Radiographic Quality pt1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
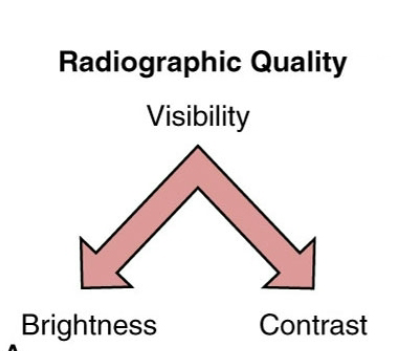
Understand Visibility
Visbility is affected by brightness and contrast

Understand Sharpness
Sharpness is affected spatial resolution and distortion

What does this image tell you about contrast
This image shows how there isnt different types of material because there isnt differing structures attenuation which makes it look almost one color bascialyl no contrast
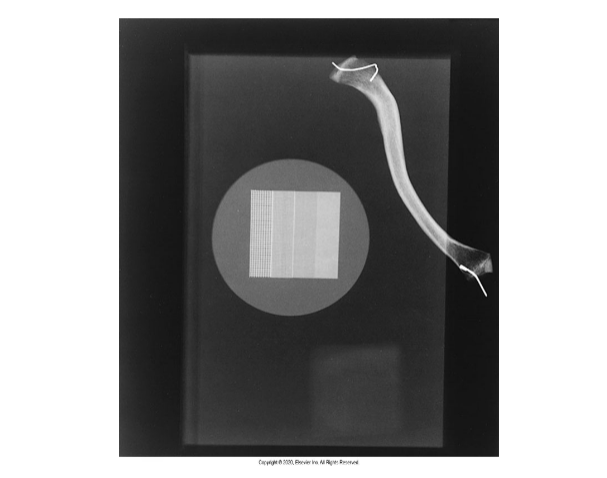
What does this image tell you about contrast
This image shows how the different itesm in the image show different attenuation giving more contrast to each other
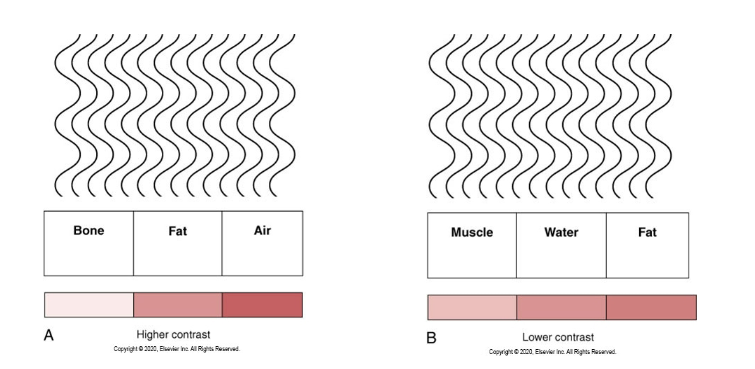
What do these two images detail

Is this high contrast or low contrast
This image just shows how the shades can look more different this image is higher contrast and this would be considered high contrast

Is this high or low contrast
This would be low contrast