PLTW Human Body Systems Lesson 3.1 Cardiopulmonary Connection
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Thease are only from 3.1.1-3.1.4 I haven't created the whole entire deck yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Skeletal Muscle: striated (true or false?)
True
Skeletal Muscle: Voluntary (true or false?)
True
Location of the skeletal Muscle
attached to all bones.
Funtion of the Skeletal Muscle
allowes for movement in the body
Smooth Muscle: Striated (true/false)
false
Smooth Muscle: Voluntary (true/false)
false
Location of the smooth Muslce
Digestive adn urinary organs, some vessles
Funtion of the Smooth Muslce
aids in blood flow, digestion, and ridding the body of toxins
Cardiac Muscle: Striated (true or false)
True
Cardiac Muscle: Voluntary (true or false)
false
Location of Cardiac Muscle
Heart
Funtion of cardiac Muscle
pumps blood through the cardiovascular system.
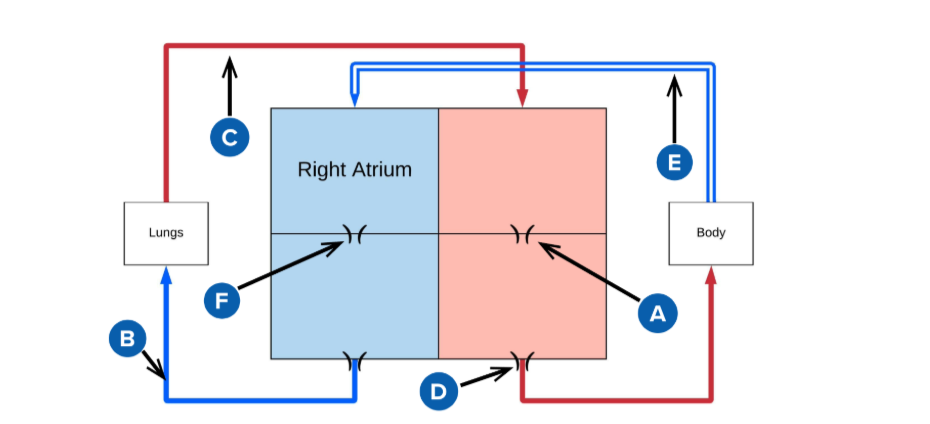
A
mitral valve
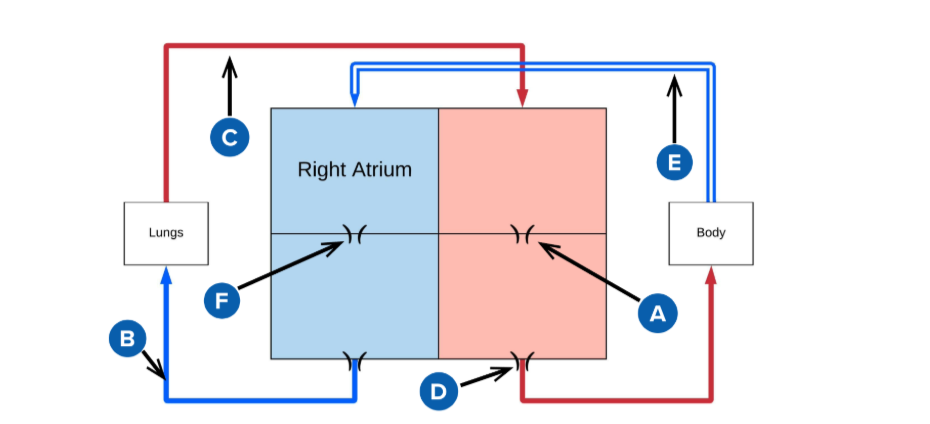
B
pulmonery artery (carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.)
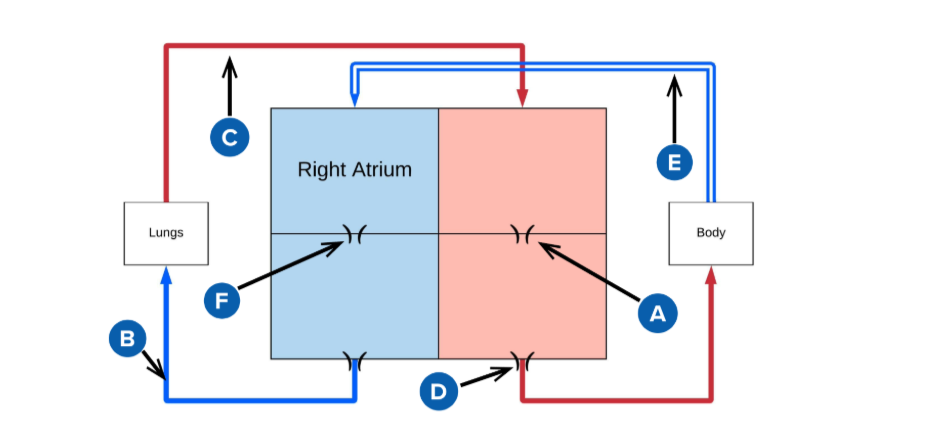
C
pulmonery veins (carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.)
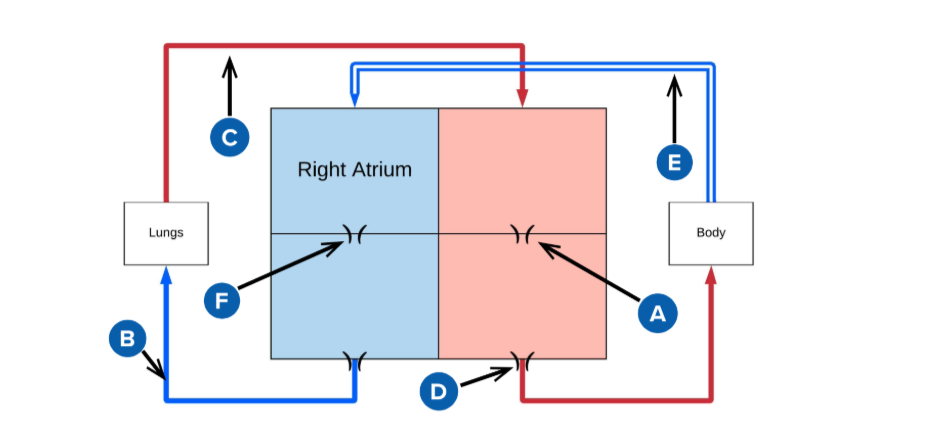
D
Aortic valve (regulates blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta, ensuring proper circulation throughout the body)
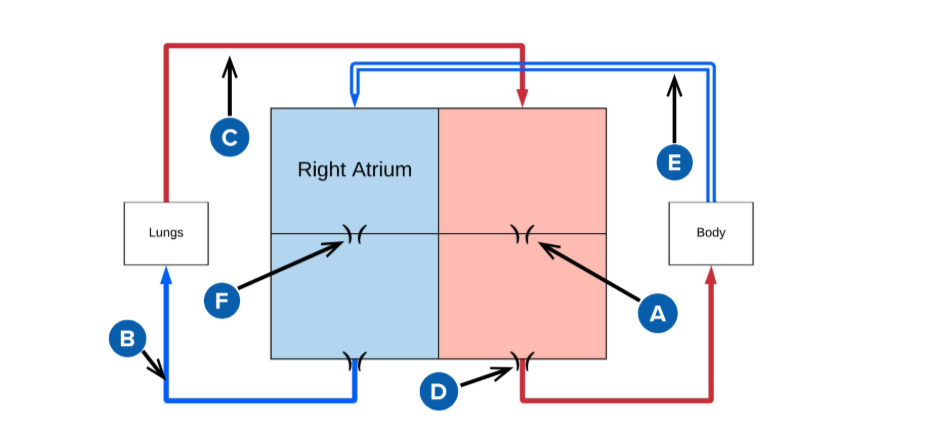
E
superior and inferior vena cava
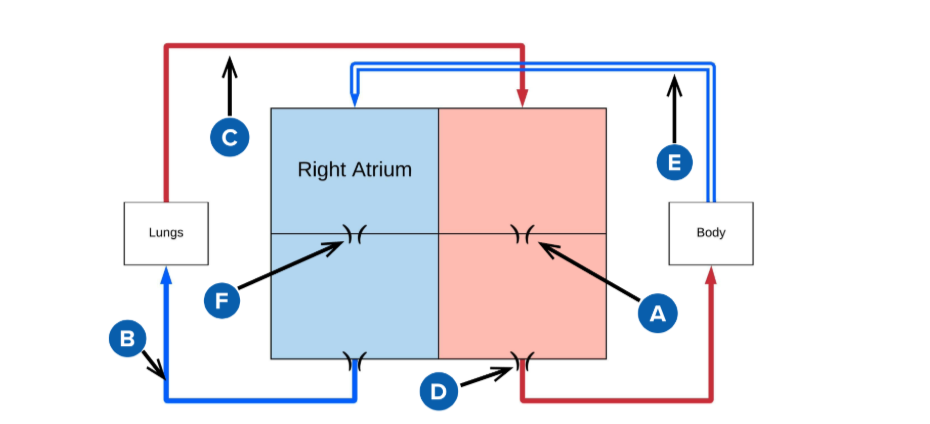
F
Triscupid Valve
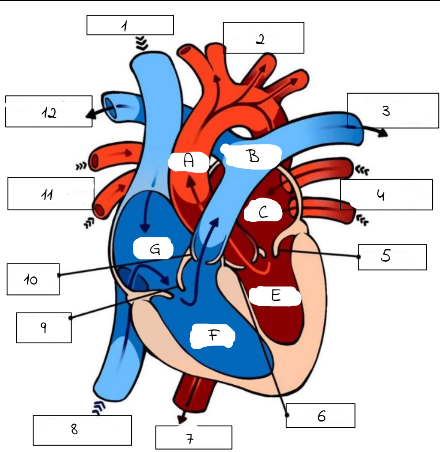
1
Superioir Vena Cava
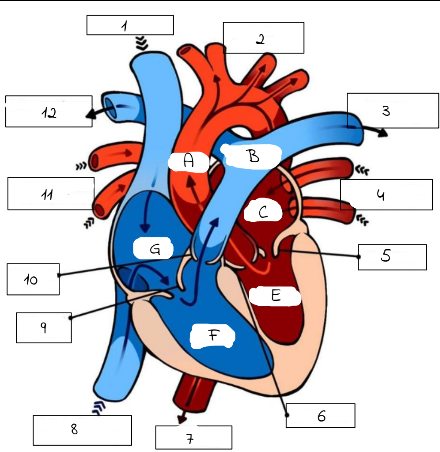
2
Aorta
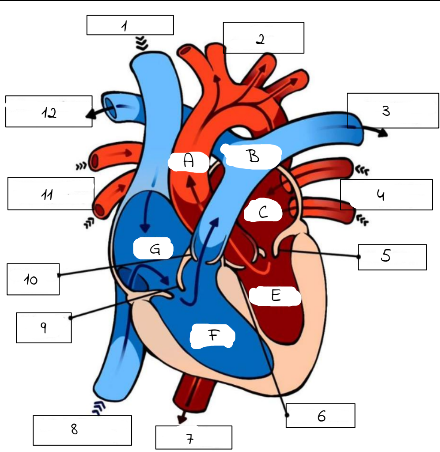
3
Pulmonary artery (to left lung)
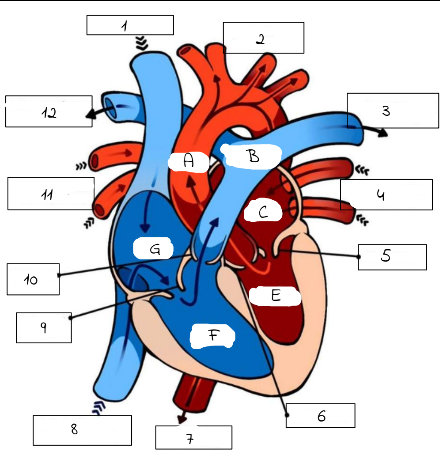
4
Pulmonary Veins (from left lung)
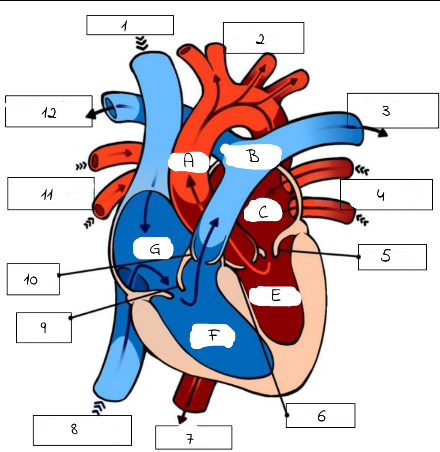
5
mitral valve
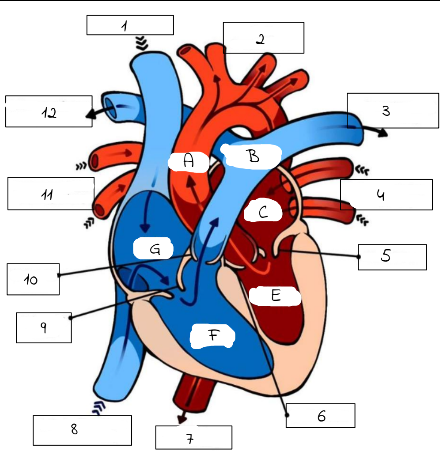
6
Aortic Valve
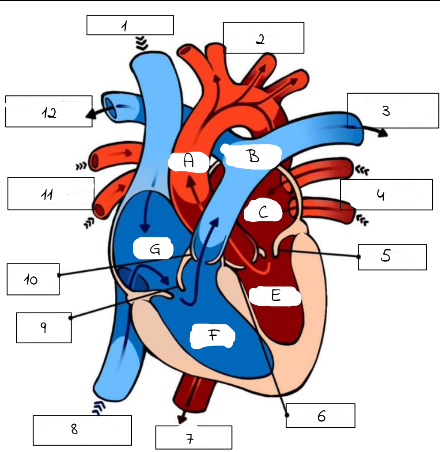
7
Aorta (to lower body)
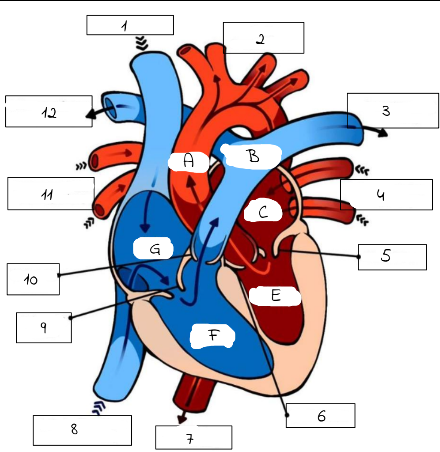
8
Inferior Vena Cava (from lower body)
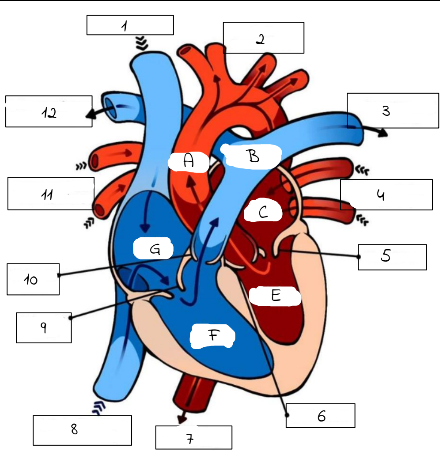
9
Tricuspid Valve
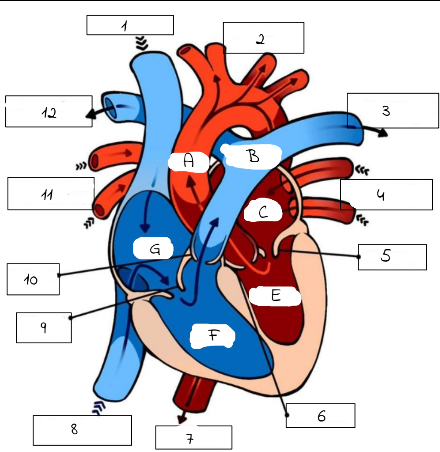
10
Pulmonic Valve
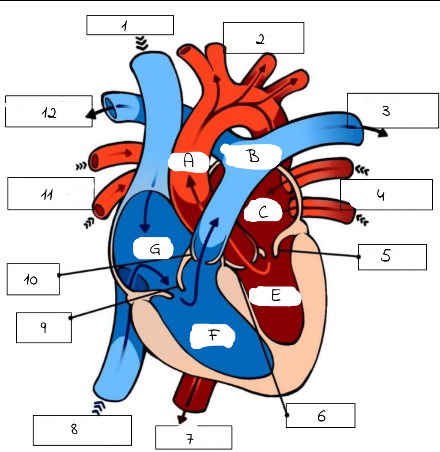
11
pulmonary Veins (from right lung)
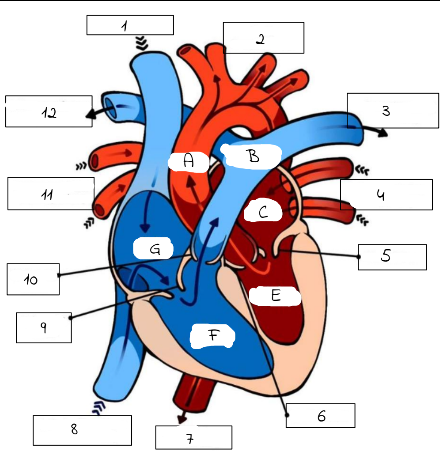
12
Pulmonary Artery (to right lung)
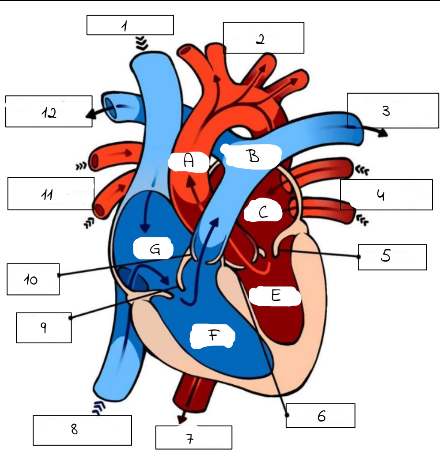
A
Aorta
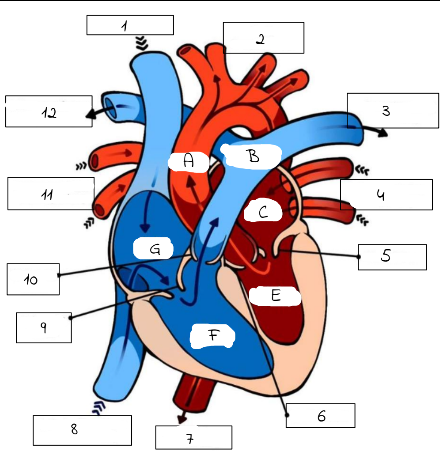
B
Pulmonary artery
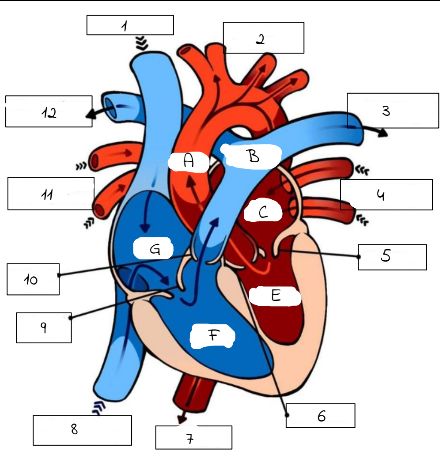
C
Left Atrium
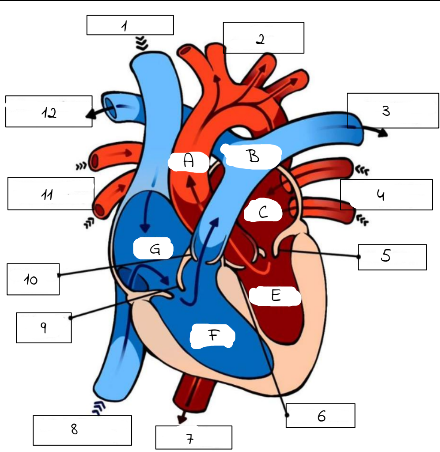
E
Left Ventricle
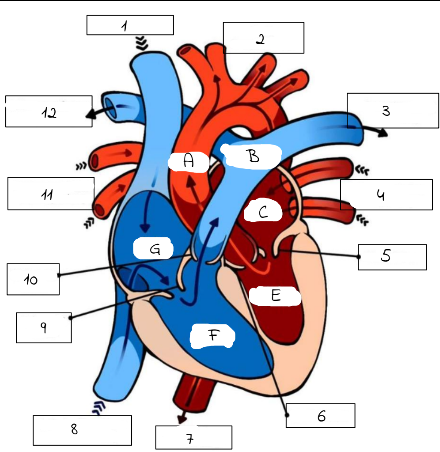
F
Right Ventricle
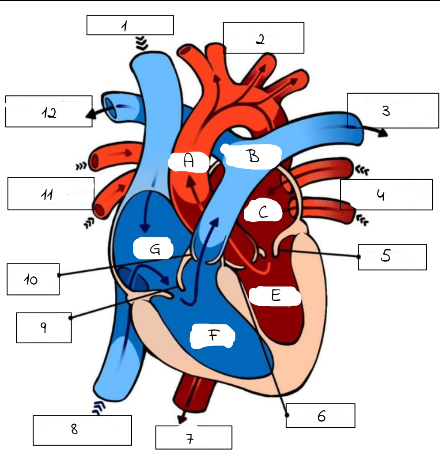
G
Right Atrium
What role do valves play in the heart?
Valves prevent the backward flow of blood through the heart.
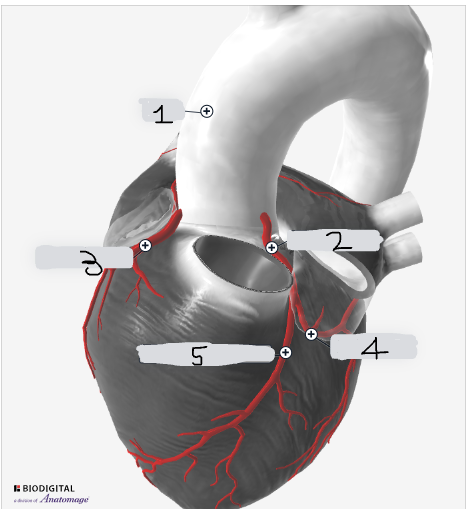
1
Aorta
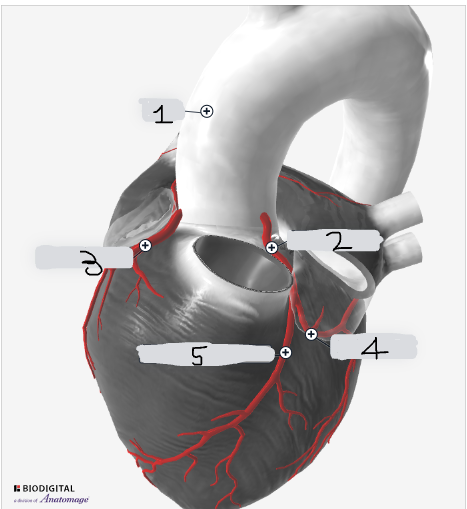
2
Left coronary artery
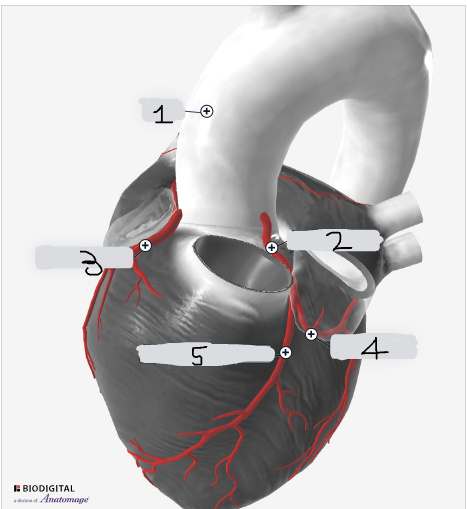
3
Right coronary artery
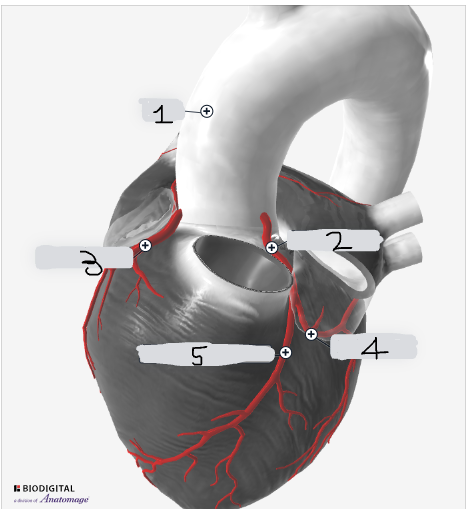
4
circumflex artery
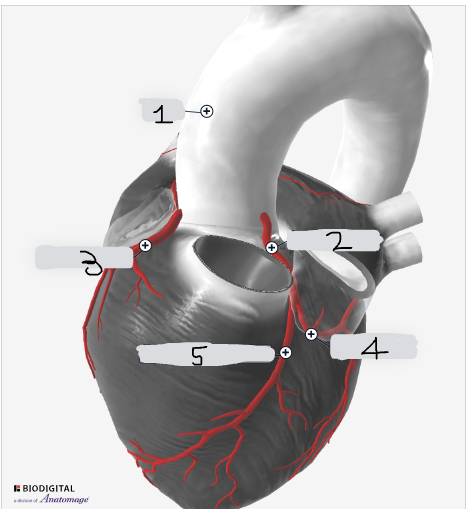
5
Left anterior descending artery
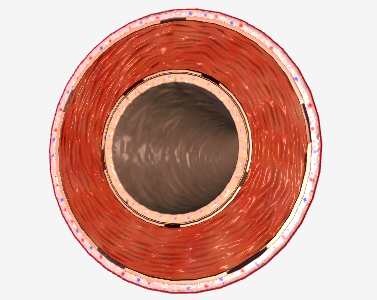
What type of blood vessel is depicted here?
Artery
What type of blood vessel is depicted here?
vein
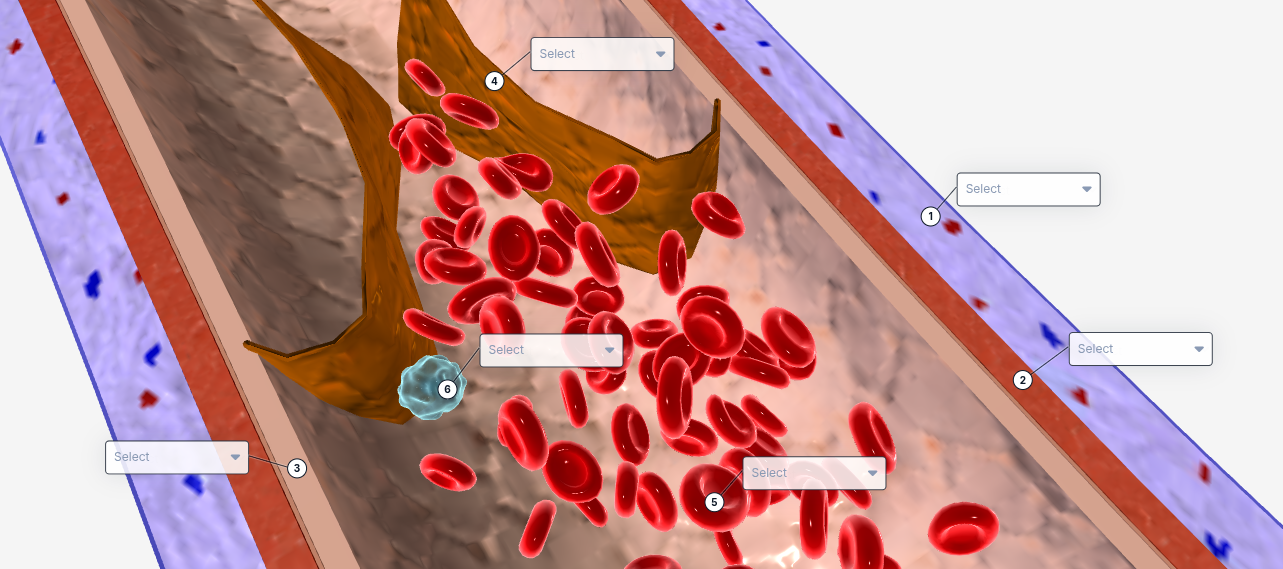
1
Tunica externa
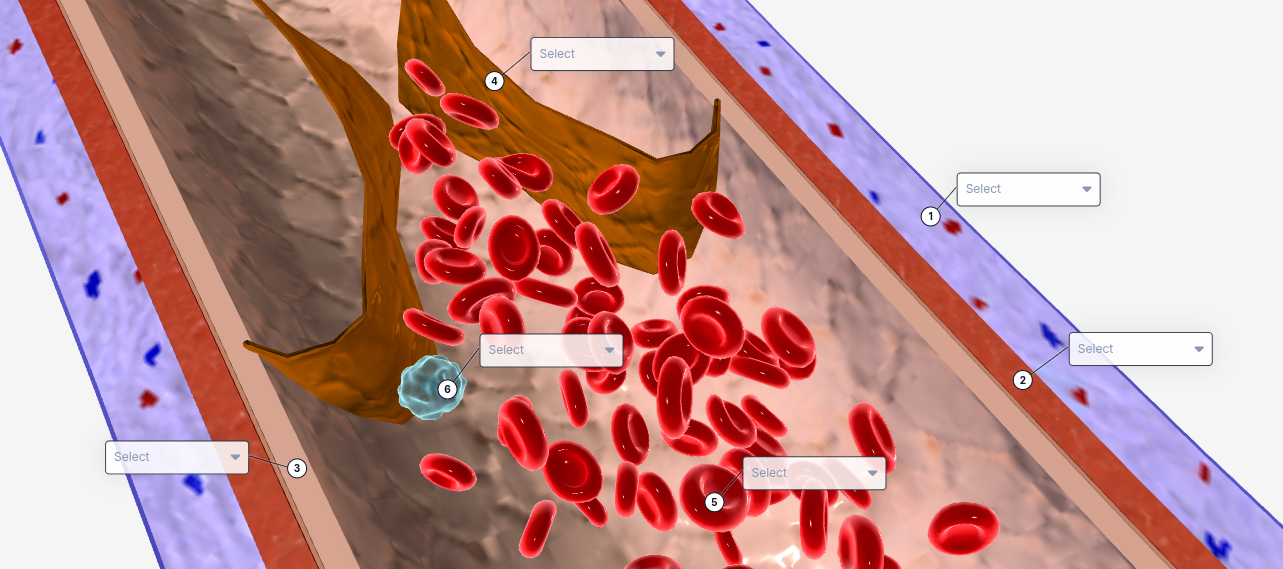
2
Tunica Media
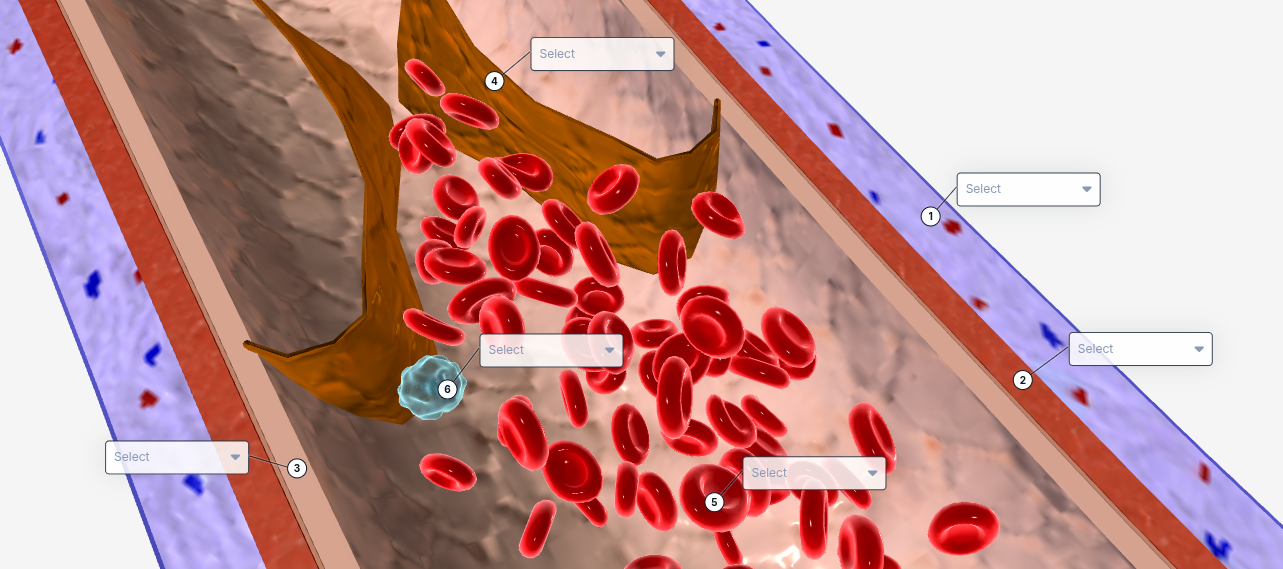
3
Tunica intima
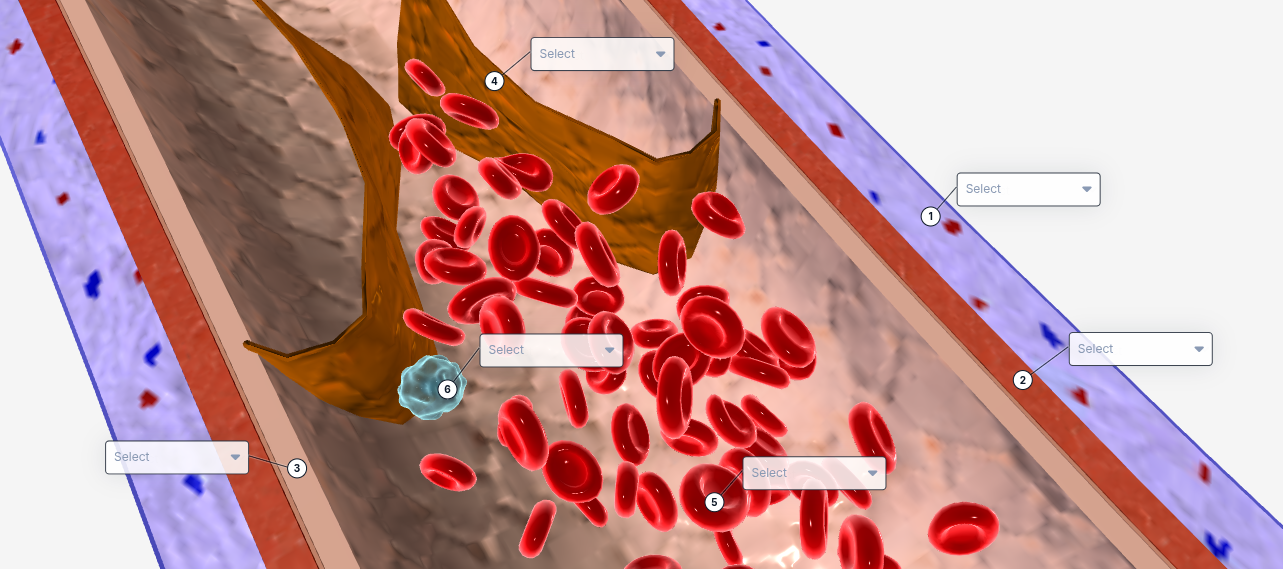
4
valve
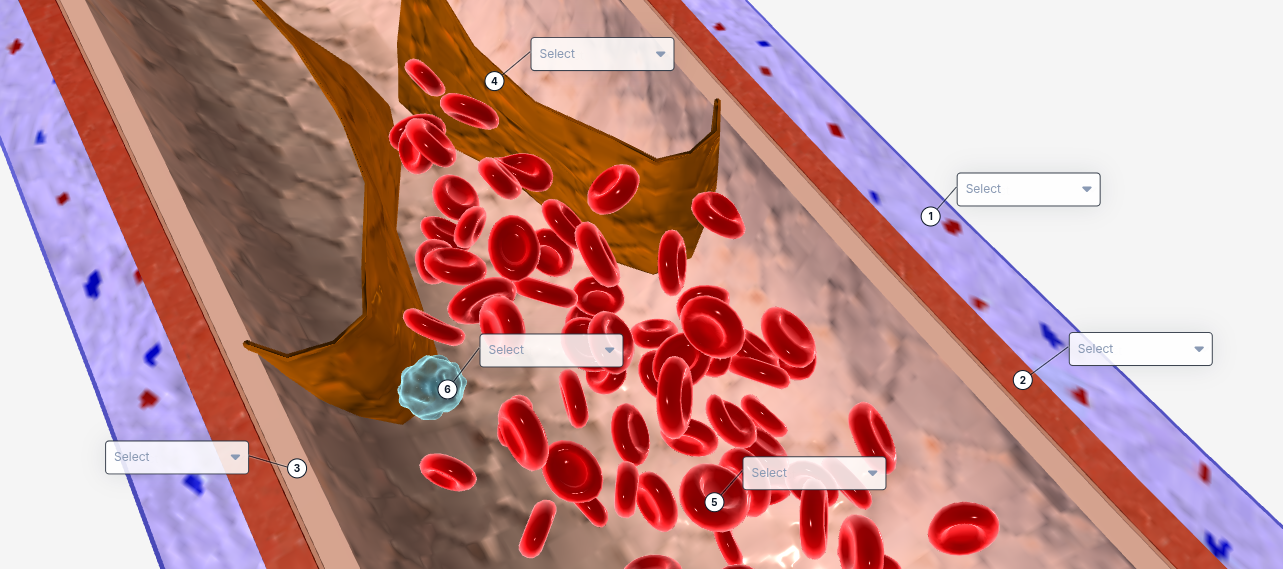
5
Red blood cell
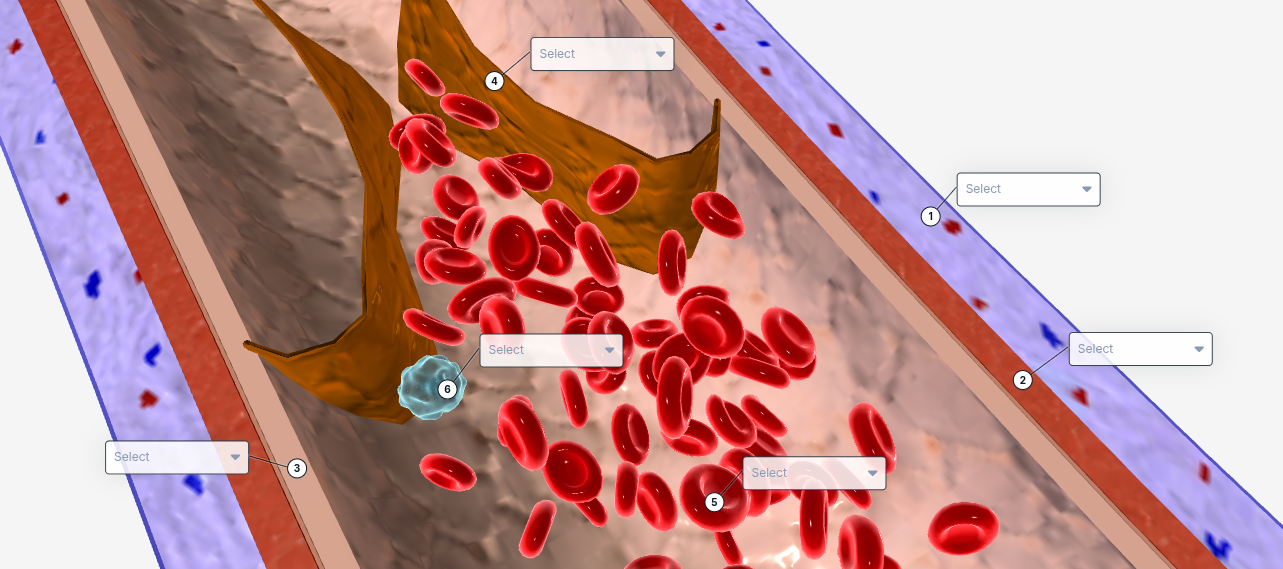
6
White blood cell
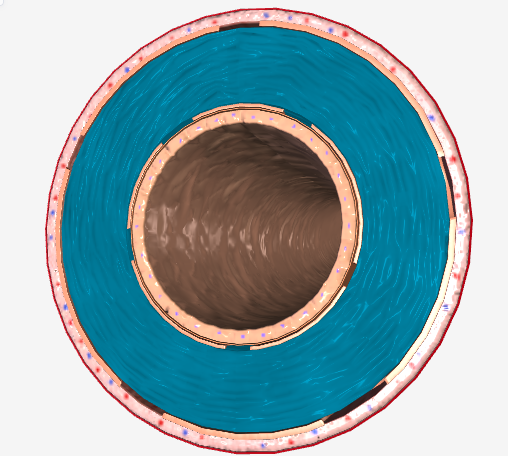
The structure that contains smooth muscle and elastic fibers, allowing the vessel to dilate and constrict to regulate blood flow.
Tunica Media
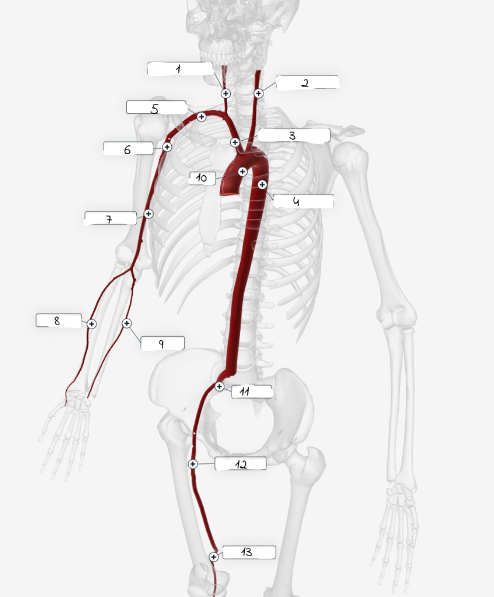
1
Right carotid artery
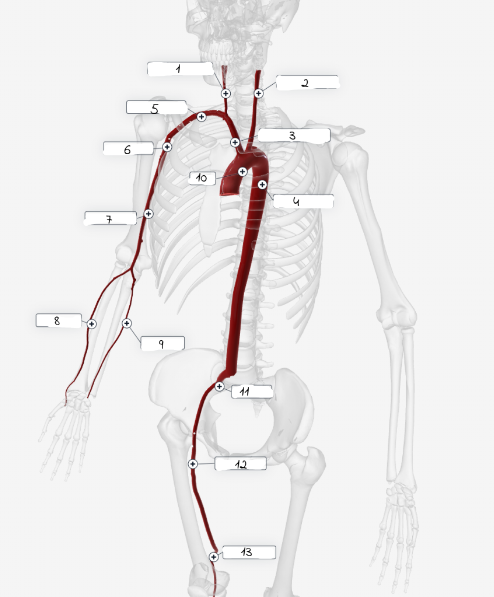
2
Left carotid artery
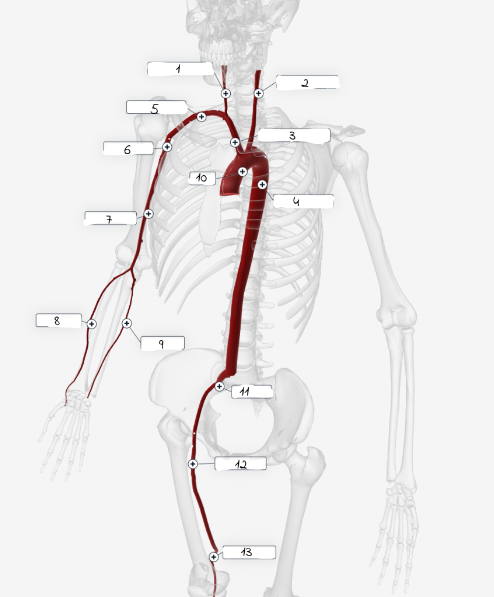
3
Brachiocephailic trunk
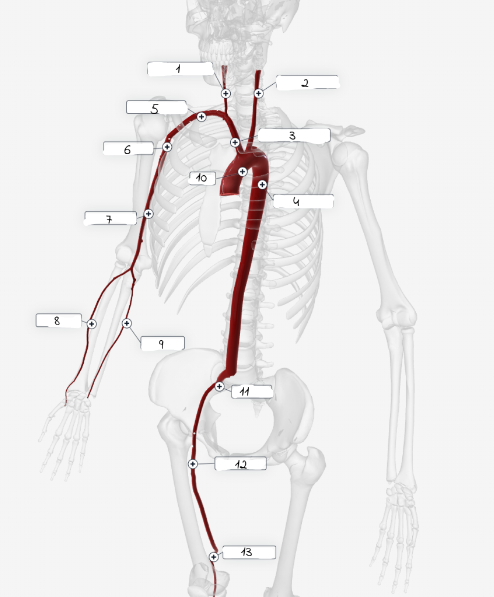
4
Descending aorta
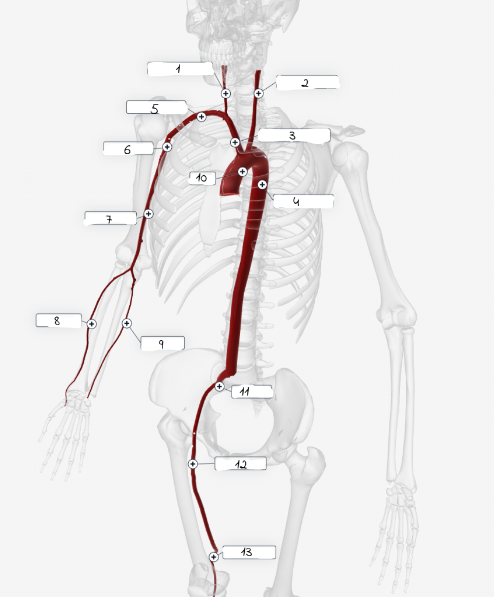
5
Subciavian artery
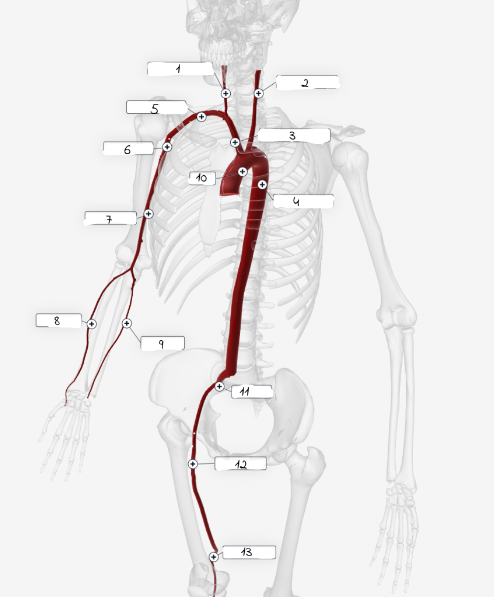
6
axillary artery
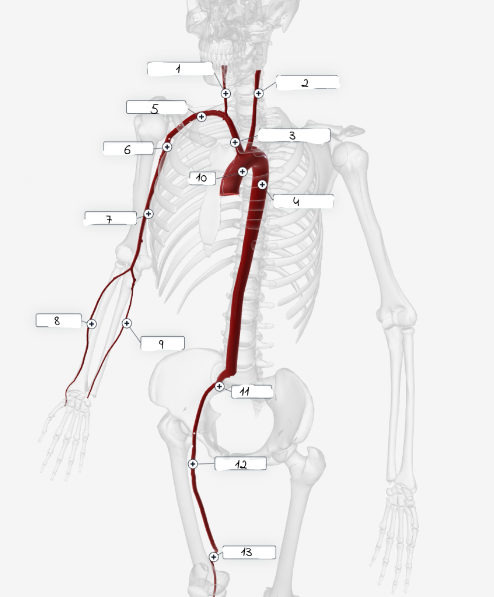
7
Brachial artery
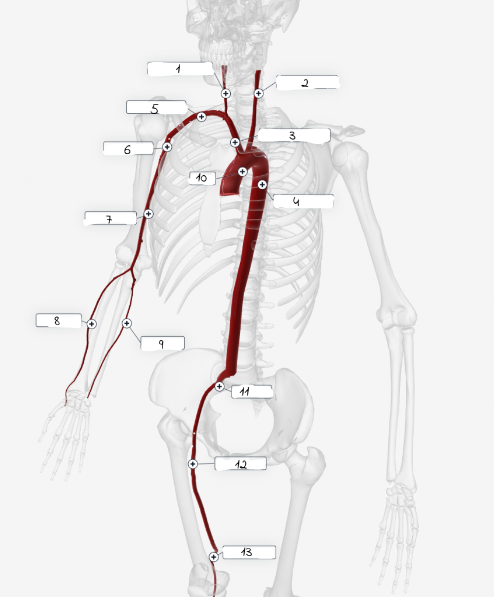
8
Radial Artery
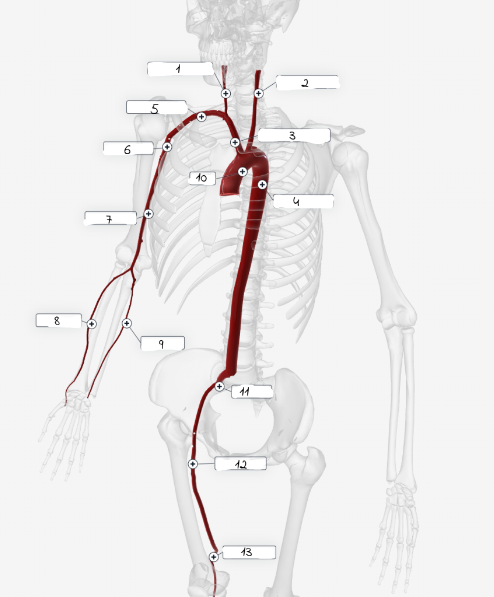
9
Ulnar artery
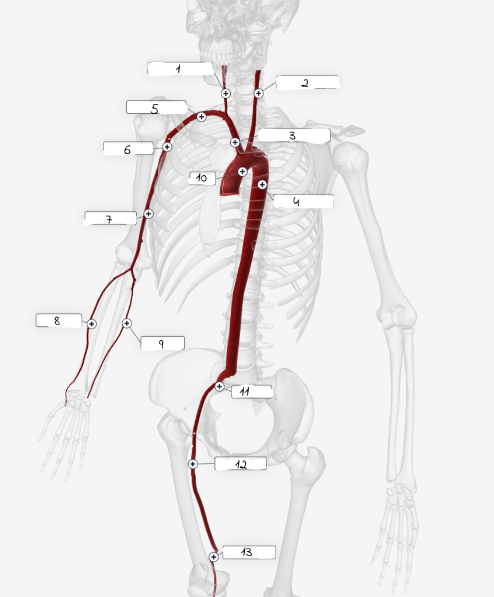
10
Aorta
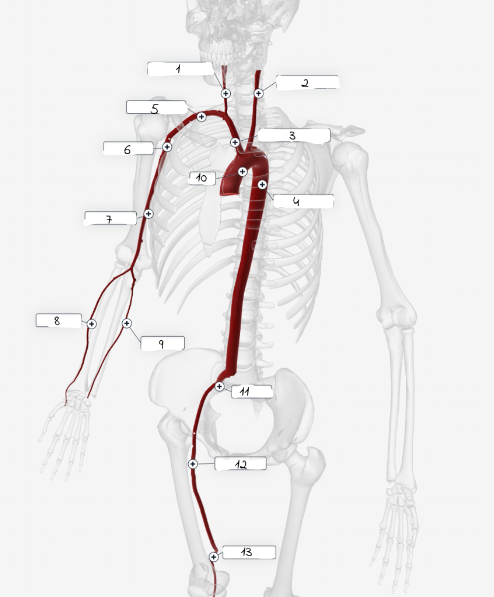
11
lliac artery
Systolic Pressure
Pressure in teh arterieswhen the heartundergoes systole-the heart contracts to push blood throughout the body
diastolic pressure
Pressure in the arteries when the heart undergoes distole-the heart is at rest, allowing the chambers to fill with blood.
Some of the more thrilling activities, like bungee jumping, can increase a person’s heart rate significantly. If a client’s heart rate jumps to 140 beats per minute, how would that affect their cardiac output?
Increase their cardiac output
Dehydration decreases cardiac output
True-Because stroke volume is decreased, the heart pumps less blood with each beat.
What are some consequences of low cardiac output?
Fatigue
Low levels of oxygen in the blood
Breathlessness or trouble breathing g
Hypotension
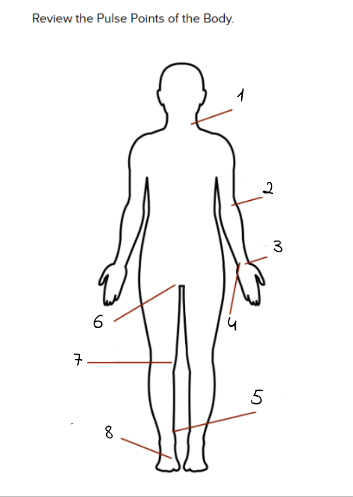
1
carotid
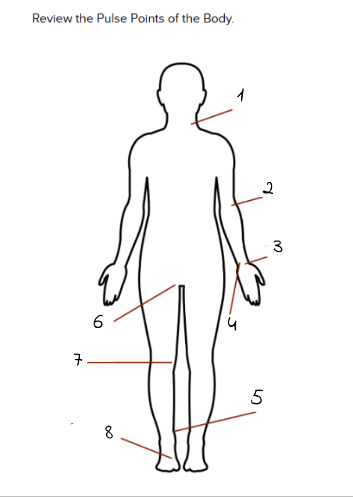
2
Brachial
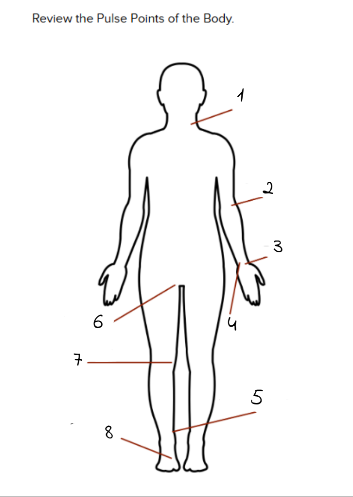
3
Radial
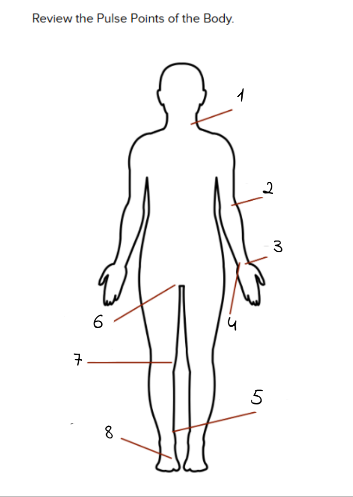
4
Ulnar
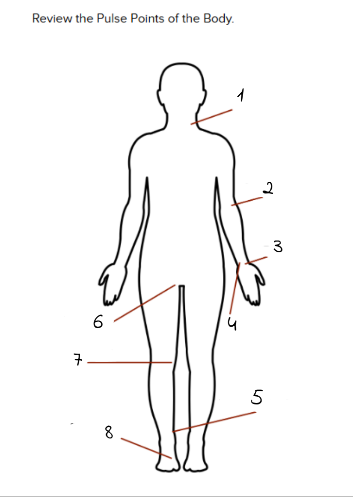
5
Tibialis Posterior
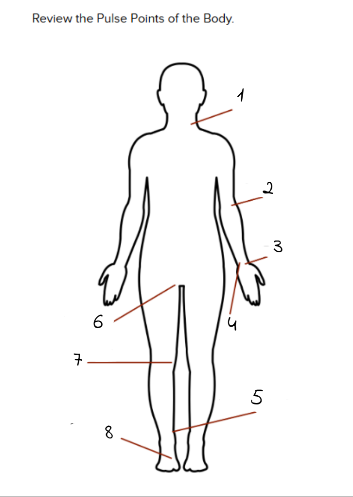
6
Femoral
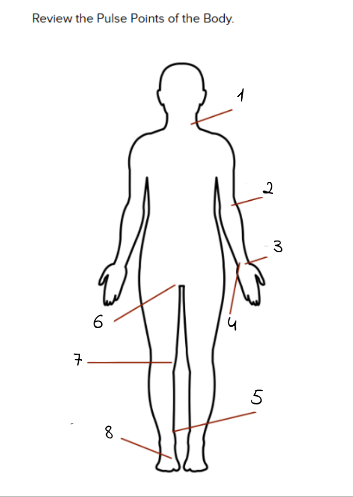
7
Popliteal
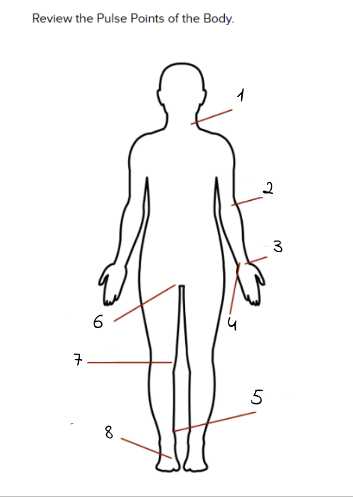
8
Dorsalis Pedis
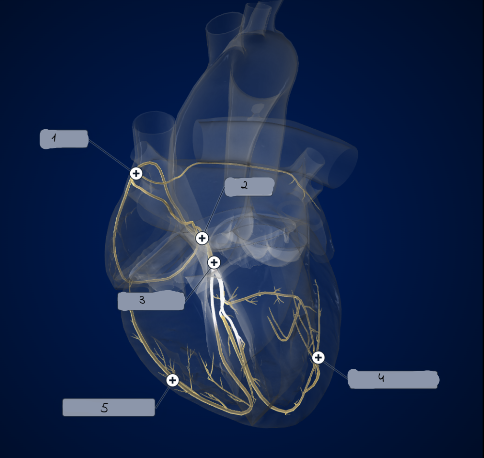
1
SA node
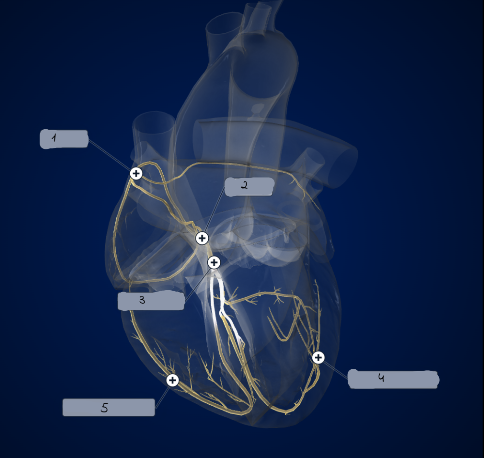
2
AV node
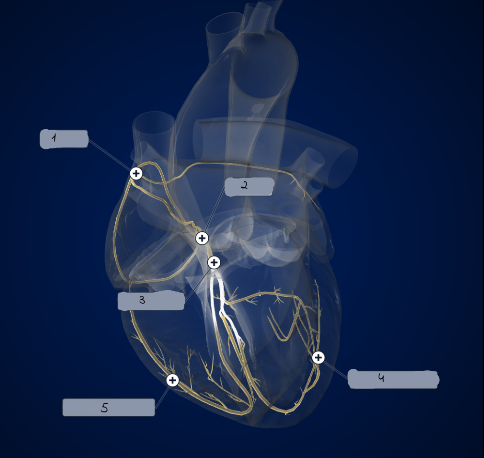
3
Bundle of His
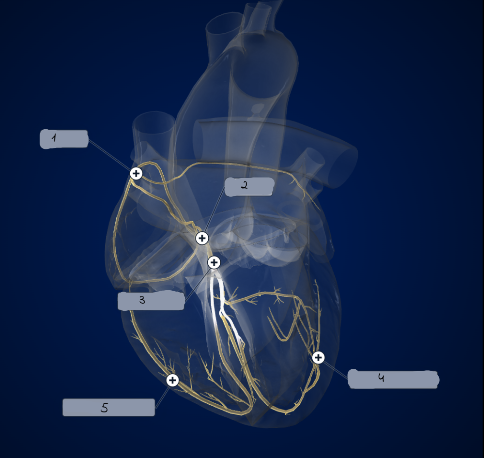
4
Left Purkinje Fibers
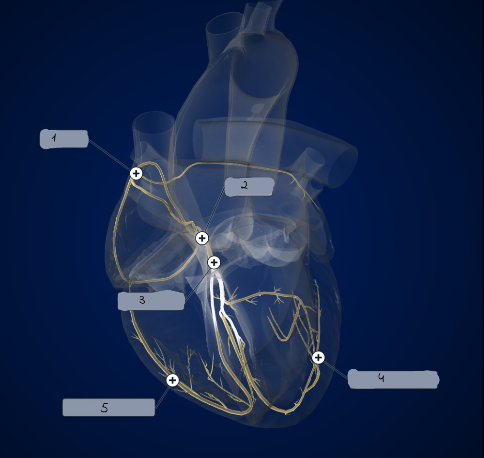
5
Right Purkinje Fibers
Arrythmia
irregular heartbeat caused when the electrical signals that coordinate the heart beat misfire.
Tachycardia
When the heart beats too fast
bradycardia
wehn teh heart beats too slow or in an unpredictible pattern
fibrillation
abnormal contraction of the chambers of the heart
Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
simple-to-use device that can analyze and interpret electrical signals within the heart and determine whether providing an electrical shock or series of shocks to the heart may help restore the heart to a normal rhythm.
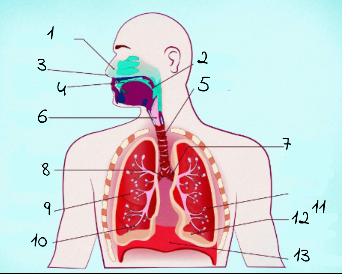
1
nasal cavity
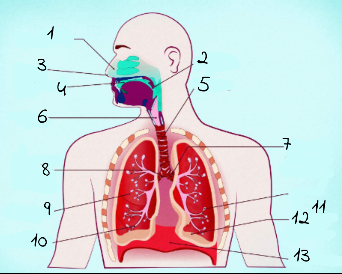
2
Pharynx
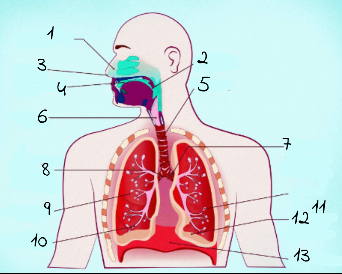
3
nostrils
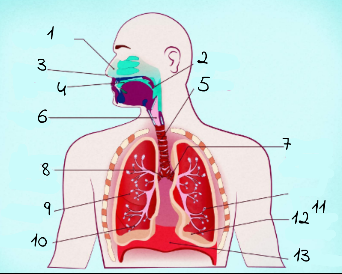
4
oral cavity
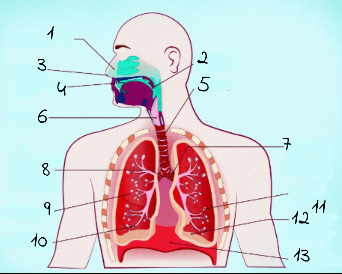
5
trachea
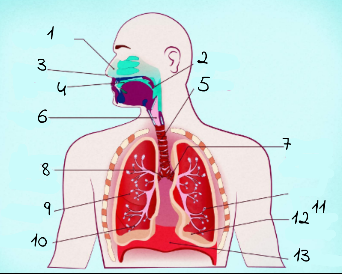
6
larynx
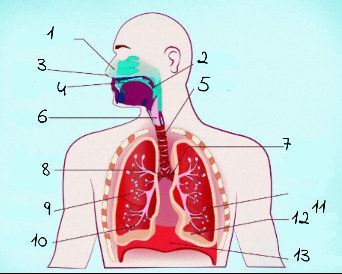
7
left main (primary) bronchus
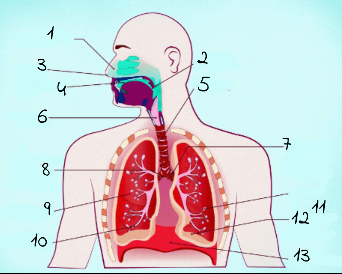
8
right main (primary) bronchus
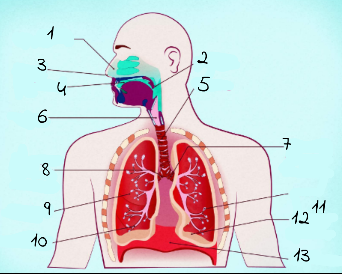
9
rightright lung
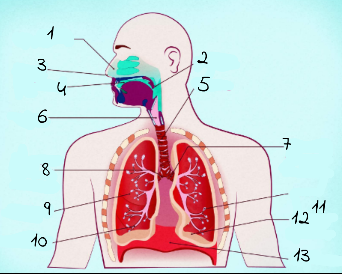
10
bronchiole
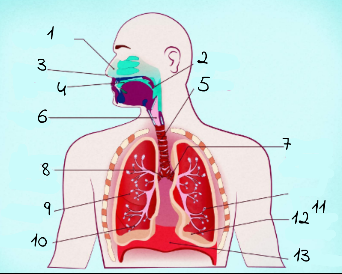
11
alveoli
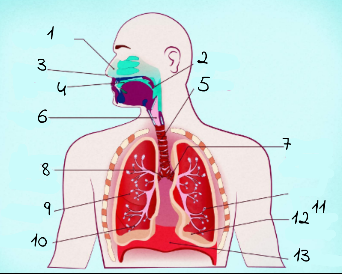
12
base of left lung
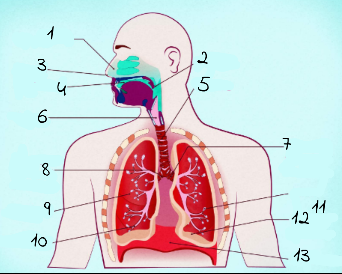
13
diaphram