echinoderms
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bio 2.2 zoology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Are sea stars bilaterally or radially symmetrical?
They are both, their larvae are bilaterally symmetrical and as adults they are radially symmetrical
why are their nervous system decentralized?
They experience their environment from 360 degrees.
How do they experience their enviornment?
they have eyespots on their arms and have chemoreceptors
osmoconformers
maintaining the osmotic pressure of their environment
what is their endoskeleton made of?
Calcium carbonate
what makes the echinoderms unique?
water-vascular system
How do they move around
they have tube feet which help them move around and catch prey.
what are the five classes of echinoderms?
Asteroidea, Ophiuroidea, Echinoidea, Holothuroidea, Crinoidea
Asteroidea
the sea star
ophiuroidea
brittle stars
echinoidea
the sand dollars and sea urchins
holothuroidea
the sea cucumbers
Crinoidea
sea lilies and feather stars
endoskeleton
made of calcareous plates fused together beneath their epidermis
dermal ossicles
calcareous plates
what makes the sea stars skeleton so unique
Their collagen can harden and soften as needed for the sea star to take a new shape.
How do they breath
via papulae
how do sea stars protect themselves?
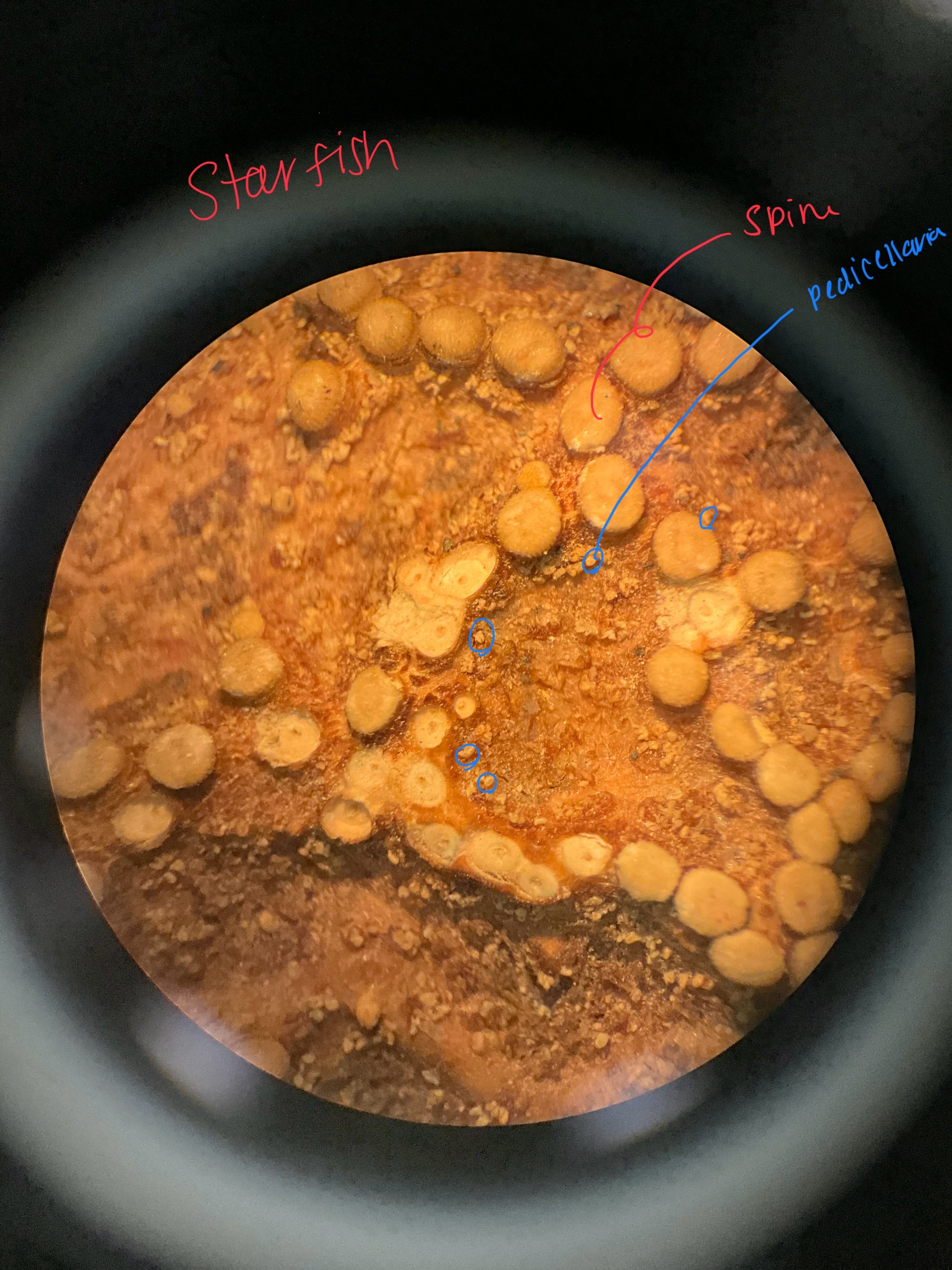
skeletal spines that stick out.
which echinoderm does not have a well defined skeleton?
sea pickles they reduced their dermal ossicles to a point where it feels as soft as a squid
pedicellareae
tiny calcareous pincers
which classes have pedicellareae
echinoids and asteroids
Papulae
pouches in the coelomic cavity that extend through gaps in the derma ossicles. Helps diffuse waste
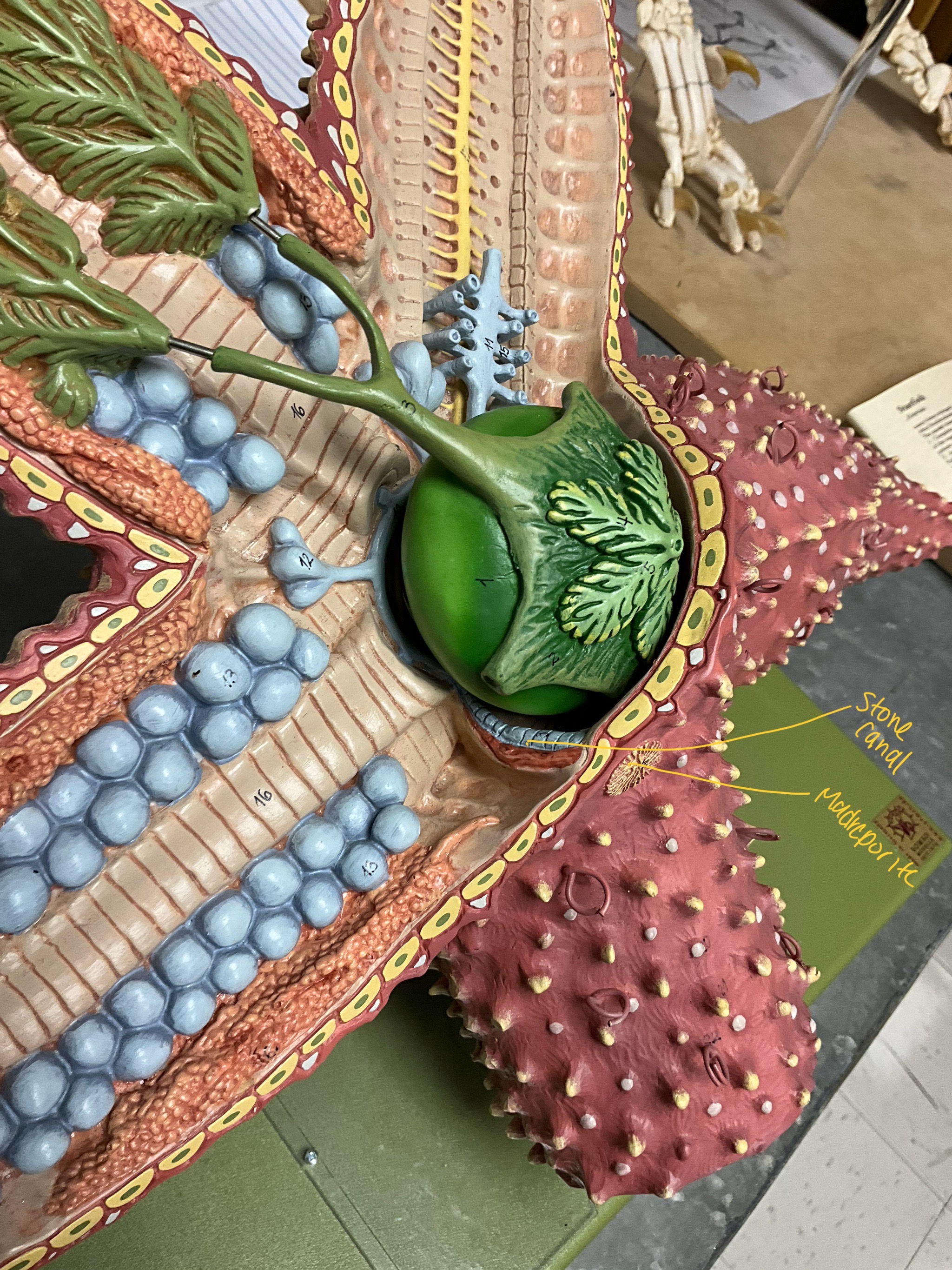
Madreporite
inlet for water which runs the water vascular system, Only on two arms
Sensory tentacles
photoreceptors and statocysts at the end of each arms
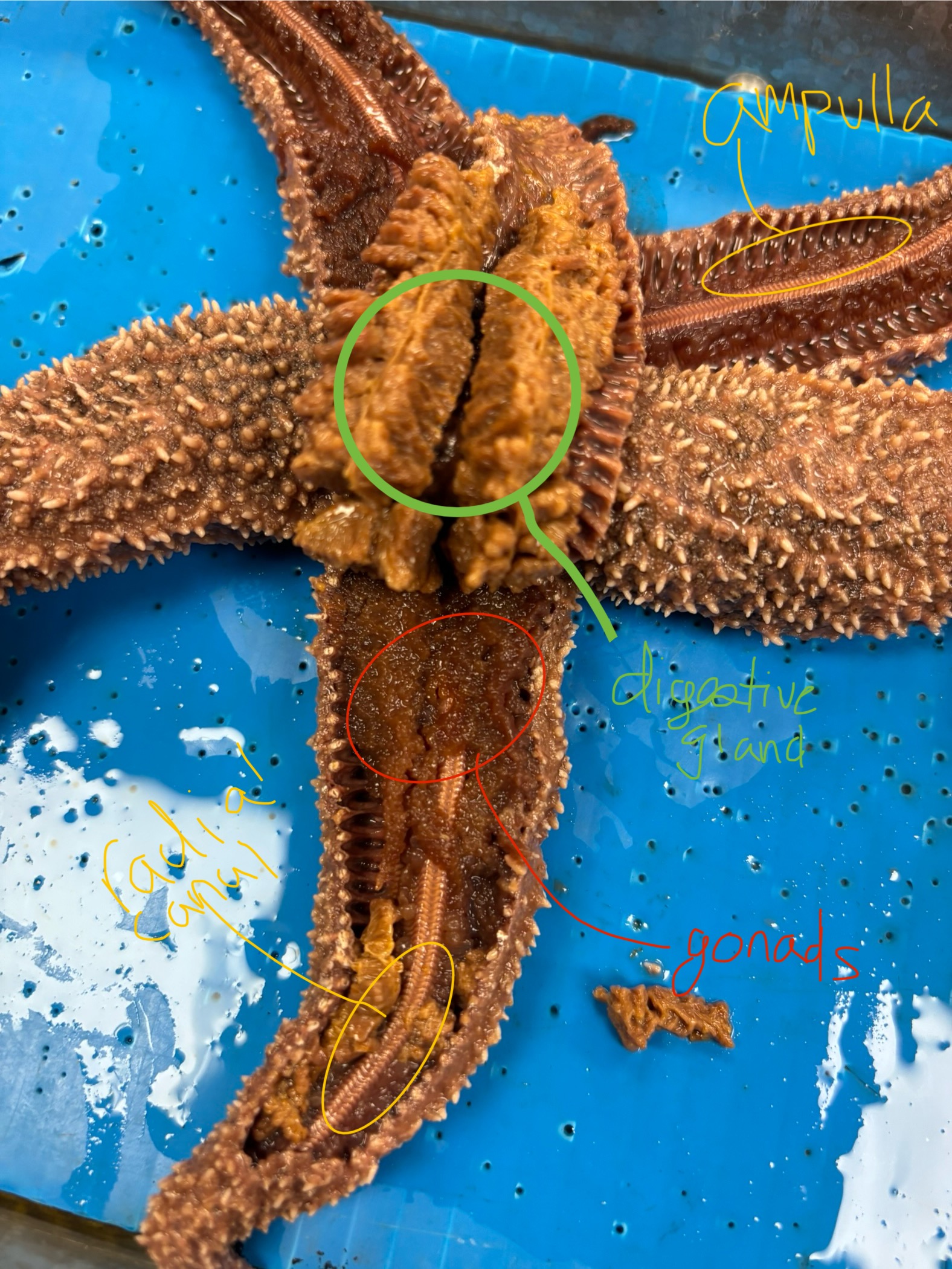
pyloric cecae
yellowish-brown digestive glands
Where can you find the gonads?
underneath the pyloric cecae
ampulla
tops of the tube feet
What does the stone canal do?
takes water to the ring canal and out to the radial canals which run down each arm
lateral canals
they have one way valves the branch off the radial canal and fill the ampullae with water
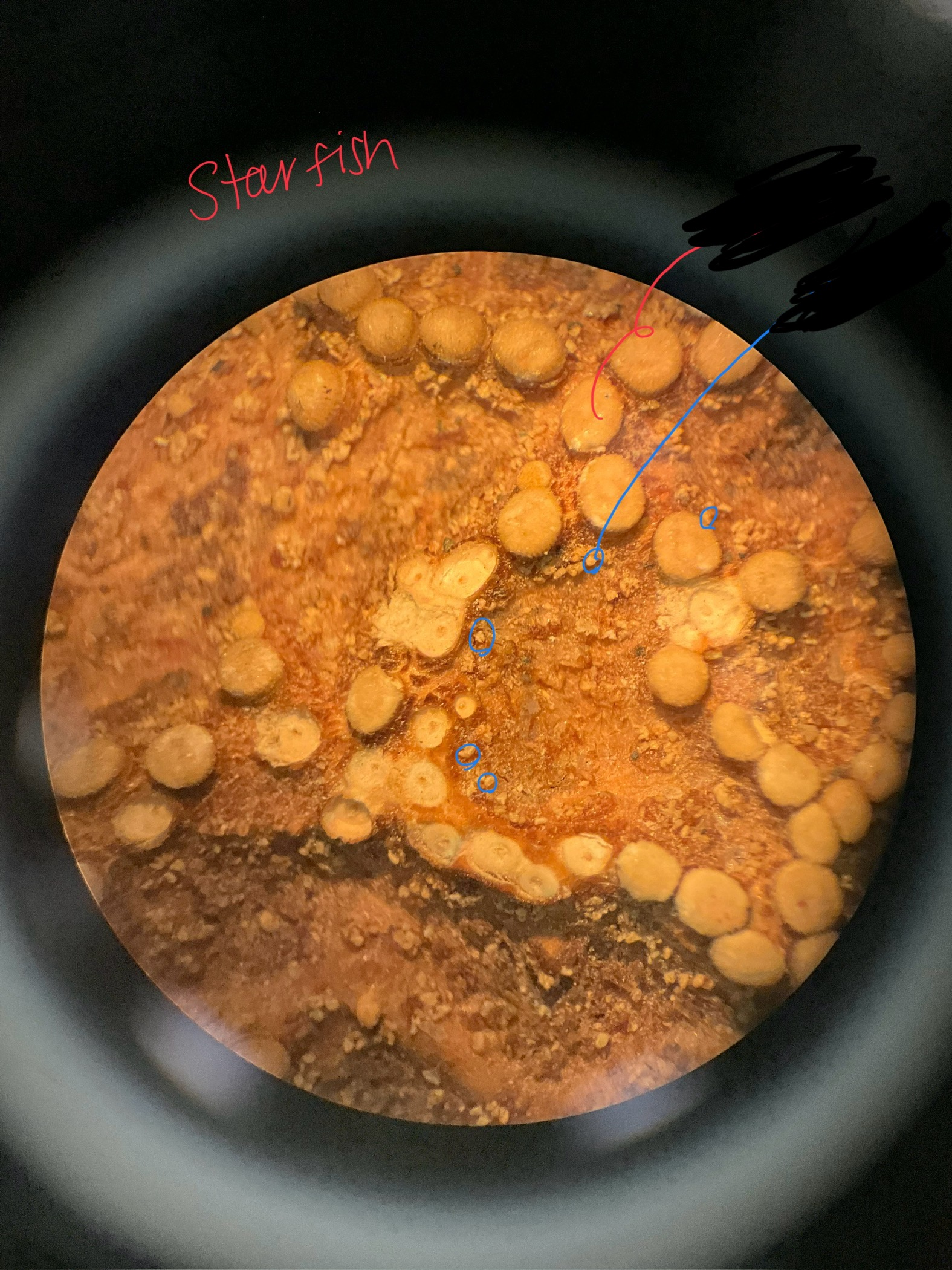
label the spines and pedicellareae
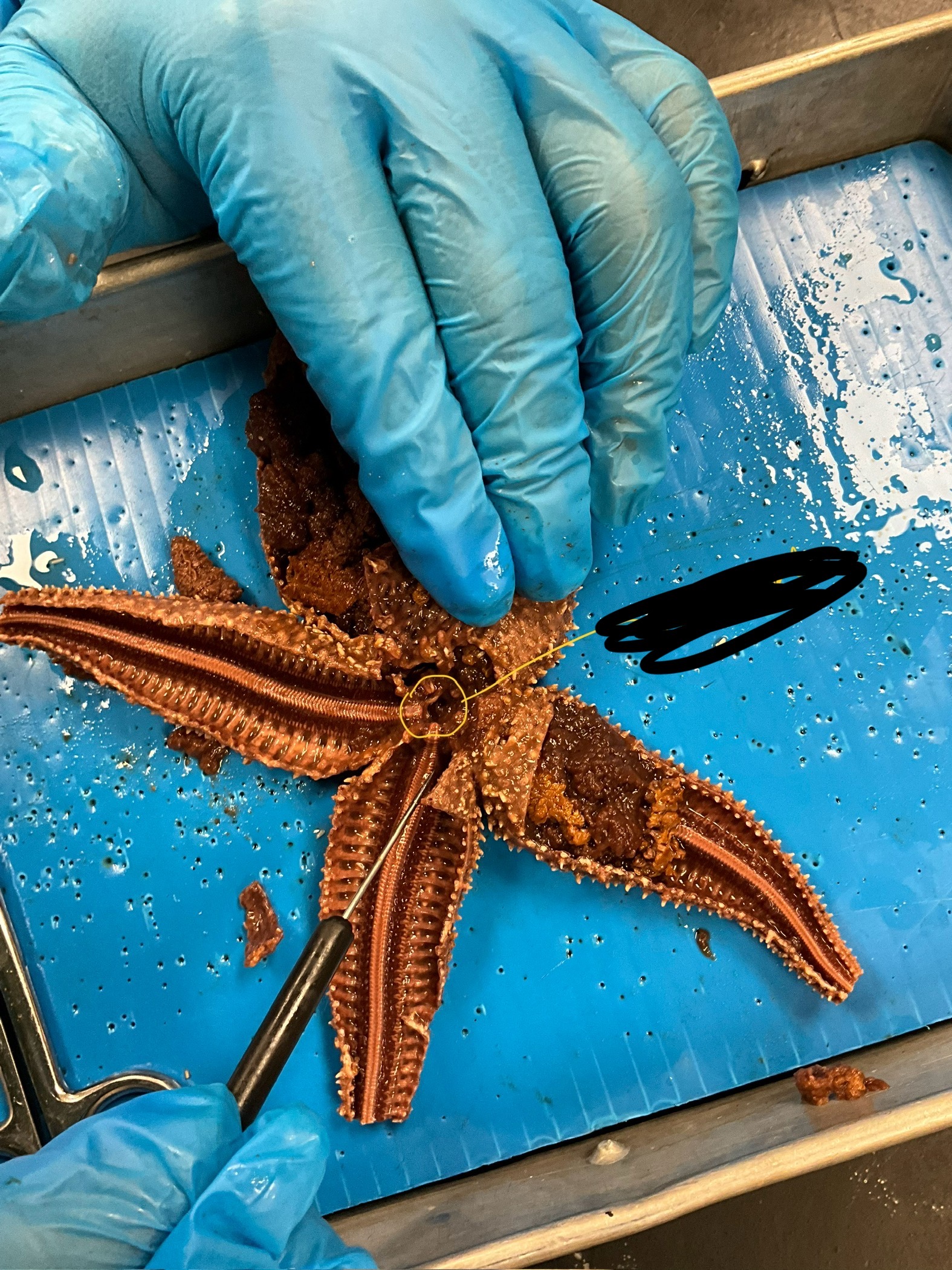

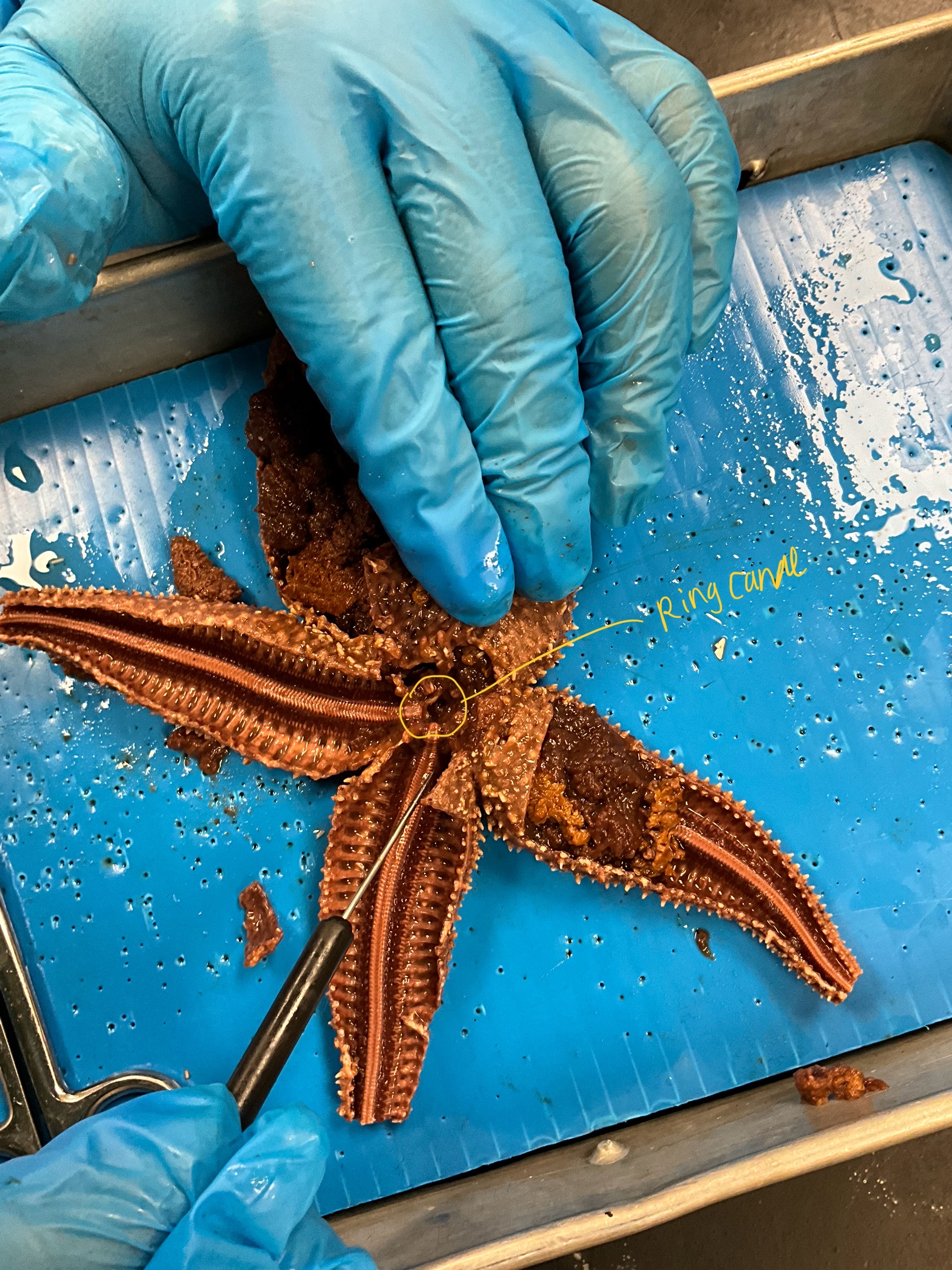
what is the circled part called?
ring canal


label: ampulla, digestive gland, gonads, and radial canal
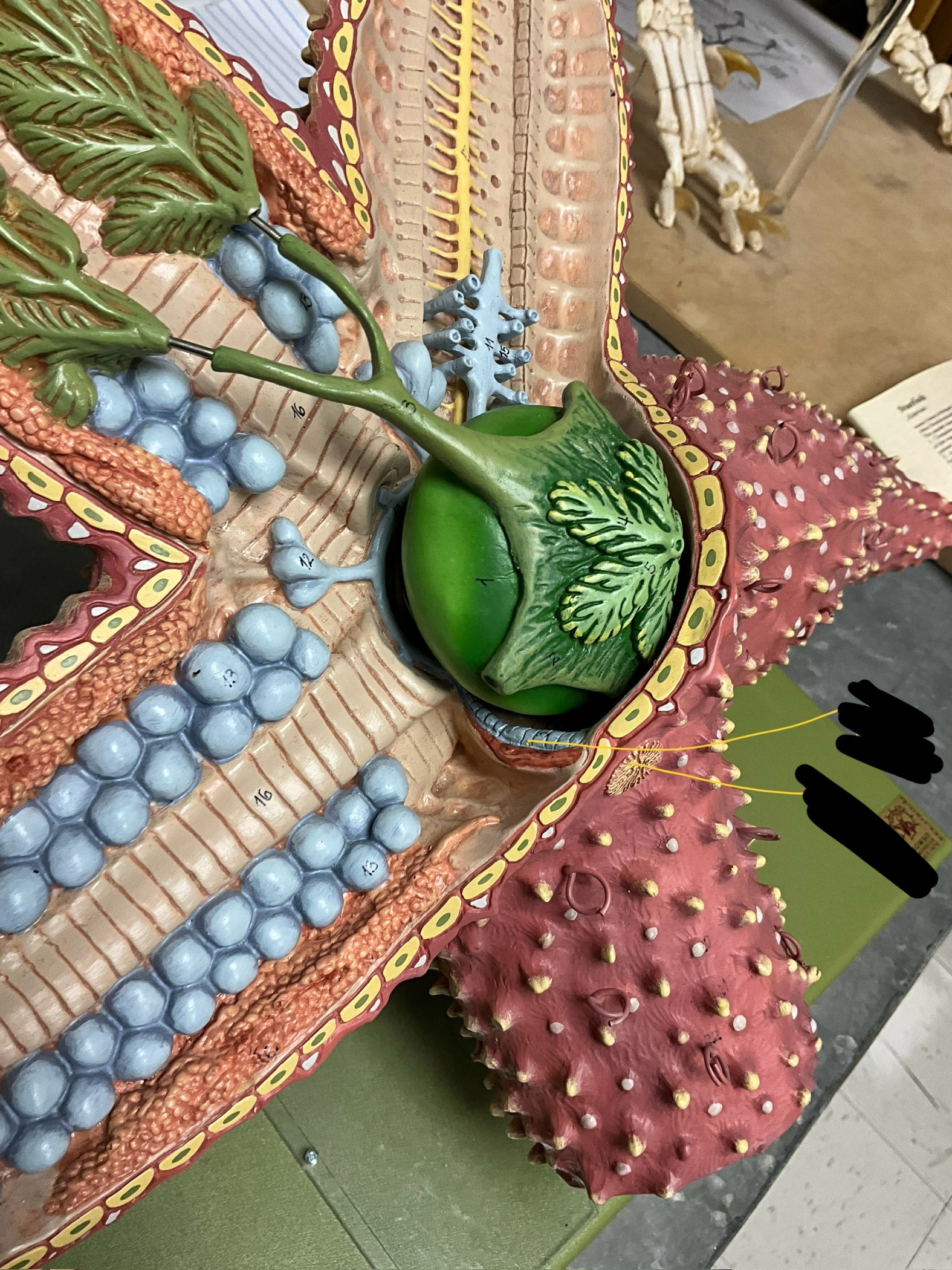


label the crossed out sections
stone canal and madreporite
