Living Earth: Soil Physical Properties
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mostly formulas and key physical properties
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Soil texture
Refers to the proportion of sand, silt, and clay sized particles that make up the mineral fraction of the soil.
Soil Profile
Soil Profile – The vertical cross section of a soil that is exposed when a soil pit is dug from the surface to the underlying bedrock.
Soil structure
The arrangement of soil particles into granules, crumbs or blocks called aggregates or peds.
What does soil structure control?
• Water movement (permeability)
• Air movement (aeration)
• Root movement and development
• Microbial habitats
• Nutrient movement
Soil aggregate
A group of primary soil particles that cohere more strongly to each other than to other surrounding particles.
Particle density
Mass of soil particles (g) divided by the volume of soil particles (cm3).
Dry bulk density (BD)
Mass of oven-dry soil (g) divided by the total volume of soil (cm3).
Pore
Space between soil particles.
Porosity
The volume of pores in the soil and the capacity of soil to hold air and water in pores, calculated as volume of pores (cm3) / total volume of soil (cm3).
Permeability
The ease with which gases, liquids, or plant roots can penetrate or pass through a mass of soil.
Soil aeration
The movement of gases in soil, primarily by diffusion through the soil pore space.
Soil compaction
Occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space and increasing bulk density.
Gravimetric water content (qg)
Mass of water (g) divided by the total mass of oven-dry soil (g).
Volumetric water content (qv)
Volume of water-filled pores (cm3) divided by the total volume of soil (cm3).
Field capacity (FC)
The moisture content of soil two days after draining from a saturated state.
Permanent wilting point (PWP)
The soil moisture content at which plants wilt to conserve water during daytime.
Available water capacity (AWC)
The amount of water available for plant growth, defined as the difference in q between field capacity and permanent wilting point.
Hydraulic conductivity (K)
The ease with which water moves through soil under saturated or near-saturated conditions.
Soil water potential (ψ)
The difference in free energy between water conditions, expressed as ψ = h ρ g.
Soil infiltration
The soil's ability to allow water movement into and through the soil profile.
Soil water holding capacity
The amount of water that a given soil can hold for plant use at field capacity.
Five factors influencing soil formation
. Climate: Moisture/temperature determines what type of weathering occurs and the vegetation that forms.
. Geology/Parent Material: The material that soil develops on, such as in situ rocks or sand dunes. Weathering creates primary and secondary minerals.
. Topography – Elevation (metres), Slope (degrees), Aspect.
. Organisms and Vegetation – What grows and lives in the soil. Microorganisms assist in the decomposition of plant matter. Humans impact soil through cultivation and drainage.
. Time – Ice age eroded all soil in northern hemisphere such as Iceland and UK. Tropics had no ice age and thus have soil that is metres deep. Soil in UK has taken 10,000 years to form, with an average depth of 50cm. It takes 400 years to form 1cm of soil in UK.
Soil Layers
O Horizon (Organic matter): Mostly decomposing leaves and other plant life.
A Horizon (Topsoil): Minerals from organic matter and parent material incorporated.
Eluviated: Leached of clay and minerals, leaving sand and silt particles of quartz.
B Horizon (Subsoil): Rich in minerals that leached from O horizon or E horizon and accumulated.
C Horizon (Parent Material): The deposit at Earth's surface from which the soil developed.
R Horizon (Bedrock)
O Horizon categorisation
leaf litter (L), fermenting leaf litter (F), and humus (H).
Soil Catena (Toposequence)
A group of different soils that occur together on a landscape having the same parent material, with topography as the dominant influencing factor responsible for the differences existing in such soils.
Soil Texture - Particle Size
Sand – 2.0 to 0.05 mm
Silt – 0.05 to 0.002 mm
Clay – less than 0.002 mm
Mottle
Spots of different colours in subsoil.
Main Anions in soil
Nitrates (NO3-)
Chloride (CL-)
Phosphate (PO4^3-)
Sulphate (SO4^2-)
Anions = Negatively charged ions.
Main Cations in soil
Sodium (Na+)
Hydrogen (H+)
Potassium (K+)
Magnesium (Mg2+)
Ammonium (NH4+)
Calcium (Ca2+)
Cations = Positively charged ions
Soil pH range
3-10
High soil pH = low H+ concentration, and vice versa.
For the crops humans eat, a neutral pH soil (5-7) is ideal.
Case Study: What pH do earthworms prefer?
5-8. Ammonium based fertilizers are toxic to earthworms due to the acidic conditions they create.
Cation Exchange
interchange of cations between clay minerals (colloid) and a solution. Interchange between a cation in solution and one on a colloid must be chemically balanced. Reaction is rapid and reversible.
Order of preferential attraction for cation exchange
Al3+> Ca2+> Mg2+>NH4+ ~ K+>Na+
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
the number of cation adsorption site per unit of soil
Expressed as the amount of charge per unit weight of soil
• centimoles per kilogram of dry soil (cmol/kg)
• milliequivalents per 100 g dry soil (meq/100g)
Base Exchange
(sum of) exchangeable bases / CE
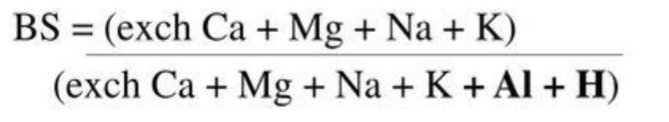
How much of UK’s carbon emissions is due to agriculture?
10%