Transition Metals
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is a transition metal?
An element that has an incomplete d sub-level in either the atom or one of the common ions
Give 4 properties of transition metals.
They form complexes
They form coloured ions
Variable oxidation states
Good catalysts
What is a complex?
A molecule consisting of a central metal ion with ligands bonded to it
What is meant by a ligand?
A species that has a lone pair of electrons and can co-ordinately bond to a metal ion
What is a unidentate/monodentate ligand?
A ligand that only forms one coordinate bond with a metal ion
Give some common monodentate ligands.
Cl-, H2O,NH3
What is a bidentate ligand?
A ligand that forms 2 coordinate bonds to a metal ion
Give the names and structures of the 2 required bidentate ligands.
ethane-1,2-diamine
ethanedioate ion
What is a multidentate ligand?
A ligand that forms more than 2 coordinate bonds with a metal ion
Name 2 multidentate ligands.
EDTA and porphyrin
How many co-ordinate bonds does EDTA form?
6
How many co-ordinate bonds does porphyrin form?
4
What is the co-ordination number of a linear complex?
2
What is the bond angle in a linear complex?
180*
When are linear complexes most commonly formed?
In silver (I) complexes
What is the co-ordination number of a square planar complex?
4
What is the bond angle in a square planar complex?
90*
When are square planar complexes formed?
With Pt2+ and Ni2+ ions
What is the co-ordination number of a tetrahedral complex?
4
What is the bond angle in a tetrahedral complex?
109.5*
When are tetrahedral complexes formed?
With larger ligands like Cl- ions
What is the co-ordination number in an octahedral complex?
6
What is the bond angle in an octahedral complex?
90*
When are octahedral complexes formed?
With smaller ligands
What is the purpose of haemoglobin?
To transport oxygen around the body
Why is carbon monoxide toxic to humans?
It bonds more strongly to the Fe2+ ion in haemoglobin than oxygen, preventing the transport of oxygen around the body
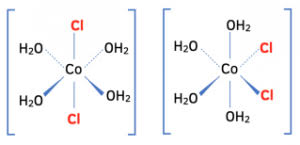
In what complex shapes does cis-trans isomerism occur?
Octahedral and Square planar
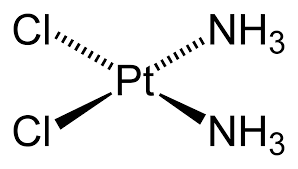
Draw the structure of cisplatin.
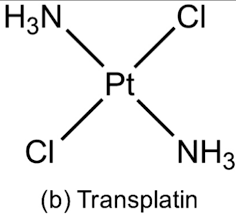
Draw the structure of transplatin.
Draw the cis and trans isomers of an octahedral complex?
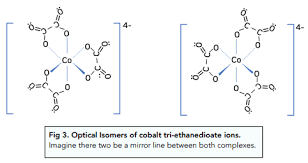
With what complex shape does optical isomerism occur?
Octahedral
When does octahedral isomerism occur in octahedral complexes?
When there are 3 bidentate ligands
Draw 2 optical isomers of an octahedral complex?
How are the d-orbitals arranged in a free transition metal ion?
They are degenerate (have the same energy)
What happens to the d orbitals in a transition metal ion when ligands are attached?
They split so some are at a higher energy than others (normally a 2-3 split)
Explain why we see coloured compounds in transition metal compounds?
Electrons in the lower energy d sub-level absorb light of a specific frequency and are excited
All other frequencies of light are reflected (which we see)
Why is visible light absorbed by d-electrons?
The energy gap between the levels is in the visible light region
Give the equation for the energy absorbed by electrons to excite them.
Energy = h x frequency
Give the value of planck’s constant.
6.63 × 10-34
What factors effect the colour of a transition metal compound?
The type of metal
The oxidation state of the metal
The ligands
The co-ordination number/ shape of the complex
What is colorimetry?
An analytical technique that uses the absorption of visible light to determine the concentration of a substance (by measuring absorbance)
What is the relationship between concentration and absorption?
They are directly proportional
How can a calibration curve be used to determine the concentration of a unknown substance?
Find the absorption value on the graph and connect to the corresponding concentration
Why do transition metals have variable oxidation states?
They can lose both s and d electrons
Give the 3 main oxidation states of manganese.
MnO4- (Mn = +7)
MnO2 (Mn = +4)
Mn2+
In what compound is the manganate ion commonly found?
KMnO4
What is the standard state of manganese oxide (MnO2)?
solid
What colour is the Mn2+ ion?
colourless
Give some properties of potassium (per) manganate.
Purple liquid
Strong oxidising agent in acidic conditions
Why are most transition metal redox titrations self-indicating?
There is a significant colour change when the metal ion changes oxidation state
Why is H2SO4 commonly used to provide the acidic conditions for a redox titration?
It provides sufficient H+ ions and does not react with the reactants or products
What is always the role of manganate ions in a redox titration?
Oxidising agent
What is the role of Fe2+ ions in a redox titration?
Reducing agent
Why is ethanoic acid not used as the acid for redox titrations?
It does not supply enough H+ ions as it is a weak acid
Give the colour change in a redox reaction between Fe2+ and MnO4- ions.
Colourless to (permanent) pink
Give an overall equation for a redox titration between Fe2+ and MnO4- ions and state the molar ratio of Fe:MnO4.
5Fe2+ + MnO4- + 8H+ —> 5Fe3+ + Mn2+ + 4H2O
5:1
Write an equation for the redox reaction between MnO4- and C2O42- ions and give the molar ratio for C2O42-:MnO4-.
5C2O42- + 2MnO4- + 16H+ —> 10CO2 + 2Mn2+ + 8H2O
5:2
What is the molar ratio when both types of reducing ions are involved in the titration?
5:3
Why are transition metals good catalysts?
They have variable oxidation states, which allow them to form intermediates
They provide a surface for reactants to adsorb
State the 2 types of catalysts?
Homogeneous and heterogeneous
What is a homogeneous catalyst?
Where it is the same state as the reactants
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
Where it is a different state to the catalyst
Name the catalyst used in the contact process.
Vanadium (V) oxide
Is the contact process heterogeneous or homogeneous?
Heterogeneous
What is the overall equation for the contact process?
SO2(g) + 1/2O2 —> SO3(g)
Give the 2 steps in the catalysed route of the contact process.
V2O5 + SO2 —> SO3 + V2O4
V2O4 + 1/2O2 —> V2O5
Describe the general process for heterogenous catalysis.
Reactants adsorb to active sites
Bonds weaken in reactant molecules and they are brought closer together in the right orientation
The reaction occurs
Products desorb from the surface
What happens when the adsorption is too strong?
The product cannot desorb from the surface and reactants cannot move around
What happens when the adsorption of the catalyst is too strong?
The reactants cannot be adsorbed
What is catalytic poisoning?
When certain substances block active sites in the catalyst, slowing the rate of reaction
Give the overall equation for the reduction of peroxydisulfate.
S2O82- + 2I- —> I2 + 2SO42-
Give the 2 half equations involved in the reduction of peroxydisulfate.
2I- —> I2 + 2e-
S2O82- + 2e- —> 2SO42-
Why is the Ea very high for the reaction between peroxydisulfate and iodide?
They are both negative ions, so there is repulsion between them
Why are Fe2+ and Fe3+ good catalysts for the reaction between peroxydisulfate and iodide?
They are positive, so attract the negative ions, and they have variable oxidation states, allowing them to form intermediates
Give the 2 equations for the alternative catalysed route for the reaction between peroxydisulfate and iodide?
2Fe3+ + 2I- —> I2 + 2Fe2+
2Fe2+ + S2O82- —> 2Fe3+ + 2SO42-