MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATON OF THE ANKLE AND FOOT (P1: Applied Anatomy, MedSurge review and Patient History)
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
"ramp down topic"
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Joints of the hindfoot:
Tibiofibular
talocrural
subtalar jts
Tibiofibular Joint
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Tibiofibular Joint
Resting position: Plantar flexion
Close packed position: Maximum dorsiflexion
Capsular pattern: Pain when joint is stressed
The tibiofibular join spreads how many mm?
During what ankle motion?
1-2mm
Dorsiflexion
True or False:
Dorsiflexion at the ankle joint causes the fibula to move superiorly, putting stress on both the inferior tibiofibular joint at the ankle and the superior tibiofibular joint at the knee.
True
The fibula carries more of the axial load when it is ____________
The fibula carries more of the axial load when it is dorsiflexed.
On average, the fibula carries about how many percent of the axial loading?
17%
Tibiofibular Joint nerve supply:
deep peroneal and tibial nerves.
Talocrural (Ankle)
Joint Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Talocrural (Ankle)
Joint Resting position: 10° plantar flexion, midway between inversion and eversion.
Close packed position: Maximum dorsiflexion
Capsular pattern: Plantar flexion, dorsiflexion
Nerve supply of talocrural joint:
Tbial and deep peroneal nerves
True or False:
the movements possible at the talocrural joint are dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, eversion, and inversion.
False:
the movements possible at the talocrural joint are dorsiflexion and plantar flexion.
Ligaments of the deltoid/medial collateral ligament of the ankle:
tibionavicular
tibiocalcaneal
posterior tibiotalar ligaments
anterior tibiotalar ligaments
ligaments which resist talar abduction:
tibionavicular
tibiocalcaneal
posterior tibiotalar ligaments
ligaments which resists lateral translation and lateral rotation of the talus:
anterior tibiotalar ligaments
Ligament which provides stability against excessive inversion of the talus:
anterior talofibular ligament
Ligament that resists ankle dorsiflexion, adduction (“tilt”), medial rotation, and medial translation of the talus
posterior talofibular ligament
Ligament which provides stability against maximum inversion at the ankle and subtalar joints
Calcaneofibular ligament
Which ligament most commonly injured by a lateral inversion ankle sprain
anterior talofibular ligament
2nd = calcaneofibular ligament (magee)
2nd = posterior talofibular ligament (S’charles)
Need to confirm
True or False:
The anterior talofibular ligament requires the lowest maximal load to result in failure of the lateral ligaments and has the lowest strain to failure of the entire lateral group
False:
The anterior talofibular ligament requires the lowest maximal load to result in failure of the lateral ligaments, although it has the highest strain to failure of the entire lateral group
Subtalar Joint
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Subtalar Joint
Resting position: Midway between extremes of range of motion (ROM)
Close packed position: Supination
Capsular pattern: Limited ROM (varus, valgus)
How many DoF does the subtalar joint have?
3
The movements possible at the subtalar joint are?
Gliding and Rotation
With injury to the area (e.g., sprain, fracture), which hindfoot joints become hypomobile?
Subtalar and talocrural joints
Medial rotation of the leg causes a ___________ movement of the calcaneus
whereas lateral rotation of the leg produces a ___________ movement of the calcaneus
Medial rotation of the leg causes a valgus (outward) movement of the calcaneus
whereas lateral rotation of the leg produces a varus (inward) movement of the calcaneus
The normal varus-valgus ROM is between how many degrees
The normal varus-valgus ROM is between 20° and 45°
The axis of the joint is at an angle of ____ inclined vertically from the transverse plane and _____ medially from the longitudinal reference of the foot
The axis of the joint is at an angle of 41° inclined vertically from the transverse plane and 23° medially from the longitudinal reference of the foot
Joints of the Midfoot (Midtarsal Joints)
Talocalcaneonavicular
cuneonavicular
cuboideonavicular
intercuneiform
cuneocuboid
calcaneocuboid jts.
Joints of the Midfoot (Midtarsal Joints)
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Joints of the Midfoot (Midtarsal Joints)
Resting position: Midway between extremes of range of motion (ROM)
Close packed position: Supination
Capsular pattern: Dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, adduction, medial rotation
Accepting load causes midfoot to __________
Propulsion causes midfoot to ____________
Accepting load causes midfoot to pronate
Propulsion causes midfoot to supinate
Other name for the midtarsal joints:
Chopart joint
Movements possible at this joint are gliding and rotation:
Talocalcaneonavicular Joint
Movements possible at this joint are slight gliding and rotation.
Cuneonavicular Joint
Cuboideonavicular Joint
Intercuneiform Joints
Cuneocuboid Joint
movement possible at this joint is gliding with conjunct rotation.
Calcaneocuboid Joint
Joints of the Forefoot:
Tarsometatarsal jt.
intermetatarsal jt.
metatarsophalangeal jt.
interphalangeal jt.
Other name for forefoot joints collectively:
Lisfranc joint
Tarsometatarsal Joints
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Tarsometatarsal Joints
Resting position: Midway between extremes of range of motion (ROM)
Close packed position: Supination
Capsular pattern: None
Intermetatarsal Joints:
CPP:
Movements:
Intermetatarsal Joints:
CPP: supination
Movements: gliding
Metatarsophalangeal Joints
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Hallux (big toe):
Second to fifth toe:
Metatarsophalangeal Joints
Resting position: 10° extension
Close packed position: Full extension
Capsular pattern:
Hallux (big toe): extension, flexion
Second to fifth toe: variable
Movements possible at the Metatarsophalangeal joints:
flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
Interphalangeal Joints
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Interphalangeal Joints
Resting position: Slight flexion
Close packed position: Full extension
Capsular pattern: Flexion, extension
Which metatarsal is important during the toe off phase?
1st metatarsal
Most common sporting injuries; responsible for
high proportion of attendances at emergency
centers
Ankle sprain
Ankle sprain characteristcs:
Age: ________
Sex predisposition: _______
MOI: ________
Area: ___________
Aggravated by:
Acute: ________
Subacute/Chronic : __________
OI: Swelling and ecchymosis ____________
ROM: Painful and limited AROM and PROM
(DF>PF/DF<PF?)MMT: Pain on resisted ankle movements
Palpation: Tenderness on involved structures
Ankle sprain characteristcs:
Age: 15-19 y/o
Sex predisposition: F>M
MOI: MC Inversion and plantarflexion
Area: Lateral ankle > Medial ankle
Aggravated by:
Acute: All movements
Subacute/Chronic : Inversion and Plantarflexion
OI: Swelling and ecchymosis anterolaterally
ROM: Painful and limited AROM and PROM
DF>PFMMT: Pain on resisted ankle movements
Palpation: Tenderness on involved structures
True or False:
Ankle sprains occur most often when the foot is plantar flexed, inverted, and abducted.
False:
Ankle sprains occur most often when the foot is plantar flexed, inverted, and adducted.
Which ligament is the strongest in the ankle region
Deltoid Ligaments
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage ______
short oblique fracture of the distal portion of the fibula occurs
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage 2
short oblique fracture of the distal portion of the fibula occurs
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage ______
fracture of the posterior aspect of the tibia
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage 3
fracture of the posterior aspect of the tibia
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage 1
rupture of the ______________ ligament
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage 1
rupture of the anterior tibiofibular ligament
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage 4
a fracture of the ______________
Supination-Lateral Rotation Injury: Stage 4
a fracture of the medial malleolus
Supination-adduction injury : Stage _______
fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deltoid ligament occurs
Supination-adduction injury : Stage 2
fracture of the medial malleolus or rupture of the deltoid ligament occurs
True or False:
In a supination adduction injury the fibular fracture is typically vertical, and that of the medial malleolus is oblique or nearly transverse.
False:
In a supination adduction injury the fibular fracture is typically transverse, and that of the medial malleolus is oblique or nearly vertical.
Supination-adduction injury : Stage 1
avulsion fracture of the distal portion of the fibula or rupture of the ______ ligaments
Supination-adduction injury : Stage 1
avulsion fracture of the distal portion of the fibula or rupture of the lateral ligaments
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage ____
rupture of the deltoid ligament or fracture of the medial malleolus
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage 1
rupture of the deltoid ligament or fracture of the medial malleolus
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage 3
A high __________fracture
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage 3
A high fibular fracture
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage _______
anterior tibiofibular ligament is ruptured
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage 2
anterior tibiofibular ligament is ruptured
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage _______
fracture of the posterior tibial margin
Pronation-lateral rotation injury : Stage 4
fracture of the posterior tibial margin
Pronation-abduction injury : Stage _______
rupture of the deltoid ligament or fracture of the medial malleolus
anterior tibiofibular ligament is ruptured
Pronation-abduction injury : Stage 1&2
rupture of the deltoid ligament or fracture of the medial malleolus (Stage 1)
anterior tibiofibular ligament is ruptured (Stage 2)
The first two stages of this injury are identical to those of the pronation-external rotation fracture complex
Pronation-abduction injury : Stage 3
________ supramalleolar fibular fracture that may be comminuted _________
Pronation-abduction injury : Stage 3
transverse supramalleolar fibular fracture that may be comminuted laterally
This grading system can be used to determine the severity of ankle sprains.
West Point Sprain Grading System
West Point Grading System
(follow up questions next slide)
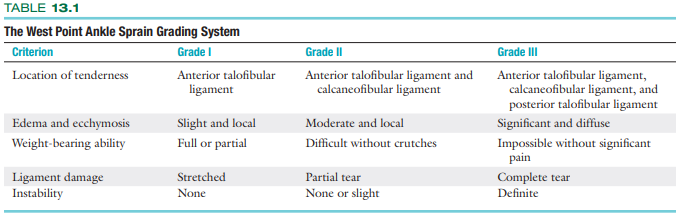
Edema and ecchymosis for a grade 2 sprain
Instability is only present at what grade/s?
Ligament damage with a grade 1 sprain
Location of tenderness in a grade 2 sprain
Moderate and Local
Grade 2 and 3
Stretched
Anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligament
Classification of Ankle Sprains (Familiarize)
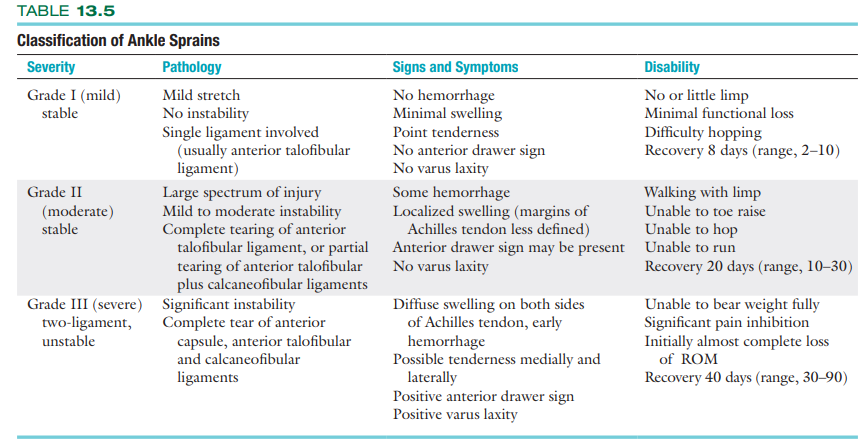
Most common overuse syndrome of the
lower leg:
Achilles Tendinopathies
Achilles Tendinopathy characteristics:
Age: ______
MOI: ____________
Area: ____________
Aggravated by: ___________
OI: ____________
ROM: __________________
MMT: __________________
Palpation: __________________
Achilles Tendinopathy characteristics:
Age: 20-40
MOI: Overuse
Area: Posterior ankle
Aggravated by: Jumping, running
OI: Minor swelling of posterior ankle
ROM: Painful and limited DF AROM and PROM
MMT: Pain on PF (on insertion or body of tendon)
Palpation: Tender posterior ankle
True or False:
Full Achilles tendon ruptures commonly have a sudden onset and usually starts without tendinitis
False:
Full Achilles tendon ruptures rarely have a sudden onset and usually starts with tendinitis (insidious onset).
True or false:
After Achilles tendon repair, a walking boot is typically worn the first few weeks.
False:
After Achilles tendon repair, a full immobilization cast is typically worn the first few weeks.
True or False:
MMT of plantarflexors is important when assessing a patient in early phases of Achilles tendon repair.
False:
MMT of plantarflexors should NOT be done during the early phases of Achilles tendon repair.
How long does the patient wear the walking boot?
8-12 weeks
True or False:
Achilles tendinopathies are insidious in onset while Gastrocnemius strains are acute and sudden.
True
Gastrocnemius Strains
Age: _______
MOI: ______________
Area: ______________
Aggravated by: _______
OI/GA: ______________
ROM: _____________________
MMT: _____________________
Palpation: ____________________________
Gastrocnemius Strains
Age: 20-40
MOI: sudden eccentric overload
Area: upper calf
Aggravated by: Heel raises
OI/GA: Antalgic gait, (-) or dec push-off
ROM: Painful and limited DF AROM and PROM
MMT: Pain on PF
Palpation: Mid to upper calf tenderness
Plantar Fasciitis factors:
Obesity
occupational
acute injury (inflammation)
anatomical, biomechanical (pes cavus and pes planus can lead to plantar fasciitis)
Plantar Fasciitis
Age: ________
MOI: ________________________
Area:________________________
Aggravated by: ________________________
OI: ________________________
ROM: ________________________
MMT: ________________________
Palpation: ________________________
Plantar Fasciitis
Age: 20-60 y/o
MOI: Gradual with no known cause
Area: Sole of the foot (under medial heel)
Aggravated by: Weight-bearing especially first
step in the morning (sharp pain in the morning)OI: Unremarkable; flatfooted and/or pronated
feetROM: Full and pain-free AROM, pain with PROM
of great toe extensionMMT: Weak foot intrinsics
Palpation: tenderness on plantar aspect of heel
Tibialis Posterior Tendinitis
Age: ________________
MOI: ________________
Area: ________________________________
Aggravated by:________________
OI: ________________
ROM:________________
MMT: ________________
Palpation: ________________
Tibialis Posterior Tendinitis
Age: 20-40 y/o
MOI: overuse with a flat pronated foot
Area: medial ankle, going up behind medial
malleolusAggravated by: activities involving WB PF
OI: possible peritendinous swelling over medial
ankleROM: pain on eversion and PF AROM;
overpressure into eversion and PFMMT: Pain on resisted inversion with PF
Palpation: tenderness on the medial ankle
Morton’s neuroma
Age: ___________
MOI: ___________
Area: ___________
Aggravated by: ______________________
OI: ___________
ROM: ______________________
MMT: ______________________
Palpation: ___________
Morton’s neuroma
Age: 40-60 y/o
MOI: Gradual with no known cause
Area: sole of foot
Aggravated by: WB
OI: Pronated foot, flattened arches
ROM: Full and pain-free AROM; overpressure into toe ext pain
MMT: Strong and painless
Palpation: tenderness on web spaces of
toes
D/dx with : midfoot sprains/trauma, midfoot overuse syndromes
old ppl only
Also known as shin splints; can lead to stress fx
Medial Tibial Stress Syndromes (MTSS)
Medial Tibial Stress Syndromes (MTSS)
Age: __________
MOI: ____________________
Area: ______________________________
Aggravated by:______________________________
ROM: ____________________
MMT: ____________________
Palpation: ____________________
Type of pain: ________
Medial Tibial Stress Syndromes (MTSS)
Age: 15-30 y/o
MOI: Overuse and change in the load of LE
Area: Anterior lower leg/posterior medial lower leg
Aggravated by: Exercise involving LE (Hopping, plyometrics (not static))
ROM: Pain with combined PF and inversion AROM;
painless PROMMMT: Pain on PF and eversion
Palpation: tenderness of posteromedial calf
Type of pain: Diffused pain
Other conditions
not in magee >:(
Anterior tibialis tendinitis
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Midfoot sprain
Metatarsal stress fractures
Ankle OA
Gout
Turf toe
Referred*
Lumbar spine, hip, knee, systemic (DM, spondyloarthropathies)
Common in runners; overuse of tibialis ant. tendon
Anterior tibialis tendinitis
True or False:
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is only due to overuse of supinated foots and cannot happen due to trauma
False:
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is due to overuse of pronated foots and can happen due to trauma
Sprain caused by overuse or increased loading on the forefoot or midfoot
Midfoot sprain
Traumatic injury common in contact sports players; equivalent to a toe sprain
Turf Toe
Chronic cases of plantar fasciitis can cause this due to pulling on the calcaneus which promotes growth of the bone.
Heel spurs
True or False:
With injury to the lateral ligaments, the structures (articular surfaces) may be damaged on the medial side owing to compression leading to medial as well as lateral pain.
True
True or False:
Anterolateral pain with history of trauma may be the result of anterior impingement especially after injury to the anterior talofibular ligament.
False:
Anterolateral pain without a history of trauma may be the result of anterior impingement especially after injury to the anterior talofibular ligament.
These inuries are usually the result of forced lateral rotation of the tibia and/or hyperdorsiflexion.
Syndesmosis injuries (“high ankle sprains”)
True or False:
Anterior ankle impingement may be due to thickening of the joint capsule and/ or bone spurs adjacent to the anterior talofibular joint
False
Anterior ankle impingement may be due to thickening of the joint capsule and/ or bone spurs adjacent to the anterior talocrural joint
True or False:
Achilles tendinosis or paratenonitis often arises as the result of overuse, increased activity, or change in a high-stress training program.
True
True or False
Achilles tendon ruptures are reported as a pop or snap as though the patient had been hit or kicked in the area of the rupture although, in most cases, there was no one near them
True
True or False:
The pain for Achilles tendon ruptures is sudden and persistent with weakness of plantar flexion.
False:
The pain for Achilles tendon ruptures is sudden and quickly dissipates with weakness of plantar flexion.
True or False:
Osteochondral lesions rarely occur with trauma and may accompany ankle sprains and fractures with symptoms being exacerbated by prolonged weight bearing or high-impact activities.
False:
Osteochondral lesions most commonly occur with trauma and may accompany ankle sprains and fractures with symptoms being exacerbated by prolonged weight bearing or high-impact activities.
A dorsiflexion injury, accompanied by a snapping and pain on the lateral aspect that rapidly diminishes, may indicate a tear of what structure?
Peroneal retinaculum.
Individuals such as dancers, soccer players, and track and field athletes may have _________ ankle impingement because of excessive repetitive plantar flexion of the foot
Individuals such as dancers, soccer players, and track and field athletes may have posterior ankle impingement because of excessive repetitive plantar flexion of the foot
Things that accompany a posterior ankle impingement:
separate ossicle =
protruding lateral tubercle of the talus =
fracture of the lateral tubercle =
Things that accompany a posterior ankle impingement:
separate ossicle = os trigonum
protruding lateral tubercle of the talus = Stieda’s process
fracture of the lateral tubercle = Shepherd’s fracture
Clinical Prediction Rule for Anterolateral Ankle Impingement:
Anterolateral ankle joint tenderness
Anterolateral ankle joint swelling
Pain on forced dorsiflexion
Pain on affected side with single leg squat
Pain with activities
Absence of ankle instability
Note: Five of six symptoms must be positive
True or False:
A fracture to the ankle causes delayed swelling that decreased as it spread into the surrounding tissue.
False:
A fracture to the ankle causes immediate swelling that decreased as it spread into the surrounding tissue.
True or False:
If the patient was able to continue the activity after the injury the injury is probably not too severe, provided there is no loss of stability.
Yeah no shit
True or False:
Inability to bear weight, severe pain, and rapid swelling indicate a severe injury
OMG NO WAY ITS TRUE!!!!!!!!!
Pain with walking is compatible with a ________ degree sprain
pain with running usually indicates a ________ injury
Pain with walking is compatible with a second degree sprain
pain with running usually indicates a first degree injury
swelling over the extensor tendons of the foot caused by irritation from doing up (i.e., lacing up) stiff ice skates too tight.
“Skate Bite”
Chronic recurrent ankle instability will be indicated by:
_________ significant lateral ankle sprains involving functional and mechanical instability
increased ________ laxity
greater ________ laxity,
history of giving way usually during __________ when walking, running, cutting, or rapidly decelerating in the last ___________.
Chronic recurrent ankle instability will be indicated by:
one or more significant lateral ankle sprains involving functional and mechanical instability
increased subtalar laxity
greater anterior laxity,
history of giving way usually during initial contact when walking, running, cutting, or rapidly decelerating in the last 6 months.
True or False:
With overuse injuries, pain initially comes on during the activity
In later stages of the problem, the pain is constantly present.
False:
with overuse injuries, pain initially comes on after the activity
In later stages of the problem, the pain is constantly present.
Pain during the activity suggests stress on the injured structure.