Excretion
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Excretion (definition)
The removal of metabolic waste from the body
Organs of excretion in animals
lungs, kidneys, skin
What do the lungs excrete?
carbon dioxide, water
What does the skin excrete?
Sweat
What is sweat made of?
Water, salts
What do the kidneys excrete?
Urine (water salts and urea)
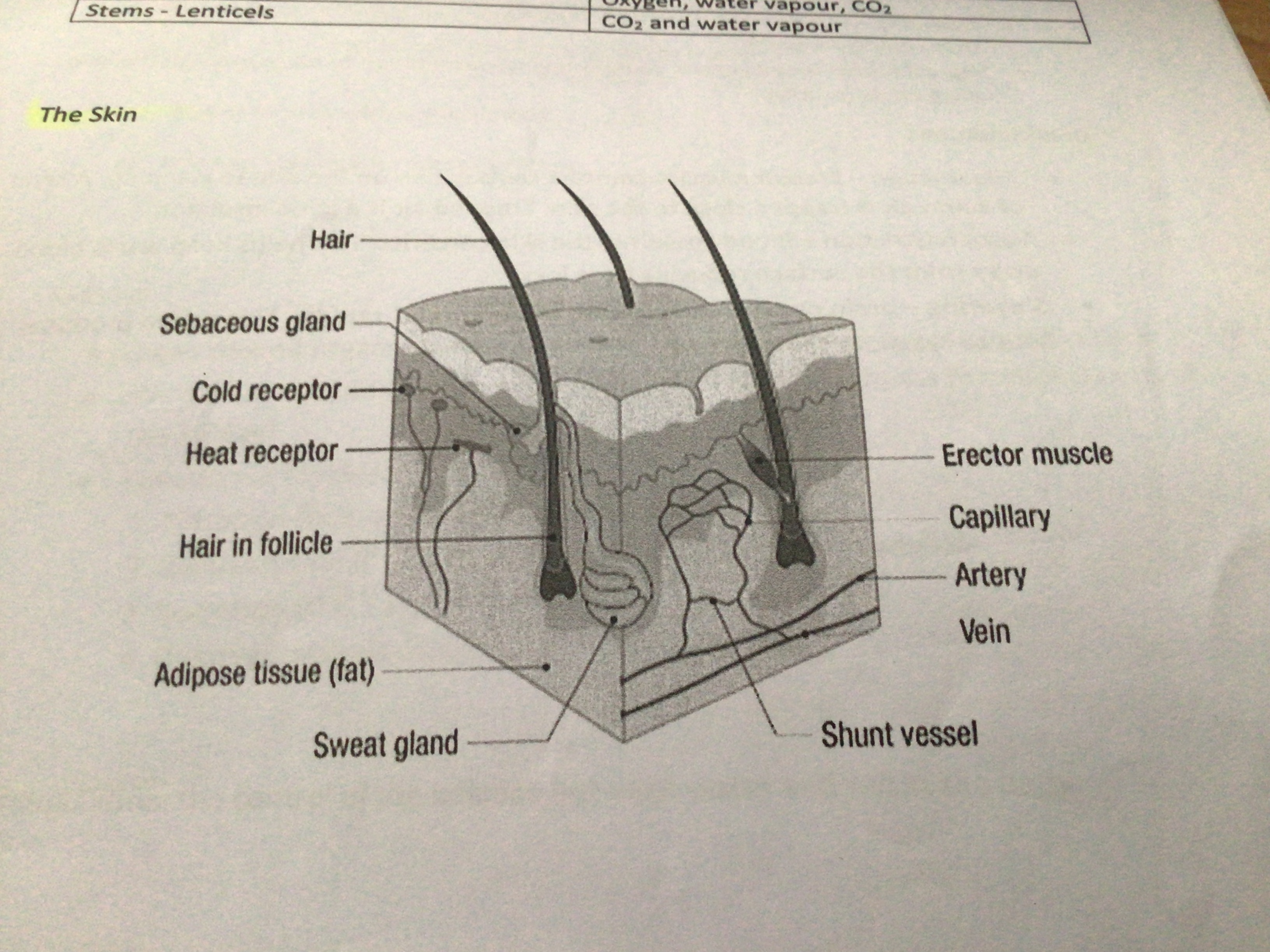
Draw and label a diagram of the skin
...
What are the organs of excretion in plants?
Leaves (stomata), stems (lenticels)
What do the leaves excrete?
Oxygen, water vapour, carbon dioxide
What do the lenticels excrete?
Carbon dioxide
Functions of skin
Protection, temperature regulation, excretion, production of vitamin D
How does our skin protect us?
Epidermis acts as a barrier to prevent water loss and entry of pathogens
What is the normal human body temperature?
37 degrees Celsius
How is heat transported around the body?
in blood plasma
Draw the urinary system
...
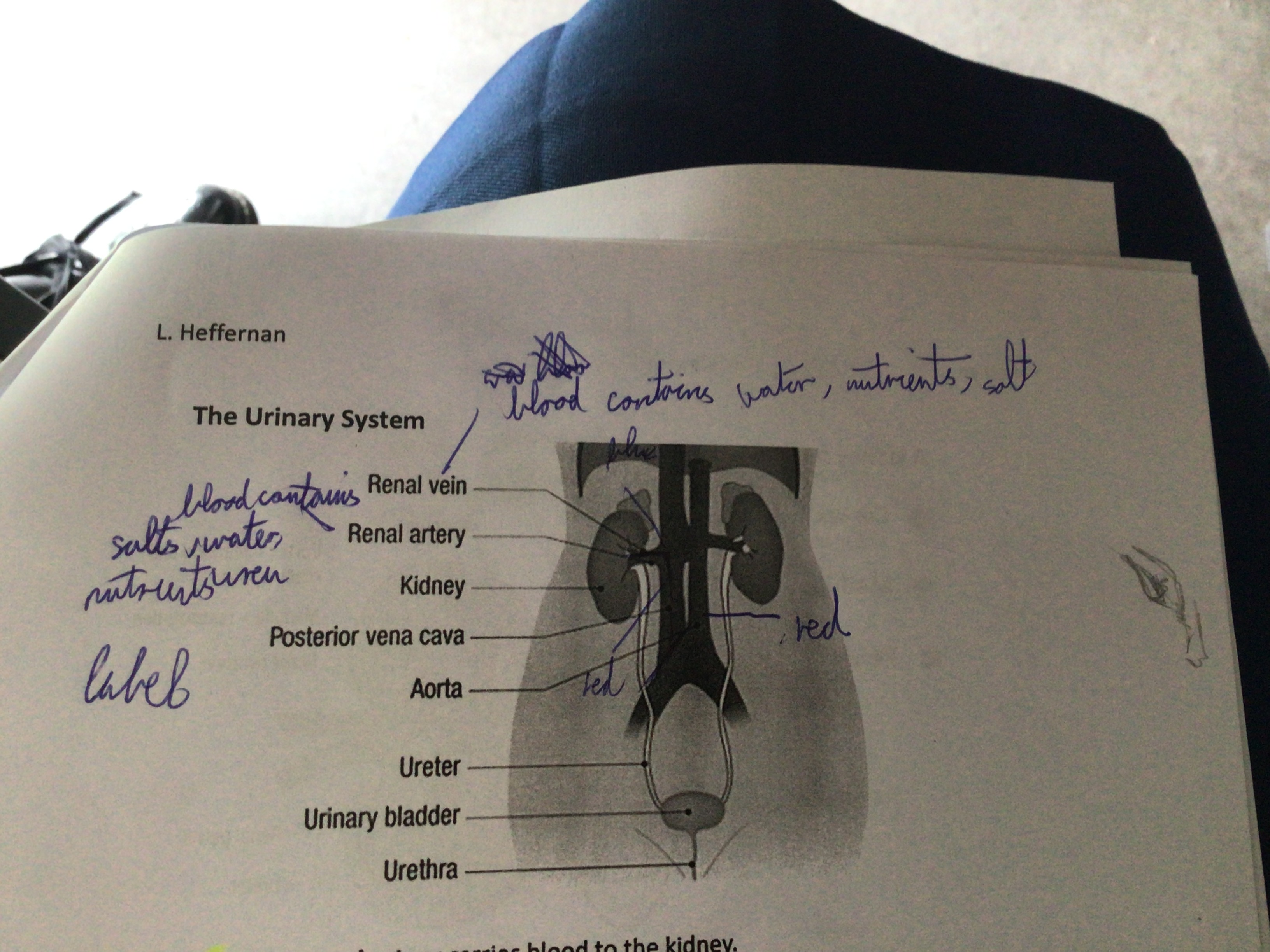
Which artery carries blood to the kidney?
Renal artery
Which vein carries blood away from the kidney?
Renal vein
What carries urine to the bladder?
Ureter
What controls the opening and closing of the bladder?
Sphincter muscle
What stores urine?
Bladder
How does urine leave the bladder?
Urethra
Where are the kidneys located?
Below the diaphragm in the back of the abdominal cavity
What are the millions of structures in kidneys called?
Nephrons
Functions of the Nephron
filtration, reabsorption, secretion, osmoregulation
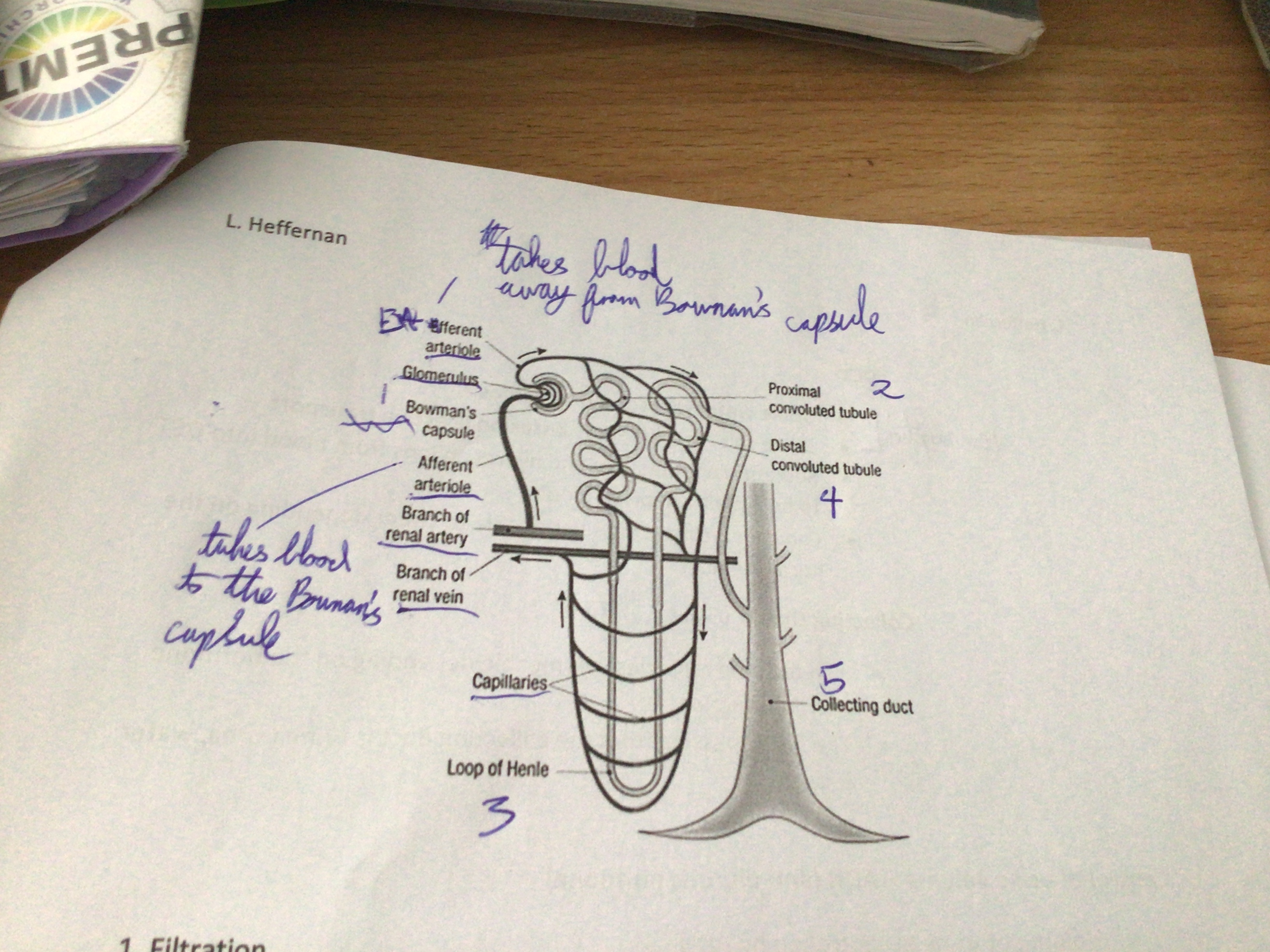
Where in the nephron does filtration occur?
Bowman's capsule (cortex)
Where in the nephron does reabsorption occur?
proximal convoluted tubule (cortex), loop of Henlé (medulla), distal convoluted tubule (cortex)
Where in the nephron does secretion occur?
Distal convoluted tubule (cortex)
Where in the nephron does osmoregulation occur?
Collecting duct (medulla)
Osmoregulation (definition)
The control of the balance between water and salt in the body
Where is the cortex of the kidney located?
outer region
Where is the medulla of the kidney located?
middle region
Where is the renal pelvis of the kidney located?
inner region
How many nephrons does a kidney have?
1-2 million
Adaptations of the nephron
Pressure in glomerulus is high due to efferent arteriole being narrower than afferent arteriole. Surface area of glomerulus capillaries is large. Walls are porous. Bowman's capsule one cell thick
Where does unfiltered blood enter the glomerulus enter from?
Afferent artiole
Where does filtration occur?
Glomerulus
What is forced out of the plasma into Bowman's capsule? What does it form?
glucose, amino acids, vitamins, water. Glomerular filtrate
What is too big to enter the glomerular filtrate?
Large proteins, white blood cells, red blood cells.
What is reabsorbed in the PCT?
food molecules, most water, most salts
How are food molecules and salts reabsorbed in the PCT?
diffusion, active transport
How is water reabsorbed in the PCT?
osmosis
What is reabsorbed in the Loop of Henle?
some water, some salts
What is reabsorbed in the DCT?
some water, some salts
What does the blood secrete?
Potassium and hydrogen ions
Why does thee blood secrete ions into the DCT
Maintain blood pH
What part of the nephron can become more/less permeable depending on ADH?
collecting duct
What controls the volume of urine?
Controlled by ADH
What part of the brain releases ADH?
pituitary gland
How does ADH reach the kidneys?
Travels by the bloodstream
What does ADH do?
Collecting duct becomes more permeable to water, allowing more water to be reabsorbed
What happens when salt concentration in the blood plasma is too high?
ADH released
What happens when salt concentration in the blood plasma is too low or normal?
ADH not released
Affect on volume of urine when ADH is released
Decreases (more concentrated)
Affect on volume of urine when ADH is not released
Increase (more dilute)
Kidney failure treatments
dialysis, kidney transplant
Draw a nephron
…