Macromolecules and Protein Synthesis
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
What were the five molecules that made up a majority of the early Earth atmosphere?
Water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia
What three conditions were stimulated by Miller-Urey apparatus to show that life could arise?
Electrodes simulated lightning, 5L flask was filled with gases found in the early atmosphere, 500mL flask contains boiling water to simulate evaporation from the oceans
What did Erwin Chargaff conclude about the four bases of DNA?
A=T and C=G
-larger and mostly made of carbon-hydrogen covalent bonds
Organic compunds
What complex compounds were formed in the apparatus after two weeks?
Carbon was converted to sugars, amino acid, and nucleic acids
Why is carbon such an essential element in the formation of organic compounds?
It can form 4 bonds (more than most elements)
-made of repeating units
Polymer
-Made of individual units
Monomer
What is the monomer of Nucleic acids?
Nucleotides
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
Glucose
What is the monomer of proteins?
Amino acids
What is the monomer of lipids?
Fatty acids
What are nucleic acids used for?
To store instructions within cells
What are examples of nucleic acids?
DNA, RNA, ATP
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Phosphate, 5-carbon sugar, nitrogenous base
-found in nucleolus, spiraling double helix, nitrogenous base
DNA (sugar= deoxyribose)
-found outside of nucleolus, single-stranded helix, nitrogenous base
RNA (sugar= ribose)
What does ATP do in cells?
Nucleotide used to transfer energy within cels (broken down to ADP when energy is released)
What elements are carbohydrates made of?
Carbon, oxygen, and hyrdogen
-carbohydrates with One sugar monomer
Monasaccharide
What do monosaccharides do? Give an example:
Short-term energy storage (glucose)
-carbohydrates with Two sugar monomers
Diasaccharide
What are disaccharides function? Give an example:
Energy storage (sucrose, lactose)
-carbohydrates with Three or more monosaccharides
Polysacchride
-energy stored in plants
Starch (function of polysaccharides)
-energy storage in animals
Glycogen (function of polysaccharides)
-cell walls in plants
Cellulose (function of polysaccharides)
-exoskeleton of insects
Chitin (functions of polsaccharides)
What are examples of lipids?
Fat, steroids
What elements are lipids made of?
Carbon and hydrogen
Are lipids considered polymers?
NO
All lipids are HYDROPHOBIC. What does this mean?
They DO NOT dissolve in water
-long chains of carbon atoms with SINGLE BONDS only, SOLIDS
Saturated fats
-long chains of carbon atoms with SINGLE AND DOUBLE bonds, liquids, healthier
Unsaturated fatty acids
What two molecules are triglycerides made of?
Gycerol (3-carbon molecule) and Three fatty acids
Where are tryglycerides found?
Arteries and body fat
How is a phospholipid different than a tryglyceride?
Phospholipid- made of 2 fatty acids and a phosphate
Triglyceride- made of 3 fatty acids
-are aranged to keep the hydrophobic tails away from water
Bilayer sheet
-lipids with four interconnected carbon rings (chloresterol, testoreone, estrogen)
Steroid
Proteins are chains of______
Amin acids (20 different types, 9 essential)
-provide framework for the body (collagen in ligaments)
Support (function of protein)
-contract and create movement (skeletal muscle)
Movement (function of protein)
-transport of material in and out of cell (glucose transporter in cell membranes)
Transport (function of proterins)
-prevent changes in ph ( proteins in blood plasma)
Buffering (functions of proteins)
-speed up the role of chemical reactions (digestive enzymes in the stomach)
Metabolic regulation (function of proteins)
-signal changes throughout the body ( hormones (insulin))
Coordination (function of proteins)
Protects against bacteria and viruses ( antibioditics in blood)
Defense (function of proteins)
What does the sequence of amino acids determine?
The shape which determines its function
-a change in the shape of a protein that causes it to loose its normal function
Denatured
What two conditions cause denaturation?
Heat and exposure to acids
-proteins that speed up chemical reacts, bind to substrates and faciliate a reaction that turns them into products
Enzyme
The inputs in an enzyme-catalyed recation are called_______
Substrate (hydrogen peroxide)
The outputs in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are called______
Product
-the minimum energy needed to initiate a reaction
Activation energy
Enzyme or no enzyme: activation energy is higher, reaction rate is slower
NO ENZYME
Enzyme or no enzyme: Activation energy is lowered, reaction rate increaeses
ENZYME
-each enzyme will only be active against the substrate thats fits its shape
Lock-and-key theory
Enzyme activity: TOO COLD
Molecules move slowly, limiting reaction
Enzyme activity: OPTIMAL TEMPERATURE
Moelcules move faster, enzyme structure is still intact, maximum reaction speed
Enzyme activity: TOO HOT
Enzyme is denatured, loosing its shape and function
What is the primary function of nucleic acid?
Store genetic information
What is the primary function of lipids?
Long-term energy
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
Short-term energy
What is the primary function of proteins?
Repair and rebuild tissue
What are the elements in nucleic acid?
C-H-O-N-P
What are the elements in lipids?
C-H
What are the elements in carbohydrates?
C-H-O
What are the elements in proteins?
C-H-O-N
-a large molecule
Macromolecule
During metabolic processes, which macromolecule is primarily broken down to provide quick energy for the body?
Carbohydrates
Which of the following is NOT one of the four primary elements that make up all living organisms: carbon, phosphorus, hydrogen, oxygen
Phosphorus
At the planet’s beginning, what gas was missing from the atmosphere?
Oxygen
What element is primary for organic compounds due to the fact this element has four bonds?
Carbon
What substance is common between DNA and RNA?
Nitrogenous Base
Sugar, startch, and cellulose are examples of______
Carbbohydrates
Surcrose is an example of________
Disaccharides
Large and varied group of macromolecules that are generally not soluble in water is known as_______
Lipids
True or False: Enzymes slow the activation energy of a substrate
FALSE
Proteins are polymers of _____
Amino acids
Glucose is also reffered to as______
Blood sugar
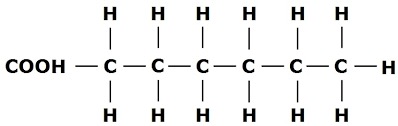
What typed of fatty acids is this?
Saturated
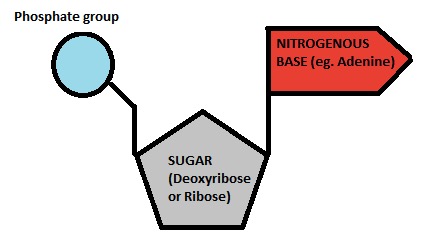
What macromolecue is shown?
Nucleic acid
What is the DNA sequence that is complimentary to the base sequence ACCGTAT
TGGCATA
Watson and Crick discovered that two strands of DNA join to form a______
Double helix
The process that makes an exact copy of a cell’s DNA is called____
Replication
When new DNA molecules are formed, almost all errors are detected and fixed by____
DNA polymerase
What is the main functions of DNA polymerase?
Binds nucleotides and corrects base pair errors
Which of the following events occurs directly after a DNA molecule is unzipped?
Free-floating nucleotides pair up with exposed bases
The central dogma of molecular biology states that information flows in one direction from_____
DNA to RNA to protiens
What is the nucleotide sequence of the RNA strand that would be complementary to the following DNA strand
CAUCAGU
The main function of tRNA is to____
Bring amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes
What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid
Codon
Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type?
Blood
What are examples of mutagens?
UV sunlight, alcohol, cigarette smoke
In humans, where does DNA replication take place?
Nucleus
During transcription, what does messenger RNA do?
It delivers DNA”S instructions for making proteins
DNA replication takes place during the ___ phase of _______ in the cell cycle
S, interphase
DNA is a polymer made of_____
Nucleotides
What is the role of deoxyribose and phosphate in the DNA molecule?
Form the spiraling double helix “backbone” of the moelcule
What is the role of the nitrogenous base in the DNA molecule?
Form the “rungs of the molecule”