Mass transport in plants
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Describe the function of the Xylem
Transports water (and mineral ions) through the stem, up the plant to leaves of plants
Suggest how xylem tissue is adapted for its function
Cells joined with no end walls forming a long continuous tube → water flows as a continuous column
Cells contain no cytoplasm and nucleus → easier water flow / no obstructions
Thick cell walls with lignin → provides support / withstand tension / prevents water loss
Pits in the sides of the wall → allows lateral movements (sideways movement)
Explain the Cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem
Water lost from leaf by transpiration - water evapourates from mesophyll cells into air spaces and water vapour diffuses through (open) stomata
Lowers water potential of Mesophyll Cells
So water draw out of xylem down a water potential gradient
Creating tension (‘negative pressure’ or ‘pull’) in xylem
Hydrogen bonds results in cohesion between water molecular (stick together) so water is pulled up as a continuous column
Water also adheres (sticks to) to walls of xylem
Water enters roots via osmosis
Describe how to set up a potometer
Cut a shoot underwater at a slant → prevent air entering xylem
Assemble potometer with capillary tube end submerged in a beaker of water
Insert shoot underwater
Ensure apparatus is watertight/ airtight
Dry leaves and allow time for shoot to acclimatise
Shut tap to reservoir
Form an air bubble - quickly remove end of capillary tube from water
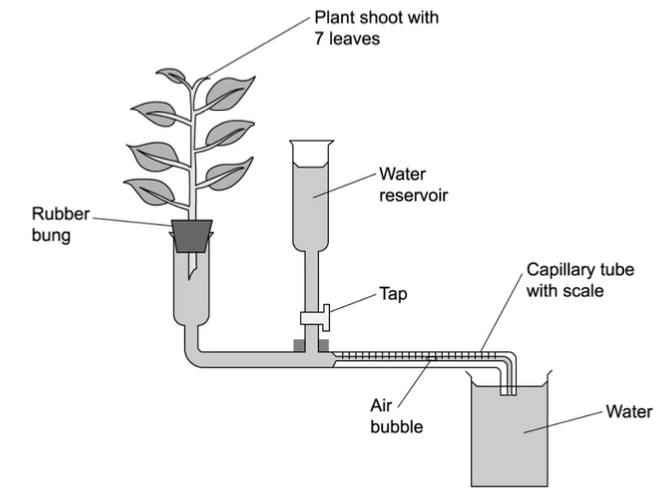
Describe how a potometer can be used to measure the rate of transpiration
Potometer estimates transpiration rate by measuring water uptake:
Record position of air bubble
Record distance moved in a certain amount of time (e.g. 1 min)
Calculate volume of water uptake in a given time:
use radius of capillary tube to calculate cross-sectional area of water (pi r2)
Multiply this by distance moved by bubble
Rate of water uptake = volume / time taken
Describe how a potometer can be used to investigate the effect of a named environmental variable on the rate of transpiration
Change 1 variable at a time (wind, humidity, light or temperature)
Eg. set up a fan or spray water in a plastic bag and wrap around the plant or change distance of a light source or change temperature of room
Keep all other variables constant
Suggest limitations in using a potometer to measure rate of transpiration
Rate of water uptake might not be same as rate of transpiration
Water used for support / turgidity
Water used in photosynthesis and produced during respiration
Rate of movement through shoot in potometer may not be same as rate of movement through shoot of whole plant
Shoot in potometer has no roots whereas a plant does
Xylem cells very narrow
Suggest how Light Intensity affects the rate of transpiration
As light intensity increases, rate of transpiration increases,
Stomata open in light to let in CO2 for photosynthesis
Allowing more water to evapourate faster
Stomata close when it’s dark so there’s a low transpiration rate
Suggest how Temperature affects the rate of transpiration
As temp increases, rate of transpiration increases,
Water molecules gain kinetic energy as temperature increases
So water evapourates faster
Suggest how Wind intensity affects the rate of transpiration
As wind intensity increases, rate of transpiration increases,
Wind blows away water molecules from around stomata
Decreasing water potential of air around stomata
Increasing water potential gradient so water evapourates faster
Suggest how Humidity affects the rate of transpiration
As humidity increases, rate of transpiration decreases,
More water in air so it has a higher water potential
Decreasing water potential gradient from leaf to air
Water evaporates slower
Describe the function of phloem tissue
Transports organic substances e.g. sucrose in plants
Suggest how Phloem Tissue is adapted for its function
Sieve tube elements
no nucleus/ few organelles → maximise space for easier flow of organic substances
End walls between cells perforated (sieve plate)
Companion Cells
Many mitochondria → high rate of respiration to make ATP of active transport of solutes
What is Translocation?
Movement of assimilates/ solutes such as sucrose
From source cells (where made, eg. leaves) to sink cells (where used/ stored, eg. roots) by mass flow
Transfer of Sucrose into Sieve Elements from Photosynthesising Tissue
Sucrose is made from photosynthesis in chloroplast-containing cells
Sucrose diffuses from photosynthesising cells into companion cells through facilitated diffusion - down a conc. gradient
H+ are actively transported from companion cells into the cell wall spaces using ATP
H+ diffuse down their conc. gradient into sieve tube elements through carrier proteins
Sucrose molecules are co-transported with H+ into sieve tube elements via co-transport proteins
Mass Flow of Sucrose Through Sieve Tube Elements
Sucrose is actively transported into sieve tubes from photosynthesising cells - this lowers the water potential
Water moves from xylem into sieve tubes by osmosis - this increases hydrostatic pressure in the sieve tubes at the source
Sucrose is removed from sieve tubes by respiring cells (used in respiration or stored as starch)
These sink cells have low sucrose levels, so sucrose is actively transported into them - this lowers the water potential
Water moves from sieve tubes into sink cells by osmosis - this lowers the hydrostatic pressure at the sink
A pressure gradient is created (high at source, low at sink)
Sucrose solution flows from source to sink by mass flow down this hydrostatic pressure gradient
Describe the use of tracer experiments to investigate transport in plants
Leaf supplied with a radioactive tracer eg. CO2 containing radioactive isotope 14C
Radioactive carbon incorporated into organic substances during photosynthesis
These move around plant by translocation
Movement tracked using autoradiography or a Geiger counter
Describe the use of ringing experiments to investigate transport in plants
Remove/ kill phloem eg. remove a ring of bark
Bulge forms on source side of ring
Fluid from bulge has higher conc. of sugars than below - sugar is transported in phloem
Tissues below ring die as can’t get organic substances