geology exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:40 PM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
1
New cards
faults are example of what kind of rock deformation?
a. plastic
b. brittle
c. elastic
d. vitric
e. ductile
a. plastic
b. brittle
c. elastic
d. vitric
e. ductile
b. brittle
2
New cards

The wall of this quarry near Seneca Falls, New York, exposes a fault that cuts across bedding in the Onondaga Limestone. The fault has caused offset in the beds delineated by the pink and yellow lines. Based on looking at the offset of the beds, which type of fault is this?
a. strike-slip fault
b. thrust fault
c. normal fault
d. unconformity
a. strike-slip fault
b. thrust fault
c. normal fault
d. unconformity
b. thrust fault
3
New cards
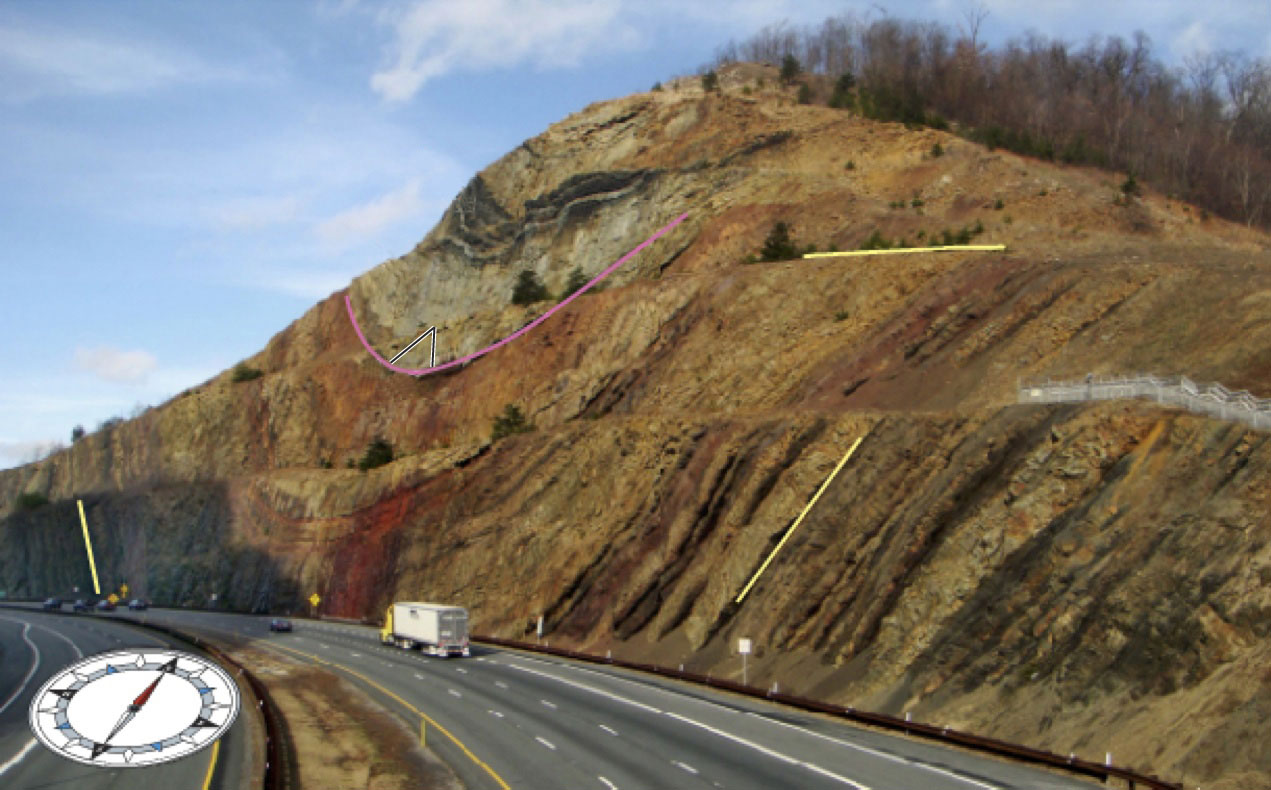

Sideling Hill, in western Maryland, is a northeast-southwest-trending ridge underlain by Paleozoic sandstone, shale, and coal. This fold formed due to the collision of Africa with North America. Note that the compass shown over the highway points approximately north. What kind of fold is this?
a. monocline
b. syncline
c. homocline
d. anticline
a. monocline
b. syncline
c. homocline
d. anticline
b. syncline
4
New cards
which statements are true about synclines?
a. they have an arch-like shape
b. they are the result of ductile deformation
c. they form from compressional stress
d. the limbs dip toward the hinge
a. they have an arch-like shape
b. they are the result of ductile deformation
c. they form from compressional stress
d. the limbs dip toward the hinge
b, c, d
5
New cards
Sort these mountain chains based on what caused them to form.
continential collision: alps, himalayas, appalachian
other causes: rockies
other causes: rockies
6
New cards
Sort outcomes related to either an increase in erosion or an increase in mountain building.
mountain building: continental crust thickens, asthenosphere is compressed, lithosphereic mantle sinks lower
erosion: continental crust thins
erosion: continental crust thins
7
New cards
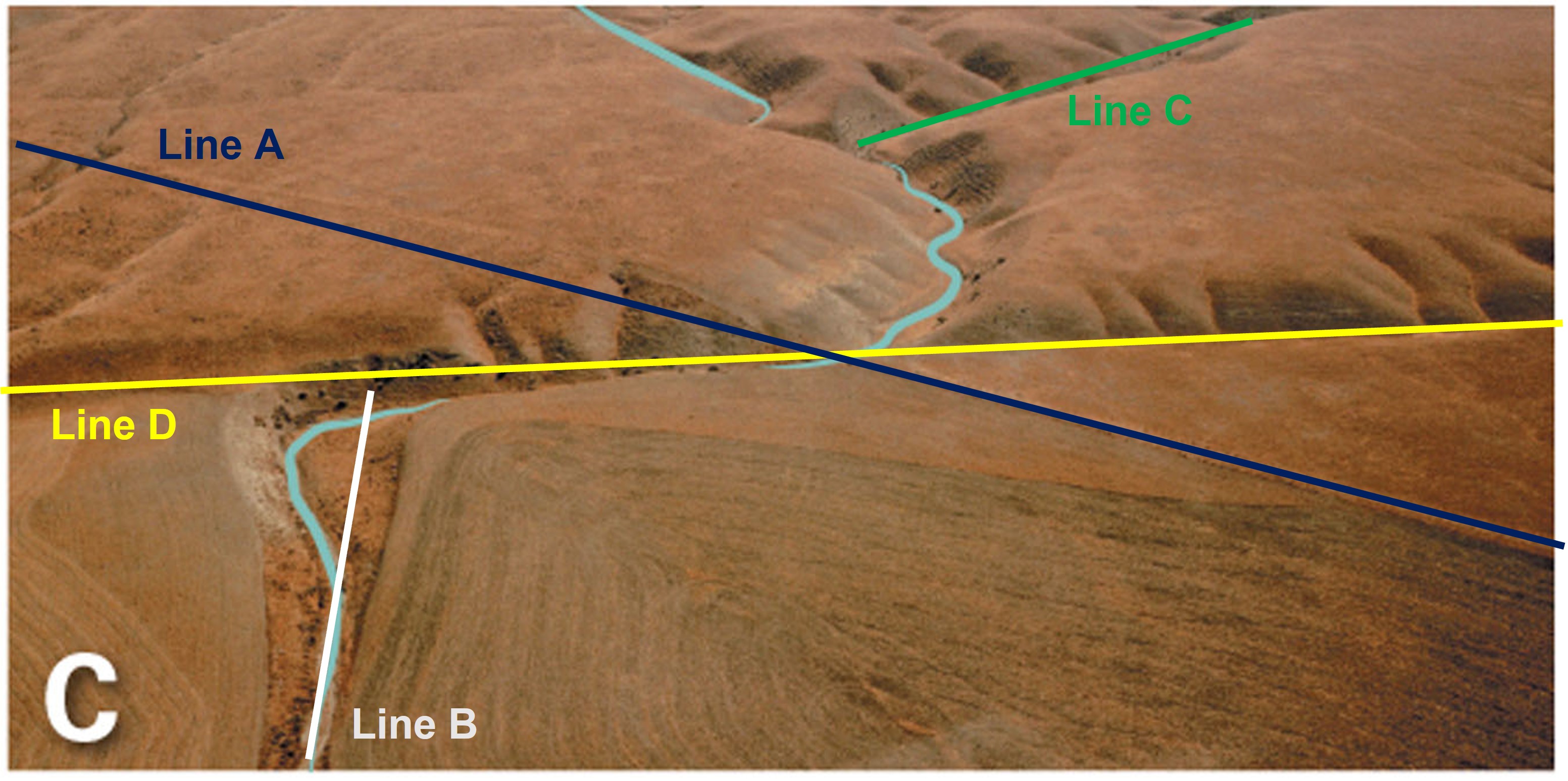
Which line on the annotated photo below represents the strike-slip fault?
a. line a
b. line b
c. line c
d. line d
a. line a
b. line b
c. line c
d. line d
d. line d
8
New cards
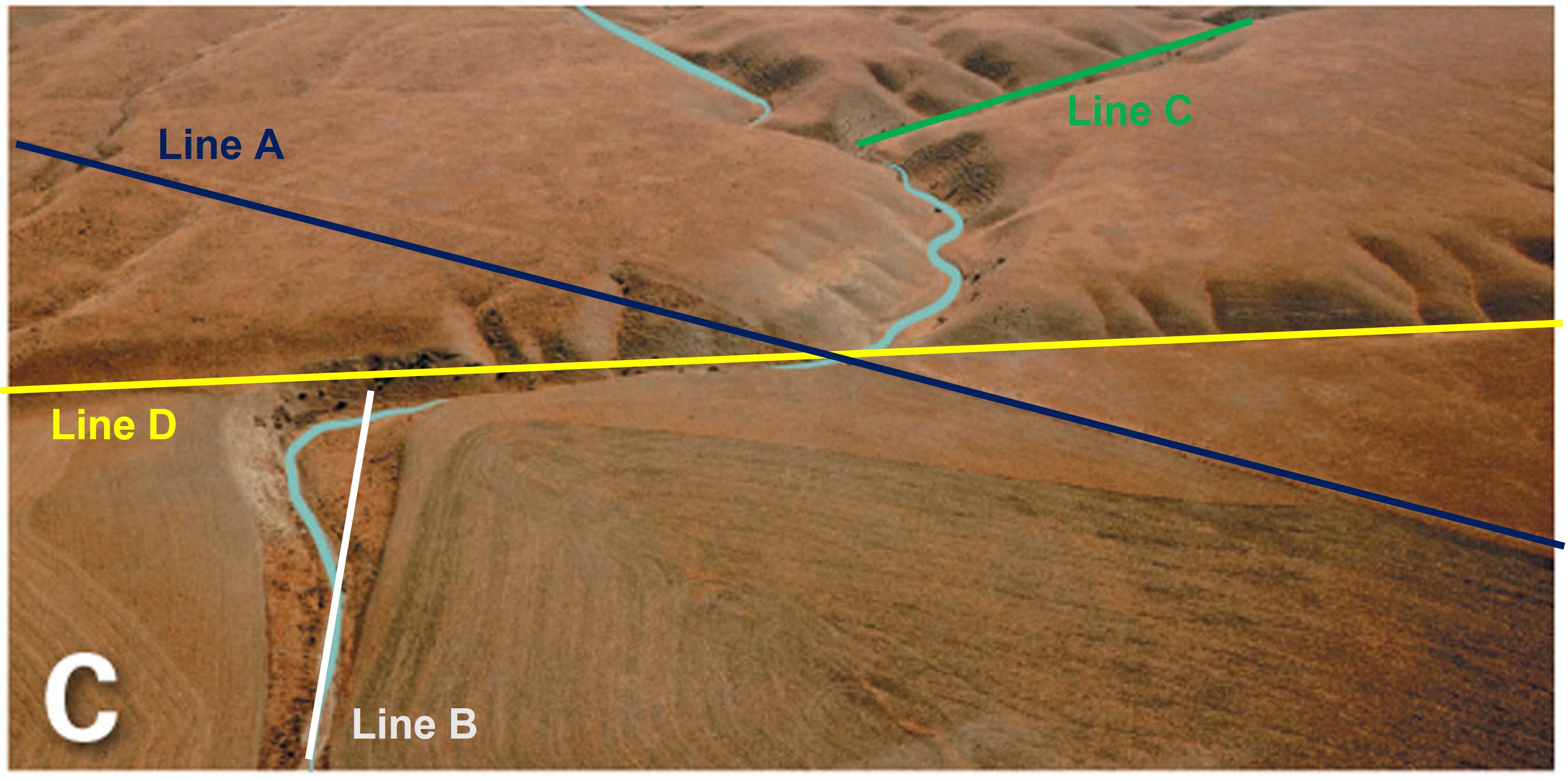
Does this strike-slip fault display left lateral slip or right lateral slip?
a. right lateral slip
b. left lateral slip
a. right lateral slip
b. left lateral slip
a. right lateral slip
9
New cards
which of the following terms refers to the process of mountain building?
a. brittle and ductile deformation
b. tectonic foliation
c. cratonic platform
d. orogeny
a. brittle and ductile deformation
b. tectonic foliation
c. cratonic platform
d. orogeny
d. orogeny
10
New cards
This image shows a fault exposed at the Yellow Mounds overview in Badlands National Park. Which of the following terms best describes this fault?
a. reverse fault
b. strike-slip fault
c. thrust fault
d. normal fault
a. reverse fault
b. strike-slip fault
c. thrust fault
d. normal fault
d. normal fault
11
New cards

In this picture, the top of two distinctive marker beds have been highlighted with purple and yellow lines. Choose the statement that best describes the fault.
a. this is a reverse fault, and the hanging wall moved up relative to the footwall
b. this is a normal fault, and the hanging wall moved down relative to the footwall
c. the sense of motion cannot be determined from this image
a. this is a reverse fault, and the hanging wall moved up relative to the footwall
b. this is a normal fault, and the hanging wall moved down relative to the footwall
c. the sense of motion cannot be determined from this image
a. this is a reverse fault, and the hanging wall moved up relative to the footwall
12
New cards
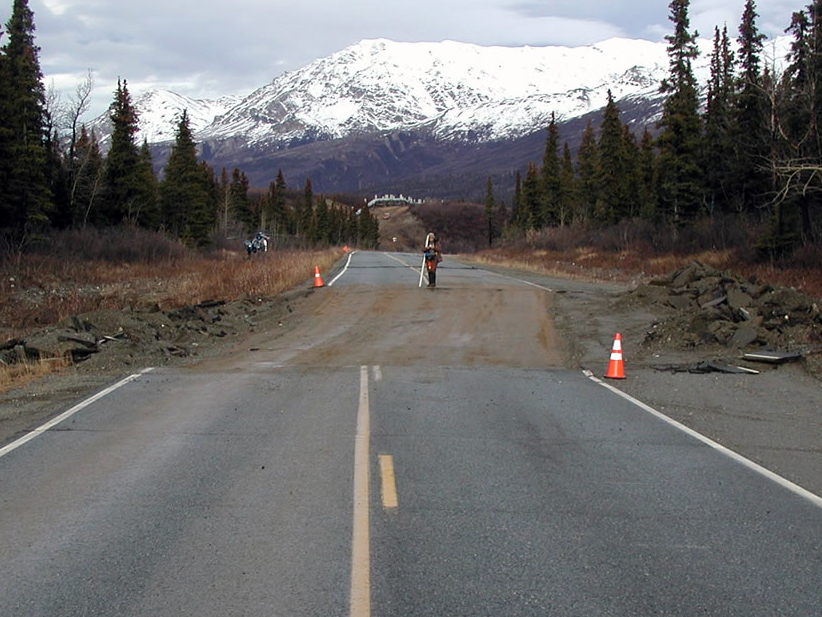

The image shows more than 8 feet of offset on the Richardson Highway in Alaska that resulted from a magnitude 7.9 earthquake along the Denali Fault in 2002. Notice the Trans Alaska Pipeline in the background. This type of offset suggests that what type of fault motion occurred in this area?
a. left-lateral strike-slip fault
b. normal faulting
c. right-lateral strike-slip faulting
d. thrust faulting
a. left-lateral strike-slip fault
b. normal faulting
c. right-lateral strike-slip faulting
d. thrust faulting
c. right-lateral strike-slip faulting
13
New cards
This satellite image shows the Himalaya Mountains, the tallest mountain range on Earth, and the Tibet Plateau. Which of the following processes is responsible for the formation of the mountains in this region?
a. thickening of the crust caused by deformation during collision
b. displacement on a large strike-slip fault
c. thinning of the crust due to stretching in a broad rift
d. formation of a passive margin basin due to cooling of the lithosphere
a. thickening of the crust caused by deformation during collision
b. displacement on a large strike-slip fault
c. thinning of the crust due to stretching in a broad rift
d. formation of a passive margin basin due to cooling of the lithosphere
a. thickening of the crust caused by deformation during collision
14
New cards
Which of the following conditions will tend to make rocks change by plastic (or ductile) deformation rather than by brittle deformation?
a. slowly applied stress
b. granitic composition
c. cool surroundings
d. pressure fairly close to the Earth’s surface
a. slowly applied stress
b. granitic composition
c. cool surroundings
d. pressure fairly close to the Earth’s surface
a. slowly applied stress
15
New cards
brittle deformation…
a. is more likely to occur deep in the crust than at the surface
b. occurs when many atomic bonds are broken quickly and rock pieces separate
c. is favored by high-temperature, high-pressure conditions
d. produces folds, like anticlines
a. is more likely to occur deep in the crust than at the surface
b. occurs when many atomic bonds are broken quickly and rock pieces separate
c. is favored by high-temperature, high-pressure conditions
d. produces folds, like anticlines
b. occurs when many atomic bonds are broken quickly and rock pieces separate
16
New cards
a shield…
a. is the same thing as a cratonic platform
b. is not part of a craton
c. has Precambrian metamorphic and igneous rocks at its surface
d. has layers of undeformed sedimentary rock that are extremely old
a. is the same thing as a cratonic platform
b. is not part of a craton
c. has Precambrian metamorphic and igneous rocks at its surface
d. has layers of undeformed sedimentary rock that are extremely old
c. has Precambrian metamorphic and igneous rocks at its surface
17
New cards
How is a fault different from a joint?
a. joints are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along faults
b. faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along joints
c. faults are joints that are larger than a square meter in area
d. there is no difference; the 2 terms are synonymous
a. joints are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along faults
b. faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along joints
c. faults are joints that are larger than a square meter in area
d. there is no difference; the 2 terms are synonymous
b. faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred; displacement does not occur along joints
18
New cards
Given the relationships shown in the block, what is the relative age of the features labeled, from oldest to youngest?
sedimentary rocks → pluton → fault → dike
19
New cards
The image shows an outcrop of granite and basalt with a pink area between them that records contact metamorphism. Use the concepts of inclusions and baked contacts to select which of the following statements best describes the relative age relationship between the granite and basalt.
a. the granite is older than the basalt
b. it is impossible to determine which rock is older
c. the basalt is older than the granite
a. the granite is older than the basalt
b. it is impossible to determine which rock is older
c. the basalt is older than the granite
a. the granite is older than the basalt
20
New cards
This outcrop of Precambrian and Paleozoic rocks in northern Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, provides a great example of the kinds of relative age relationships that geologists observe in the field. Put the features in order from oldest (bottom) to youngest (top). The rocks have not been overturned.
fault → conglomerate → mafic intrustion → felsic crystalline rocks
21
New cards
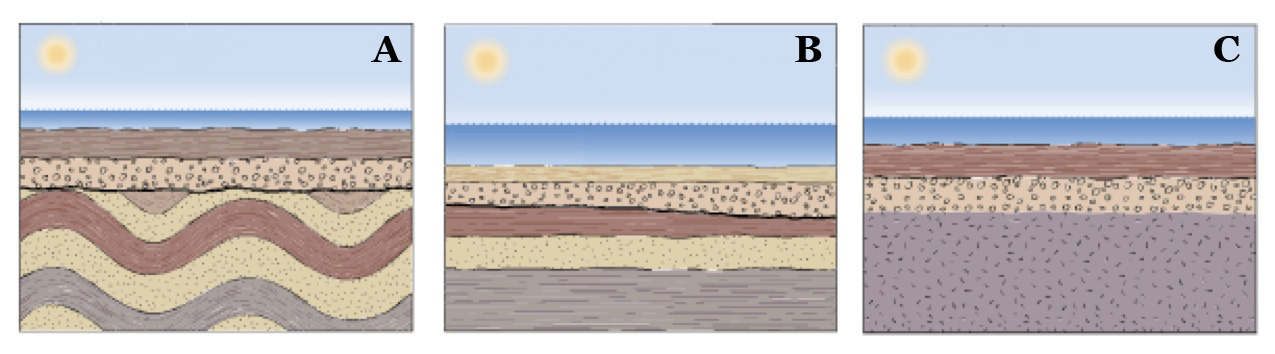
Unconformities develop when new sedimentary layers accumulate atop old, eroded layers, resulting in a geologic hiatus. Which of the illustration represents a disconformity?
a. illustration a
b. illustration b
c. illustration c
a. illustration a
b. illustration b
c. illustration c
b. illustration b
22
New cards
Order the steps in the formation of a disconformity.
sediments were deposited in a marine environment → sea level fell, exposing marine deposits subaerially → erosion took place → sea level rose, covering the erosional surface, which was buried by marine sediments
23
New cards
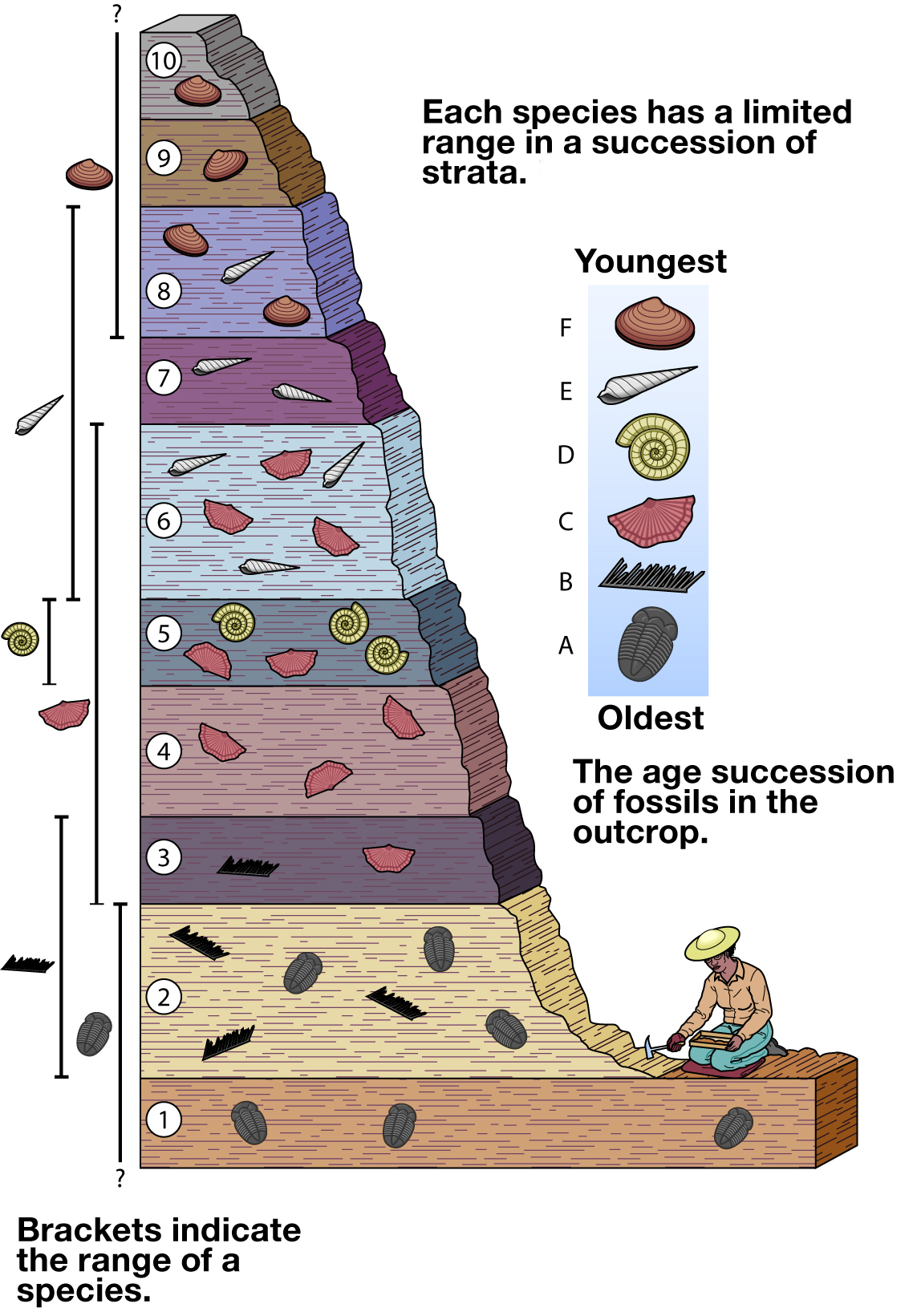
Below is an image of fossils found in an outcrop. A limestone in another outcrop 150 miles away contains fossils C and E. Which bed (labeled 1 through 10 on the image) does this limestone correlate to?
bed 6
24
New cards
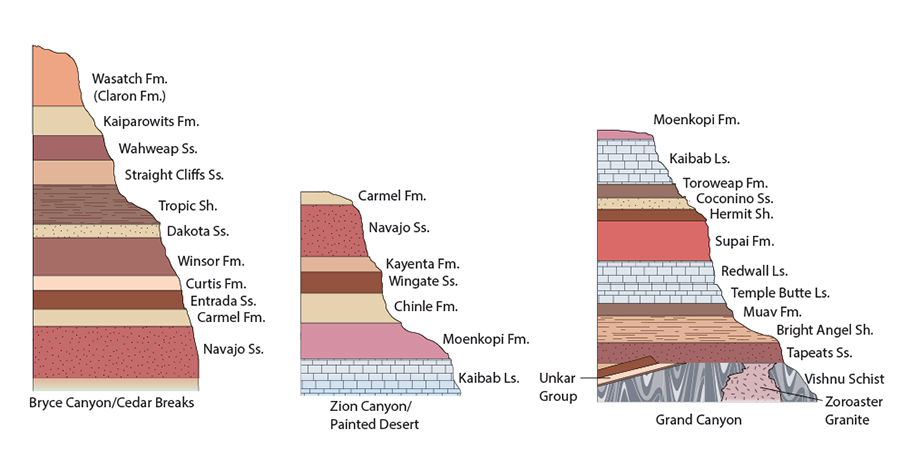
Use the above drawings of stratigraphic columns in Bryce Canyon/Cedar Breaks, Zion Canyon/Painted Desert, and the Grand Canyon area, and the principles of cross correlation, to place the geologic formation in time order.
dakota sandstone → curtis formation → wingate sandstone → supai formation → zoroaster granite → vishnu schist
25
New cards
Put the names from the geologic column in order from oldest at the bottom to youngest at the top.
Cenozoic → Mesozoic → Paleozoic → Precambrian
26
New cards
Why are geologists not able to date sedimentary rocks directly?
a. sedimentary rocks are too fine-grained to accurately date
b. sedimentary rocks are too coarse-grained to accurately date
c. sedimentary rocks are older than their composite materials
d. sedimentary rocks are younger than their composite materials
a. sedimentary rocks are too fine-grained to accurately date
b. sedimentary rocks are too coarse-grained to accurately date
c. sedimentary rocks are older than their composite materials
d. sedimentary rocks are younger than their composite materials
d. sedimentary rocks are younger than their composite materials
27
New cards
Relative age describes __________.
a. the numerical age of a geological feature
b. the age of one geologic feature with respect to another in a sequence
c. how geologists determine the rates of erosion and deposition of sediment
d. the geochemical relationship between 2 geologic features
a. the numerical age of a geological feature
b. the age of one geologic feature with respect to another in a sequence
c. how geologists determine the rates of erosion and deposition of sediment
d. the geochemical relationship between 2 geologic features
b. the age of one geologic feature with respect to another in a sequence
28
New cards
This outcrop photo shows two features, layers of limestone and a basalt dike. Which feature is older?
a. they are the same age
b. limestone layers
c. basalt dike
a. they are the same age
b. limestone layers
c. basalt dike
b. limestone layers
29
New cards
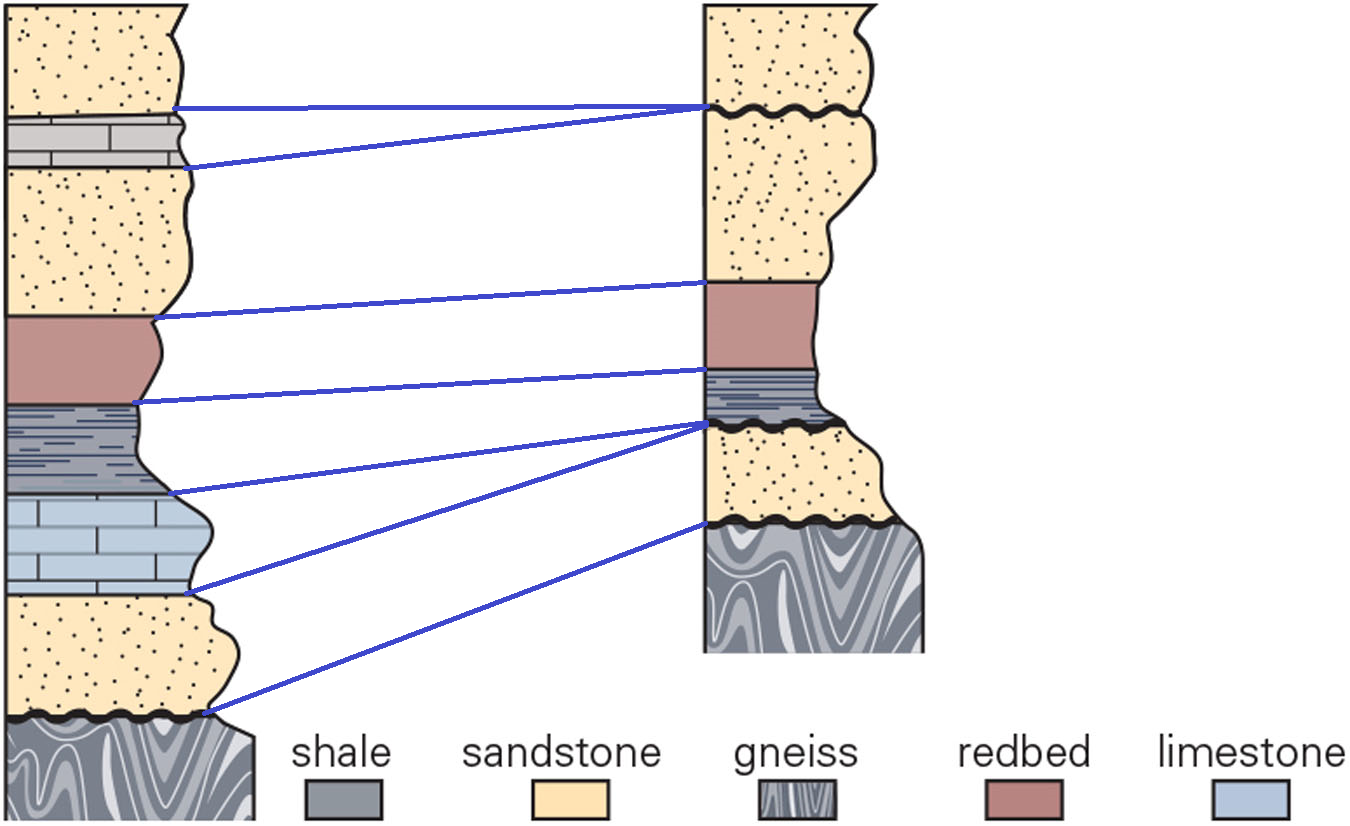
Which interpretation best correlates the left column with the right column? What do the wavy horizontal lines represent?
b. unconformities
30
New cards
Why can radioisotopic dating methods be used to determine the numerical age of igneous rocks but not of sedimentary rocks?
a. minerals will recrystallize during lithification, altering the radiometric isotopes of the rock
b. sedimentary rocks are too fine-grained to utilize radiometric dating
c. numerical ages of minerals in sedimentary rocks provide the age the minerals crystallized in their original rock
d. minerals in sedimentary rocks do not contain radiometric isotopes that can be used to determine numerical ages
a. minerals will recrystallize during lithification, altering the radiometric isotopes of the rock
b. sedimentary rocks are too fine-grained to utilize radiometric dating
c. numerical ages of minerals in sedimentary rocks provide the age the minerals crystallized in their original rock
d. minerals in sedimentary rocks do not contain radiometric isotopes that can be used to determine numerical ages
c. numerical ages of minerals in sedimentary rocks provide the age the minerals crystallized in their original rock
31
New cards
What does the term *uniformitarianism* mean?
a. all of the possible answers are correct
b. we can interpret the processes that formed ancient rock by examining the processes that form similar rock today
c. the physical processes on Earth today are different from those in the past
d. the Earth’s surface is unchanging
a. all of the possible answers are correct
b. we can interpret the processes that formed ancient rock by examining the processes that form similar rock today
c. the physical processes on Earth today are different from those in the past
d. the Earth’s surface is unchanging
b. we can interpret the processes that formed ancient rock by examining the processes that form similar rock today
32
New cards
Which of the following statements is true?
a. a paleosol is a rock layer identified by such factors as a rock type and approximate geologic age
b. an unconformity is a break in the rock record indicating that the area was underwater for millions of years
c. the generally accepted age of the Earth is 4.56 million years
d. varieties of an element that differ only in the number of neutrons are called isotopes
a. a paleosol is a rock layer identified by such factors as a rock type and approximate geologic age
b. an unconformity is a break in the rock record indicating that the area was underwater for millions of years
c. the generally accepted age of the Earth is 4.56 million years
d. varieties of an element that differ only in the number of neutrons are called isotopes
d. varieties of an element that differ only in the number of neutrons are called isotopes
33
New cards
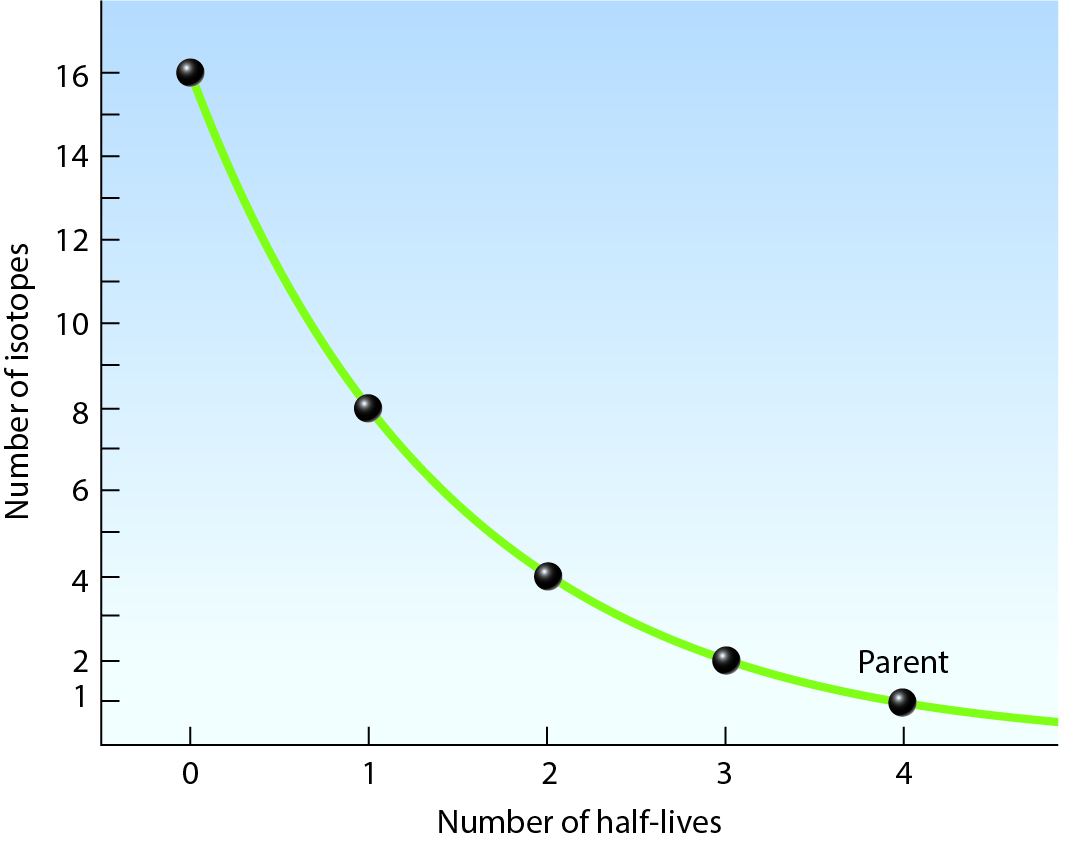
In the diagram shown,
a. if the half-life of the parent material is 4000 years, 3 on the horizontal axis pf the graph represents 120000 years
b. in 2 g of parent material is present after three half-lives, 6 g of daughter material will also be present
c. equal amounts of parent and daughter material are present after the passage of 2 half-lives
d. the area above the curve represents the amount of parent material present
a. if the half-life of the parent material is 4000 years, 3 on the horizontal axis pf the graph represents 120000 years
b. in 2 g of parent material is present after three half-lives, 6 g of daughter material will also be present
c. equal amounts of parent and daughter material are present after the passage of 2 half-lives
d. the area above the curve represents the amount of parent material present
a. if the half-life of the parent material is 4000 years, 3 on the horizontal axis pf the graph represents 120000 years
34
New cards
Charcoal (burned wood) that was used to make prehistoric drawings on cave walls in France was scraped off and analyzed. The results showed 4 mg carbon-14 (parent isotope) and 60 mg nitrogen-14 (daughter isotope). The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years. How old are the cave drawings?
a. 22920
b. the sample is too old to be analyzed by carbon dating
c. 11460
d. 17190
a. 22920
b. the sample is too old to be analyzed by carbon dating
c. 11460
d. 17190
a. 22920
35
New cards
What type of unconformity occurs when sedimentary rocks overlie either igneous or metamorphic rocks?
a. disconformity
b. angular unconformity
c. baked contact
d. nonconformity
a. disconformity
b. angular unconformity
c. baked contact
d. nonconformity
d. nonconformity
36
New cards
The principle of lateral continuity says that
a. the feature doing the cutting is younger than the feature it cuts
b. rocks containing inclusions is younger than the inclusions
c. in a sequence of sedimentary beds, the oldest on the bottom
d. sedimentary layers began as continuous expanses of sediment
a. the feature doing the cutting is younger than the feature it cuts
b. rocks containing inclusions is younger than the inclusions
c. in a sequence of sedimentary beds, the oldest on the bottom
d. sedimentary layers began as continuous expanses of sediment
d. sedimentary layers began as continuous expanses of sediment
37
New cards
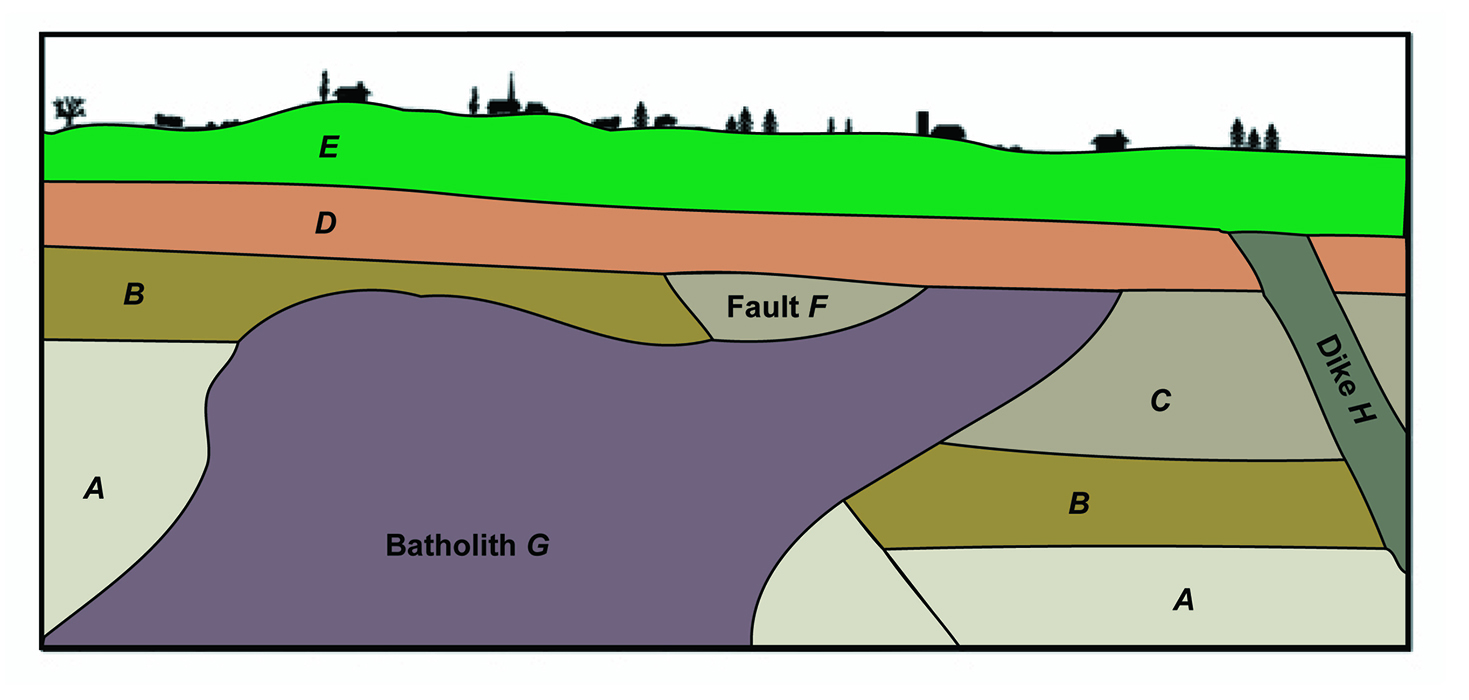
Place the units shown in the diagram into their order of occurrence by dragging labels into the correct position in the ranking (youngest at the top; oldest at the bottom).
bed e → dike h → batholith g → fault f → bed a
38
New cards
rank the three types of sediment load in a stream from smallest to largest
dissolved load → suspended load → bed load
39
New cards
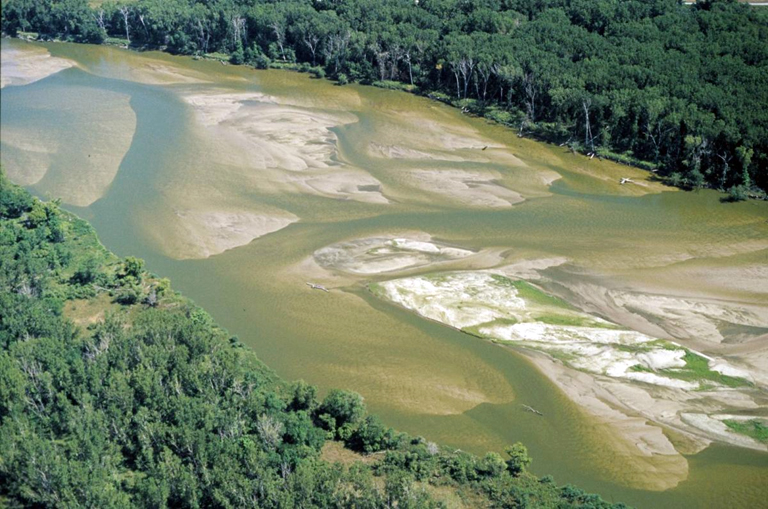

This image shows the Platte River in eastern Nebraska. Which of the following terms best describes the morphology of this stream?
a. braided river
b. delta
c. meandering river
d. alluvial fan
a. braided river
b. delta
c. meandering river
d. alluvial fan
a. braided river
40
New cards
Sort the following characteristics of cut banks and point bars.
cut bank - outer bank, erosion dominates, faster flow velocities
point bar - inner bank
point bar - inner bank
41
New cards
Which illustration correctly depicts the way the river will migrate over time?
\
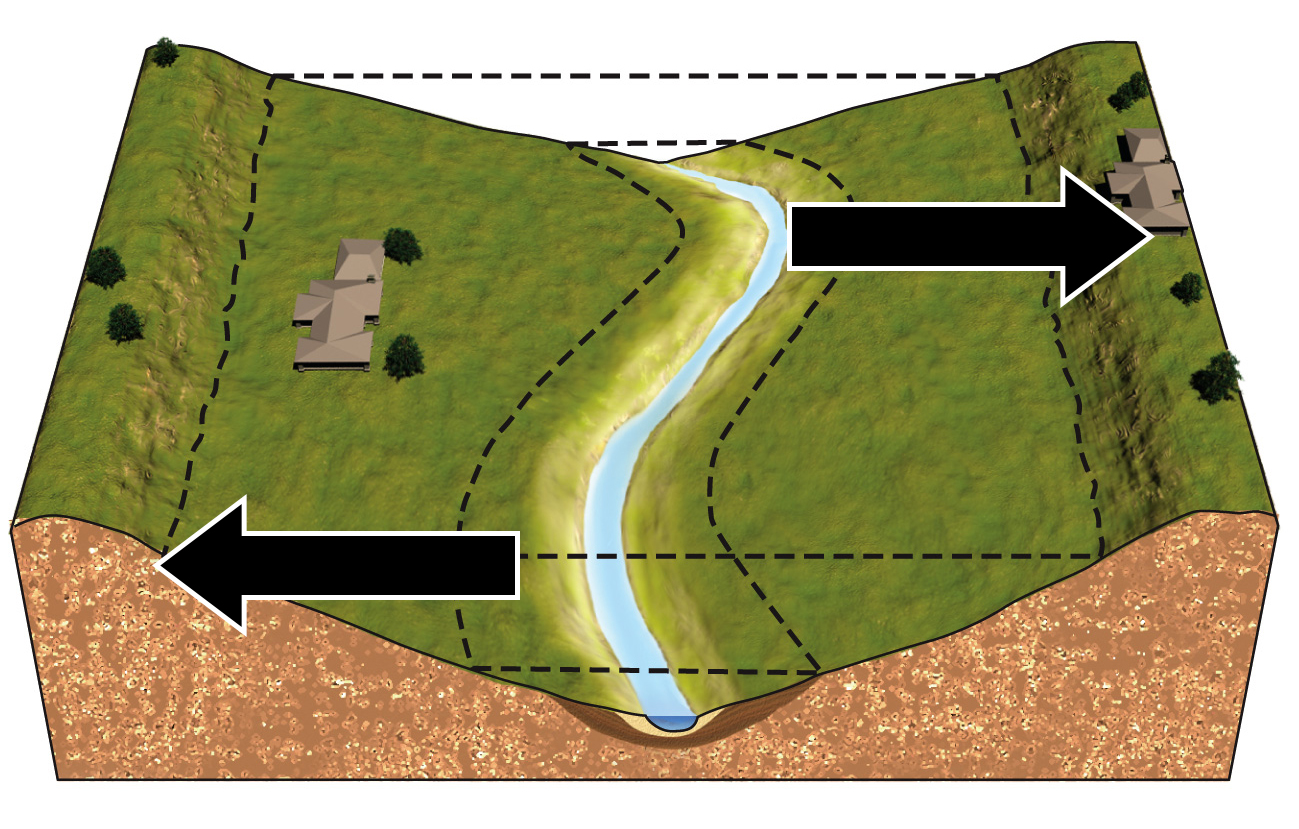
42
New cards
While flash floods can take place in any climate, they are especially dramatic in which type of climate?
a. polar, tundra
b. dry, arid
c. mild, humid, subtropical
d. tropical, wet
a. polar, tundra
b. dry, arid
c. mild, humid, subtropical
d. tropical, wet
b. dry, arid
43
New cards
What is the probability that a 100-year flood will occur in any given year?
a. 0.01%
b. 1%
c. 10%
d. 100%
a. 0.01%
b. 1%
c. 10%
d. 100%
b. 1%
44
New cards
Which of the following describes a braided stream?
a. a stream with no sediment being transported
b. a stream that has a series of waterfalls and rapids
c. a stream that is divided into numerous strands weaving back and forth
d. a stream with a single channel that winds its way across the landscape
a. a stream with no sediment being transported
b. a stream that has a series of waterfalls and rapids
c. a stream that is divided into numerous strands weaving back and forth
d. a stream with a single channel that winds its way across the landscape
c. a stream that is divided into numerous strands weaving back and forth
45
New cards
What causes a braided stream to form?
a. an extremely low gradient causes the channel to cut horizontally into the landscape
b. a stream channel dries up, leaving behind a channel of sediment
c. an intense amount of runoff enters a stream during a storm
d. abundant coarse sediment chokes the channel and prevents the formation of steep banks
a. an extremely low gradient causes the channel to cut horizontally into the landscape
b. a stream channel dries up, leaving behind a channel of sediment
c. an intense amount of runoff enters a stream during a storm
d. abundant coarse sediment chokes the channel and prevents the formation of steep banks
d. abundant coarse sediment chokes the channel and prevents the formation of steep banks
46
New cards
Which of the following statements about the hydrologic cycle is true?
a. surface snow and ice are not part of this cycle
b. headward erosion causes sheetwash
c. water that manages to infiltrate the land is lost in the cycle
d. there is an exchange of water among oceans, land, and atmosphere
a. surface snow and ice are not part of this cycle
b. headward erosion causes sheetwash
c. water that manages to infiltrate the land is lost in the cycle
d. there is an exchange of water among oceans, land, and atmosphere
d. there is an exchange of water among oceans, land, and atmosphere
47
New cards
Identify the statement that is true about an ephemeral stream.
a. in dry climates, it can become a dry wash
b. it is replenished by both precipitation and groundwater
c. it flows year-round
d. its bed lies below the water table
a. in dry climates, it can become a dry wash
b. it is replenished by both precipitation and groundwater
c. it flows year-round
d. its bed lies below the water table
a. in dry climates, it can become a dry wash
48
New cards
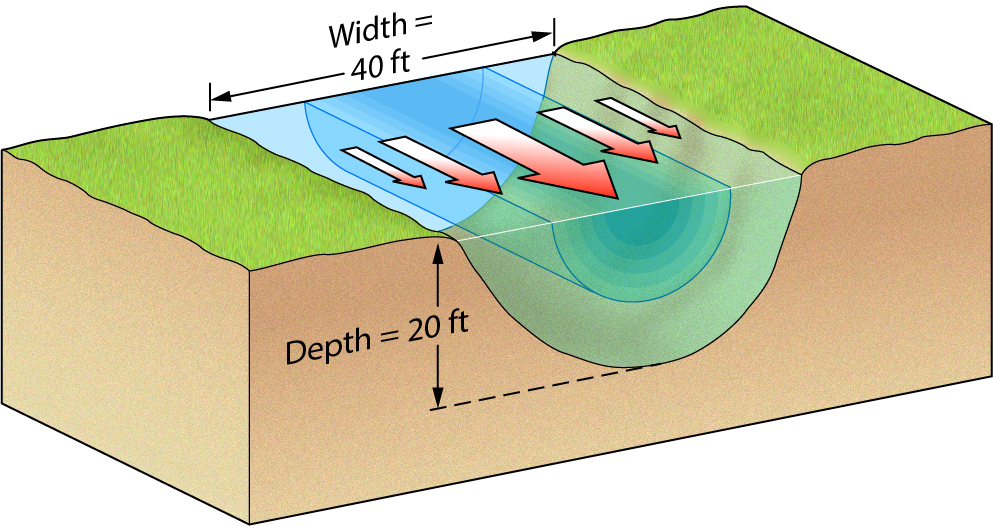
The stream in this diagram flows at a velocity of 6 feet per second. Its discharge is
a. 120 cubic feet per second
b. 240 cubic feet per second
c. 66 cubic feet per second
d. 4800 cubic feet per second
a. 120 cubic feet per second
b. 240 cubic feet per second
c. 66 cubic feet per second
d. 4800 cubic feet per second
d. 4800 cubic feet per second
49
New cards
The discharge of a stream is
a. calculated by dividing its cross-sectional area by its velocity
b. constant for the length of the stream
c. typically lower in the spring than during the summer
d. likely to decrease downstream in arid regions and increase downstream in temperate regions
a. calculated by dividing its cross-sectional area by its velocity
b. constant for the length of the stream
c. typically lower in the spring than during the summer
d. likely to decrease downstream in arid regions and increase downstream in temperate regions
d. likely to decrease downstream in arid regions and increase downstream in temperate regions
50
New cards
The total sediment load of a stream includes
a. dissolved load
b. bed load
c. suspended, bed, and dissolved loads
d. suspended load
a. dissolved load
b. bed load
c. suspended, bed, and dissolved loads
d. suspended load
c. suspended, bed, and dissolved loads
51
New cards
Which of the following statements is true?
a. a stream with a single channel is called a braided stream.
b. all of the possible answers are correct
c. a meander bed that gets but off from the main channel becomes an oxbow lake
d. a meandering stream has many active channels flowing at once
a. a stream with a single channel is called a braided stream.
b. all of the possible answers are correct
c. a meander bed that gets but off from the main channel becomes an oxbow lake
d. a meandering stream has many active channels flowing at once
c. a meander bed that gets but off from the main channel becomes an oxbow lake
52
New cards
Identify the true statement.
a. A 200-year flood has a recurrence interval of, on the average, once every 200 years.
b. An annual probability of 4% means that there's a 1 in 4 chance that a flood of some given size will happen in any given year.
c. The size of a flood and its recurrence interval are inversely related; the larger the flood, the shorter its recurrence interval.
d. Two 100-year floods cannot occur in the same year (or in consecutive years).
a. A 200-year flood has a recurrence interval of, on the average, once every 200 years.
b. An annual probability of 4% means that there's a 1 in 4 chance that a flood of some given size will happen in any given year.
c. The size of a flood and its recurrence interval are inversely related; the larger the flood, the shorter its recurrence interval.
d. Two 100-year floods cannot occur in the same year (or in consecutive years).
a. A 200-year flood has a recurrence interval of, on the average, once every 200 years.
53
New cards
Identify the true statement.
a. a 100-year flood has a 1% chance of occuring in any given year
b. two 100-year floods cannot occur in the same year or in consecutive years
c. an annual probability of 4% means that there's a 1 in 4 chance that a flood of some given size will happen in any given year.
d. the size of a flood and its recurrence interval are inversely related; the larger the flood, the shorter its recurrence interval.
a. a 100-year flood has a 1% chance of occuring in any given year
b. two 100-year floods cannot occur in the same year or in consecutive years
c. an annual probability of 4% means that there's a 1 in 4 chance that a flood of some given size will happen in any given year.
d. the size of a flood and its recurrence interval are inversely related; the larger the flood, the shorter its recurrence interval.
a. a 100-year flood has a 1% chance of occuring in any given year
54
New cards
Identify the statement that best describes the effects of urbanization on stream flow as shown in these two diagrams.
a. flooding potential for a stream is less after urbanization than before
b. diagram a illustrates that there is more infiltration after urbanization, and therefore less water reaches the stream channel
c. diagram b shows a stream responding faster and more intensely to a rainfall event
d. diagram a shows water from the storm getting into the stream channel faster than it does in Diagram B.
a. flooding potential for a stream is less after urbanization than before
b. diagram a illustrates that there is more infiltration after urbanization, and therefore less water reaches the stream channel
c. diagram b shows a stream responding faster and more intensely to a rainfall event
d. diagram a shows water from the storm getting into the stream channel faster than it does in Diagram B.
c. diagram b shows a stream responding faster and more intensely to a rainfall event
55
New cards
Evapotranspiration
a. describes the release of water to the atmosphere from the surface, plants, or animals
b. is a form of precipitation
c. only occurs in the ocean
d. is when evaporation transpires
a. describes the release of water to the atmosphere from the surface, plants, or animals
b. is a form of precipitation
c. only occurs in the ocean
d. is when evaporation transpires
a. describes the release of water to the atmosphere from the surface, plants, or animals
56
New cards
What percentage of the water on Earth is available for human consumption?
a. 1%
b. 0.88%
c. 99%
d. 2.5%
a. 1%
b. 0.88%
c. 99%
d. 2.5%
a. 1%
57
New cards
What percentage of the water available for human consumption is trapped in void spaces in the subsurface?
a. 0.88%
b. 1%
c. 99%
d. 30.1%
a. 0.88%
b. 1%
c. 99%
d. 30.1%
c. 99%
58
New cards
This image shows artificial ponds in the San Francisco Bay that are used to produce salt. The orange color comes from algae and brine shrimp that thrive in the ponds during the early stages of the process; the white material is salt that is almost ready to be collected. Which of the following parts of the hydrologic cycle causes the salt to become concentrated in these ponds?
a. transpiration
b. condensation
c. precipitation
d. infiltration
e. evaporation
a. transpiration
b. condensation
c. precipitation
d. infiltration
e. evaporation
e. evaporation
59
New cards
Rank the following reservoirs in order of the amount of freshwater they store in the hydrologic cycle.
polar ice caps, snow caps, and glaciers → oceans, rivers, and lakes → the atmosphere, including clouds, ice crystals, and water vapor
60
New cards
Which of these are characteristics of either porosity or permeability?
a. permeability is the same thing as secondary porosity
b. porosity is a measure of the amount of the substance composed of empty spaces
c. permeability is a measure of how well the pores are connected
d. porosity describes the ability of pores to form conduits though the material
a. permeability is the same thing as secondary porosity
b. porosity is a measure of the amount of the substance composed of empty spaces
c. permeability is a measure of how well the pores are connected
d. porosity describes the ability of pores to form conduits though the material
b and c
61
New cards
Which of the following statements is true about lakes?
a. the presence of a lake indicates a lack of groundwater in a region
b. the surface of a lake corresponds to the surface of the groundwater table nearby
c. the bottom of a lake bed represents the groundwater table in the region
d. a lake is surface water; it is not associated with groundwater
a. the presence of a lake indicates a lack of groundwater in a region
b. the surface of a lake corresponds to the surface of the groundwater table nearby
c. the bottom of a lake bed represents the groundwater table in the region
d. a lake is surface water; it is not associated with groundwater
b. the surface of a lake corresponds to the surface of the groundwater table nearby
62
New cards
How does the rate of groundwater flow compare with that of ocean currents or river currents?
a. the rate of groundwater flow is about the same speed as that of surface-water currents
b. the rate of groundwater flow is slower than that of surface-water currents
c. the rate of groundwater flow can be faster or slower than that of surface-water currents, depending on conditions
d. the rate of groundwater flow is faster than that of surface-water currents
a. the rate of groundwater flow is about the same speed as that of surface-water currents
b. the rate of groundwater flow is slower than that of surface-water currents
c. the rate of groundwater flow can be faster or slower than that of surface-water currents, depending on conditions
d. the rate of groundwater flow is faster than that of surface-water currents
b. the rate of groundwater flow is slower than that of surface-water currents
63
New cards
The flow of water from an above-ground storage tank to a faucet in your house is most analogous to which of the following systems?
a. ordinary well
b. flowing artesian well
c. nonflowing artesian well
d. spring formed where an impermeable layer intersects the ground
a. ordinary well
b. flowing artesian well
c. nonflowing artesian well
d. spring formed where an impermeable layer intersects the ground
b. flowing artesian well
64
New cards
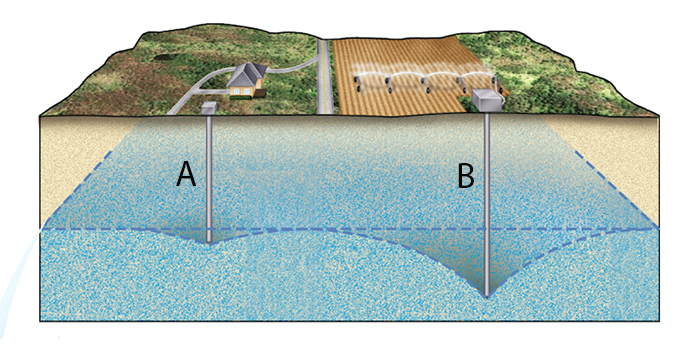
Which of the following statements accurately describe what is happening in the subsurface?
a. continued pumping of well a will cause the water table to rise
b. water is being injected into the subsurface though well b
c. well a will run dry before well b
d. the size of the cone of depression is primarily a function of pumping rate
e. well b will run dry before well a
f. the size of the cone of depression is a function only of well depth
a. continued pumping of well a will cause the water table to rise
b. water is being injected into the subsurface though well b
c. well a will run dry before well b
d. the size of the cone of depression is primarily a function of pumping rate
e. well b will run dry before well a
f. the size of the cone of depression is a function only of well depth
c and d
65
New cards
Identify possible consequences of rapid groundwater withdrawal.
a. a cone of depression forms
b. wells go dry
c. pore collapse occurs
d. swamps form
a. a cone of depression forms
b. wells go dry
c. pore collapse occurs
d. swamps form
a, b, and c
66
New cards
Upon seeing this photograph of karst topography, one could infer that
a. there are faults in the region
b. solution caves have formd below the ground
c. the region most likely has extensive limestone layers
d. the area is tectonically active
a. there are faults in the region
b. solution caves have formd below the ground
c. the region most likely has extensive limestone layers
d. the area is tectonically active
b and c
67
New cards
Consider Darcy's law. If a hydraulic gradient becomes steeper and conductivity increases, what happens to the rate of flow?
a. the rate of flow would decrease
b. flow rate will either increase or decrease depending on the difference between the hydraulic gradient and the hydraulic conductivity
c. the rate of flow would increase
d. the steeper gradient increases flow rate, but the increased conductivity decreases flow rate. so there would be no change
a. the rate of flow would decrease
b. flow rate will either increase or decrease depending on the difference between the hydraulic gradient and the hydraulic conductivity
c. the rate of flow would increase
d. the steeper gradient increases flow rate, but the increased conductivity decreases flow rate. so there would be no change
c. the rate of flow would increase
68
New cards
Porosity decreases
a. as sedimentary rock weathers
b. with decreasing compaction of sediments
c. with the cementing of sediments by mineral grains from groundwater
d. when rocks develop joint or faults
a. as sedimentary rock weathers
b. with decreasing compaction of sediments
c. with the cementing of sediments by mineral grains from groundwater
d. when rocks develop joint or faults
c. with the cementing of sediments by mineral grains from groundwater
69
New cards
Which of the following sedimentary units would have the highest primary porosity?
a. conglomerate
b. poorly sorted sandstone
c. fractured shale
d. crystalline limestone
a. conglomerate
b. poorly sorted sandstone
c. fractured shale
d. crystalline limestone
a. conglomerate
70
New cards
the water table…
a. rises to higher elevation around the bottom of a well
b. mimics the topography of the land it underlies
c. lies within a few meters of the surface in arid areas
d. is always located beneath the ground surface
a. rises to higher elevation around the bottom of a well
b. mimics the topography of the land it underlies
c. lies within a few meters of the surface in arid areas
d. is always located beneath the ground surface
b. mimics the topography of the land it underlies
71
New cards
water underground that
a. seeps up from the water table because of the electrostatic attraction of water molecules to mineral surfaces is called phreatic-zone water
b. partially fills pores in the unsaturated zone is called capillary fringe
c. completely fills pores in the saturated zone is called groundwater
d. adheres temporarily to sediment particles and evaporates back into the atmosphere or is absorbed by plant roots is called groundwater
a. seeps up from the water table because of the electrostatic attraction of water molecules to mineral surfaces is called phreatic-zone water
b. partially fills pores in the unsaturated zone is called capillary fringe
c. completely fills pores in the saturated zone is called groundwater
d. adheres temporarily to sediment particles and evaporates back into the atmosphere or is absorbed by plant roots is called groundwater
c. completely fills pores in the saturated zone is called groundwater
72
New cards
the rate of groundwater flow
a. depends on the permeability of the material it flows through and on the hydraulic gradient
b. typically varies between 4 and 500 miles per year
c. is comparable to the rate of flow in an average surface stream
d. is determined theoretically; it can’t be measured, since it happens underground
a. depends on the permeability of the material it flows through and on the hydraulic gradient
b. typically varies between 4 and 500 miles per year
c. is comparable to the rate of flow in an average surface stream
d. is determined theoretically; it can’t be measured, since it happens underground
a. depends on the permeability of the material it flows through and on the hydraulic gradient
73
New cards
darcy’s law
a. cannot be used to decide practical issues, such as whether sufficient groundwater exists to supply a city’s needs
b. states that discharge equals the hydraulic conductivity coefficient multiplied by the hydraulic gradient multiplied by the area involved
c. is method to determine the degree of water saturation at any specified depth
d. is used to theoretically model the direction of groundwater flow in an aquifer
a. cannot be used to decide practical issues, such as whether sufficient groundwater exists to supply a city’s needs
b. states that discharge equals the hydraulic conductivity coefficient multiplied by the hydraulic gradient multiplied by the area involved
c. is method to determine the degree of water saturation at any specified depth
d. is used to theoretically model the direction of groundwater flow in an aquifer
b. states that discharge equals the hydraulic conductivity coefficient multiplied by the hydraulic gradient multiplied by the area involved
74
New cards
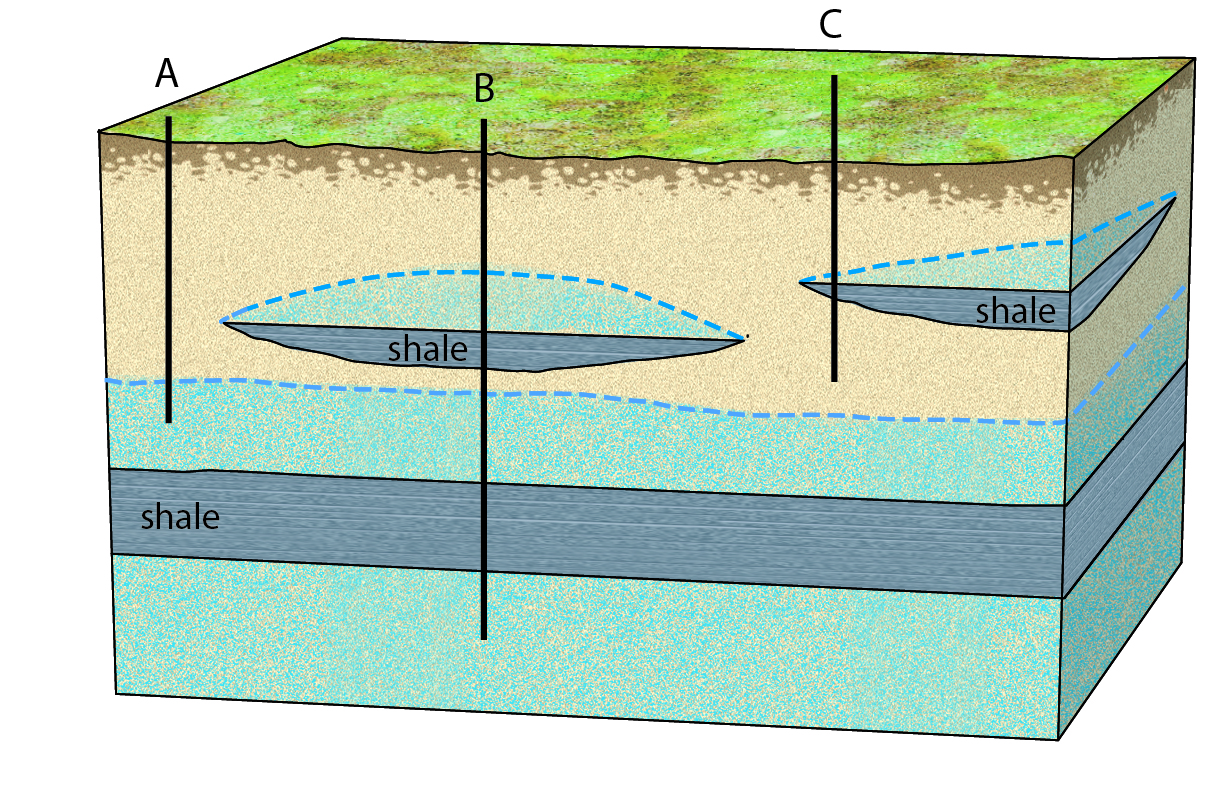
Which of the following statements about this diagram is true?
a. since sandstone is an aquitard, all three wells would be dry
b. the shale layer is a confining unit
c. the bottom of well c sits within the saturated zone
d. only well b would draw water, since it pierces an unconfined aquifer
a. since sandstone is an aquitard, all three wells would be dry
b. the shale layer is a confining unit
c. the bottom of well c sits within the saturated zone
d. only well b would draw water, since it pierces an unconfined aquifer
b. the shale layer is a confining unit
75
New cards
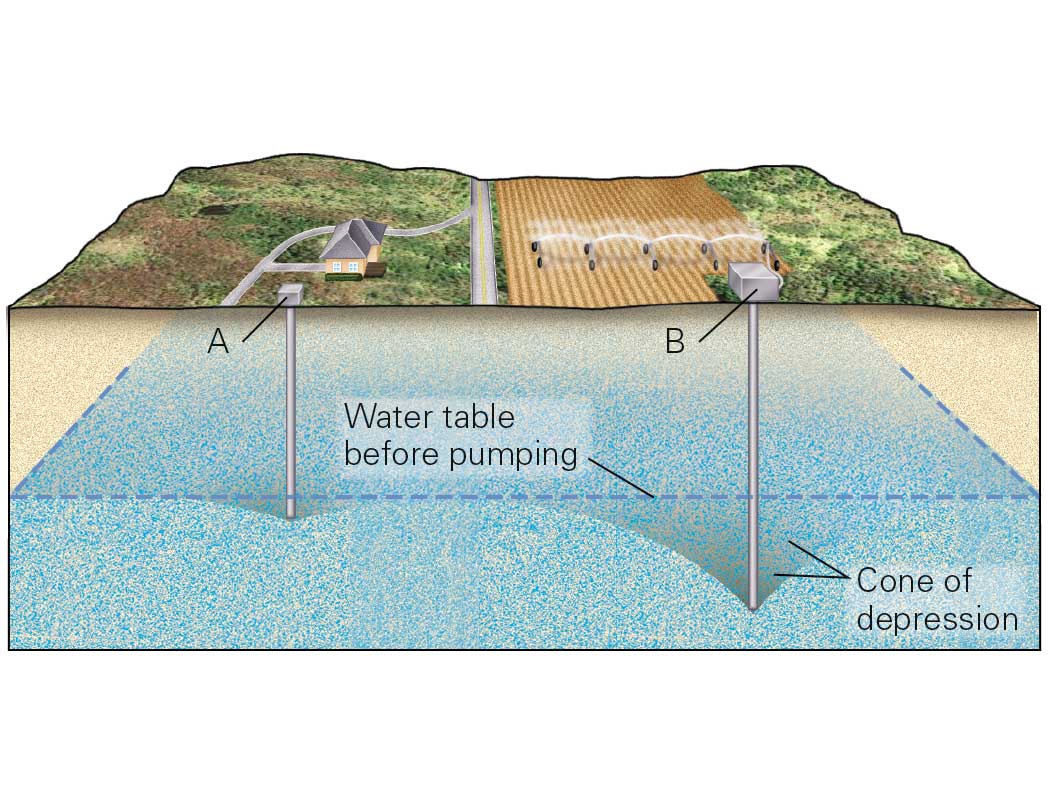
Which of the following statements about this diagram is true?
a. pumping from well a will reverse the flow of groundwater into well b
b. all of the possible answers are correct
c. pumping from well a may cause well b to run dry
d. pumping from well b may cause well a to run dry
a. pumping from well a will reverse the flow of groundwater into well b
b. all of the possible answers are correct
c. pumping from well a may cause well b to run dry
d. pumping from well b may cause well a to run dry
d. pumping from well b may cause well a to run dry
76
New cards
Which of these are sources of groundwater contamination?
a. petroleum
b. dissolved ions
c. sewage
d. recharge
a. petroleum
b. dissolved ions
c. sewage
d. recharge
a, b, and c
77
New cards
In the diagram above, what do the arrows represent?
a. the flow paths of the groundwater
b. the origin of the groundwater
c. the point of recharge
d. the primary reservoir on the surface
a. the flow paths of the groundwater
b. the origin of the groundwater
c. the point of recharge
d. the primary reservoir on the surface
a. the flow paths of the groundwater
78
New cards
orogenesis
process of mountain building
79
New cards
deformation
changes characteristics of rocks via changes in location (displacement), orientation (rotation), OR shape (distortion)
80
New cards
stress
force applied per unit area on a plane
81
New cards
→
compression occurs at a convergent boundaries
82
New cards
tension at divergent boundaries
83
New cards
→
shear at transform boundaries
84
New cards
strain
the change in shape of rocks caused by stress and deformation
* unstrained
* shortening/contraction
* shear
* stretching/elongation
* unstrained
* shortening/contraction
* shear
* stretching/elongation
85
New cards
brittle deformation
occurs in the shallow crust at low temperature and pressure conditions -rocks break by fracturing
86
New cards
ductile deformation
occurs deeper in the crust at high temperature and pressure - rock bends or fold
87
New cards
structural geology
the study of geological processes that causes stress and strain
88
New cards
strike
compass direction a dipping rock trends
89
New cards
dip
angle a rock tilted off the horizontal
90
New cards
joints
planar fractures that develop from tensional stress
91
New cards
veins
fractures/joints that are filled with mineral precipitates
92
New cards
faults
a fracture in rock with measurable offset or displacement
93
New cards
folds
layered rock can be deformed into complex folds by compression; convergent collision zones
94
New cards
anticlinal
a fold that looks like an arch
95
New cards
synclical
a fold that opens up
96
New cards
plunging
hinge titled off the horizontal
97
New cards
domes
fold with the appearance of an overturned bowl
98
New cards
basins
a fold shaped like an upright bowl
99
New cards
convergent boundary mountains
crust thickens, fold-thrust belt develops on the landward edge
100
New cards
collision
2 continental plates crust thickens and deforms