42) Liver
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
General liver
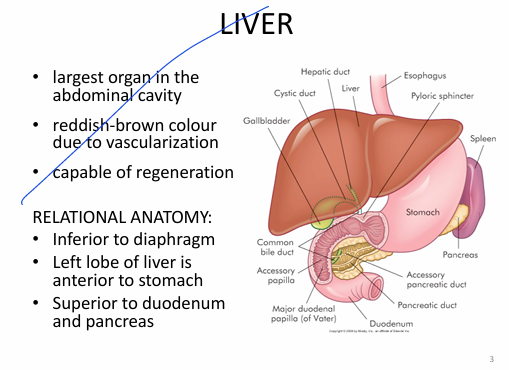
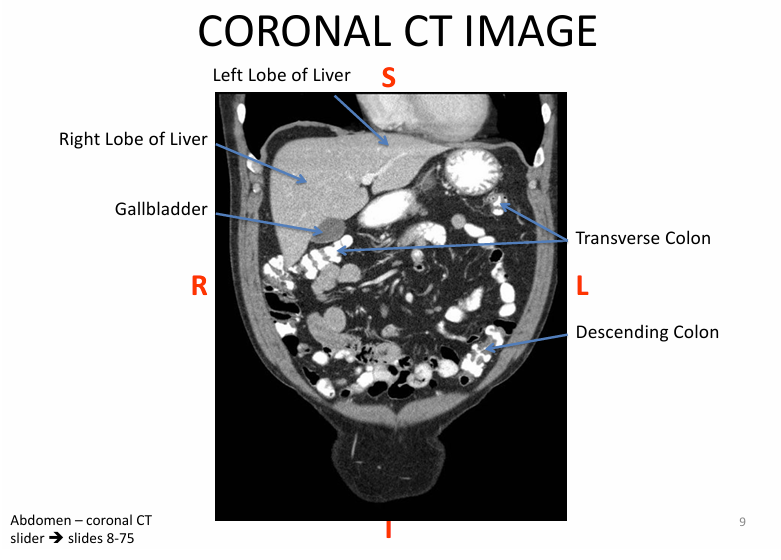
Relational anatomy:
- inferior to diaphragm
-left lobe of liver is ANTERIOR to stomach
-liver SUPERIOR to duodenum & pancreas
What are the LOBES of the liver?
Right & left (separated by falciform ligament)
Caudate (next to IVC)
Quadrate (next to gallbladder)
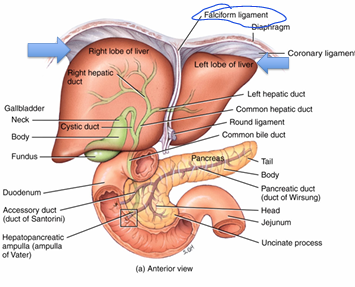
What’s the significance of the falciform ligament?
-separates left and right lobe
-extends to anterior abdominal wall (holds liver in place)
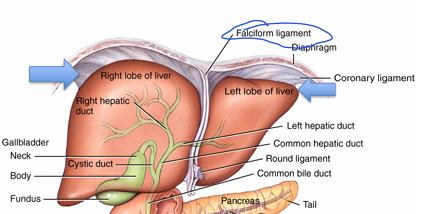
What’s the significance of the CORONARY ligament?
creates BARE area (portion of liver NOT covered in peritoneum)
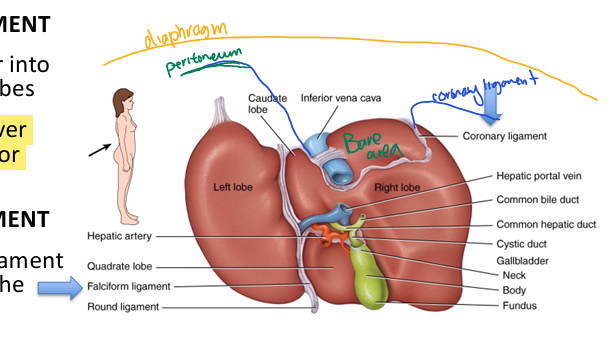
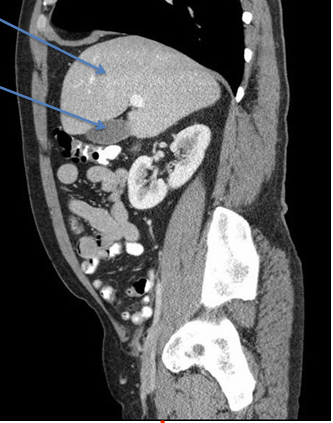
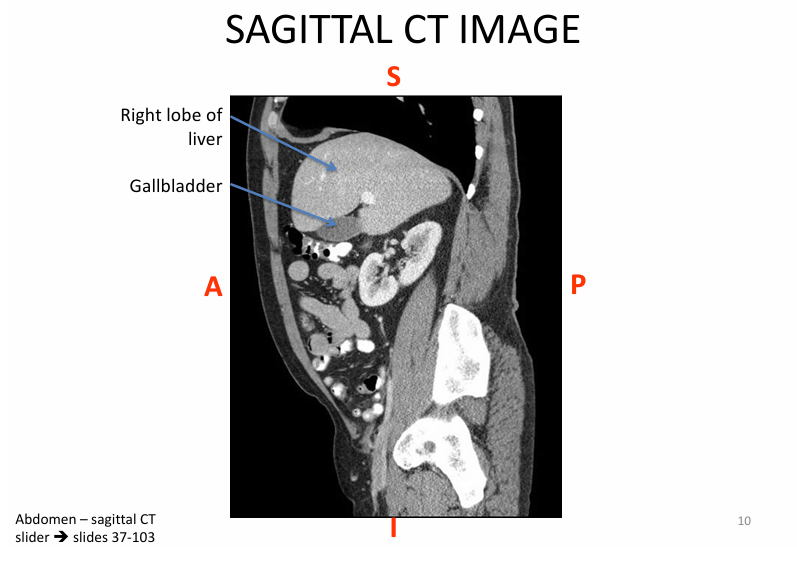
What’s the significance of the LESSER omentum in terms of the liver?
lesser omentum = double layer peritoneum - connects liver to stomach
*note lesser omentum is a MESENTERY (contains vessels)
Discuss the contents WITHIN the lesser omentum
Porta hepatis
- hepatic portal vein (nut rich deoxy blood to liver)
-hepatic artery PROPER (oxy blood to liver)
-common hepatic duct (opp direction of the above 2)
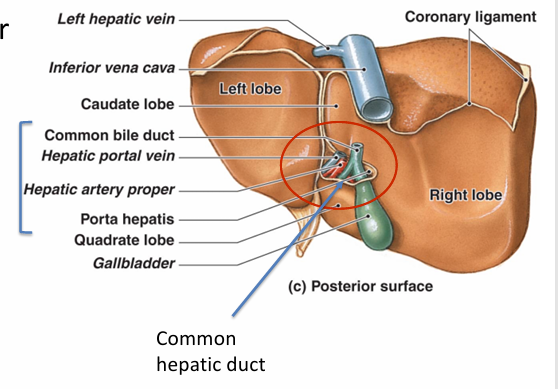
What is the blood vessels of hepatic artery proper (more in depth) (20% of blood to liver)
Aorta
→ celiac trunk
→ common hepatic artery
→ hepatic artery proper
→ left OR right hepatic artery
What is the hepatic portal vein (more in depth) (80% of blood to liver)
all the following converge into hepatic portal vein:
- inferior mesenteric vein
- superior mesenteric vein
- splenic vein
What is the histology of the liver?
1) hepatocytes
2) bile duct + bile canaliculi (carry bile)
3) network of blood vessels
All 3 = hepatic LOBULE
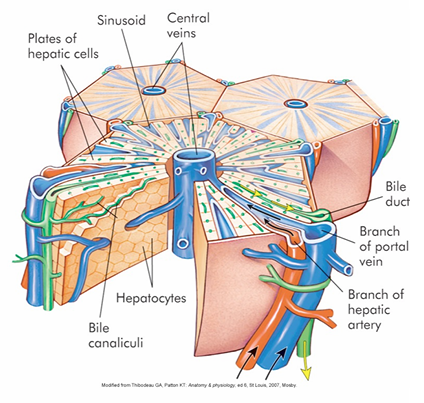
Discuss the hepatic lobule
Hepatic lobule = whole thing
3) edge of hepatic lobule contains:
PORTAL TRIAD
- BRANCH of hepatic artery
- BRANCH of hepatic portal vein
- BILE DUCT
*this blood goes through hepatic laminae & sinusoids take w/e is needed → blood then drains into central vein)
1) hepatic laminae = collection of hepatocytes
2) hepatic laminae separated by HEPATIC SINUSOIDS (large holes, permeable)
4) As blood runs INTO portal triad
→ portal triad drains into CENTRAL VEIN
5) central vein → HEPATIC VEIN → IVC
—
*2.5) Kupffer cells (inside sinusoids) = engulf pathogens (Same fxn as spleen)
- stellate reticuloendothelial cells
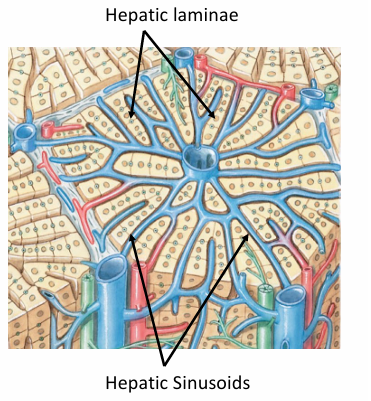
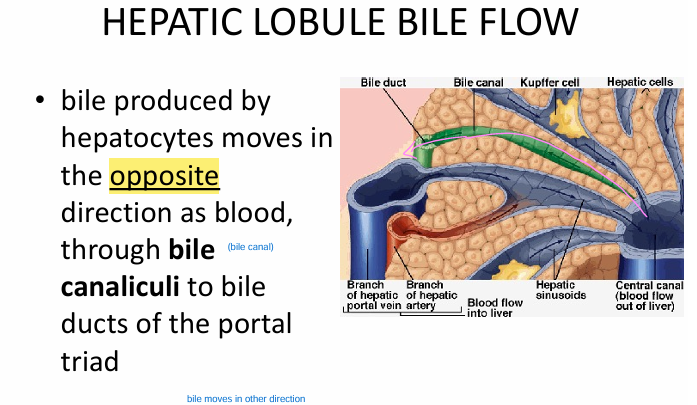
Hepatic lobule bile transport
bile produced by hepatocytes go in OPPOSITE direction of blood through BILE CANALICULI
→ bile duct (of portal triad)
→ L/R hepatic duct → common hepatic → common bile