Period 5 (1844–1877)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Manifest Destiny
Belief that the U.S. was destined to expand across North America.

James K. Polk
11th president; expansionist who annexed Texas, gained Oregon, and led U.S. into Mexican-American War.

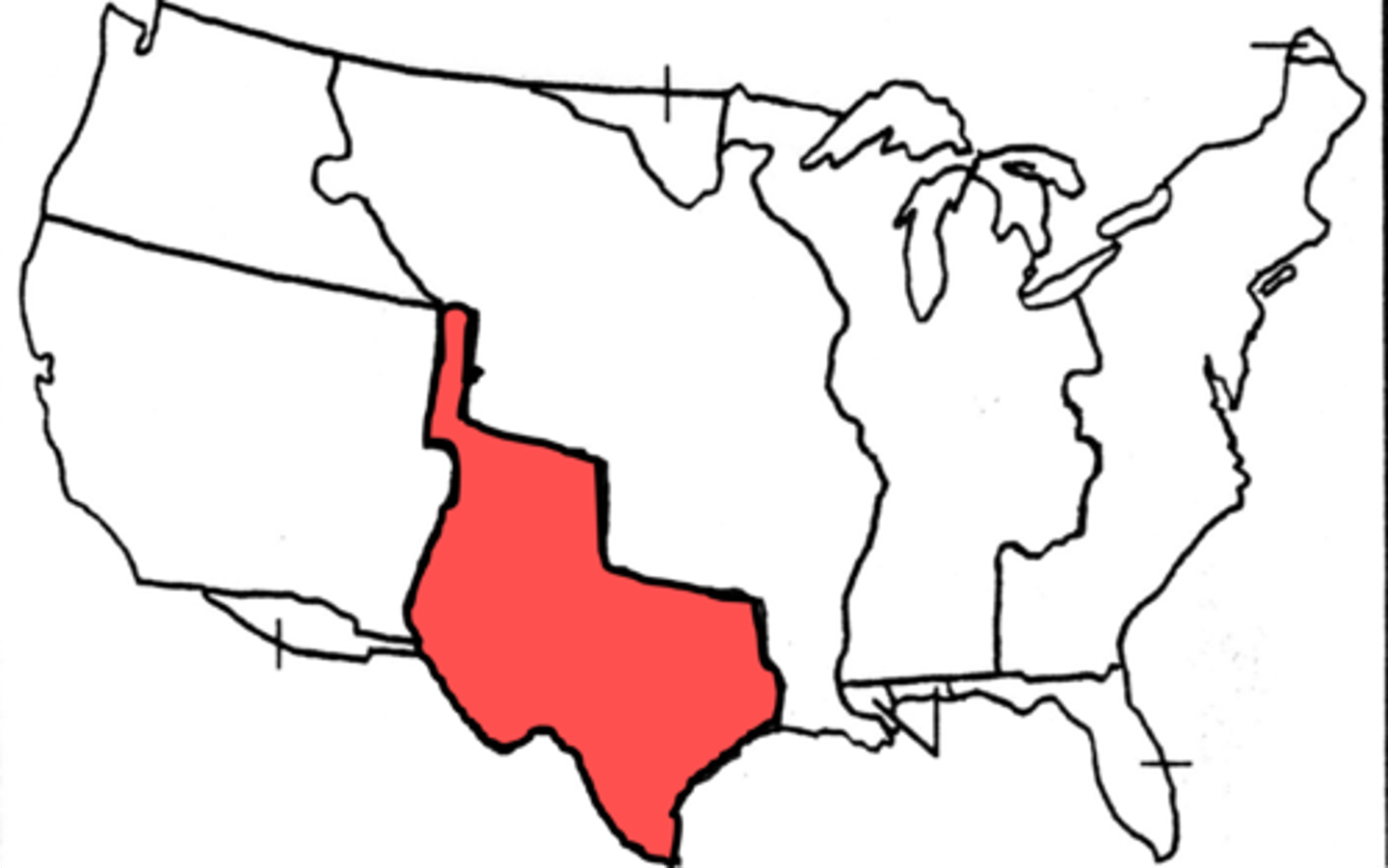
Annexation of Texas (1845)
U.S. added Texas as a state, angering Mexico and sparking tensions.
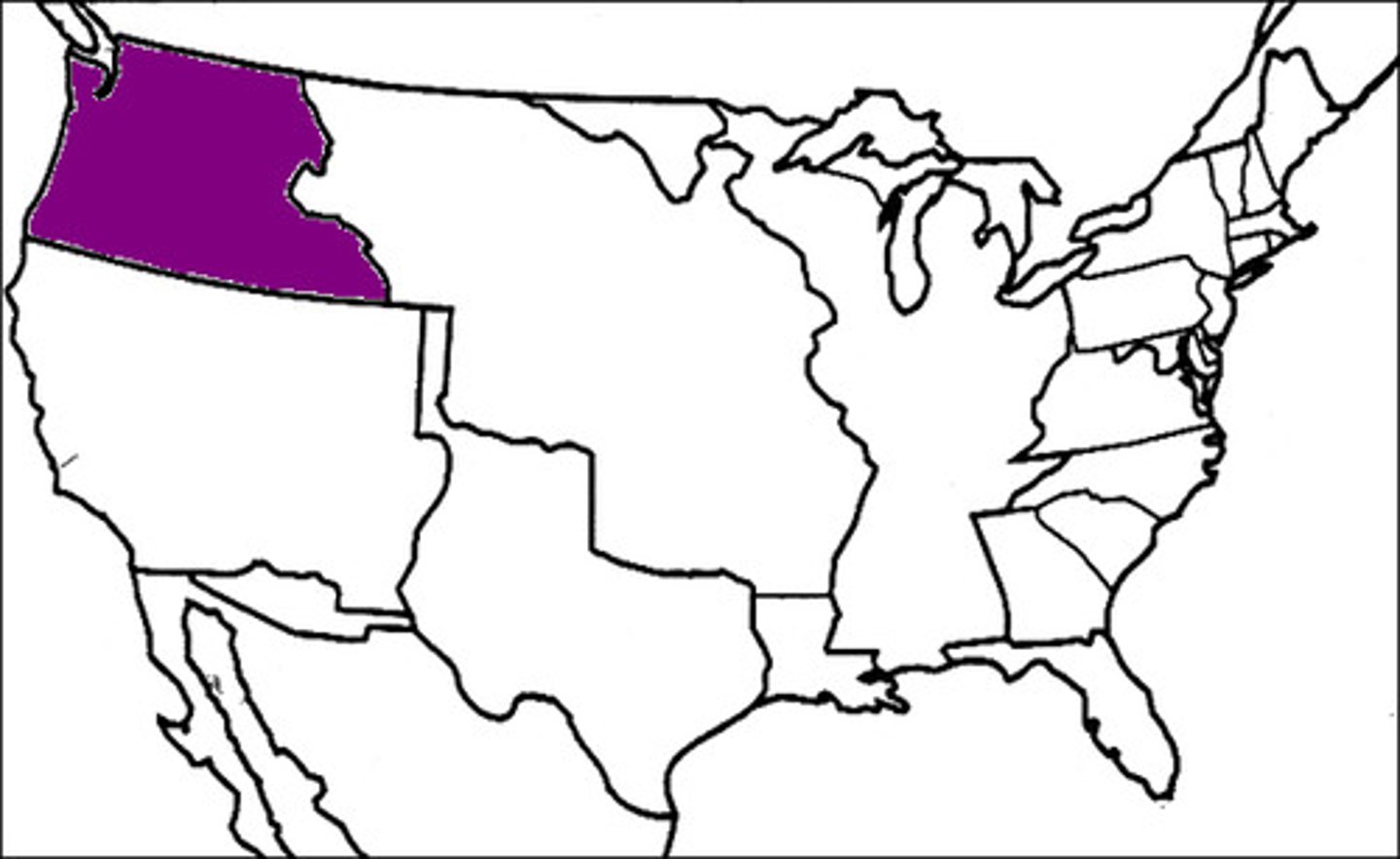
Oregon Territory
Land jointly occupied by Britain and U.S.; split along the 49th parallel in 1846.
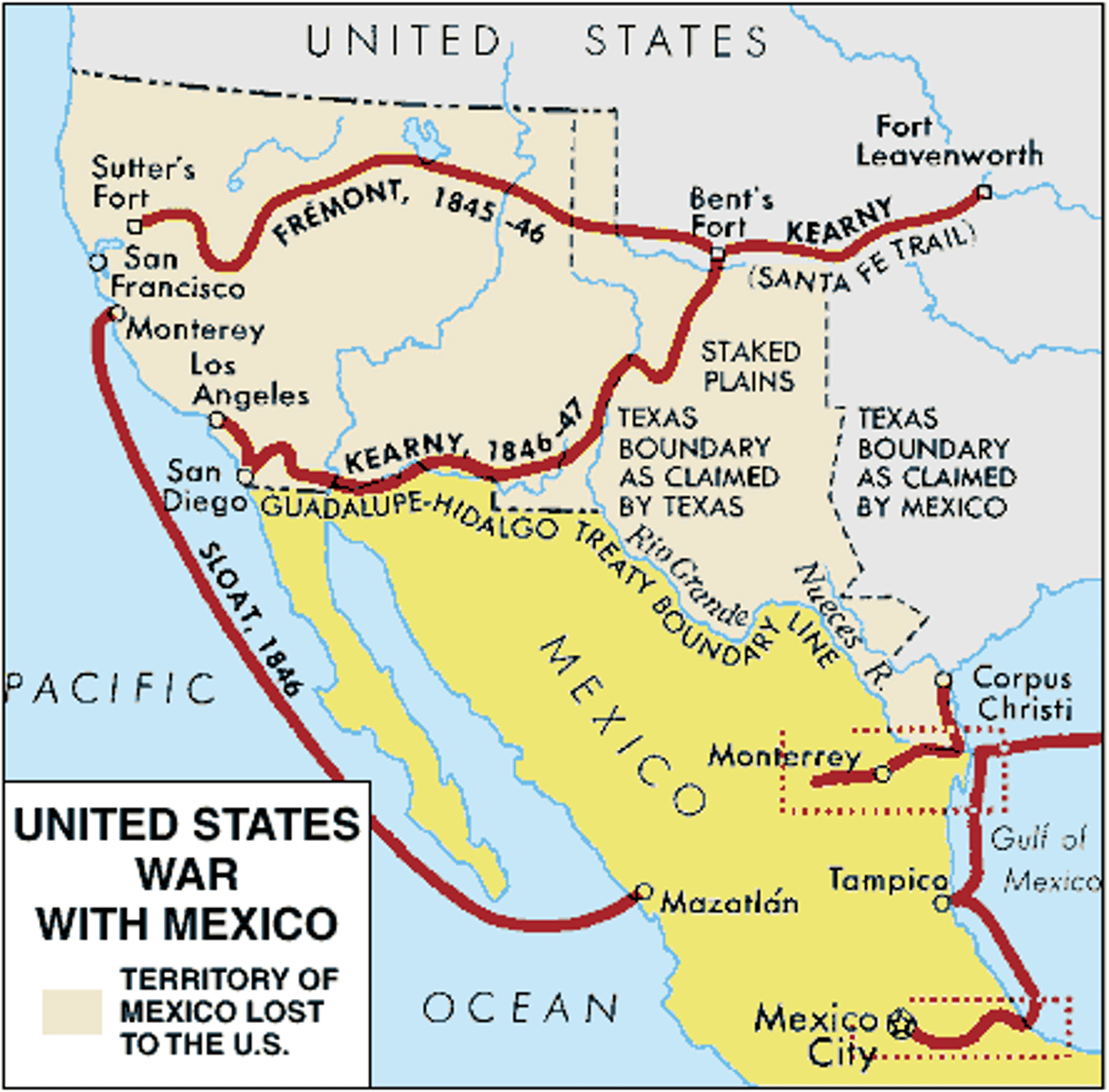
Mexican-American War (1846-1848)
Conflict over Texas and California; ended with Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.
Spot Resolutions
Lincoln's challenge to Polk to show the exact spot where American blood was shed.

Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848)
Ended Mexican-American War; U.S. gained California and Southwest.
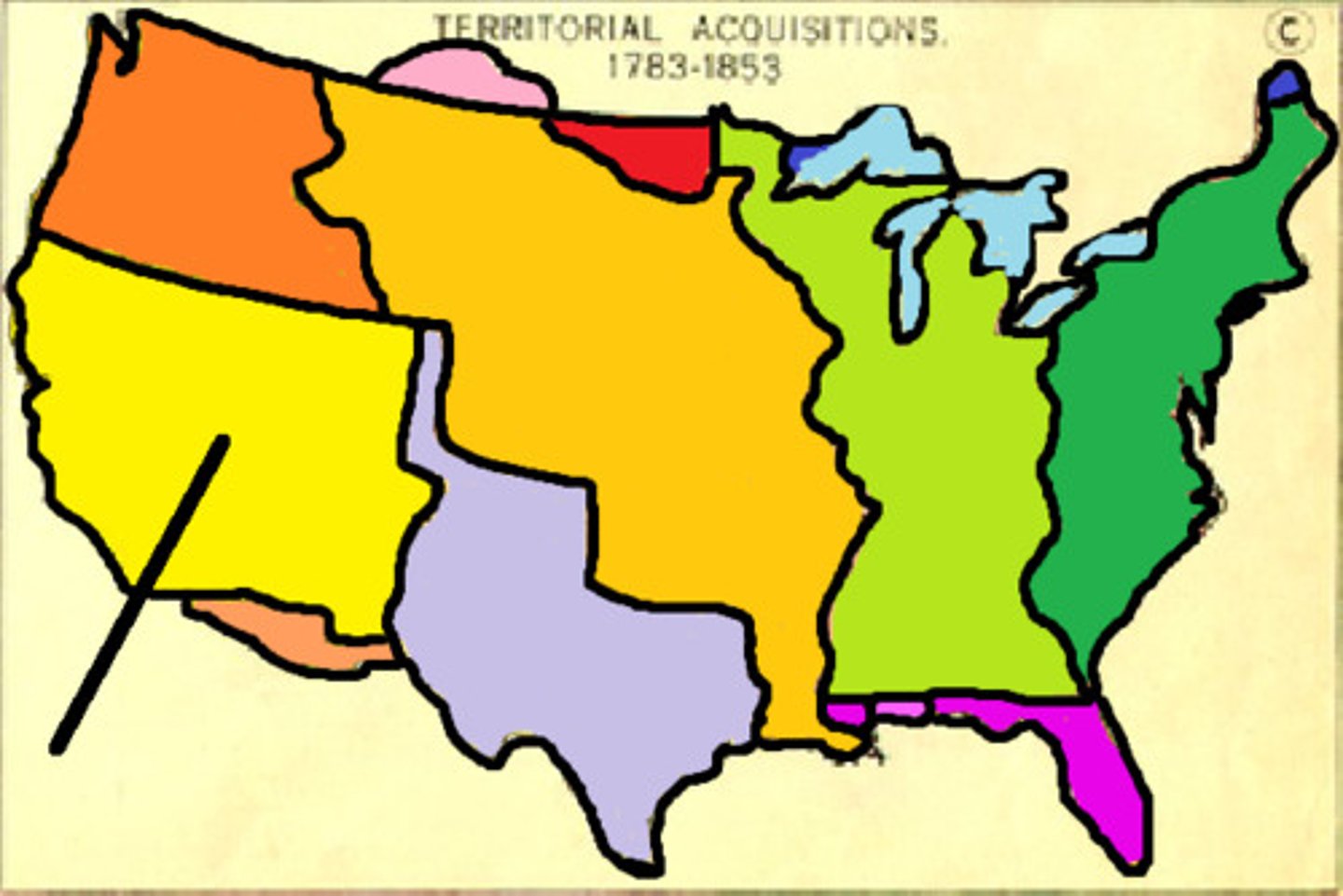
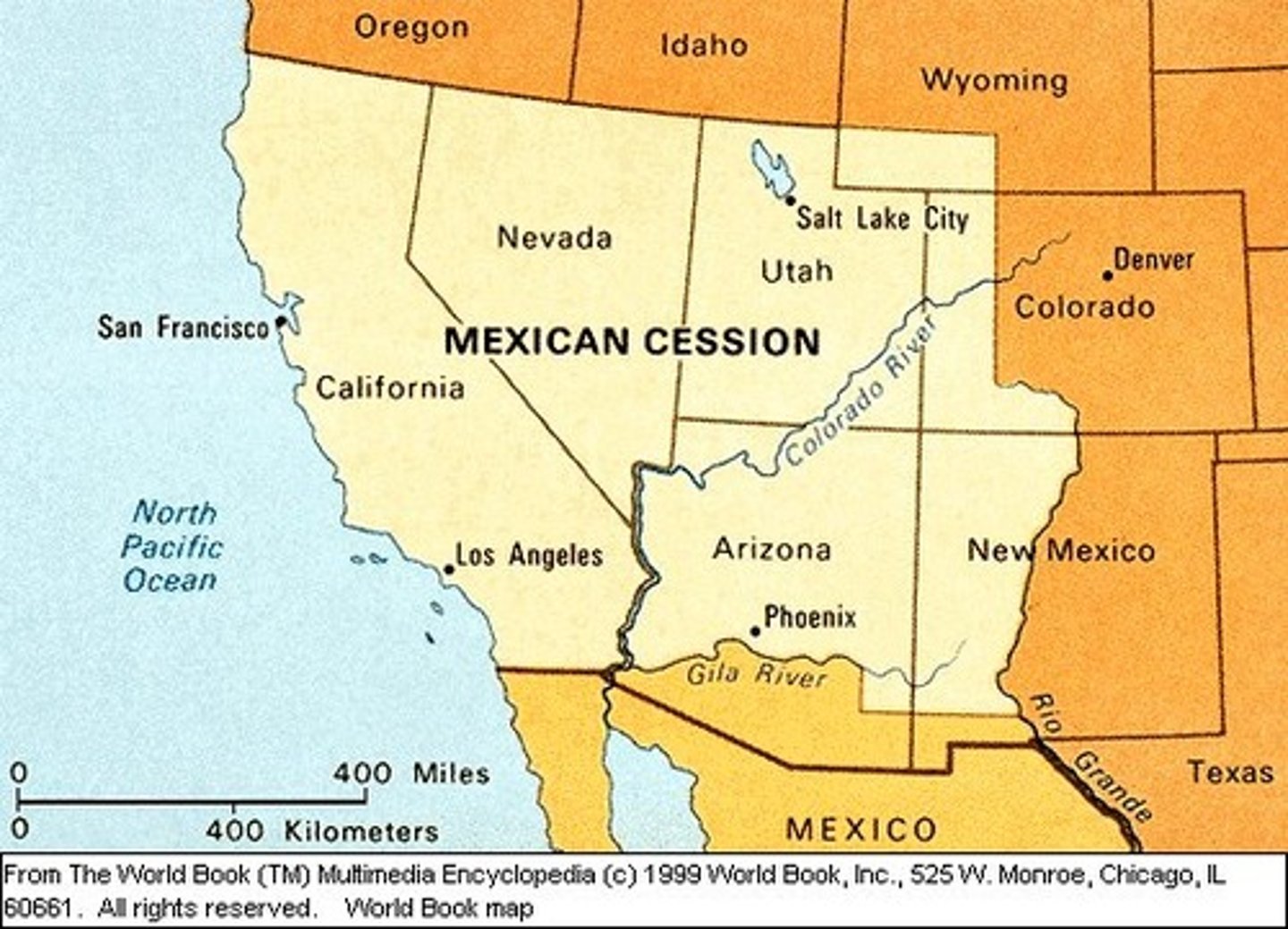
Mexican Cession
Land gained from Mexico including CA, AZ, NM, NV, UT, CO, and WY.
Wilmot Proviso (1846)
Proposed ban on slavery in territories won from Mexico; never passed.

Free Soil Party
Political party opposing expansion of slavery into western territories.

California Gold Rush (1849)
Mass migration to California after discovery of gold; led to statehood.

Compromise of 1850
California admitted free, stricter Fugitive Slave Law, popular sovereignty in new territories.
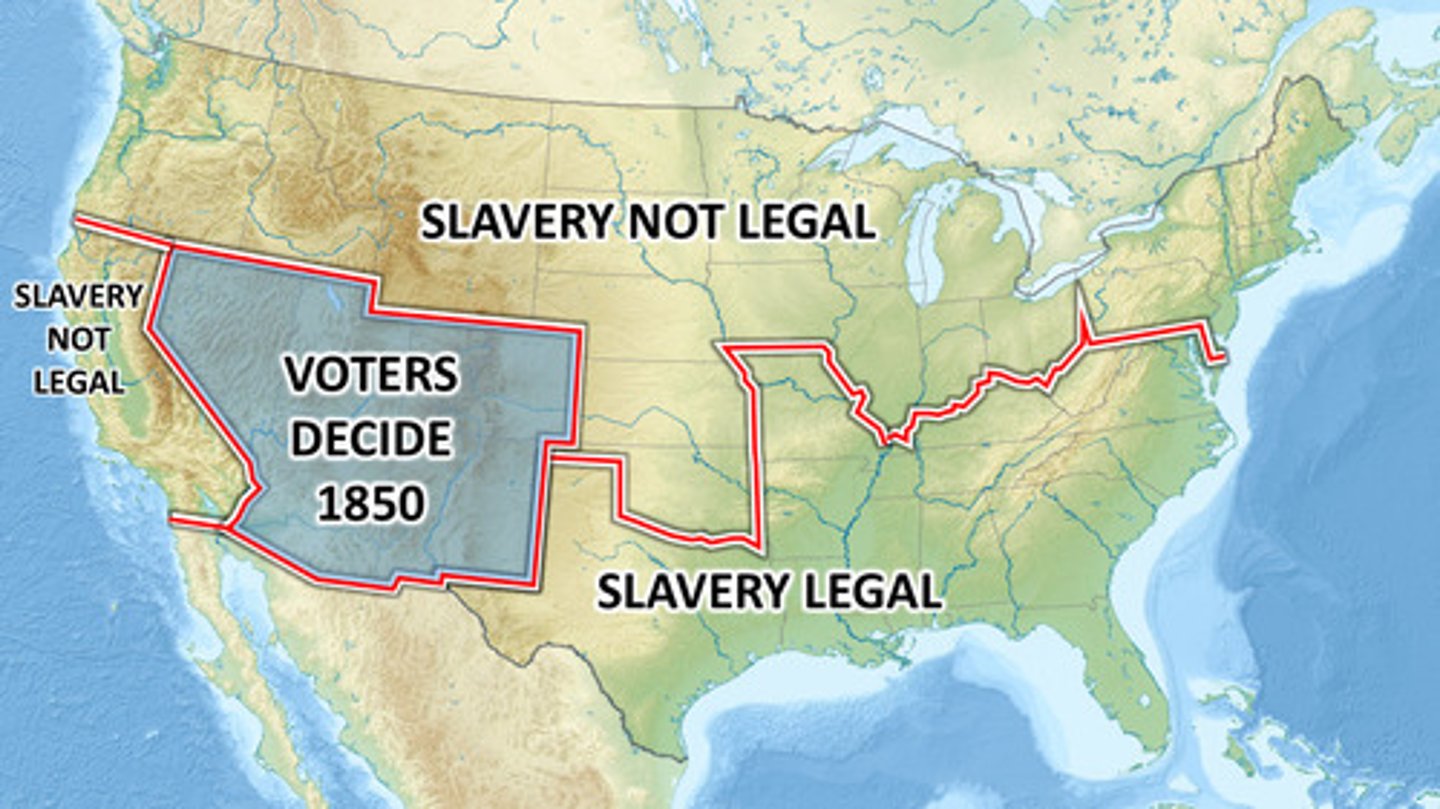
Popular Sovereignty
Policy allowing settlers in a territory to vote on slavery.

Fugitive Slave Act (1850)
Required return of escaped slaves; angered Northern abolitionists.

Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852)
Harriet Beecher Stowe's novel that fueled anti-slavery sentiment in the North.

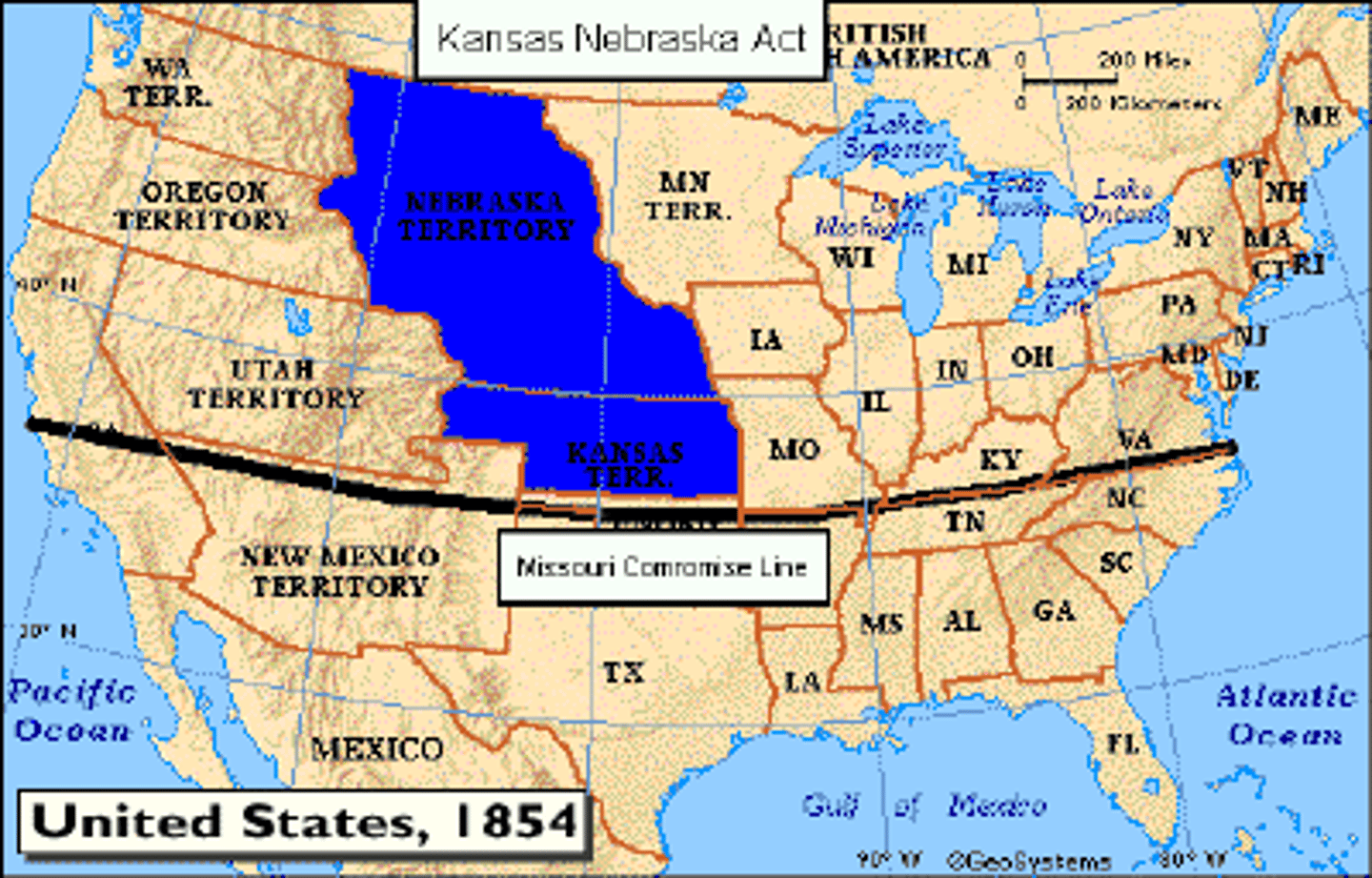
Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)
Repealed Missouri Compromise; allowed popular sovereignty in Kansas and Nebraska.
Bleeding Kansas
Violent conflict over slavery in Kansas after passage of Kansas-Nebraska Act.

Caning of Charles Sumner
Brutal attack by Congressman Preston Brooks on Senator Sumner for anti-slavery speech.

Republican Party
Anti-slavery party founded in 1854; united former Whigs, Free-Soilers, and anti-Nebraska Democrats.

Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)
Supreme Court ruled African Americans were not citizens; Congress couldn't ban slavery in territories.

Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858)
Series of debates over slavery between Senate candidates; boosted Lincoln's national profile.

Freeport Doctrine
Douglas's idea that local laws could effectively exclude slavery despite Dred Scott ruling.

John Brown's Raid (1859)
Failed attempt to start a slave uprising at Harper's Ferry; deepened sectional tensions.
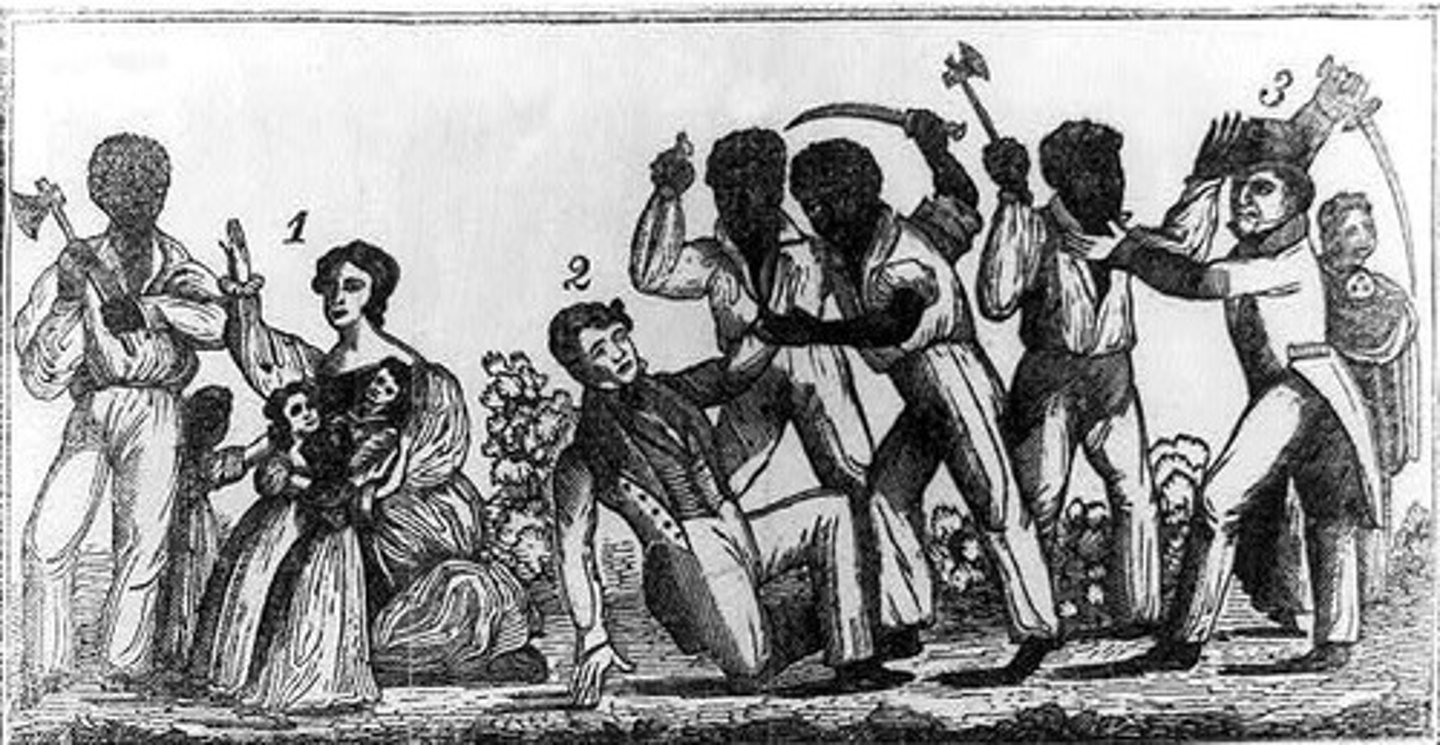
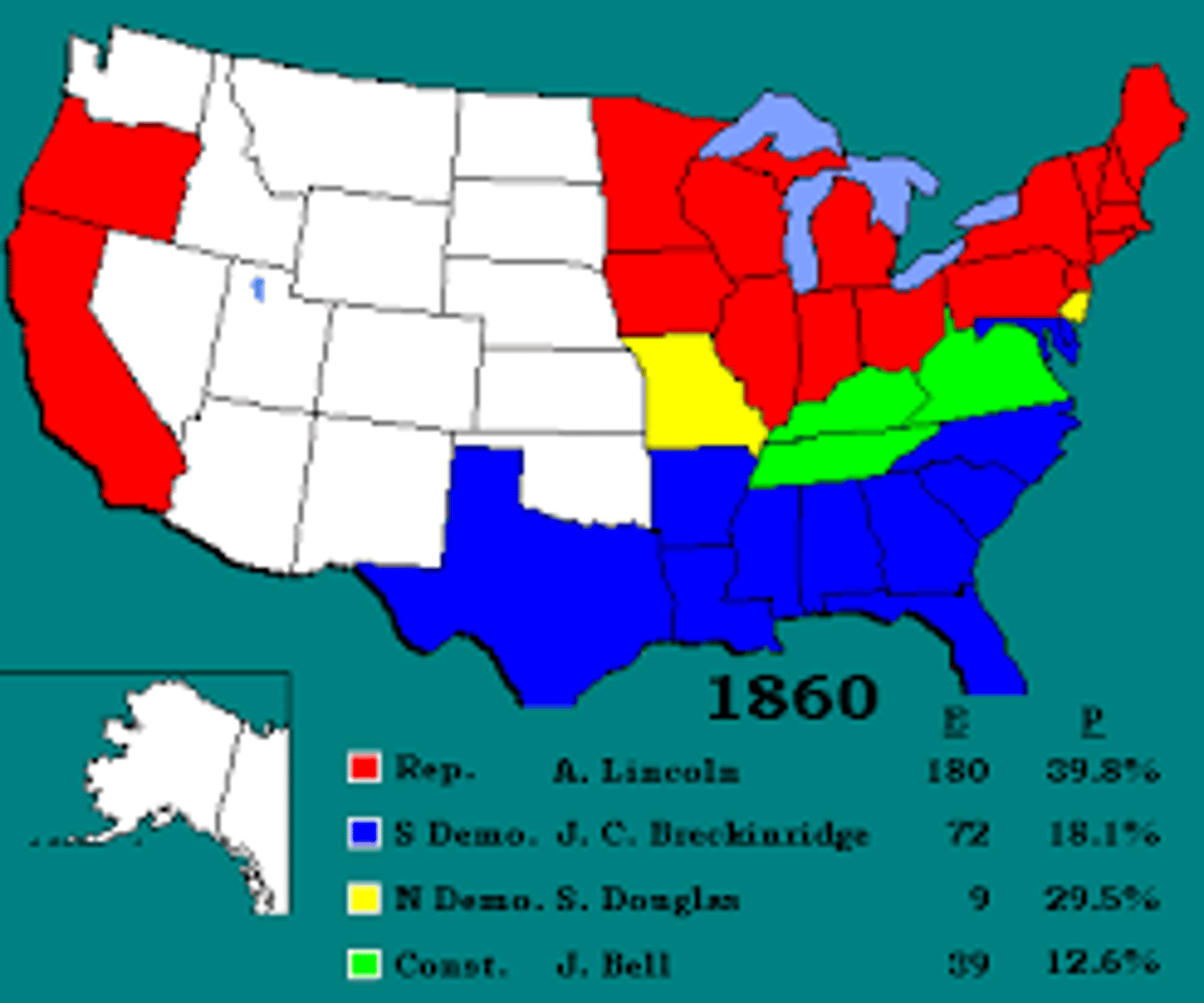
Election of 1860
Lincoln elected president; led to Southern secession.
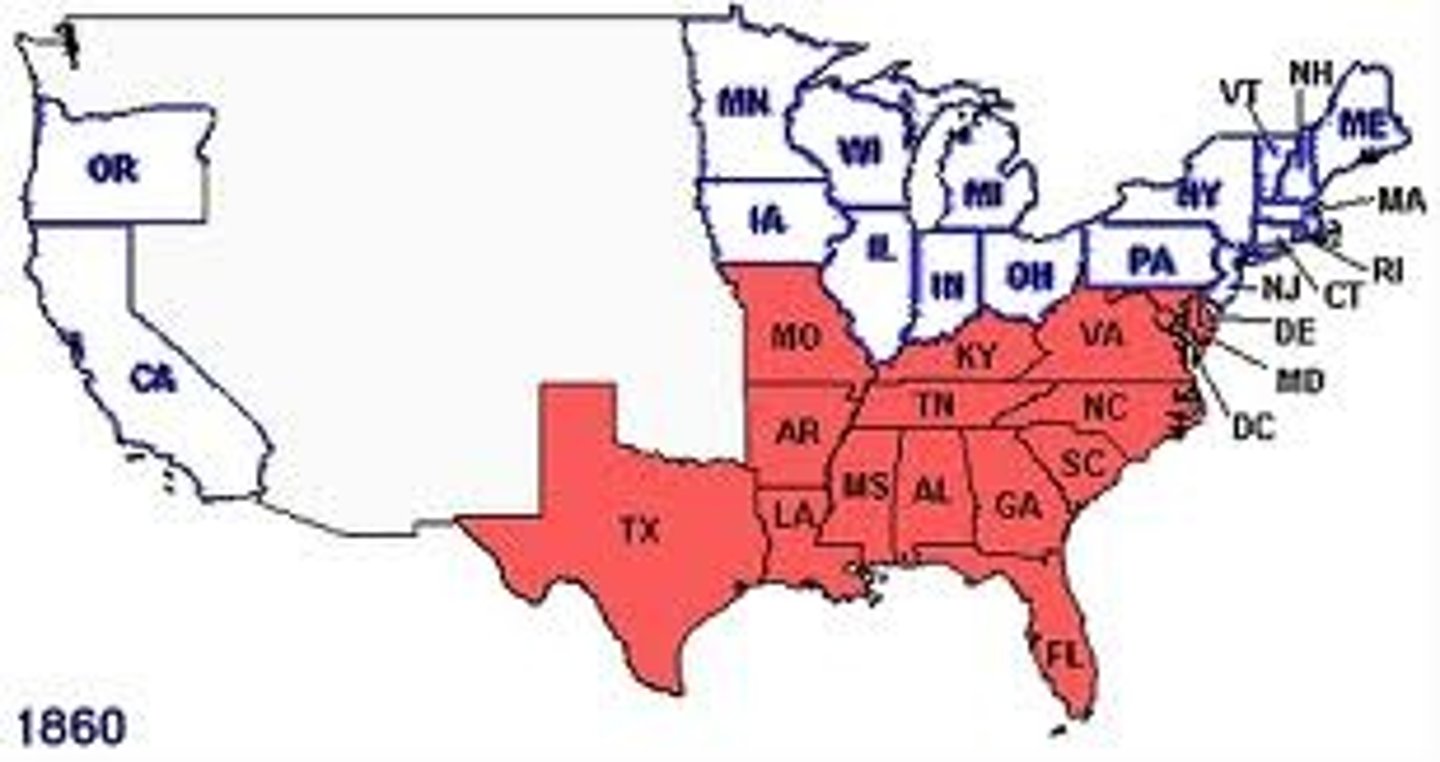
Secession
Southern states left the Union following Lincoln's election.
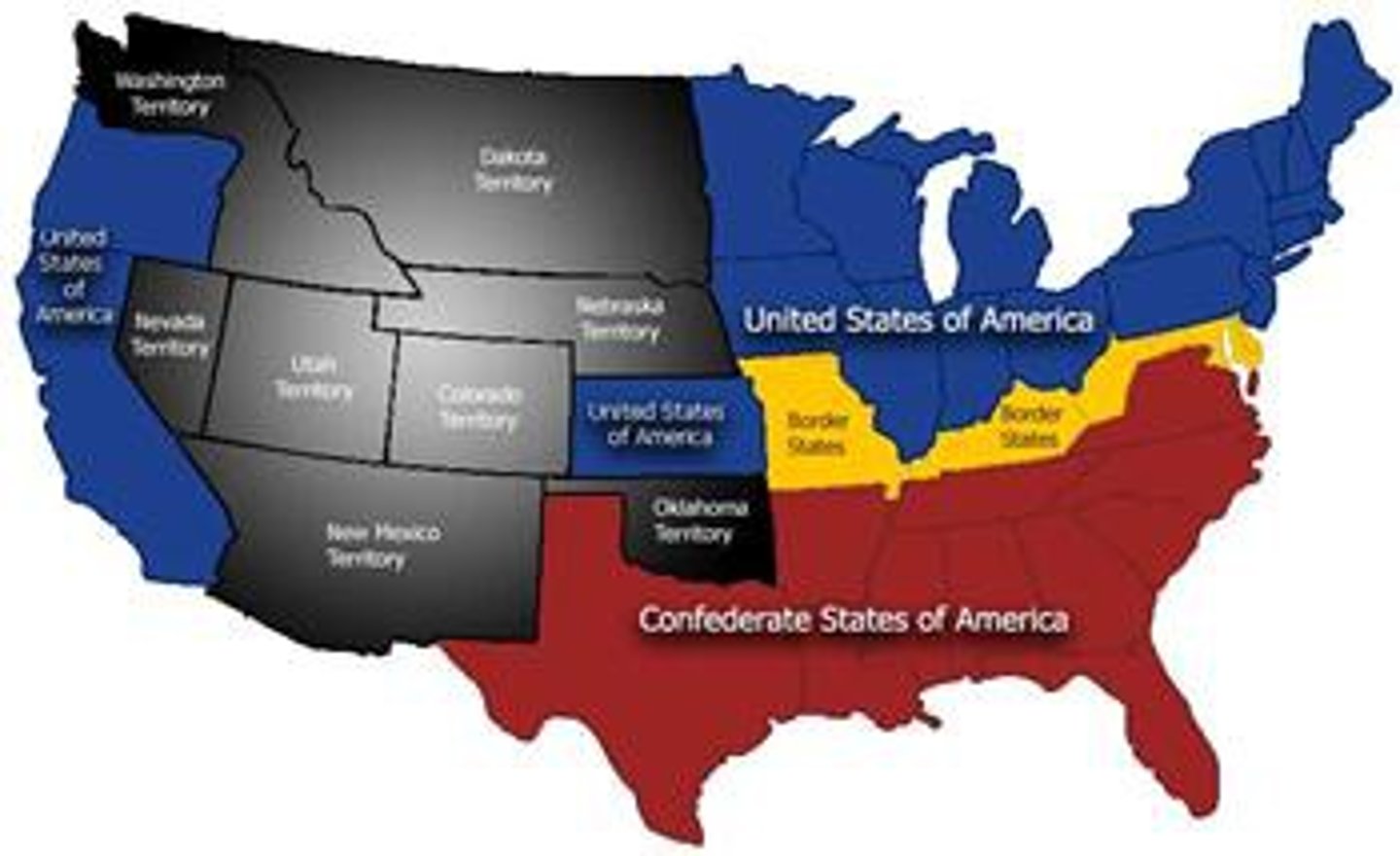
Confederate States of America
Nation formed by seceding Southern states; Jefferson Davis as president.
Fort Sumter (1861)
First shots of the Civil War; Confederate attack on Union fort in South Carolina.

Border States
Slave states (MD, KY, MO, DE) that stayed in the Union.
Homestead Act (1862)
Gave 160 acres of land to settlers willing to farm it for five years.

Pacific Railway Act (1862)
Authorized transcontinental railroad construction.

Emancipation Proclamation (1863)
Freed slaves in Confederate-held territory; gave war a moral cause.

Battle of Gettysburg (1863)
Turning point battle in the Civil War; Union victory ended Confederate advance into the North.

Gettysburg Address (1863)
Lincoln's speech emphasizing national unity and liberty.

13th Amendment
Abolished slavery in the U.S.

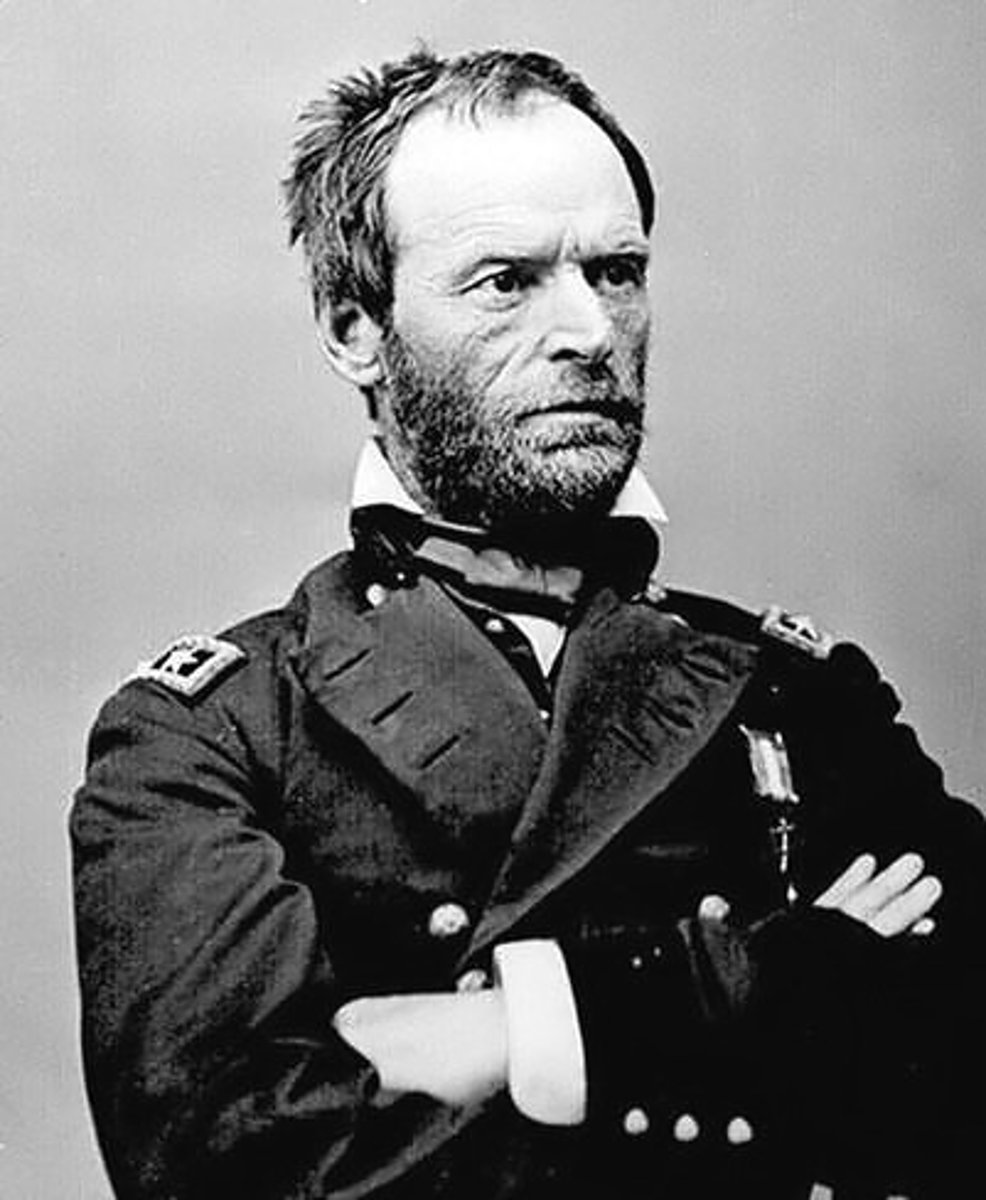
Sherman's March to the Sea
Union general's destructive campaign through Georgia; example of total war.

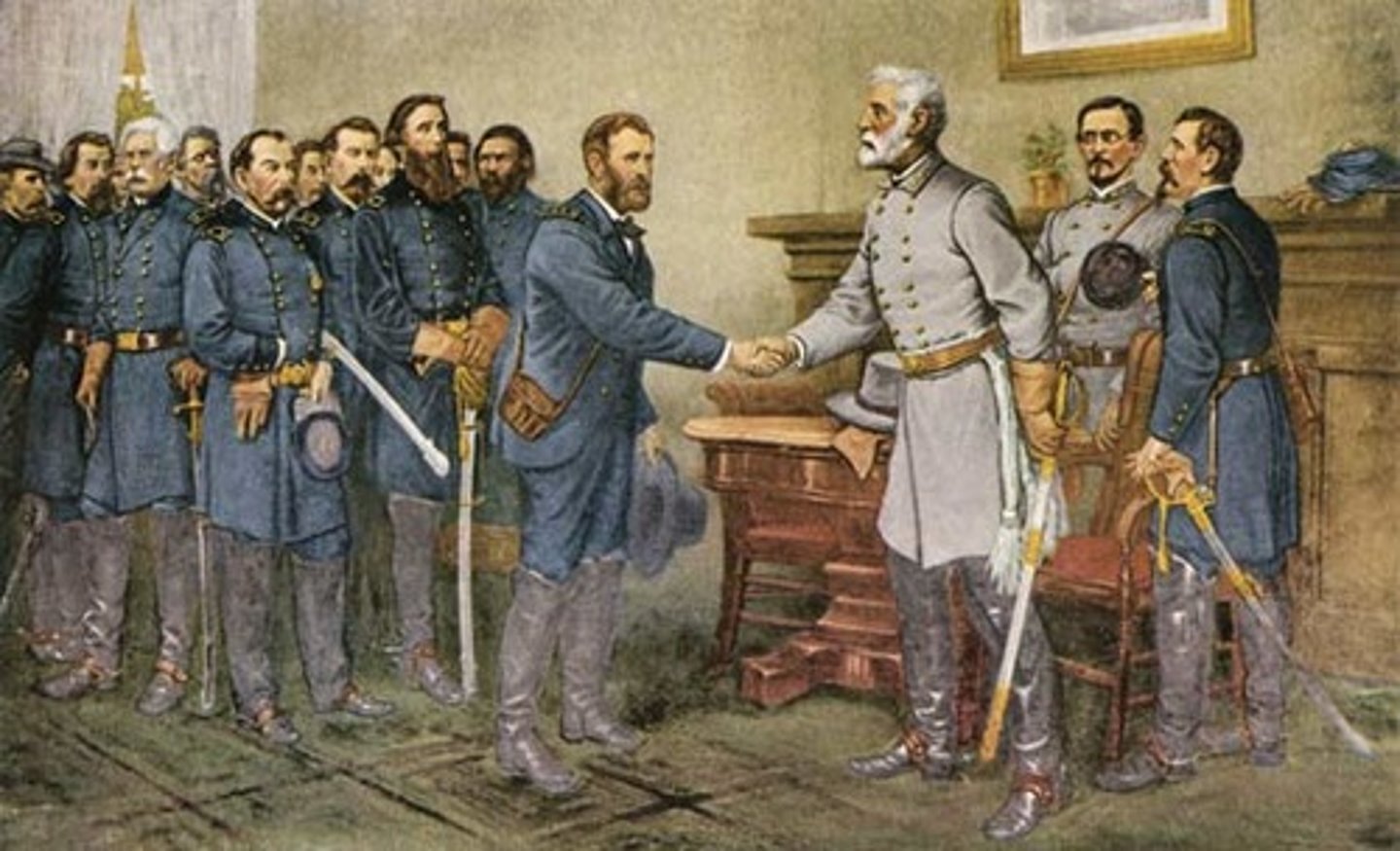
Appomattox Court House (1865)
Site of Confederate surrender; ended the Civil War.

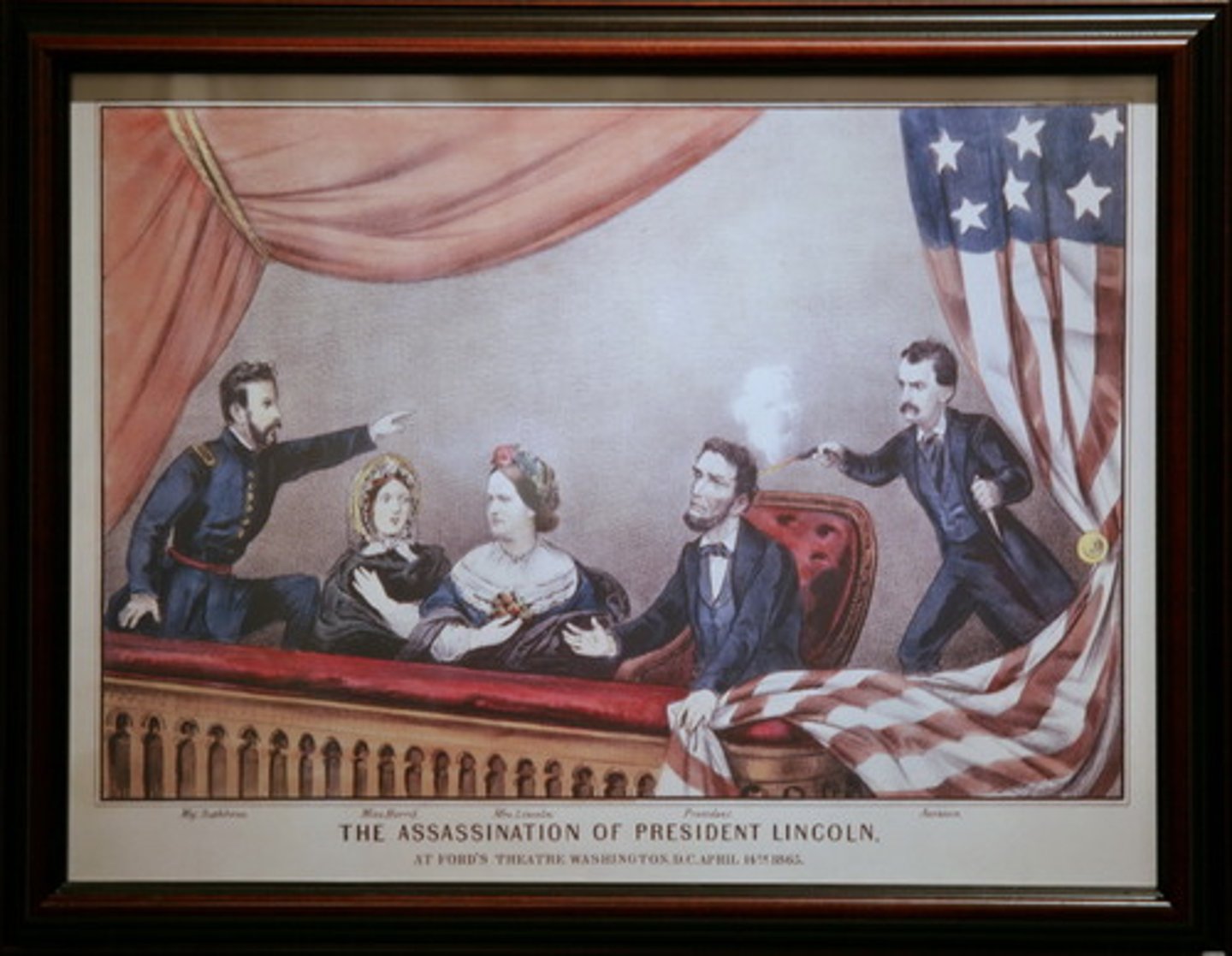
Lincoln's Assassination (1865)
Lincoln killed by John Wilkes Booth; stunned the nation post-war.

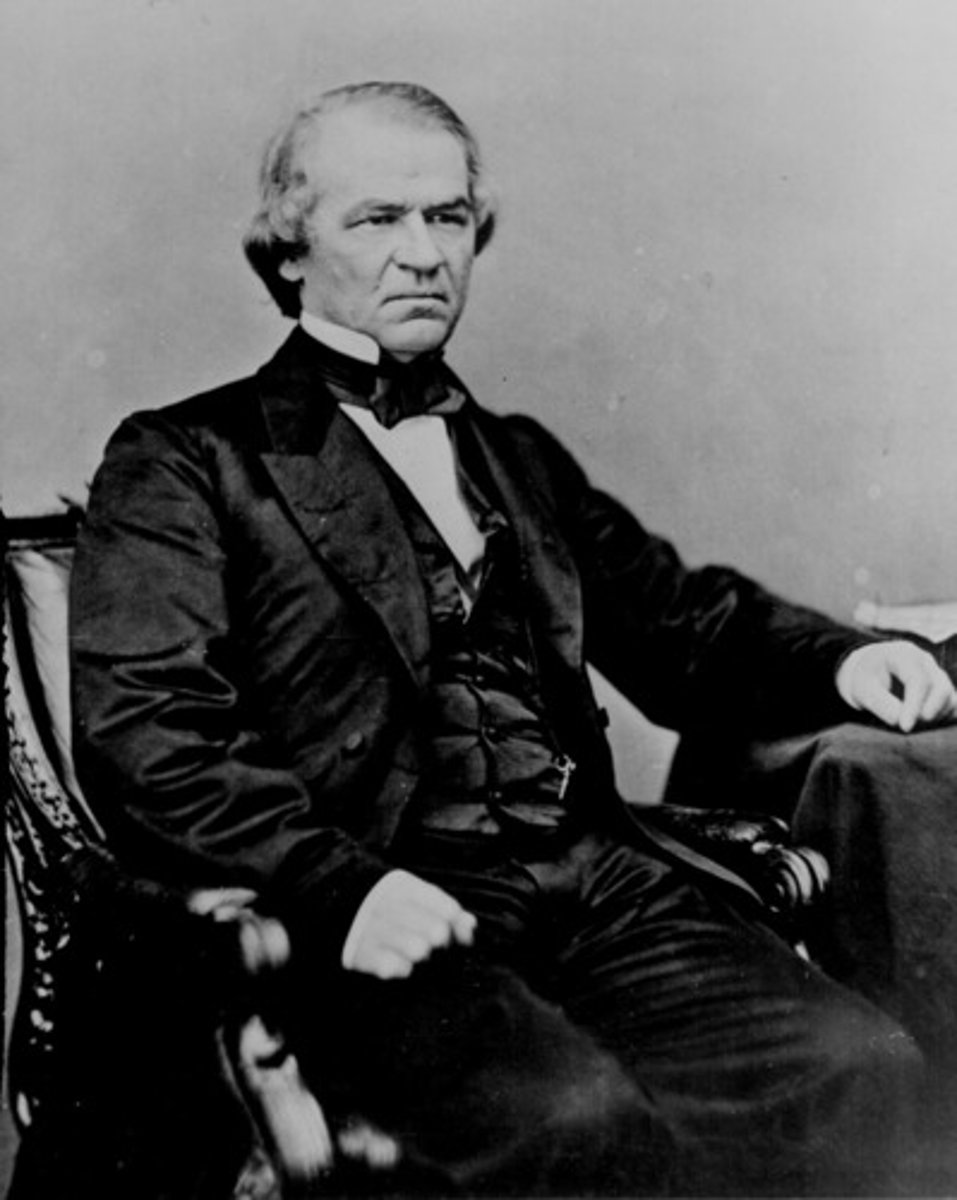
Presidential Reconstruction
Lenient policies under Lincoln and Johnson to reintegrate Southern states.

Radical Republicans
Favored strict Reconstruction and full rights for freedmen.

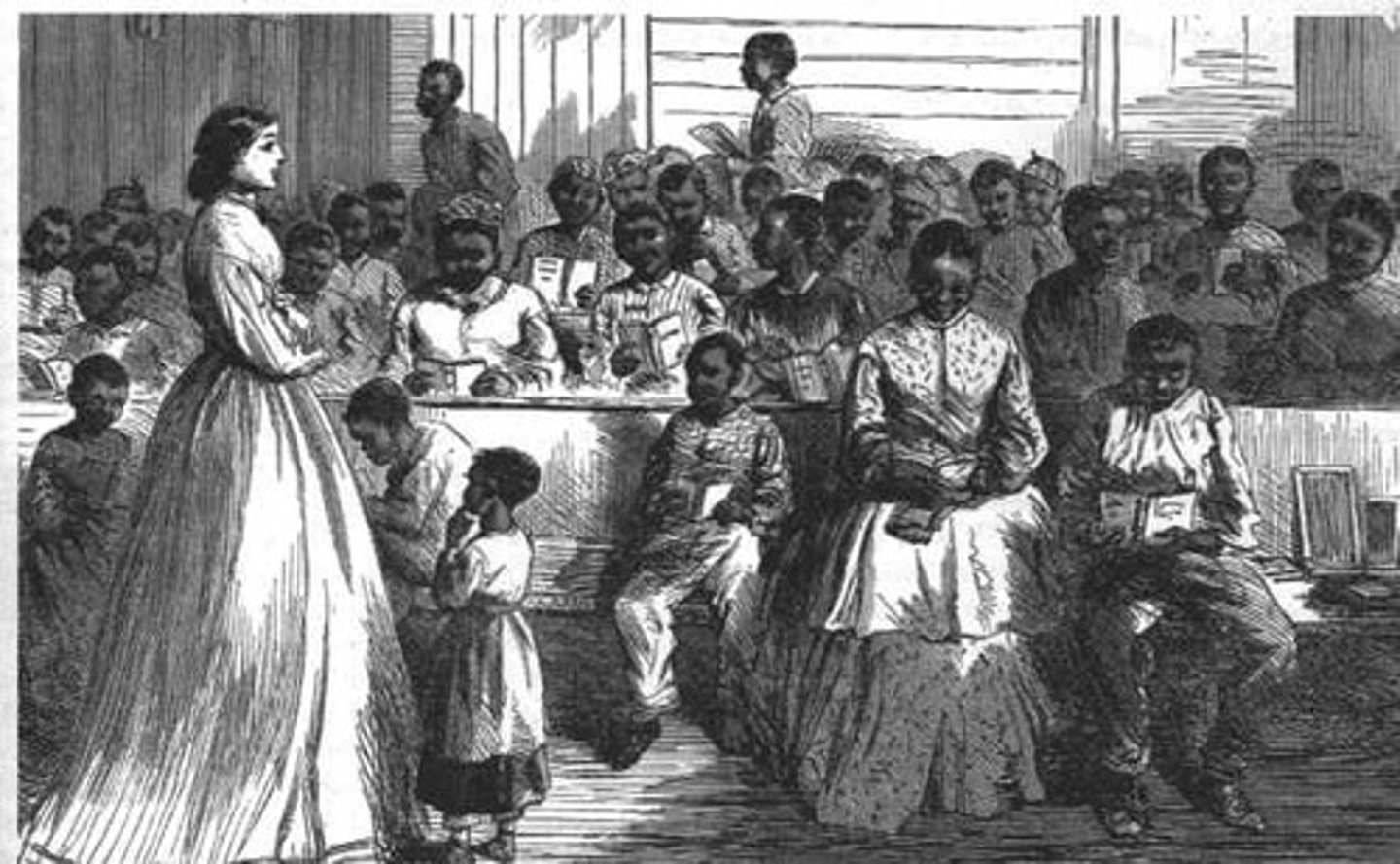
Freedmen's Bureau
Federal agency to assist former slaves with food, education, and legal help.

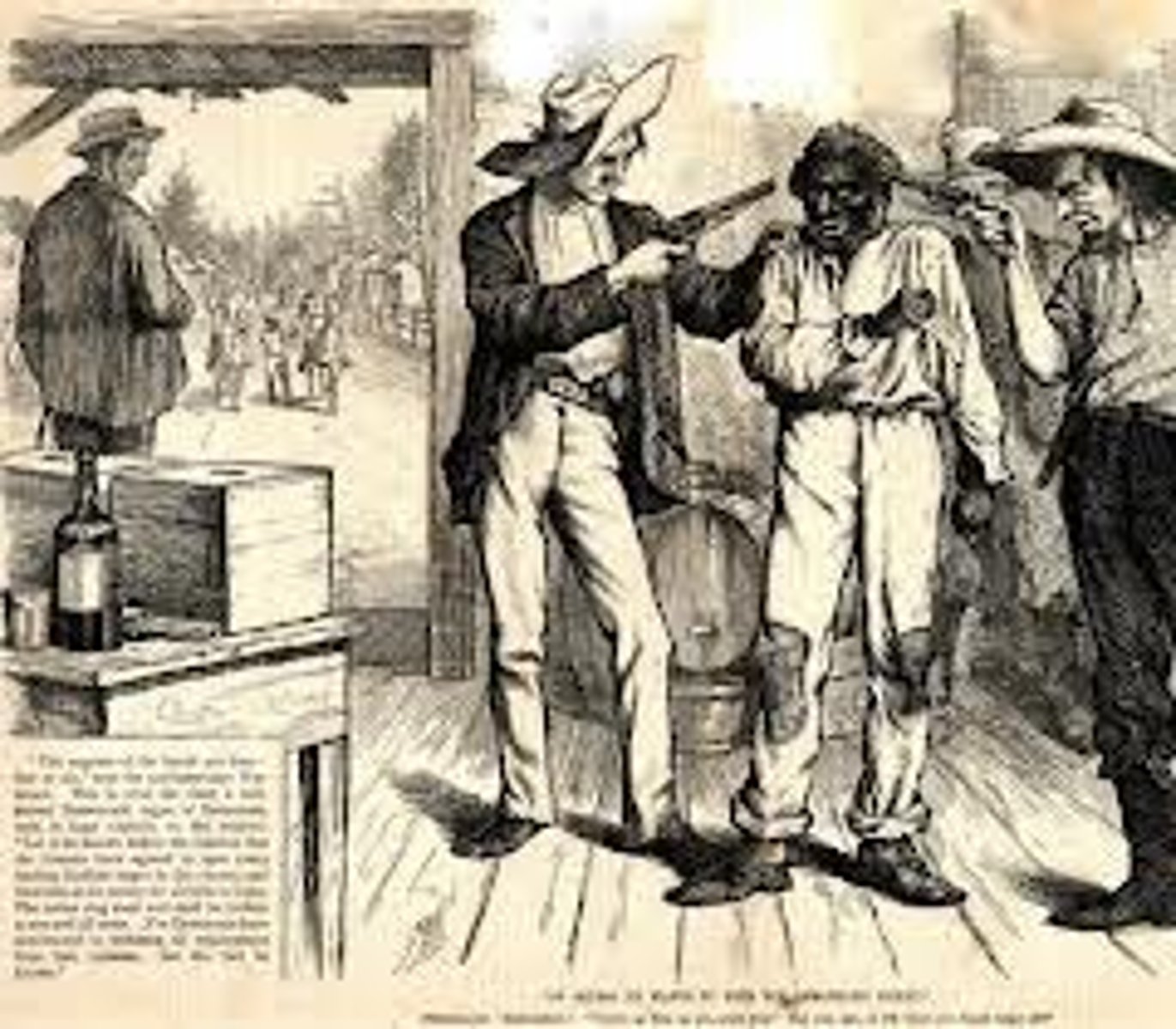
Black Codes
Southern laws restricting African Americans' rights after the Civil War.

14th Amendment
Granted citizenship and equal protection to all born in the U.S.

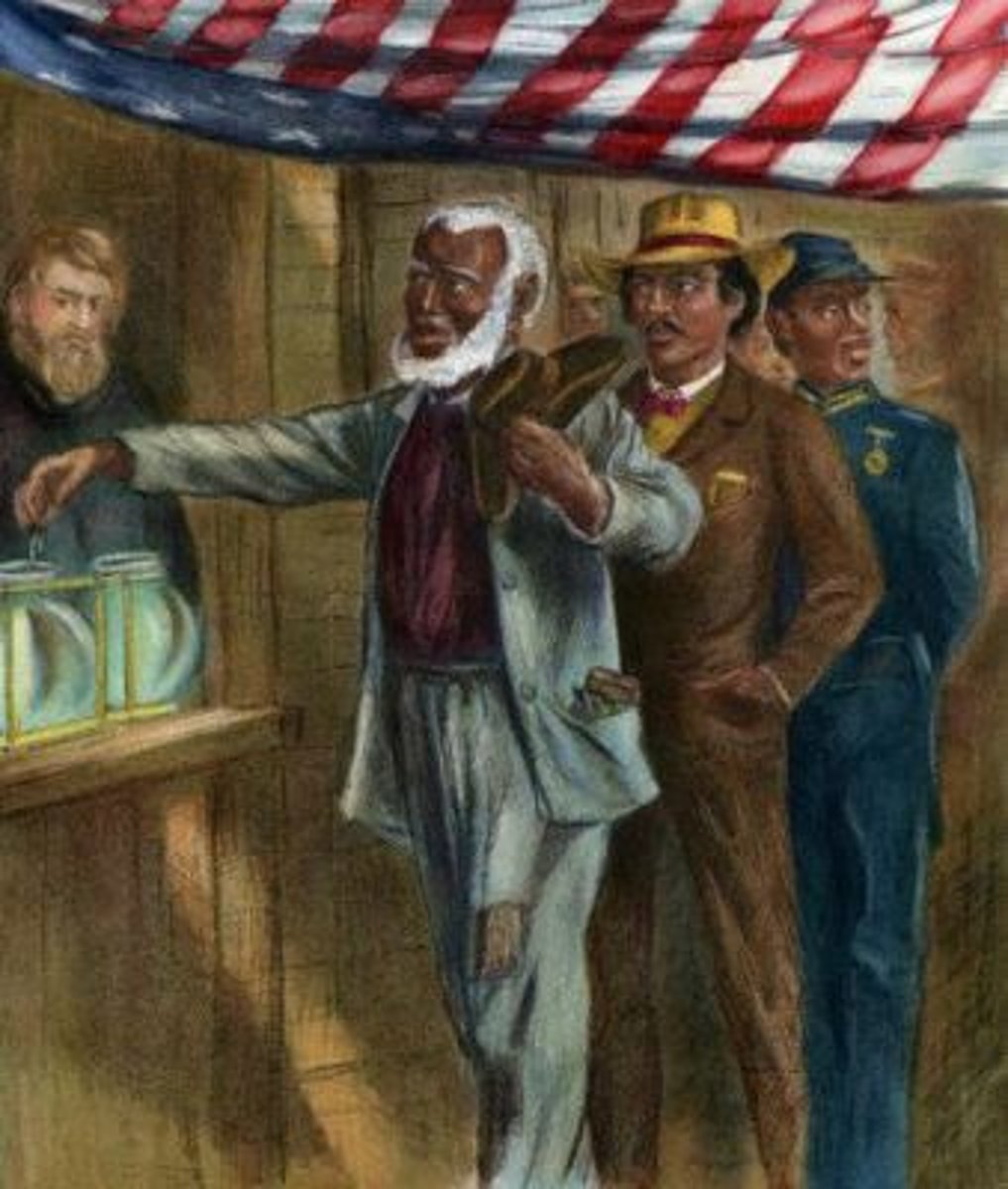
15th Amendment
Prohibited voting discrimination based on race or previous condition of servitude.

Reconstruction Acts (1867)
Divided South into military districts; required new constitutions and black suffrage.
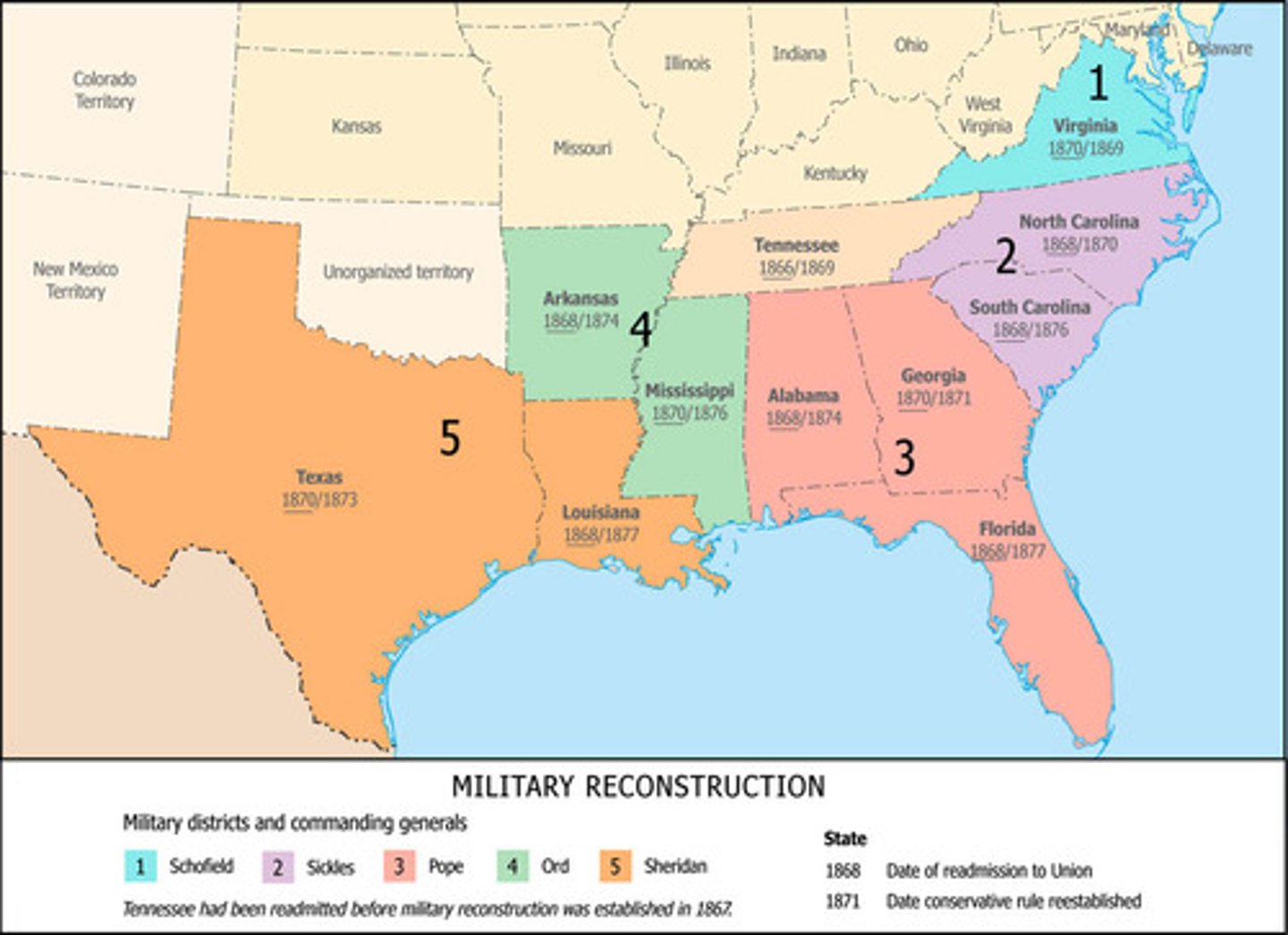
Impeachment of Andrew Johnson
Johnson violated Tenure of Office Act; impeached but not removed.

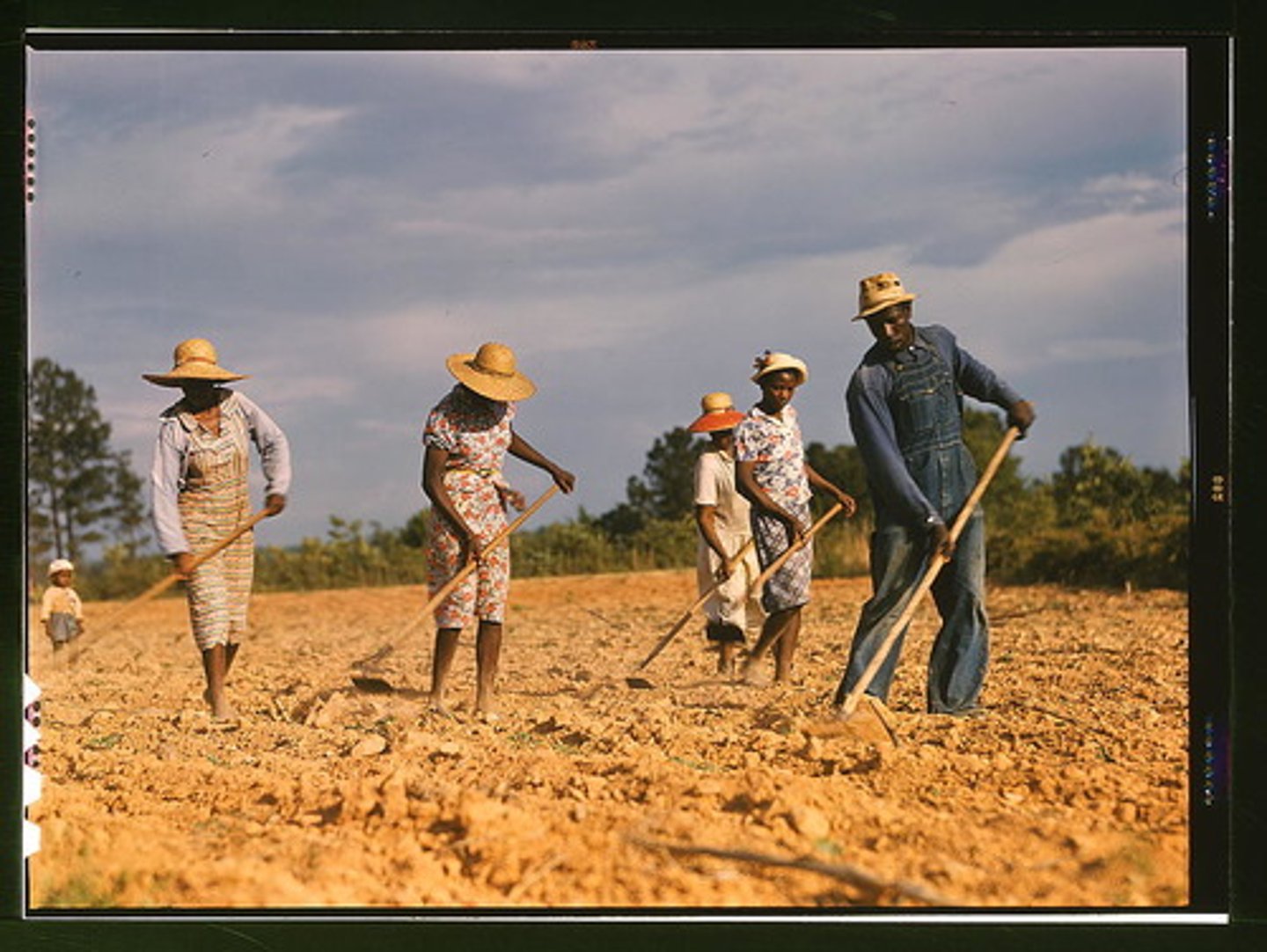
Sharecropping
Labor system where freedmen worked land for a share of the crop; often led to debt and poverty.

Compromise of 1877
Ended Reconstruction; Hayes became president, and federal troops left the South.

Redeemer Governments
Southern Democratic regimes that reversed Reconstruction reforms and suppressed black rights.
