity
Composites-The combination of metals, ceramics and polymers to show the combination of each component, fiberglass is a type of glass fiber-reinforced plastics, the strength from glass fibers and the flexibility is from polymers
The relationship between Processing, Structure, Properties, and Performance is known as what?
The Materials Paradigm.
What type of materials are known for being stiff, strong, hard, and brittle and are poor electrical and thermal conductors?
Ceramics.
In materials science, what does the term 'macrostructure' refer to?
Large-scale features visible to the naked eye.
What defines advanced materials?
Materials that exhibit unique properties and functions, such as semiconductors, biomaterials, smart materials, and nanomaterials.
What are the main categories of properties for materials?
Mechanical, Electrical, Thermal, Magnetic, Optical, Deteriorative.
Describe the significance of 'smart materials'.
They respond to external stimuli such as temperature or electric/magnetic fields by changing shape or properties.
What is a key characteristic of semiconductors?
They have electrical properties between conductors and insulators.
What influences material properties according to the materials paradigm?
Structure, which is influenced by processing methods.
Provide an example of a composite material and its application.
Fiberglass used in aerospace and sports equipment.
What does 'microstructure' refer to in materials science?
Features visible under a microscope
What is meant by 'nanoscale structure' in materials science?
Features of materials at the nanometer scale, often influencing unique properties and behaviors.
Atomic level
The arrangement of atoms in materials (2 different arrangements of the same atom at this level can have different properties: carbon and diamond)
Subatomic level
Electron structure of individual atoms that defines interactions among atoms(interatomic bonding)
Microscopic structure
Arrangement of small grains of material that can be identified by microscopy
What are properties?
Properties represent a kind and magnitude of response to a specific stimulus
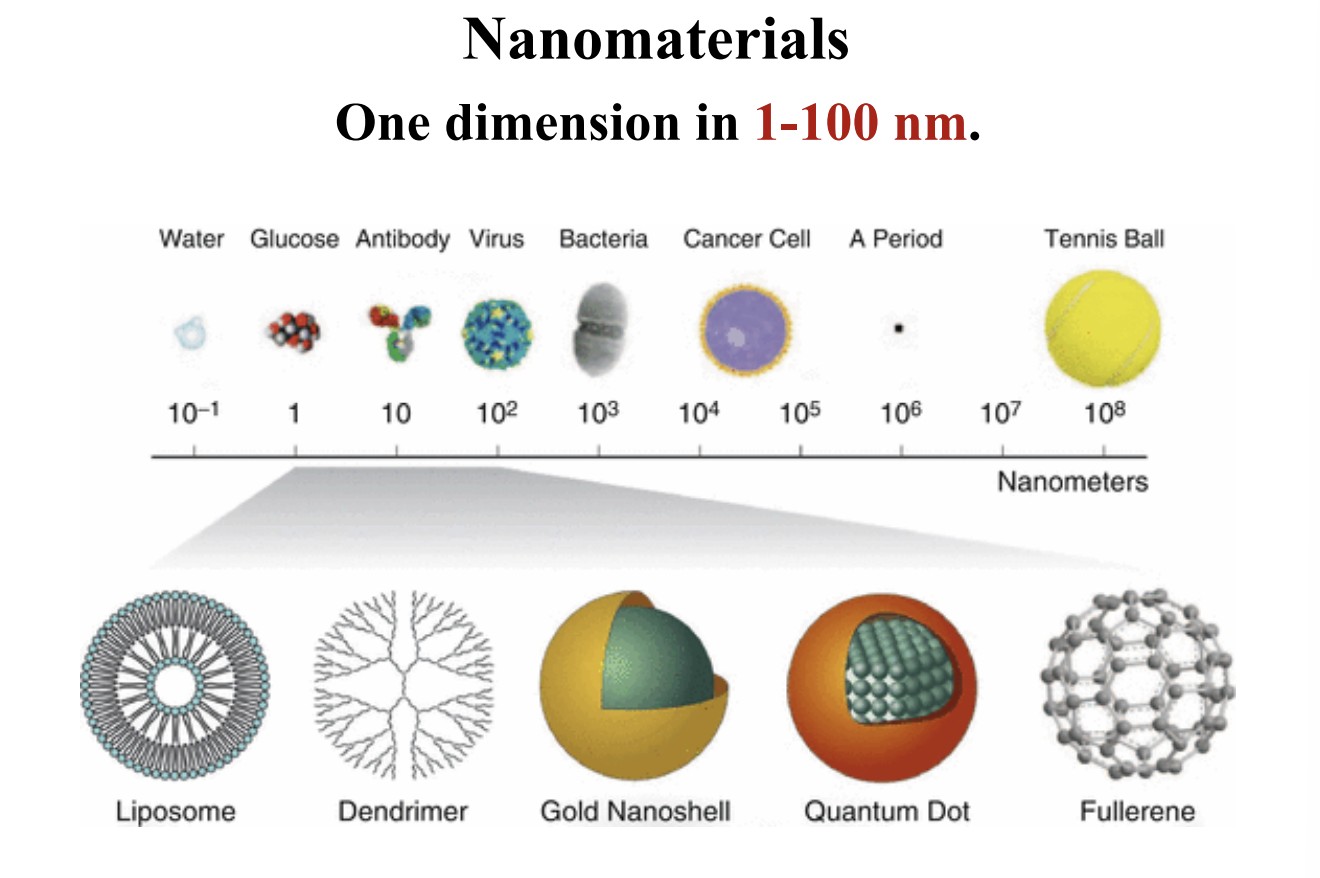
Size of a nanomaterial
1-100 nm