Geomorphology and Human Impacts
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts in geomorphology and its relationship with human activities, relevant for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Anthropocene
A proposed epoch that begins when human activities started to have a significant global impact on Earth's geology and ecosystems. (Dixon et al., 2018)

Tectonic settings
Structural features of the Earth that influence uplift, downthrow, and warping of landforms. (Dixon et al., 2018)

Cumulative global impacts
Gradual build-up of environmental effects that can lead to significant global consequences. (Dixon et al., 2018)
Human activities influence landscape dynamics
(Goudie and Viles, 2016)

Urban geomorphology
The study of landforms in urban environments and how human activities influence these landscapes. (Goudie and Viles, 2016)

Global climate change influence landscape dynamics
(Goudie and Viles, 2016)

Earth’s landscapes are becoming more hazardous
Goudie and Viles, 2016

Subsidence
The gradual settling or sudden collapse of the ground's surface, often due to mining or extraction processes. (Dixon et al., 2018)
from areas where they are mining salt
Megacities
Urban areas with a population of over 10 million, many of which are found in the global South. (Dixon et al., 2018)
Sinkholes
Depressions or holes in the ground caused by the removal of ground water leading to land collapse. (Dixon et al., 2018)
Examples:

Erosion
The process by which surface material is worn away and transported by wind, water, or ice. (Goudie and Viles, 2016)
Hazards
Natural or human-induced events that pose a threat to life, property, and the environment. (Goudie and Viles, 2016)
Geomorphic equilibrium
A state in which the processes of erosion and deposition are in balance within a landscape. (Goudie and Viles, 2016)
Deforestation
The clearing or thinning of forests to make way for agriculture, urban development, or other uses. (Dixon et al., 2018)
Climate change
Long-term alterations in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other elements of the Earth's climate system. (Dixon et al., 2018)
Successful environmental management needs geomorphic input
Dixon et al., 2018

Timeline for the Anthropocene

Human impacts on the palaeoanthropocene
Steffen, 2010

Human impacts on geomorphology in the industrial era
Steffen, 2010

Gullies
sediment being trapped and stored
cut down erosion
in extreme environments - led to gullies
a landform created by running water, mass movement, or both, which erodes soil to a sharp angle, typically on a hillside or in river floodplains or terraces.
Goudie and Viles, 2016
Human impacts in Great Acceleration
Steffen, 2010

Sand wars
Goudie and Viles, 2016

Case study: Dubai
Goudie and Viles, 2016

Linking humans to geomorphology

continued

case study: Yangtze River

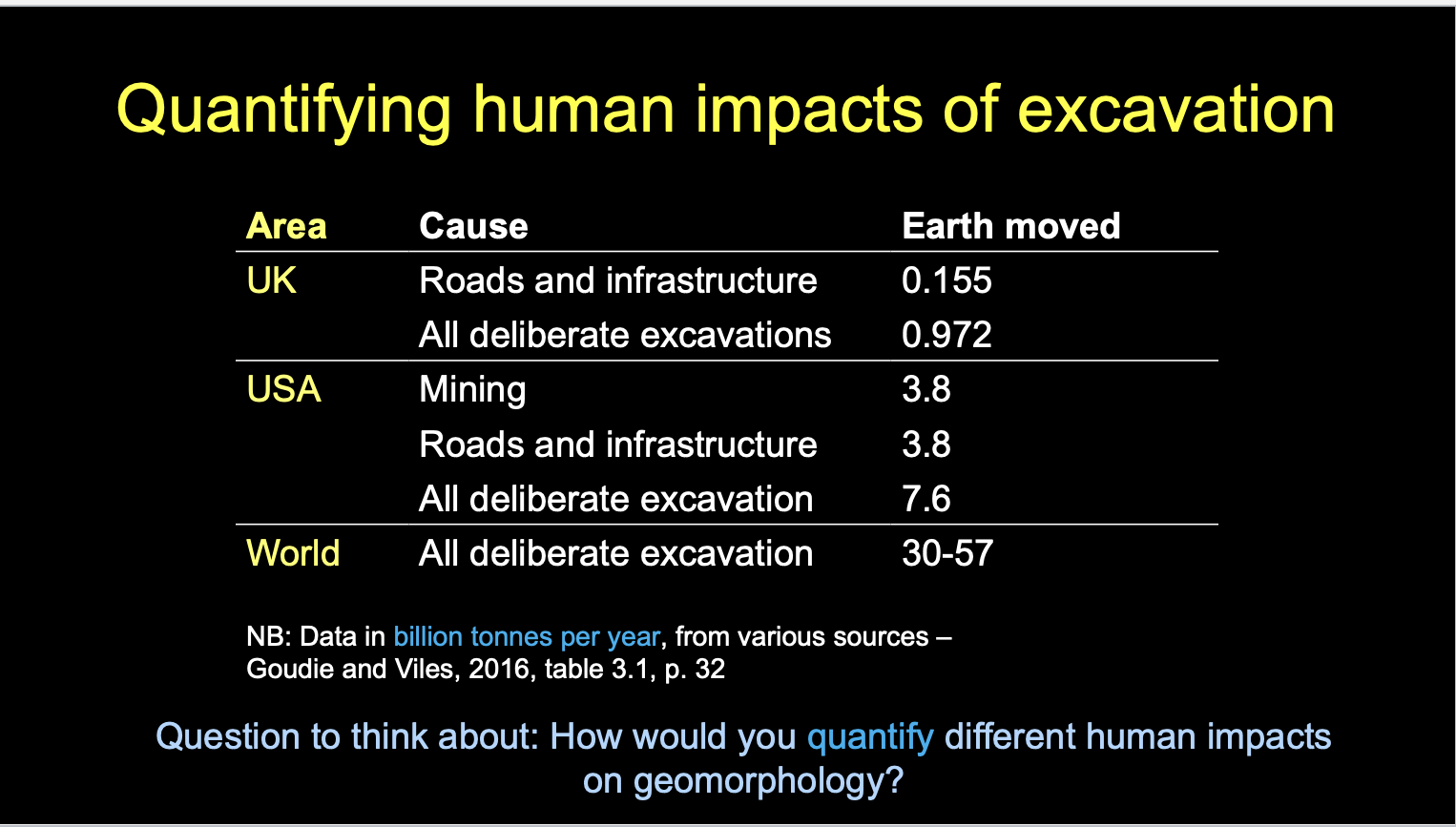
Quantifying human impacts of excavation