B3.1 Nervous System OCR Gateway GCSE
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Stimulus
Change in the environment
Receptor
Cell that detects a stimulus
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord
Effector
Muscle or gland that carries out a response
Coordinated Response
Several effectors working together
Sensory Neurone
Carries impulses from receptor to CNS
Relay Neurone
Neurone in CNS
Motor neurone
Carries impulses from CNS to effector
Synapse
Gap between neurones
Axon
Long extension of cell body
Myelin Sheath
Fatty layer that insulates axon and speeds up impulse
Reflex
Fast, innate, automatic, involuntary response
Cornea Function
Refracts Light
Accommodation
Focusing on objects near and far away
Diverging Lens
Used to correct short sightedness
Converging Lens
Used to correct long sightedness
Cone Cell
Receptors in eye that detect colour
fMRI
Functional MRI, Detects blood flow to parts of brain to help show function
Peripheral Nervous System
The neurones that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
What does the CNS help do?
Make decisions
Stage 1 of Nervous Response
Stimulus
Stage 2 of Nervous response
to Receptor
Intermediate stage between 2 and 3
An electrical impulse is sent from the receptor to the CNS through the sensory neurone
Stage 3
at CNS
Intermediate stage between 3 and 4 (of a nervous response)
An electrical impulse is sent from the CNS to the effector through the motor neurone.
Stage 4
to Effectors
Stage 5
Response
Sense organ: Eye
Receptor Cells: Rod and Cone, Stimulus: Light
Sense Organ: Tongue
Receptor Cells: Taste Buds, Stimulus: Chemical
Sense organ: Skin
Receptor Cells: Ruffini Capsule and Merkel Disks, Stimulus: Touch, heat and pain
Sense organ: Nose (receptor cells, stimulus)
Receptor Cells: Smell receptors, stimulus: chemical (smells and odours)
Brain is protected by…
skull
What does a muscle effector do?
Contracts to make a movement (and relaxes as well)
What does a gland effector do?
secretes a substance
“to secrete” Meaning
discharges/produces a substance
Neurones
Cells that transmit electrical impulses as part of the nervous response, there are 3 types of them.
Part of neurone: Cell body
Where the nucleus is found
Part of neurone: Dendrites
small branches at the end of the neurone which join to other neurones to form networks or to work as an effector
Structure of Sensory Neurone (from left to right)
Receptor, dendron, cell body, axon (myelin sheath (formed by schwann cells) around axon and dendron), dendrites (at the end of the sensory neurones which connects to CNS
Structure of Motor Neurone (from Left to right)
(end next to CNS) Cell body, axon (with myelin sheath wrapped around), dendrites (end next to effector)
Structure of Relay Neurone
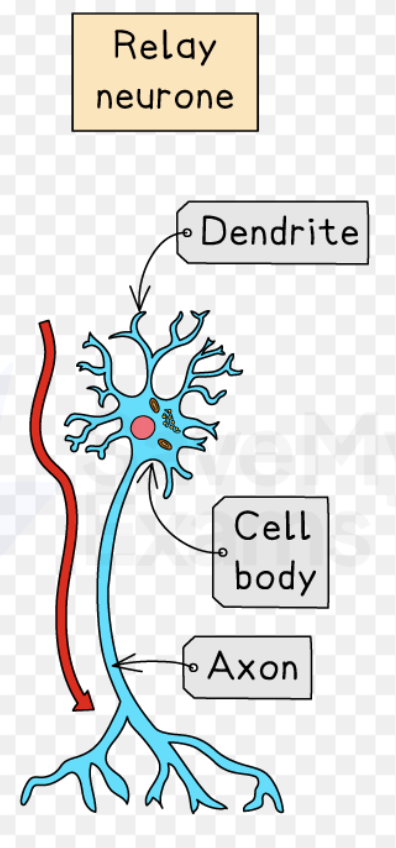
Why are reflexes quick?
to help us survive
Reflexes are automatic which means…
they are involuntary, you don’t think about it
Reflexes are innate, meaning that:
You don’t learn them, you’re born with them
Reflex example: Pupil reflex
Pupils constrict in bright light to protect retina.
Reflex example: Rooting reflex in babies
helps baby to feed
Reflex example: Salivating
You produce saliva when smelling food
What does a reflex arc diagram show?
How a reflex works
Reflex arc diagram structure
Receptors —> Sensory Neurone —> CNS (almost junction maybe) —> Relay Neurone (Synapse between neurones) —> Motor Neurone —> Effector
Reflex arc shape
like a backwards C
Stage 1 of how electrical impulses cross a synapse gap
They arrive at the synapse, this causes neurotransmitter to be released
Stage 2 of how electrical impulses cross a synapse gap
the neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse extremely quickly
Stage 3 of how electrical impulses cross a synapse gap
It is detected by receptors on the other neurone which causes a new electrical impulse to start
Ciliary Muscle
Controls the shape of the lens
Cornea
forms the outer protective membrane of the eye and bends the light in towards the pupil
Iris
Gives the eye its colour and controls the amount of light entering the eye by controlling the diameter of the pupil
Lens
Changes shape in order to focus the light on the retina (especially on the fovea at the back of the eye)
Retina
Made of light receptors (rod and cone cells). These receptors turn light into nerve impulses.
Optic Nerve
Carries nerve impulses to the brain
Suspensory Ligament
Connects ciliary muscle to lens
Blind Spot
The point where the optic nerve meets the retina
Which 2 parts of the eye refract light?
Cornea and the Lens
If an object is near, what do the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments do and what shape is the lens?
Ciliary muscles contract, suspensory ligaments slacken and the lens shape is fat and round.
If an object is far away what do the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments do and what shape is the lens?
Ciliary muscles relax, suspensory ligaments stretch and the lens shape is thinner and flatter.
Common Problems with eyesight
Red-green colour blindness and short and light sightnedness
The Retina is made up of:
rod and cone cells, (cone cells are less sensitive)
Rod cells
Very sensitive cells, can see in low light and only detect/see black and white
Problem with cone cells:
Can lead to red green colour blindness (where a person can’t tell the difference between red and green, it’s inherited usually and more common in men)
Test for colour blindness
Ishihara test
Long Sightedness Symptoms
Hard to focus on objects close up
Causes of Long Sightedness (in terms of lens and eye shape)
Lens is too thin and/or eye is too flat
When you have long sightedness…
Light is focused behind the retina when you look at close up objects
Short sightedness symptoms
Hard to focus on things further away
Causes of Short Sightedness (in terms of lens and eye shape)
Lens too fat and round, eye shape is like a rugby ball and too long
How is light focused when someone has short-sightedness?
In front of the retina (especially when things are far away)
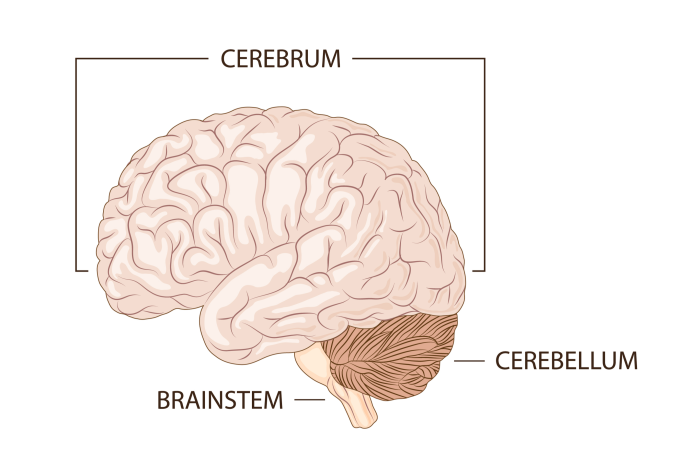
The Cerebrum is also known as…
the cerebral cortex
Cerebrum
controls complex behaviour (conscious movement and thought, personality, memory, emotion and learning
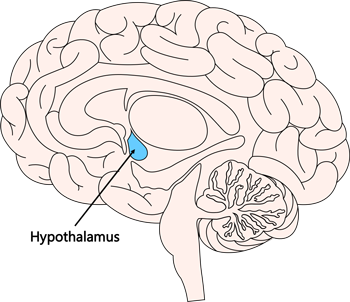
Hypothalamus
Maintains body temperature and water levels in blood
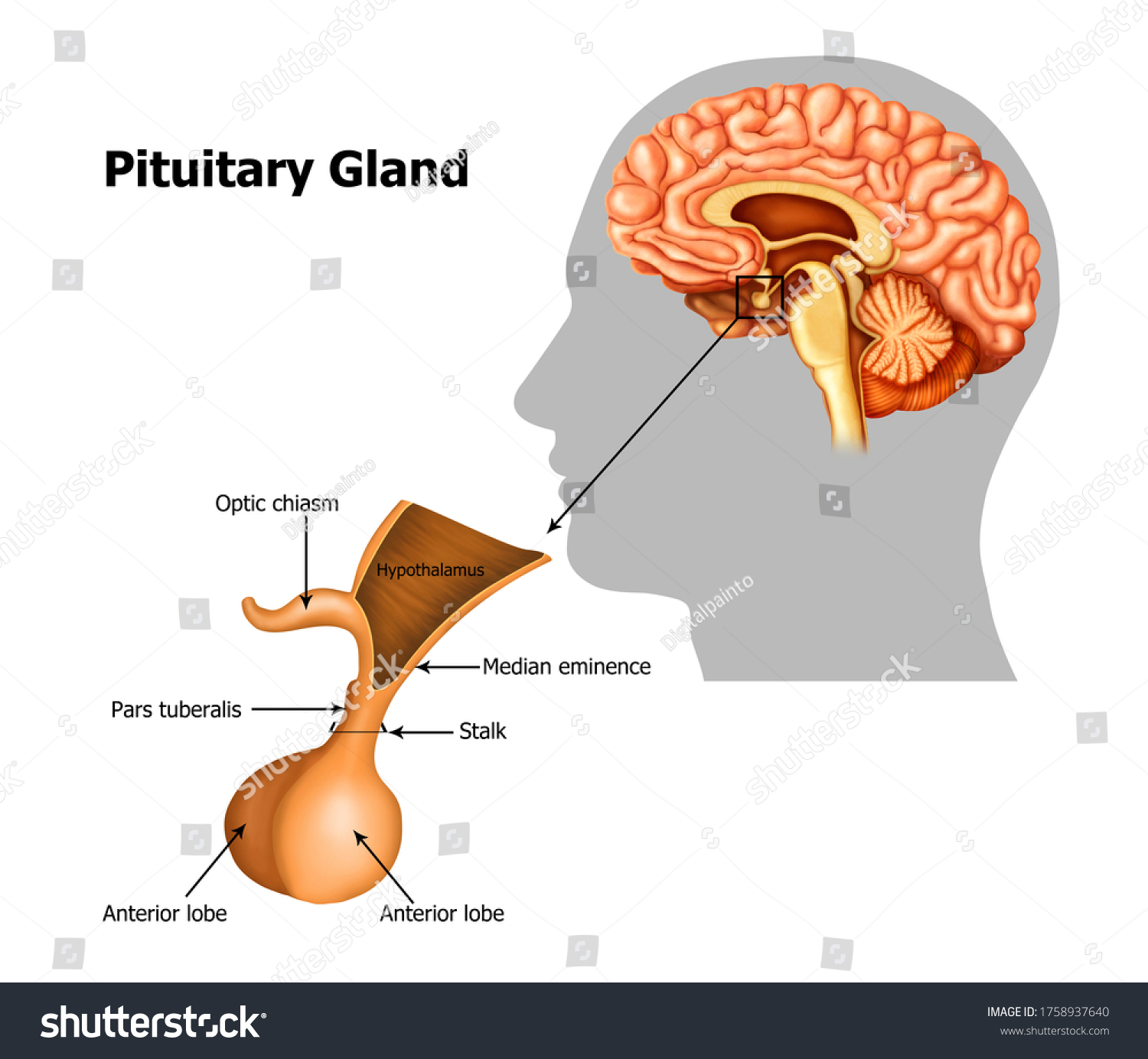
Pituitary gland
Releases hormones into bloodstream
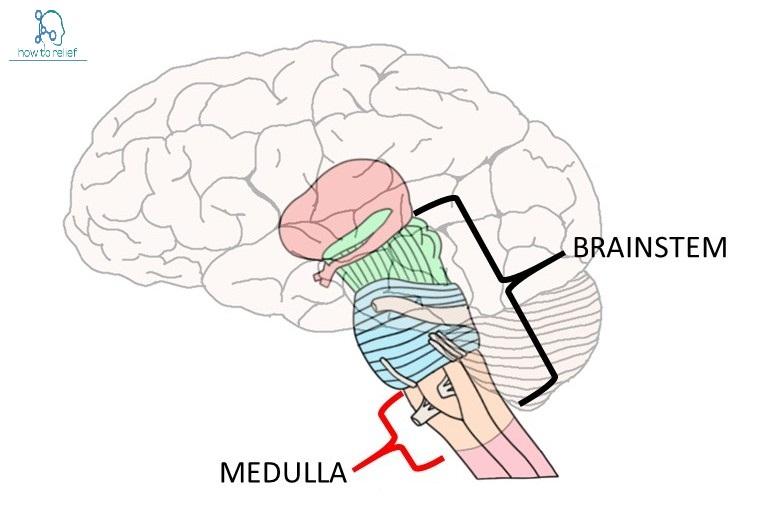
Medulla
Controls breathing and heart rate
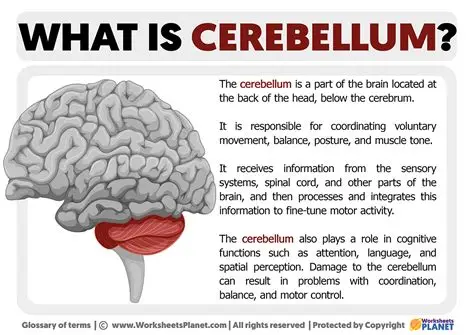
Cerebellum
Where muscle memory is and controls your balance
Brain damage studies
studying effects of damage to the brain caused by things such as strokes (blockage in a blood vessel which stops oxygen to the brain tissue).
CT Scans
An X-Ray scan that can produce a 3D image of the brain to identify abnormalities.
Electrode Stimulation
Studying the response of a patient when a part of the brain is stimulated with an electrode. This is often done during “awake surgery”.
Damage to the nervous system can be caused by
injury (e.g. a cut), disease (e.g. measles, diabetes) and genetic conditions (e.g. huntingdon’s disease).
Damage to the Peripheral Nervous System can cause:
inability to detect pain, numbness and loss of coordination.
Damage to the Central Nervous System can cause:
a loss of control of body systems, partial or complete paralysis, memory loss or processing difficulties