AP psychology U1
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
heredity definition
the predisposed characteristics that influence an individual’s physical, behavioural and mental traits and processes inherited from parents through genes.
environment definition
the external factors that an individual experiences, such as a person’s family, friend groups, school and other societal factors
how does evolution affect behaviour in terms of genes?
it focuses on natural selection, the passing down of genes, and how many of our behaviours and mental processes actually come from our ancestors
eugenics definition
improving the genetic quality of the human population by promoting the reproduction of individuals with desirable traits and discouraging reproduction among those with traits deemed undesirable
heritability definition
the mathematical measure to estimate how much variation there is in a population related to its genes (populations, not individuals)
range of heritability
0 to 1
for example, what does it mean when the heritability is 0.7
70% of gene variations in a population is caused by genetics
30% is due to the environment
epigenetic definition
study of how the environment and a person’s behaviours affect their genes and how they work
plasticity definition
when the brain changes and builds new neural pathways in response of a persons’ experiences
central nervous system is made up of…
brain and spinal cord
central nervous system function
controlling and processing all body functions
brain function (5)
processing sensory information
thinking
controlling motor functions
emotions
regulating bodily functions
peripheral nervous system is made up of…
nerves branching out from the spinal cord and brain
peripheral nervous system function
connects CNS to the body cells
afferent neurons
sensory neurons
send signals from the sensory receptors to the CNS
Approaches brain
efferent neurons
motor neurons
signals from CNS to spinal cord to the PNS
Exits brain
somatic nervous system controls…
voluntary muscle movement
autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary functions (crucial for survival)
sympathetic division
(fight or flight response)
increases heart rate, dilates eyes, decreases breathing, slows down digestion
parasympathetic division
(rest and digest)
increases digestion, slows down heart rate, increases breathing, saves and stores energy
what is the reflex arc?
the neural pathway that tells the body to respond to the stimulus without thinking / process the information
what is the path of neural signals in a reflex arc?
sensory neurons (afferent) → interneurons → motor neurons (efferent)
what is a interneuron
neurons within the CNS that communciate internally and connect afferent to efferent neurons to transport signals to muscles to make them react
nociceptors
pain receptors
glial cells function (7)
provide support for neurons
supporting the whole nervous system
insulates neurons
speed up signal transmission
facilitate communication between neurons
transport nutrients
removing waste products
where do we find glial cells?
axon of neurons
how does a neuron work
the cells have a resting negative cell membrane potential. it is more negatively charged on the inside due to more negative ions
dendrites receive action potential which begins depolarisation across the axon, where positive ions (Na+) flow into the neurons, causing the inside of the cells to be more positive. this disturbance in the membrane potential causes electrical signal to pass along the axon
the myelin sheaths and nodes of ravelin speeds up the travel of action potential / electrical signal
when the signal reaches the axon terminal, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, which diffuse across it to attach to receptors on the post-synaptic receptors on the adjacent neurons
action potential starts in the other neuron
what happens to a neuron after depolarization
After depolarization, repolarization occurs when positive ions rush out of the cell, so the membrane potential is returned to its normal negative resting potential
The neuron goes through the absolute refractory phase, where it cannot fire an action potential temporarily
when are electrical synapses used
sending quick and immediate messages
excitatory neurotransmitters
Increases likelihood for neuron to start depolarization and fire an action potential
inhibitory neurotransmitters
increases hyperpolarization which decreases the likelihood that the neuron will send an action potential
serotonin
manages arousal, sleep, pain sensitivity, mood and hunger
dopamine
Manages movement, emotions, learning, attention and reward
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric acid)
Inhibitory neurotransmitter → sleep, movement, slow down nervous system
Glutamate
Excitatory neurotransmitter → long term memory and learning (counterpart to GABA)
Norepinephrine
increases heart rate, BP, alertness, (FOF response) (a lack thereof is implicated in depression)
Endorphins
pain control, impacts pain tolerance
Acetylcholine
Muscle action, learning, memory
substance P
transmits pain from sensory nerves to CNS
hyperpolarization
when the insides of the neuron becomes more negative, moving it further away from the threshold for it to fire an action potential
what happens to neurotransmitters when it binds to the receptors
it unbinds and either break down or is reabsorbed
soma
neuron cell body which allows for the neuron to function
dendrite
receive chemical information from neighbouring neurons through receptor sites
axon fibre
carries signals away from the soma and towards the axon terminal
Schwann cell
wraps around the axon and produces the myelin sheath
myelin sheath
covers and protects the axon from damage and increases how fast the action potential can travel down the axon
nodes of ranvier
gaps between myelin sheath — promotes the continuing action potential
multiple sclerosis
myelin sheath is damaged, resulting in the disruption in the transmission of electrical signals
symptoms: muscle fatigue, weakness…
myasthenia gravis
autoimune disorder, affects the comuniaiton between nerves and muscles
antibodies block or destroy acetylcholine receptors, preventing muscle contraction and leading to muscle weakness and fatigue
Agonist drugs
increase effect of neurotransmitter through
mimicking the neurotransmitters by binding to the receptors
increasing production of NT
or blocking reuptake → more neurotransmitters in the synapse since they are not reabsorbed
antagonists drugs
decreases effect of neurotransmitter
block neurotransmitters from being released from the PreST
block post-synaptic receptors
stimulants
excite and promote neural activity
give individual energy
reduce apetite
awakeness, irritability
depressants
reduce neural activity
drowsy, muscle relaxation, reduced breathing, death
hallucinogens
reduce motivation, lead to panic
hallucinate
opioids
pain relief
addictive depressants
constant use of drugs causes…
a person to develop a higher tolerance, more drugs need to be consumed to achieve the same effect → addiction, withdrawal symptoms
adrenaline
response to high emotional situations, forms memories, expands air passages, redistribute blood (FOF response)
leptin
regulate energy balance, inhibit hungers
gherkin
hunger, release of growth hormones
melatonin
(produced by pineal gland) regulates sleep-wake cycle
oxytocin
(hypothalamus, released by pituitary gland) love hormones, promotes feelings of affection and emotional bonding
brain stem consists of
mid brain
pons
medula oblongata
medula function
controls autonomic function
pons function
connects different parts of the nervous system, maintains sleep and dreaming
cerebellum function
controls muscle movement, balance, procedural learning
procedural learning meaning
a type of long-term memory that involves learning how to perform tasks or actions through repetition and practice often without conscious awareness
reticular activating system (anatomy + function)
a bundle of nerves that runs through the brain stem
regulating consciousness and arousal / awareness
filter incoming sensory information and highlights important ones
brain’s reward centre function
feel satisfaction and pleasure
use neurotransmitters to feel rewarded (especially dopamine)
limbic system consists of
and where is it found?
thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala
between the cerebral cortex and the brain stem
thalamus
receives sensory information, excepts for smell, then sends the information to the right part of the brain to be interpreted
limbic system function
emotion, memory, learning, motivation
hypothalamus
maintains homeostasis, hunger, thirst, body temperature, sexual behaviours
regulates endocrine system by signalling the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
(the master gland)
releases hormones that affect growth metabolism, and other glands throughout the body
hippocampus
forms new long term memories, especially explicit memories
(does not store memories)
amygdala
involved in emotions, especially fear and aggression
what are the lobes of the cerebral cortex
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
temporal lobe
occipital lobe
corpus callosum
a thick band of neurons that connects the left and right hemispheres and allows them to communicate with each other
occipital lobe location and function
processes visual information
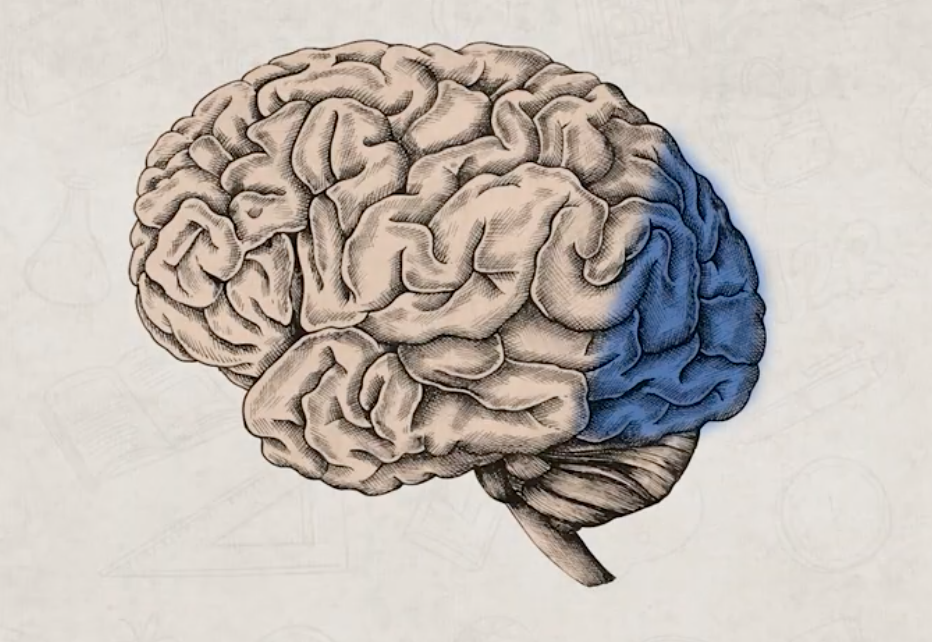
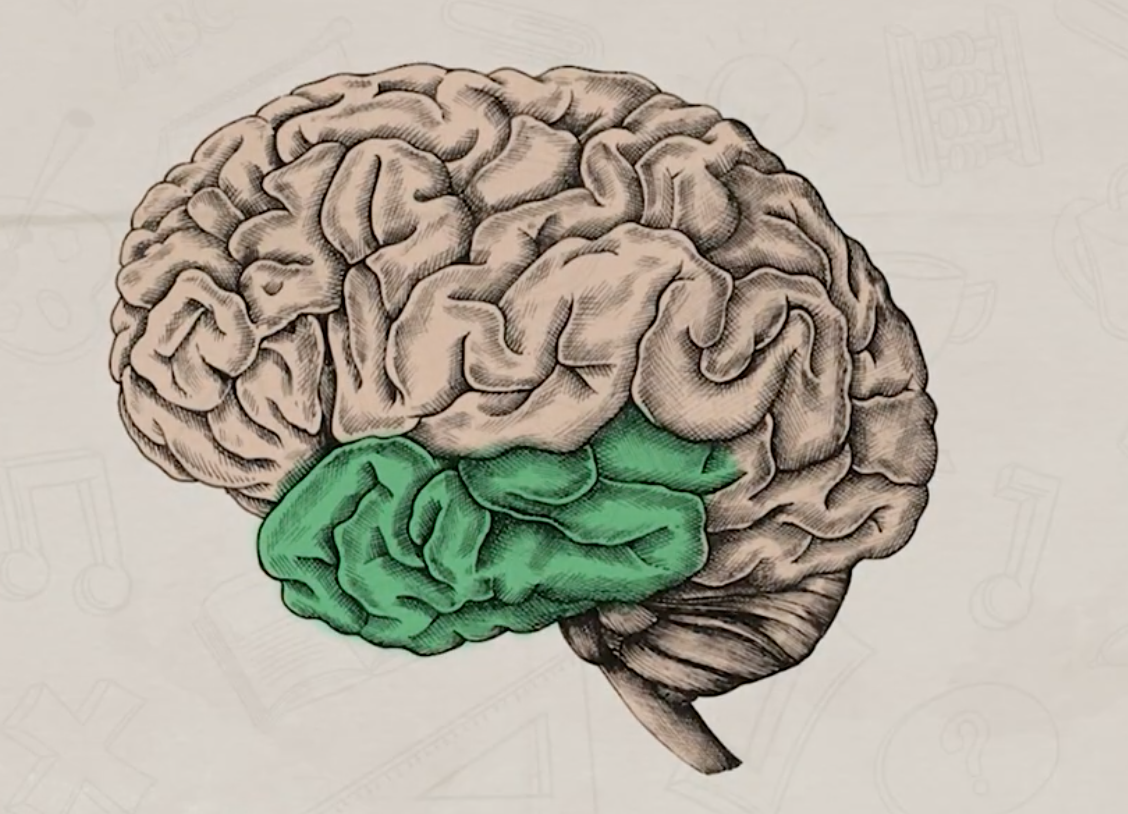
temporal lobe location and function
process sounds, helps with language and comprehension
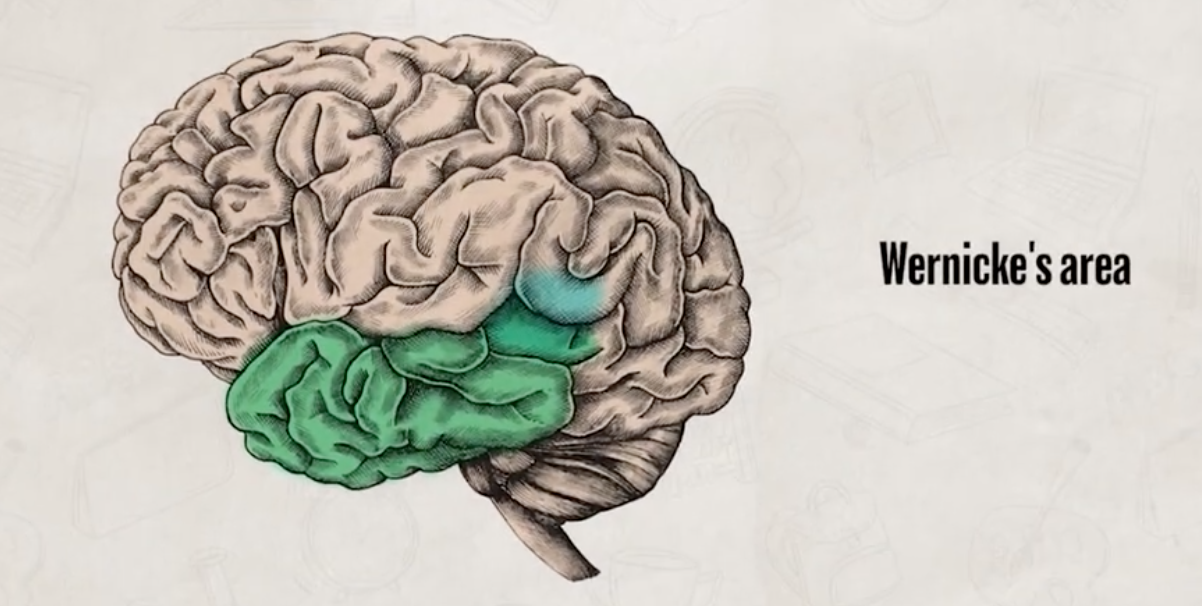
Wernicke’s area
responsible for language and comprehension
Wernicke’s aphasia
where the individual’s Wernicke’s area is damaged, having difficulty comprehending spoken language
association areas
regions that help the brain organise and make sense of information
somatosensory cortex
processes touch, pressure, pain, from the body, get a sense of where your body is
contralateral organisation
each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body
parietal lobes
processes sensory information like touch, temperature, and pain
spatial awareness, navigation, and coordinating body movements
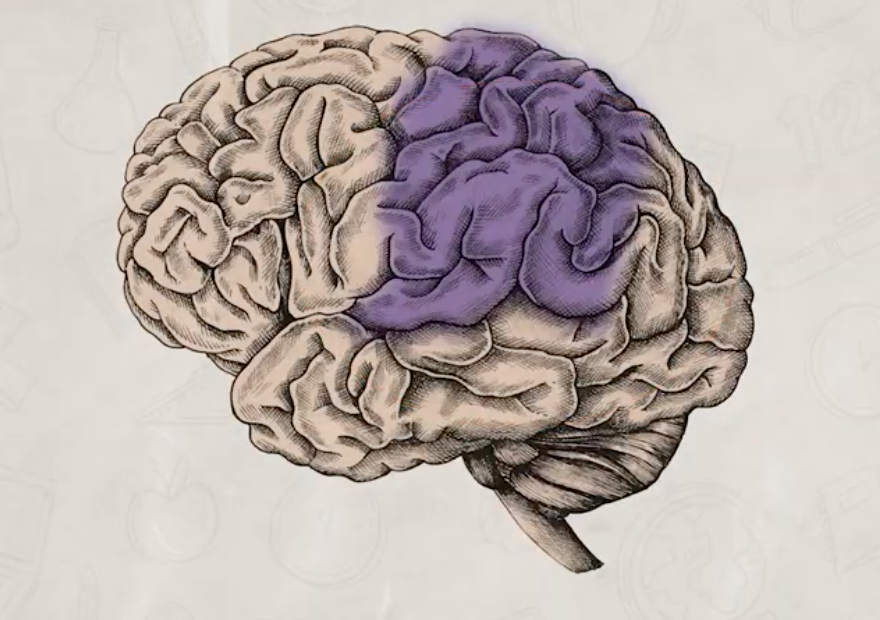
frontal lobes
responsible for higher level thinking and executive functions
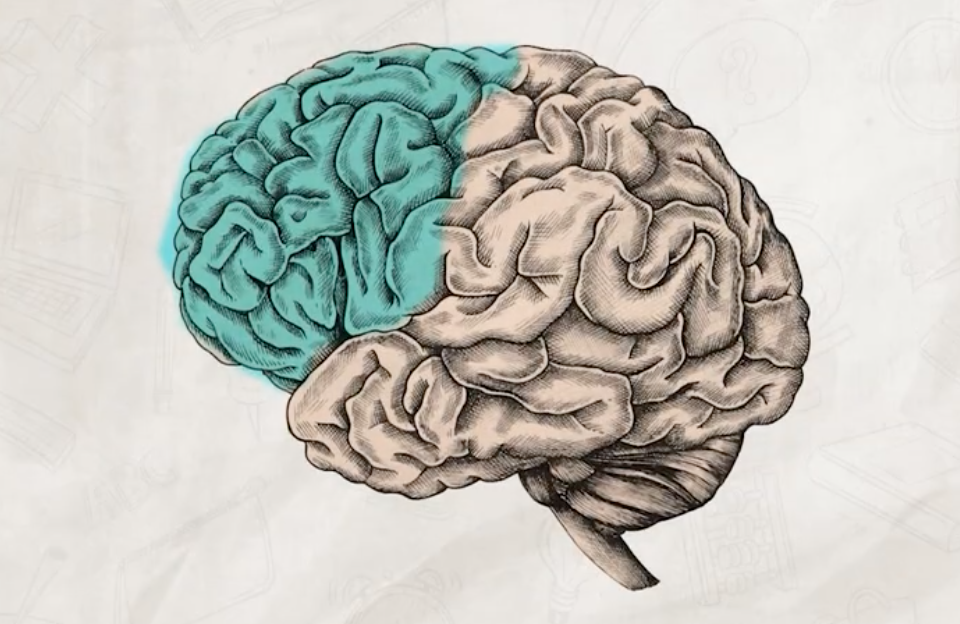
what are the two main areas of the frontal lobe and where are they located?
prefrontal cortex
motor cortex
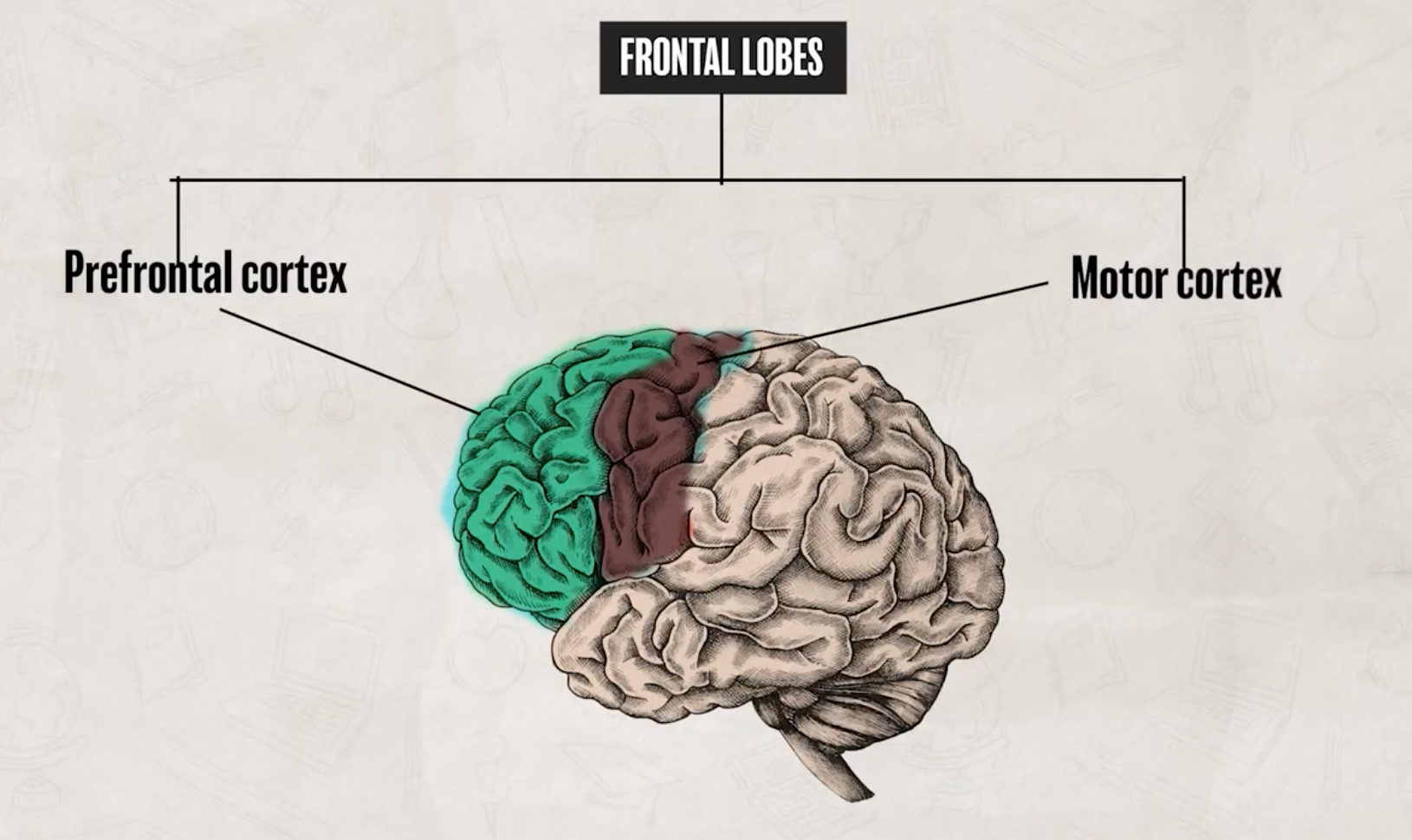
prefrontal cortex is involved in…
judgment
planning
foresight
attention
complex thought
emotional regulation
motor cortex is involved in…
voluntary muscle movement
broca’s area function and location
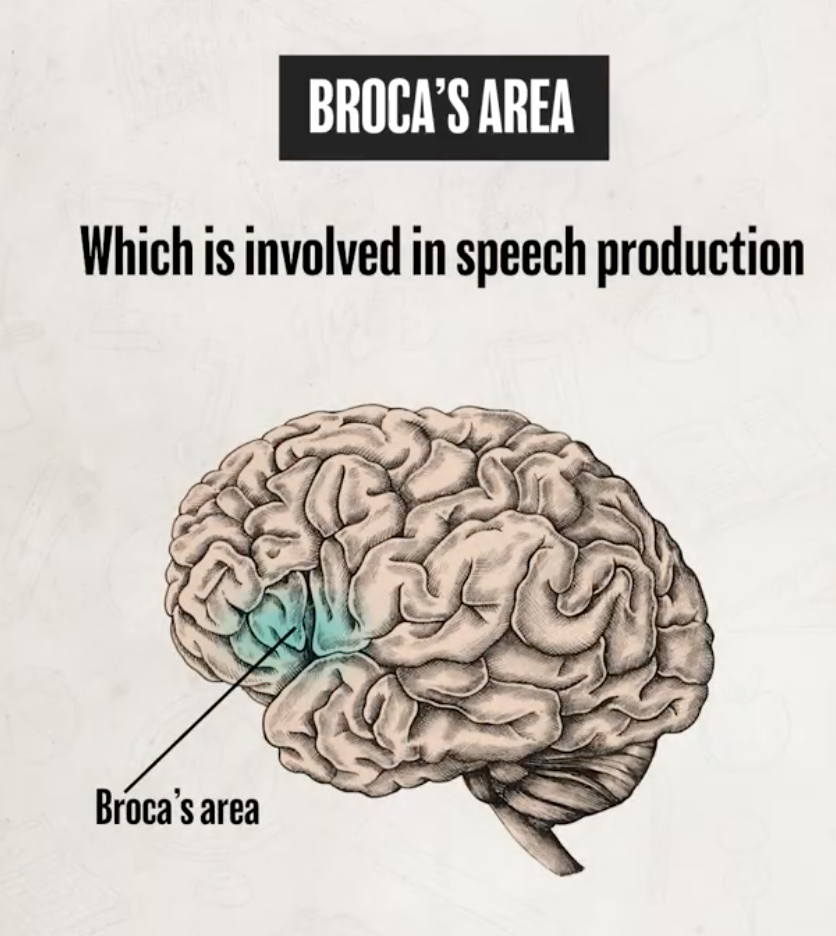
Broca’s aphasia
difficulty in producing speech when the Broca’s area is damaged
cortical specialisation

lesion studies
where researchers destroy certain parts of the brain to gain insight into their functions
autopsy
examining a dead body to understand the cause of death
EEG (electroencephalogram)
measures electrical activity in the brain by placing electrodes on an individual’s scalp
FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
shows which areas of the brain is active by measuring changes in blood flow