Chemical Energetics
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
All chemicals possess energy stored in the form called…
chemical energy
What do most energy changes involve?
loss or gain in heat energy
What is ΔH?
amount of energy absorbed or released in a chemical reaction
What does ΔH represent?
difference in energy level between products and reactants
Unit for ΔH
kJ mol-1
What is standard enthalpy change of a reaction (ΔHፀ)?
amount of energy absorbed or released in a chemical reaction when molar quantities of reactants stated in the chemical equation react under standard conditions of 298K and 1 bar.
What are the standard conditions?
> temperature = 298 K
> pressure = 1 bar
> concentration = 1 mol dm-3
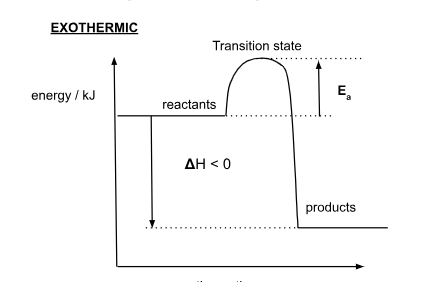
What is an exothermic reaction?
reaction where heat is released to the surroundings
What happens to the surroundings during an exothermic reaction?
The temperature of the surroundings increases and the reaction container becomes hot.
Formula for ΔH?
ΔH = ∑ Hproducts - ∑ Hreactants
How is ΔH in an exothermic reaction?
In exothermic reaction, Hproducts is less than Hreactants → ΔH is negative
In an exothermic reaction, ΔH is …
negative
How is negative ΔH represented?
single arrow line pointing downwards
Examples of exothermic reactions
combustion
neutralization
haber process
respiration
freezing and condensation
gas → liquid → solid
Examples of endothermic reactions
thermal decomposition of carbonates
dissolution of potassium or ammonium salts
photosynthesis
melting and boiling
solid → liquid → gas
What happens to energy lost during exothermic reactions?
given out in the form of heat
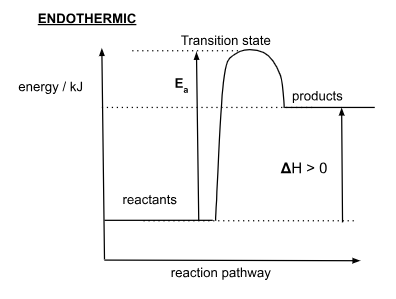
What is an endothermic reaction?
reaction where heat is absorbed from the surroundings
What happens to the surroundings during an endothermic reaction?
The temperature of the surroundings decreases and the reaction container becomes cold.
How is ΔH in an endothermic reaction?
In endothermic reaction, Hproducts is more than Hreactants
In an endothermic reaction, ΔH is …
positive
How is positive ΔH represented?
single arrow line pointing upwards
What is Activation Energy?
the minimum amount of energy that molecular collisions must possess in order for a chemical reaction to occur
What must happens to bonds in reactant particles before a product can be formed?
Whether exothermic or endothermic → bonds in reactant particles must be broken before new bonds in product particles can be formed
Reactant particles must possess energy … activation energy in order to break original chemical bonds
greater than/equal to
What is the transition state?
the point at which reactants are about to change to products; occur at maximum point/point of highest energy
Exothermic Energy Profile Diagram
Endothermic Energy Profile Diagram
Explain in terms of bond forming and bond breaking about [exothermic reaction].
In an exothermic reaction, energy given out to form bonds in [product particles] is larger than energy absorbed to break bonds in [reactant particles].
Explain in terms of bond forming and bond breaking about [endothermic reaction].
In an endothermic reaction, energy given out to form bonds in [product particles] is smaller than energy absorbed to break bonds in [reactant particles].
Why is the formation of water exothermic?
The energy absorbed to break the 2H – H bonds and 1 O = O bond is smaller than the energy given out to form 4 O – H bonds.
Bond breaking is…?
Bond breaking = absorbs energy → endothermic, ΔH is positive
Bond forming is…?
Bond formation = releases energy → exothermic, ΔH is negative
In exothermic, energy for bond forming is … than bond breaking
greater
In endothermic, energy for bond forming is … than bond breaking
less
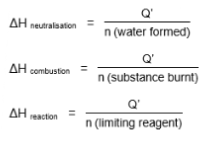
Standard enthalpy change of combustion (ΔHcፀ)
Standard enthalpy change of combustion (ΔHcፀ) of a substance is the heat energy released when one mole of the substance is completely burnt in excess oxygen at standard conditions of 298K and 1 bar.
Reaction between a compound / element and oxygen under heat releases energy to the surroundings.
*Standard enthalpy change of neutralisation (ΔHnፀ)
*Standard enthalpy change of neutralisation (ΔHnፀ) is the heat energy released when an acid and base react to form one mole of water at standard conditions of 298K and 1 bar.
Reaction between an acid and an alkali releases heat to the surroundings
What is bond energy?
Bond energy of X–Y bond is the average energy absorbed to break one mole of covalent bond in the gas phase into constituent gaseous atoms under standard conditions.
Give an example of splitting a compound to its base form.
1 X–Y(g) → X(g) + Y(g)
Bond energy is only used for …
covalent bonds.
Bond energy is … to covalent bond strength
proportional
Stronger covalent bond = …
More energy required to break → bond energy is greater
Calorimetric Method Procedure [5]
A simple calorimeter can be constructed using a poor thermal conductor like a polystyrene cup.
Using a measuring cylinder, place 25cm3 of X in a polystyrene cup and note the temperature.
Using another measuring cylinder, measure 25cm3 of Y.
To X in the polystyrene cup, add Y.
Stir carefully with the thermometer and record the maximum/minimum temperature reached.
EASIER:
Add X into cup.
Note temperature of X.
Add Y to X.
Stir.
Record maximum/minimum temperature.
ΔT Formulas
ΔT = Temperature change of a solution
ΔT = Maximum/Minimum Temperature – Initial Temperature
ΔT = Tmax/min – Tinitial
Heat change of a solution, Q Formula
Q = mcΔT
Q = C ΔT
Q’ = –Q OR Q
Enthalpy change formula with mol
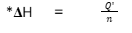
ΔH =
enthalpy change of reaction
kJ mol-1
1 kJ mol-1 = 1000 J mol-1
Q’ =
heat change of reaction
J or kJ
Q =
heat change of solution
J or kJ
m =
mass of solution
g
V =
total volume of solution
cm3
c =
specific heat capacity of solution
[usu. 4.18 J g-1K-1]
J g-1 K-1
ΔT =
change in temperature of solution
K
n =
amount
mol
What is specific heat capacity?
Specific heat capacity, c of a substance is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of the substance by 1 K; J g-1 K-1
What is heat capacity?
Heat capacity, C of a substance is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of m g of the substance by 1 K; J g-1 K-1
Formula of C, heat capacity
C = m c
ΔH formulas for neutralisation, combustion and general reaction
Density =
Mass / Volume
When mixing a solid and a solution, just use the mass of …
the mass of the SOLUTION!!!!!! No solid mass should be used.
Assumptions made while calculating enthalpy change [3]
No heat loss to surroundings due to insulation
Density of solution is approximated to water (1.00 g cm-3)
Specific heat capacity of solution is approximated to water (4.18 J g-1 K-1)