ORGO exam 2 (alkene, A-B rxn)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What goes at the end of an alkene IUPAC nomenclature?
-en- (most likely ene)
how does the IUPAC nomenclature of a alkene change when there is two double bonds in a molecule?
the end will change to -adiene instead
how does the IUPAC nomenclature of a alkene change when there is three double bonds in a molecule?
the ending will change to -atriene instead
what is an alkene
molecule has a double bond, 120 degree bond angle, CnH2n
nucleophile
species that have high abundance of electrons, will donate electrons (Lewis bases)
electrophile
species that have low abundance of electrons and will receive electrons (Lewis acid)
common name for CH2=
methylene
common name for CH2=CH-
vinyl
common name for CH2=CHCH2-
allyl
which isomers are more stable, cis or trans
trans isomers are more stable
the lower the pKa…
the stronger the acid
sulfuric acid pKa (H2SO4)
-10
hydroiodic acid (HI) pKa
-10
hydrobromic acid (HBr) pKa
-9
hydrochloric acid (HCl) pKa
-6
benzenesulfonic acid pKa
-3
Protonated oxygen pKa
-2
hydrofluoric acid (HF) pKa
3
carboxylic acid pKa
5
protonated amines (NH4+) pKa
9
hydrogen cyanide (HCN) pKa
9
thiols (H2S) pKa
9
dicarbonyls pKa
10-13
water pKa
16
alcohol pKa
17
ketone and aldehyde pKa
19
nitrile pKa
25
alkyne pKa
25
sulfoxide pKa
30
amine (NH3) pKa
35
hydrogen pKa
35
alkene pKa
45
alkane pKa
50
what are the requirements for an aromatic structure
planar, cyclic, Huckel’s rule, fully conjugated
Huckel’s rule
4n+2= (answer should be 2,6,10,14,18…)
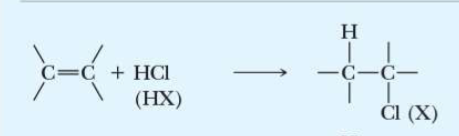
name the addition reaction
hydrochlorination (hydrohalogenation)
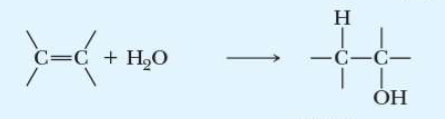
name the addition reaction
hydration

name the addition reaction
bromination (halogenation)
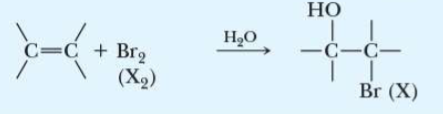
name the addition reaction
bromo(halo)hydrin formation
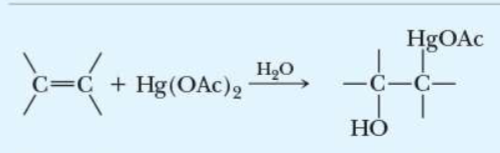
name the addition reaction
oxymercuration
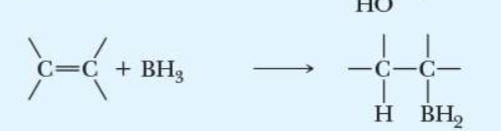
name the addition reaction
hydroboration
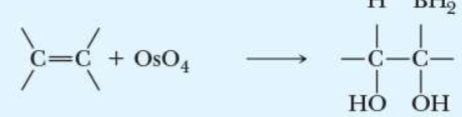
name the addition reaction
diol formation (oxidation)

name the addition reaction
hydrogenation (reduction)
BDE equation
change of H= BDE of reaction - BDE of product
Markovnikov’s Rule
in addition to HX, H2O, ROH to alkene, the H adds to the carbon (of the double bond) with the greater number of hydrogen
how to find the most substituted carbon?
the carbon that is connected to the most substituents (tertiary is greater than primary)
how to find the most stable carbocation?
the most substituted carbon is most stable
carbonation
the molecule’s ability to have rearrangement
IUPAC (E)
molecule that has substituents on opposite sides of the double bond
the stronger the acid…
the weaker the conjugate base
IUPAC (Z)
molecule that has substituents on the same side of the double bond
how to find the major product
the product that follows Markovnikov’s rule is the major product
higher pKa means…
more stable molecule
racemic mixture
enantiomer (one dash, one wedge)
hydrohalogenation
HX
Acid-Catalyzed
H2O, H2SO4
Halogenation
X2
Halohydrin formation
X2, H2O
oxymercuation (reduction)
Hg(OH)2, H2O
NaBH4
Hydroboration (oxidation)
BH3
H2O2m NaOH
Syn Dihydroxylation
OsO4
NaHSO3, H2O
or
OsO4
tBuOOH
Catalytic Reduction
H2, Pd/C
Ozonolysis
Os
(CH3)2S