Chapter 9 : Imperfect Competition: Monopolistic competition and Oligopoly (Micro)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Monopolistic Competition
Have characteristics of both a monopoly and perfect competition.
Sell their own product that is slightly different from competitors.
VERY competitive due to entries and exits into the market
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
Easy entry and Exit → When new firms arrive, it decreases the demand for existing firms in the market. When firms leave, it increases demand for firms still producing. The intense competition results in elastic demand curve.
Zero economic profit in the long run: Due to easy entry and exit, any short run profits attract new firms until economic profits have disappeared
DIFFERENTIATED PRODUCTS AND NONPRICE COMPETITION
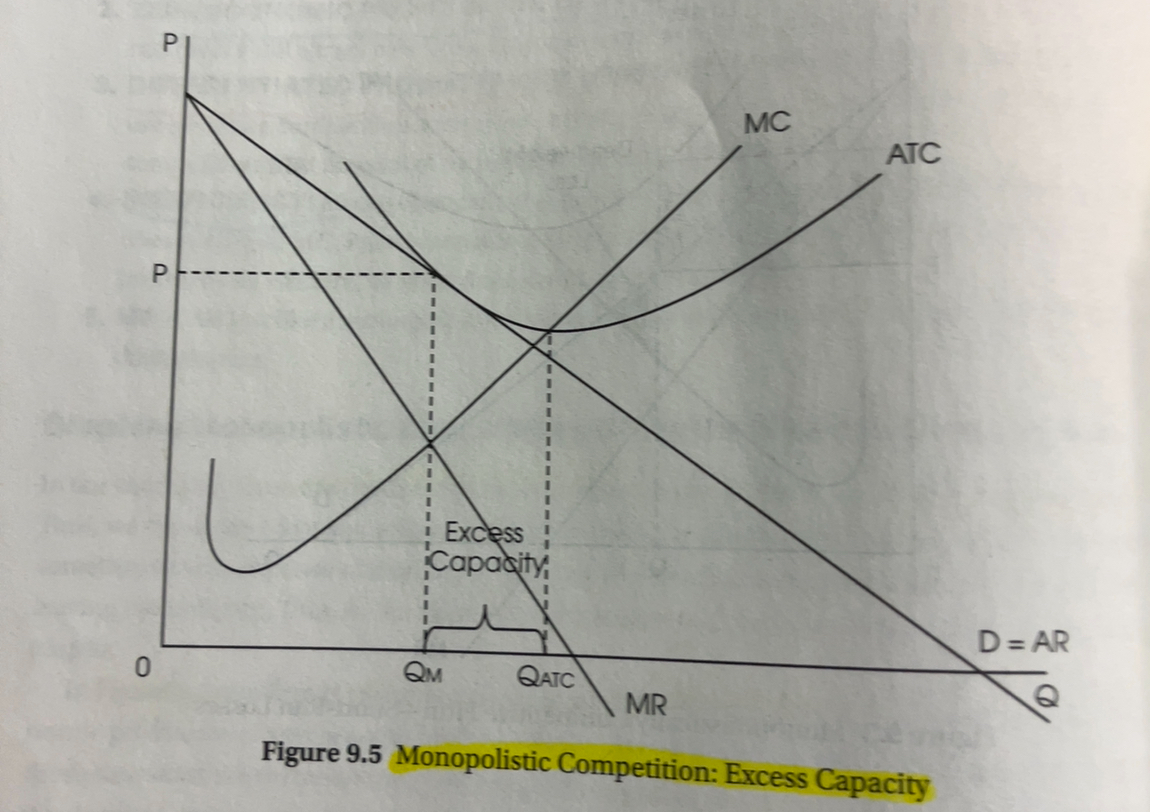
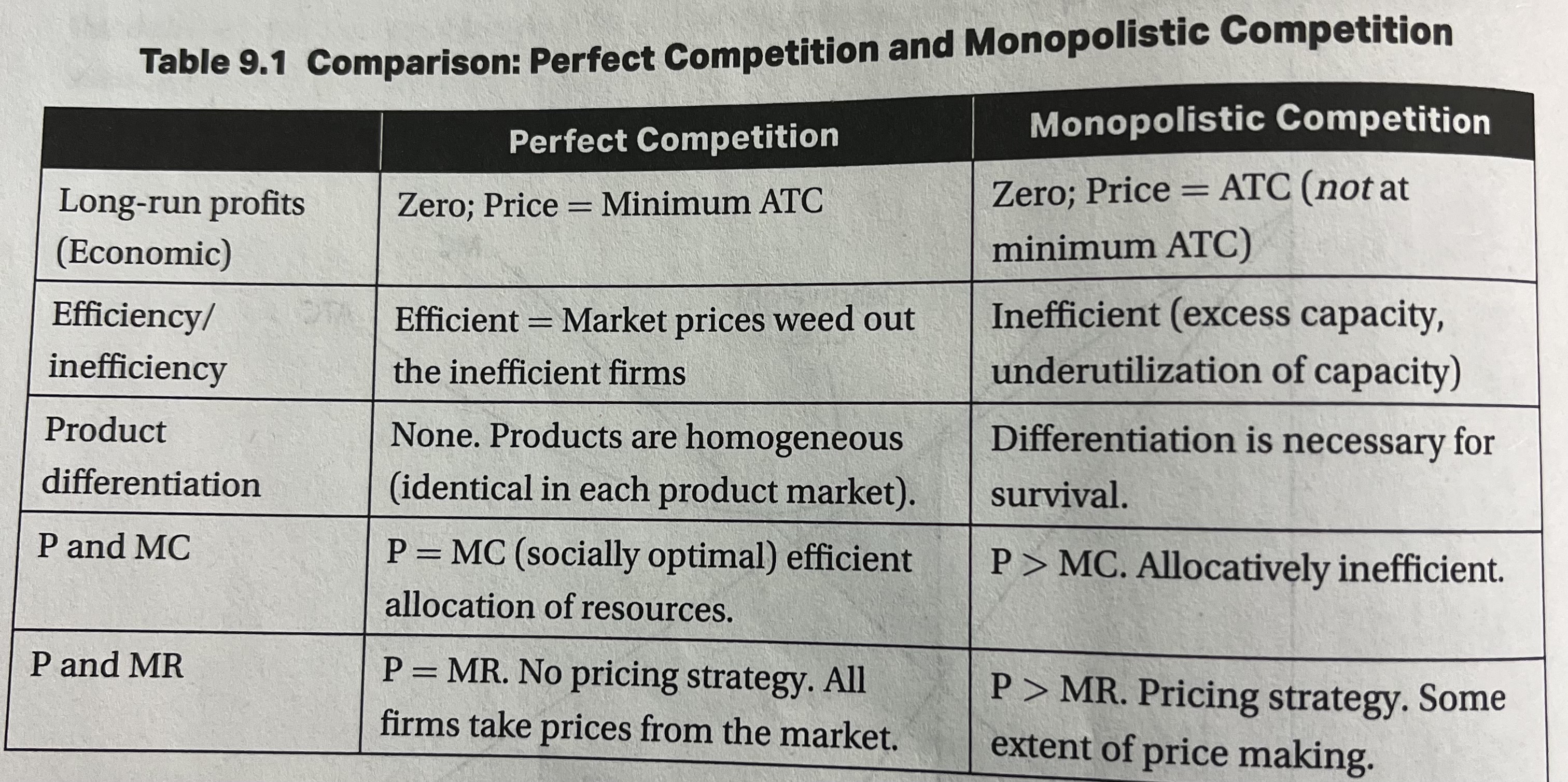
Inefficiency: Monopolistically competitive firms are not allocatively efficient because P not equal MC, P is actually greater. They are also not productively efficient , P does not equal minimum ATC.
MR < D
Graphing Monopolistic Competition in short run ( profits )
The firm is earning economic profits in the short run . as a result of the economic profits ,new firms see the opportunities for profit and enter the industry
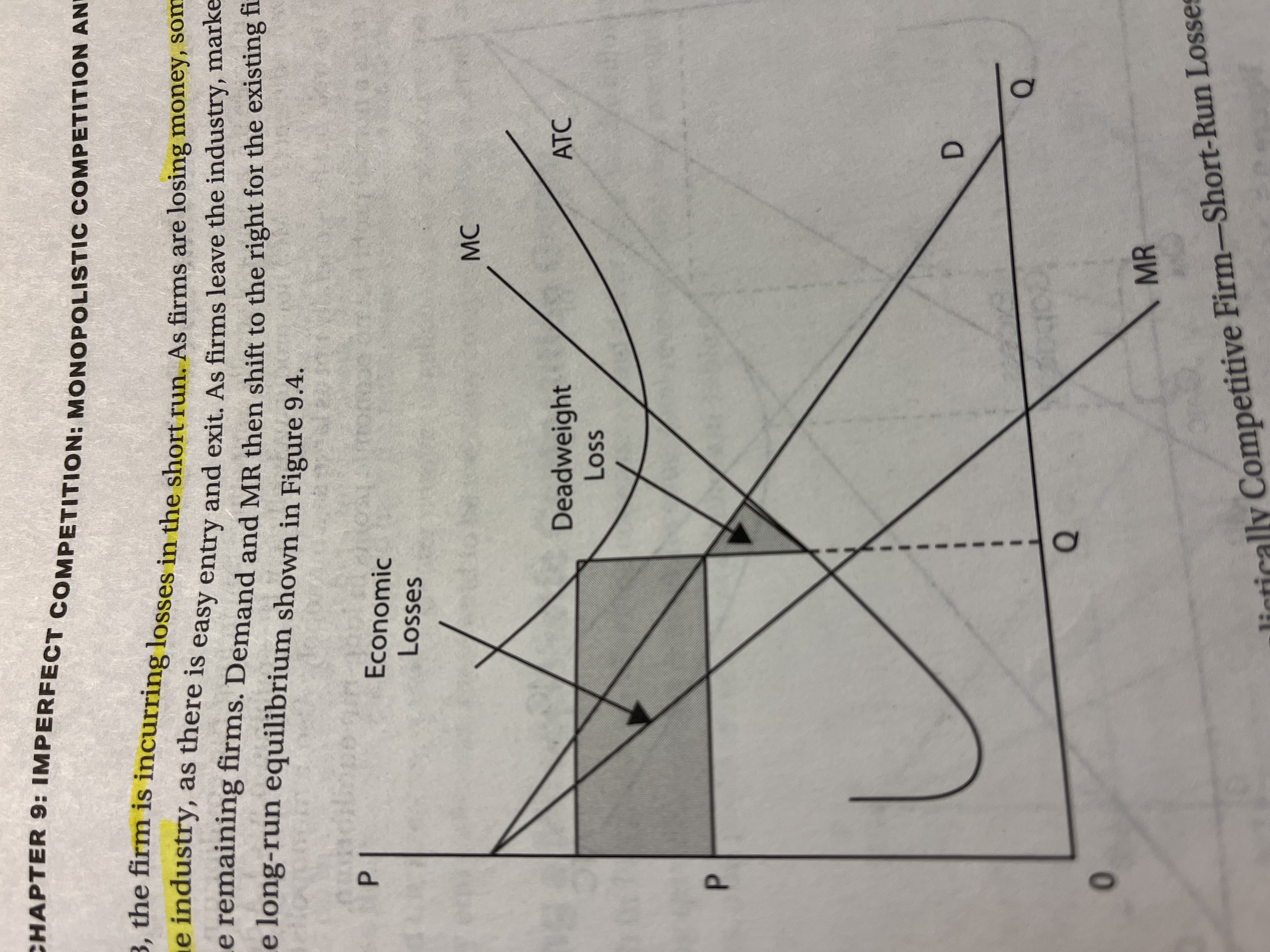
Graphing Monopolistic Competition in short run ( losses )
The firm is incurring losses in the short run as firms are losing money, some start to leave the industry as there Is easy entry and exit
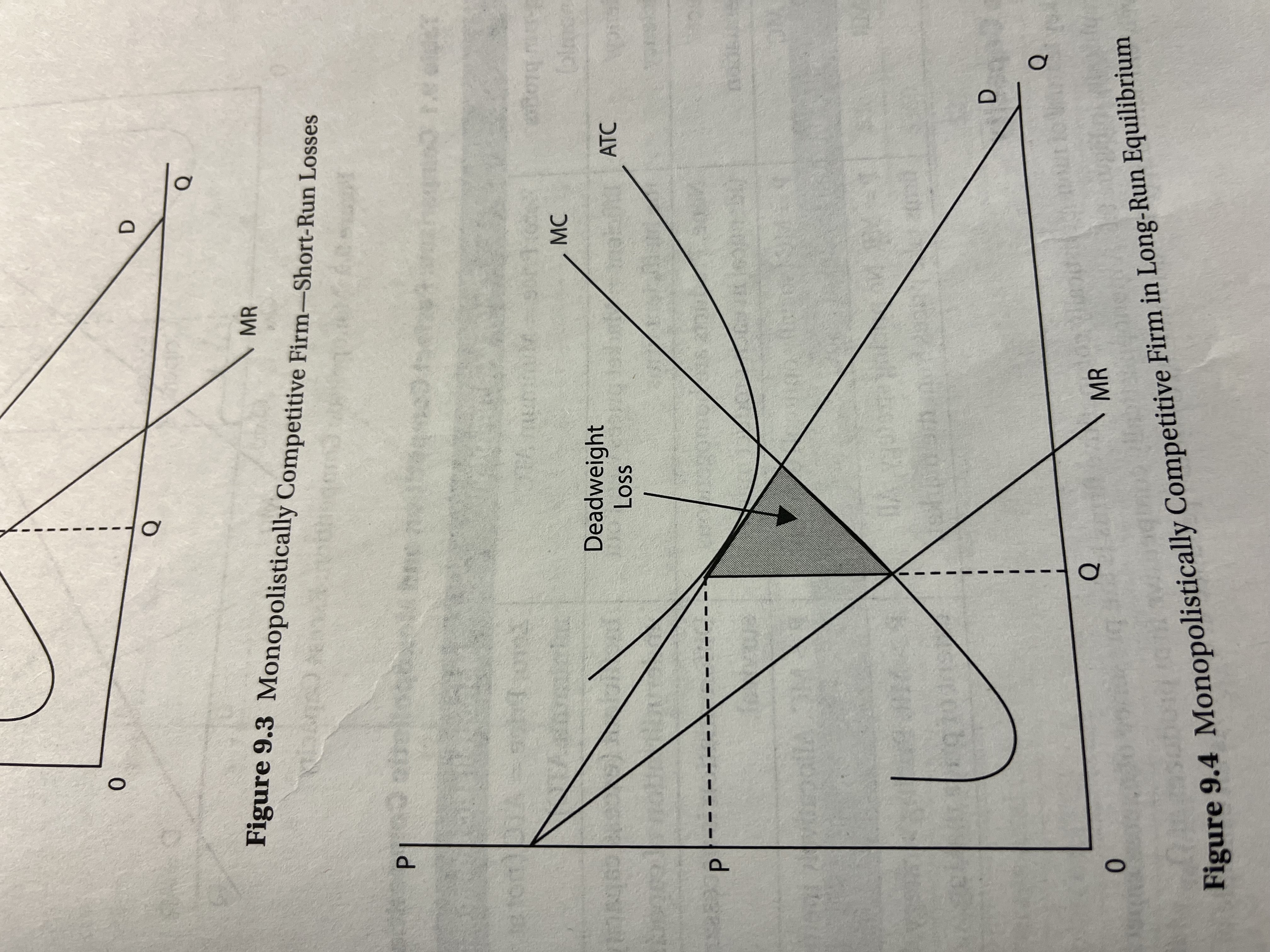
Graphing Monopolistic Competition in long run equilibrium
After some firms leave the industry, demand and MR shift to the right, ending up in long run equilibrium,
excess capacity monopolistic competition
Caused by product differentiation that leads to product variety and and quality and goood for consumers but causes waste .
Implies that fewer firms could produce the same industry output at a lower total cost.
Perfect competition and monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Very small number of firms who have market dominance
Interdependence on rival oligopolists
Oligapolists closely consider the actions of other firms , as the output and price decisions of one firm can have a big impact on the market
Collusion
Agreement, usually illegal, made to agree on what price and quantity will be produced in a market.
sometimes decide to form a cartel, which is a group of firms that act together And have a formal agreement not to compete, although they may cheat
to solve collusion in the us..
ANTITRUST POLICY
prevents oligopolies from being monopoly with no competition for the benefit of consumers and society
Game theory
Study of how people and firms act strategically in the context of a game.
Dominant Strategy
Best choice for a player regardless of what the other player chooses.
Nash Equilibrium
Set of strategies, one for each player, such that no player has the incentive to change his or her strategy given why the others players are doing.
Prisoners Dilemma
two people acting in their own self interest end up with a worse outcome than if they had cooperated.
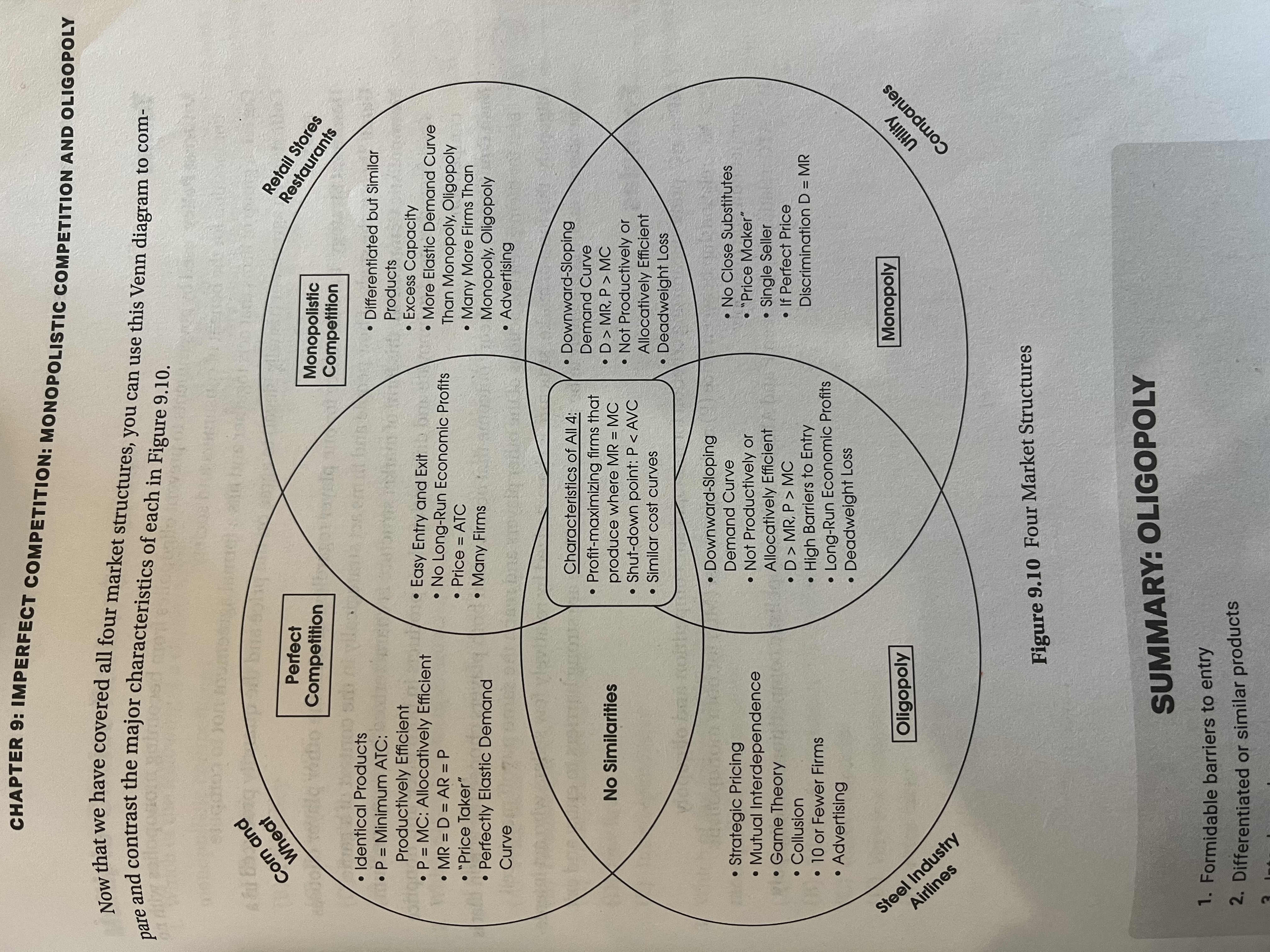
4 Market structures with characteristics