cell cycle quick flashcards
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
why do cells divide
growth & development - increase no. somatic cells
repair - replace cells lost through apoptosis
reproduction - asexual & sexual
what are some cells that don’t divide
mature red blood cells
neurons
difference in DNA between eukaryotes and prokaryotes
eukaryotes - a number of DNA molecules
prokaryotes - a single DNA molecule
eukaryotic chromosomes
DNA + protein (chromatin)
condense during cell division
what are somatic cells
have two sets of chromosomes
nonreproductive cells
what are gametes
have 1 set of chromosomes
reproductive cells
how are eukaryotic chromosomes organized
normally spread out in dispersed form (chromatin)
during interphase, DNA is replicated
during mitosis, chromosomes condense
what are sister chromatids
identical chromosomes
attached by cohesins
each duplicated chromosomes contains 2 identical DNA molecules. one in each chromatid
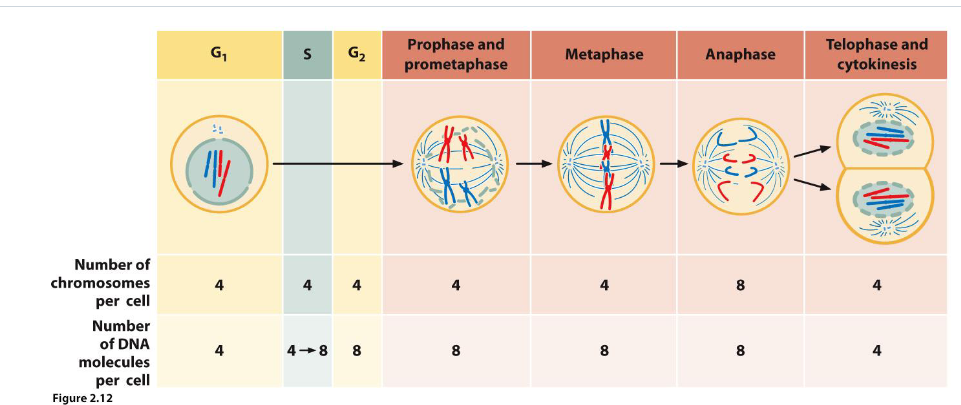
what is interphase
90% of the cycle
where most biogenesis and cell growth occurs
DNA replicates, centrosomes duplicate
G1 phase
S phase
G2 phase
what is cytokinesis
the cell divides into two daughter cells
genetically identical to each other and parent cell
how can be observe interphase as
intact nuclear envelope
dispersed chromatin - allow access to promoter regions
what is G1 phase
cell grows and makes organelles
what is the S phase
DNA is replicated - each chromosome is duplicated into two sister chromatids
what is the G2 phase
final preparations for cell division
centrosome duplication
what is the M phase
mitosis - division of genetic material
cytokinesis - division of cytoplasm
sister chromatids segregate into two cells and each daughter cell has one complete set of chromosomes
each daughter cell also recieves one centrosome
what is prophase
chromosomes condense
nuclear envelope intact
mitotic spindle forms
duplicated centrosomes separating to act as spindle poles
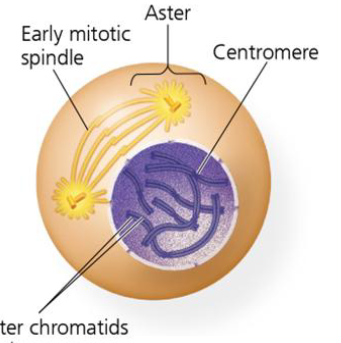
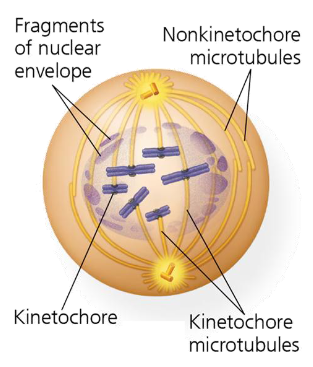
what is prometaphase
breakdown of nuclear envelope
chromosomes condense and sister chromatids start to “resolve” (cohesin digestion)
kinetochores are assembled at centromeres
spindle microtubules bind to kinetochores
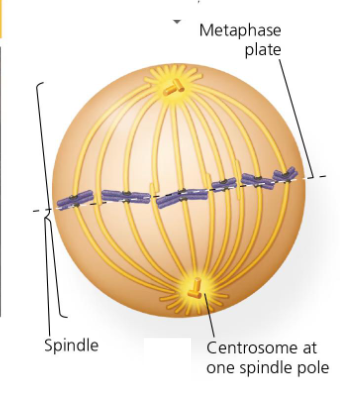
what is metaphase
chromosomes align at metaphase plate
kinetochore microtubules attach sister chromatids to opposite poles of the spindle
cohesins along arms fully digested, cohesins only remain at centromeres
what is anaphase
shortest stage
chromosome segregation
cohesins at centromeres destroyed by separase
sister chromatids seperate and move to opposite poles
microtubules shorten to pull chromatids apart
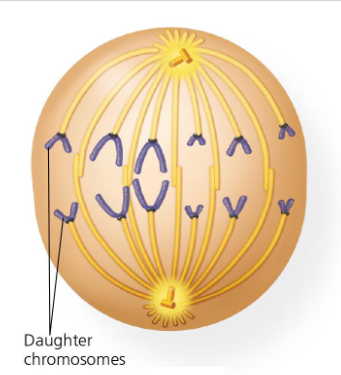
what is telophase
chromosomes decondense, 2 new nuclear envelopes re-assemble
mitotic spindle disassembles
cytokinesis begins with contraction of the contractile ring
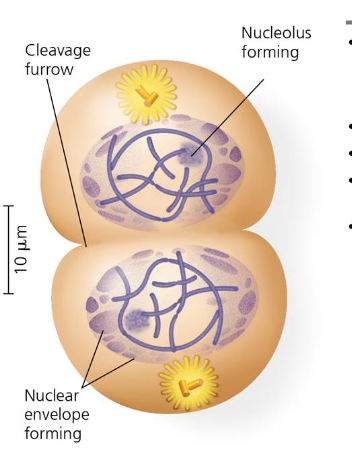
what happens in cytokinesis in animal cells
contractile rings of actin and myosin create cleavage furrow → pinches cell in two
fusion of intracellular vesicles with plasma membrane insert a new membrane
what happens in cytokinesis in plant cells
during telophase, vesicles derived for Golgi Apparatus move along microtubules to form cell plate
Cell plate enlarged until its surrounding membrane fuses with plasma membrane
results in 2 daughter cells with own plasma membrane
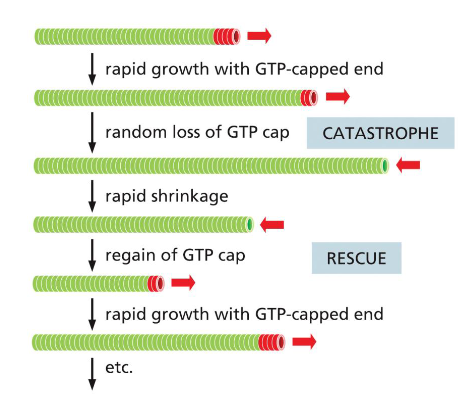
explain microtubules’ dynamic instability
they grow (rescue) and disassemble (catastrophe) alternatively
depending on the presence (rescue) or absence (catastrophe) of a GTP capping at their end
what are kinetochores
protein complexes that form a plaque on the surface of the centromere
in animal cells, each kinetochore binds 10-40 spindle microtubules
how do chromosomes move during mitosis
kinetochore proteins bind to sides of microtubules near plus end, with many labile bonds that ber
what is the result of mitosis
two genetically identical cells
each new cell has a full complement of chromosomes
each new cell has half the cytoplasm and organelle of the parental cell