Microbio exam 3
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Chapter 9
Taxonomy
(greek word for orderly arrangement) is the science of classifying organisms. (the picture shows the taxonomic hierarchy)
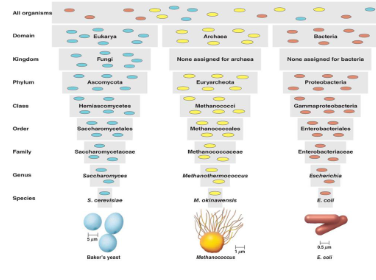
What does taxonomy provide?
shows degree of similarity and differences between organisms
provides structure to biological diversity
Allows communication, comparison, and prediction.
Systematics (phylogeny)
the study of the evolutionary relationships among organisms
organisms are grouped based on shared characteristics and evolutionary history
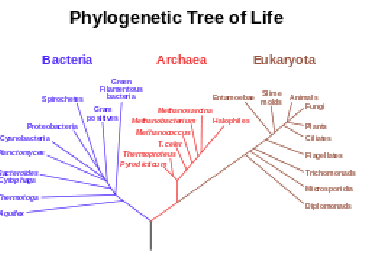
Evolution of classification systems: 1735
Linnaeus: Two kingdoms- plantae and animalia
1800’s
Bacteria and fungi included plantae; kingdom protista proposed.
1969
Whittaker: five kingdom system- Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
1978
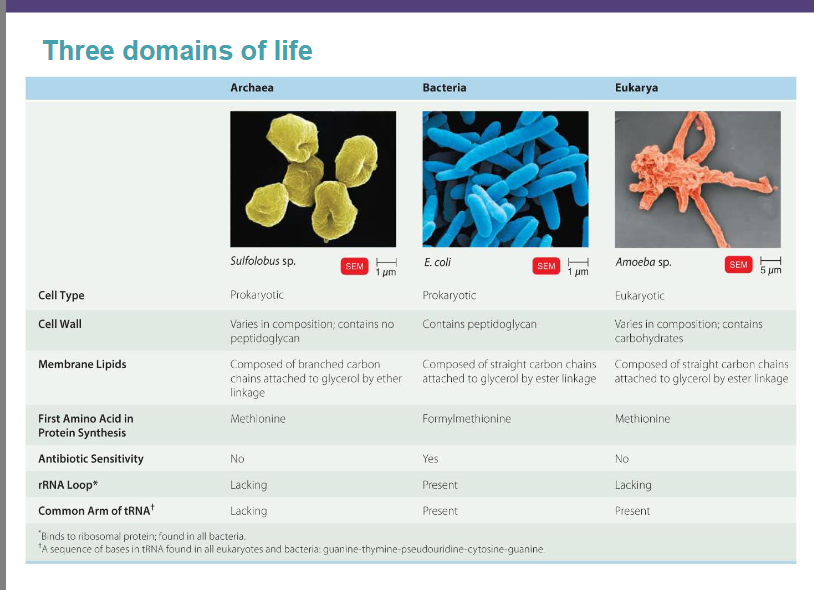
Woese: Three domain system based on rRNA sequences- bacteria, archaea, eukarya
Remember: The shifts reflect increasing understanding of genetic relationships
Three domains of life
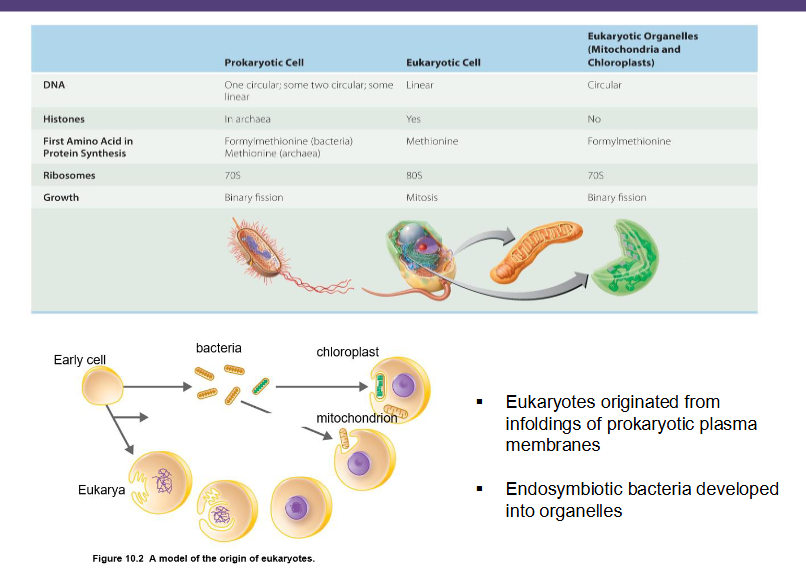
Where did Eukaryotes originate from?
infoldings of prokaryotic plasma membranes
endosymbiotic bacteria developed into organelles
Prokaryotes
Unicellular, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Smaller and simpler cell structure than eukaryotes
Reproduce asexually (mainly by binary fission)
DNA is circular and found in the nucleoid region
Bacteria: found in many environments, some pathogenic
Archaea: often live in extreme environments (e.g., hot springs, salt lakes)
Eukaryotes:
Protists: mostly unicellular, diverse nutrition, grouped by genetics
fungi: unicellular or multicellular, absorb nutrients, reproduce by spores
plantae: multicellular, photosynthetic, cellulose walls
animalia: multicellular, ingest food, no cell walls
Viruses:
not a part of any domain- not living by classical definition
DNA or RNA, protein coat, replicate inside host
Viral species: population of viruses with similar characteristics (morphology, genes, and enzymes) that occupies a particular ecological niche (host cell)
Traditional Identification Methods
Morphology, Staining, Biochemical tests, and culture characteristics
morphology
(shape and motility)
observation of size and shape, arrangement (ex. cocci, bacilli, spirilla)
motility assessed via wet mount or motility agar
staining
gram, acid fast
biochemical tests
detects enzymatic activity (ex. catalase, oxidase, urease)
identifies metabolic pathways (ex. fermentation of sugars, use of specific characteristics)
culture characteristics
colony morphology on agar (shape, color, margin, elevation)
growth conditions (aerobic/anaerobic, temperature, pH range)
Identification tools
Bergey’s manual
Bergey’s Manual
standard reference for identifying and classifying bacteria and archaea using features like cell wall composition, morphology, differential staining, O2 requirements, and biochemical traits
most bacteria/archaea remain uncultured; identification relies on indirect methods
Approved list of bacterial names: includes -11,500 species with accepted taxonomy; and less than 5% are human pathogens.
Serology
study of serum and their immune responses
Antigens: microorganisms are antigenic- they stimulate the body to form Antibodies in the serum/blood.
Strains with different antigens are called serotypes, serovars, or biovars
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
most popular and widely used method
known antibodies and an unknown type of bacterium are added to a well; a reaction identifies the bacteria
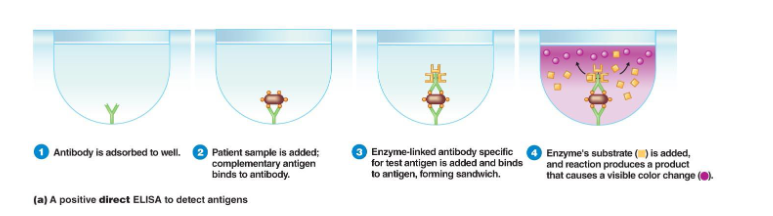
Phage typing