AP Biology - The Chemistry of Life
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions from the Campbell Global Approach Twelfth Edition. There may be some superfluous definitions as the textbook is more in depth that the AP. Good luck for your exams :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Essential Element
Elements necessary for an organism to live a healthy life. This can differ for different species.
Phosphorylated intermediate
The recipient of the inorganic phosphate during the ATP cycle
Energy coupling
The use of an exergonic reaction to an endergonic one
Endergonic
A reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings
Exergonic
A reaction that releases free energy into its surroundings
Enzyme
A macromolecule that acts as a catalyst
Activations energy
The initial energy require to start a reaction
Substrate
The reactant an enzyme acts upon
Active site
The region of the enzyme in which the substrate binds
Allosteric regulation
Any case in which the active site of an enzyme is affected by a molecule bind at a seperate site. This could be beneficial or detrimental to the enzymes activities.
Cooperation
The mechanism that allows a substrate to act as a allosteric activator to a different site.
Feedback inhibition
The process in which a product of a multi-enzyme reaction can double as an inhibitor for an earlier enzyme in the chain. This neatly slows the production as the product increases :)
Metabolism
The totality of a organisms metabolic reactions.
Catabolic pathways
Metabolic pathways that break down complex molecules into simpler compounds. Eg cellular respiration. Catabolic pathways release energy (exothermic)
Anabolic pathways
Endothermic reactions that cause simpler compounds to bond and create more complex ones.
Energy
The capacity to create change
Chemical energy
In biology chemical energy refers to potential energy available to be released in a chemical reaction.
Spontaneous
Energetically favourable
Atomic Nucleus
The centre of an atom where proton and neutrons are tightly packed
Dalton
A unit of measurement for atomic mass. Where a proton = 1. (Also known as atomic mass measurement or amu)
Atomic Number
Amount of protons in an atom.
Atomic mass
Mass of an atom (usually measured in Daltons)
Covelent Bond
Two atoms sharing a pair of valence electrons.
A double bond
Atoms sharing two pairs of electrons. Written as = in lewis dot structure
Lewis dot structure
A method of depicting electron distribution and bonding
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
A covalent bond where atoms have atoms have equal electronegativity.
Electronegativity
The attraction of a given for the electrons of a convalent bond.
Polar Covalent Bond
An atom bonded to another atom with high electronegativity - resulting in an uneven sharing of the electron.
Cation
A positively charged ion (has lost an electron)
Anion
A negatively charged ion (has gained an electron)
Ionic Bond
An anion and cation attracting one another because of their opposite charges.
Note: This attraction does not need to be this the atom they transferred electrons with.
Isotope
Variation of neutron in different atoms of the same element.
Radioactive Isotope
An unstable isotope in which the nucleus decays spontaneously
van der Waals interactions
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial changes.
- Think about how a gecko climbs up a wall. Large surface area on the feet allow molecules to stick together (randomised from opposites attract in placement of the electrons in the electron cloud) - hence the gecko being able to scale the wall.
Reactants
Chemicals before a reaction.
Products
Resulting materials from a chemical reaction.
Polar molecule
A molecule with uneven overall charge.
Temperature
Average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
Thermal energy
Total kinetic energy in a substance.
Heat
The transfer of thermal energy
Calorie (cal)
A unit of measurement (which is the amount of heat it takes to raise one gram of water one degree)
Kilocalorie (kcal)
A unit of measurement (which is the amount of heat it takes to raise 1000 gram of water 1 degree)
Calories on food packet actually refer to kilocalories
Joule (J)
A unit of energy. Aprox 0.239 the size of a calorie.
Specific Heat
The amount of energy that must be absorbed or lost for a substance to change temperature by one degree.
For water this is 1 calorie per gram per degrees celsius. This is abbreviated to 1cal/(gxdegrees)
Heat of vaporisation
The quantity of heat a liquid mist absorb for one gram of it to be converted into the gaseous form.
Evaporative Cooling
The molecules with the greatest kinetic energy evaporate and the temperature of the substance drops.
Hydration shell
The sphere of water molecule that surround each dissolved ion - When a solute is being dissolved in an aqueous solution.
Hydrophilic
Substances with an affinity towards water
Hydrophobic
A substance with no affinity to water; tending to coalesce and form droplets in water. It repels water and does not dissolve in it, due to having nonpolar molecules.
Molecular Mass
The sum of all the masses of atoms in a molecule (measure in daltons)
Mole (mol)
6.02 × 10²³ (Avagordo’s number)
Molarity
The number of moles in a solute (per litre)
pH
-log[H+]
Buffer
A substance that minimises changes of concentration of H+ and OH-.
It does this my absorbing hydrogen ions when they are in excess and donating hydrogen ions when they have depleted.
Abiotic
Nonliving component of an ecosystem.
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules consisting of only hydrogen and carbon
Isomers
Compounds that have the same number of atoms of the same elements but different structures, hence, different properties.
There are three main types:
Structural Isomers
Cis-Trans Isomers/Geometric Isomers
Enantiomers
Structural Isomers
Isomers that differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms.
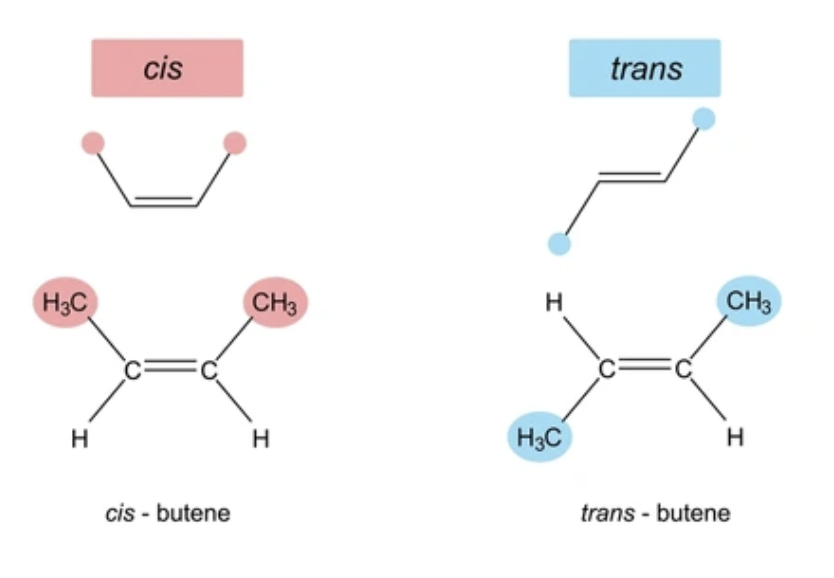
Cis-trans Isomers (also known as geometric isomers)
Isomers than differ in their spatial arrangements, due to the inflexibly of double bonds.

Enantiomers
Isomers that are mirror images of each other and differ in shape due to the presence of a asymmetric carbon.
Functional group
A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions.
Hydroxyl Group
-OH

Carbonyl group
C=O

Carboxyl Group
O
//
-C
\
OH
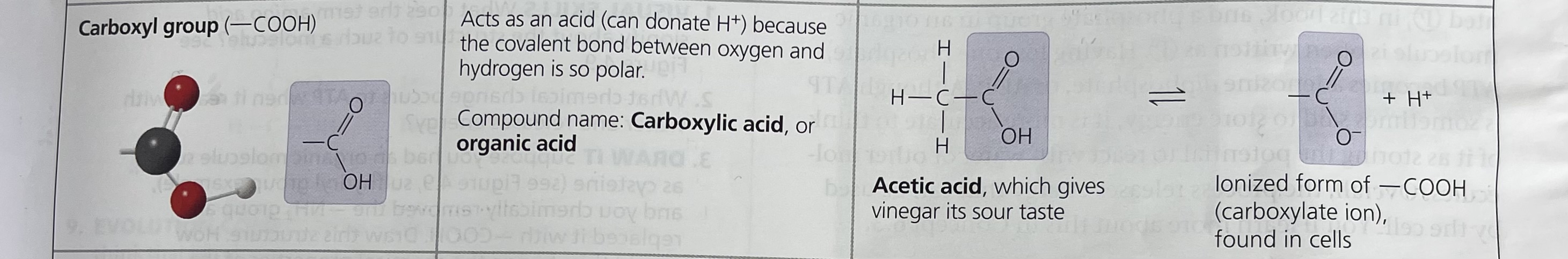
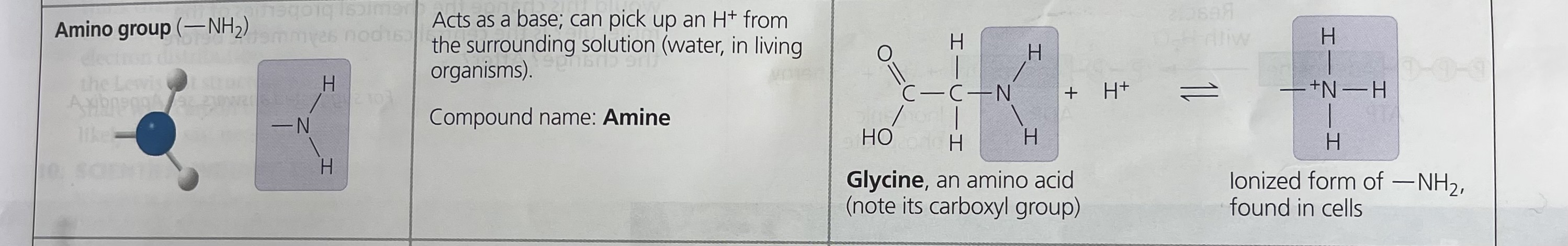
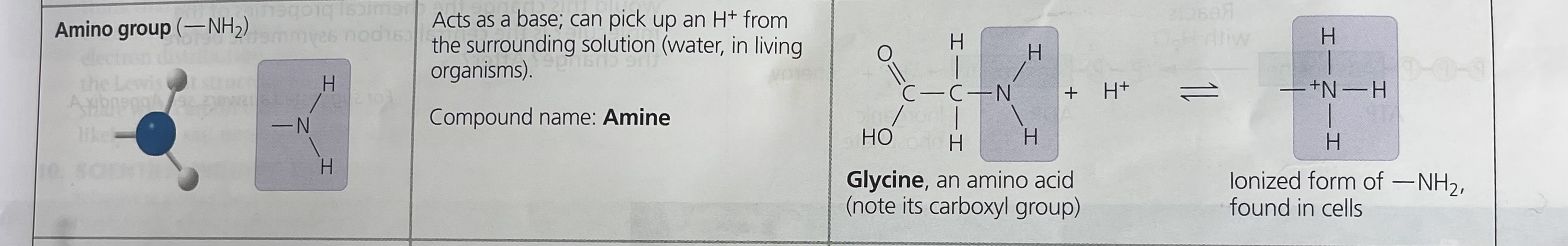
Amino group
H
/
–N
\
H
Sulfhydryl Group
Phosphate Group

Methyl Group

Macromolecules
A giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules. Polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids are macromolecules.
Polymers
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
Monomers
The subunits of polymers.
Dehydration reaction
A reaction in which two molecules become convalently bonded to each other due to the removal of a water molecule; functions in assembling monomers into polymers.
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that breaks bonds between two molecules by the addition of water; functions in disassembling polymers into monomers.
Carbohydrate
A sugar, or a polymer of a sugar.
Monosaccharide
The simplest carbohydrate, active along, or serving as a monomer for disaccharides and polysaccharides. Also called simple sugars, monosaccharides generally have molecular formulae of a multiple of CH2O.
Glycosidic Linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides joined by a Glycosidic Linkage.
Polysaccharide
Macromolecules that are polymers consisting of few hundred to a few thousand monomers connected by a glycoside link.
Glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and stomach of animals; the animal equivalent to starch.
Stores energy. Is replenished my food intake.
Chitin
The carbohydrate used by arthropods to build their exoskeleton.
Lipids
A diverse range of hydrophobic molecules.
Fats
A glycerol molecule joined to three fatty acids.
Fatty acid
A long carbon skeleton (16-18 carbons long) that generally compose the ‘tail’ of a fat.
Ester Linkage
The bond between a fatty acid and a glycerol molecule.
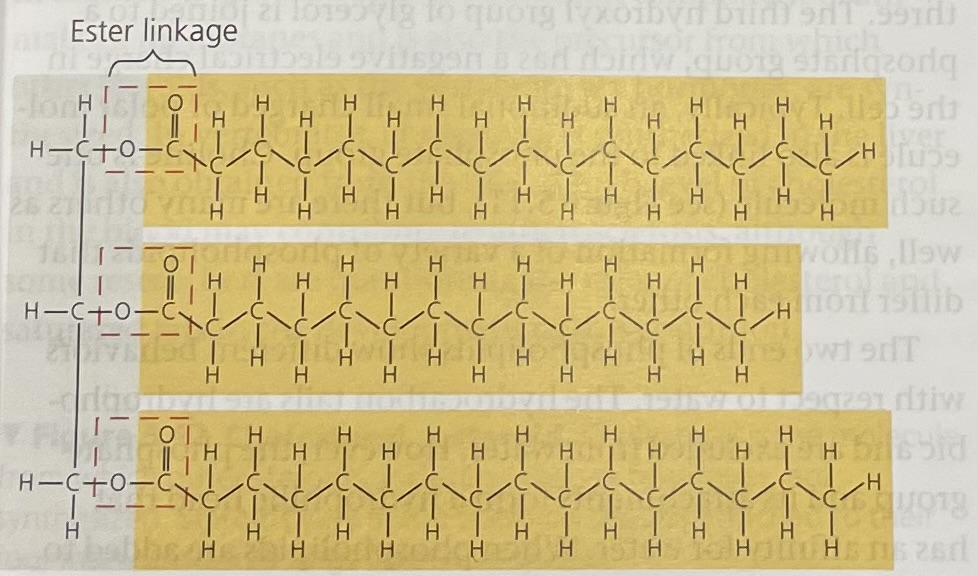
Saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid with no double bonds; more hydrogen. Hence it being *saturated* with hydrogen.
Unsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid with one or more double bond.
Note:
Most naturally occurring double bond in fatty acids are cis, therefore it causes a kink in the hydrocarbon chain.
Trans fats
Fatty acids with trans double bonds.
Can lead to coronary heart disease.
Phospholipid
A lipid made up of glycerol joined my two fatty acids and a phosphate group. The hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids acids are non polar (hydrophobic tails), and the head of the molecule is polar (hydrophilic head). Phospholipids form bilayers that function as biological membranes.
Steriods
Lipids that are characterised by their carbon skeleton that consists of four fused rings.
Peptide bond
The bond between amino acids
Polypeptide
A polymer of amino acids
Protein
A biologically functional molecule composed of one or more polypeptides, twisted into a specific shape.
Amino acid
An organic molecule with both an amino group and a carboxyl group.
Globular protiens
Proteins that are roughly spherical.
Fibrous Proteins
Proteins that are shaped like long fibres.
Primary structure
A sequence of amino acids
Tertiary Structure
The overall shape of a protein molecule due to interactions of side chains and the polypeptide backbone. (Hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, disulfide bridges ect)
Hydrophobic interactions
A type of weak chemical reaction where non-polar molecule coalesce to exclude water.
Disulfide bridges
A strong covalent bond between two cysteine sulphur monomers.