Chapter 4: Inside the Cell
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Cells
smallest unit of life
Why are cells limited in size?
Cells are small to have a larger ratio surface area to internal volume that would allow them to move nutrients into the cell and remove wastes outside the cell. It is important for cell function
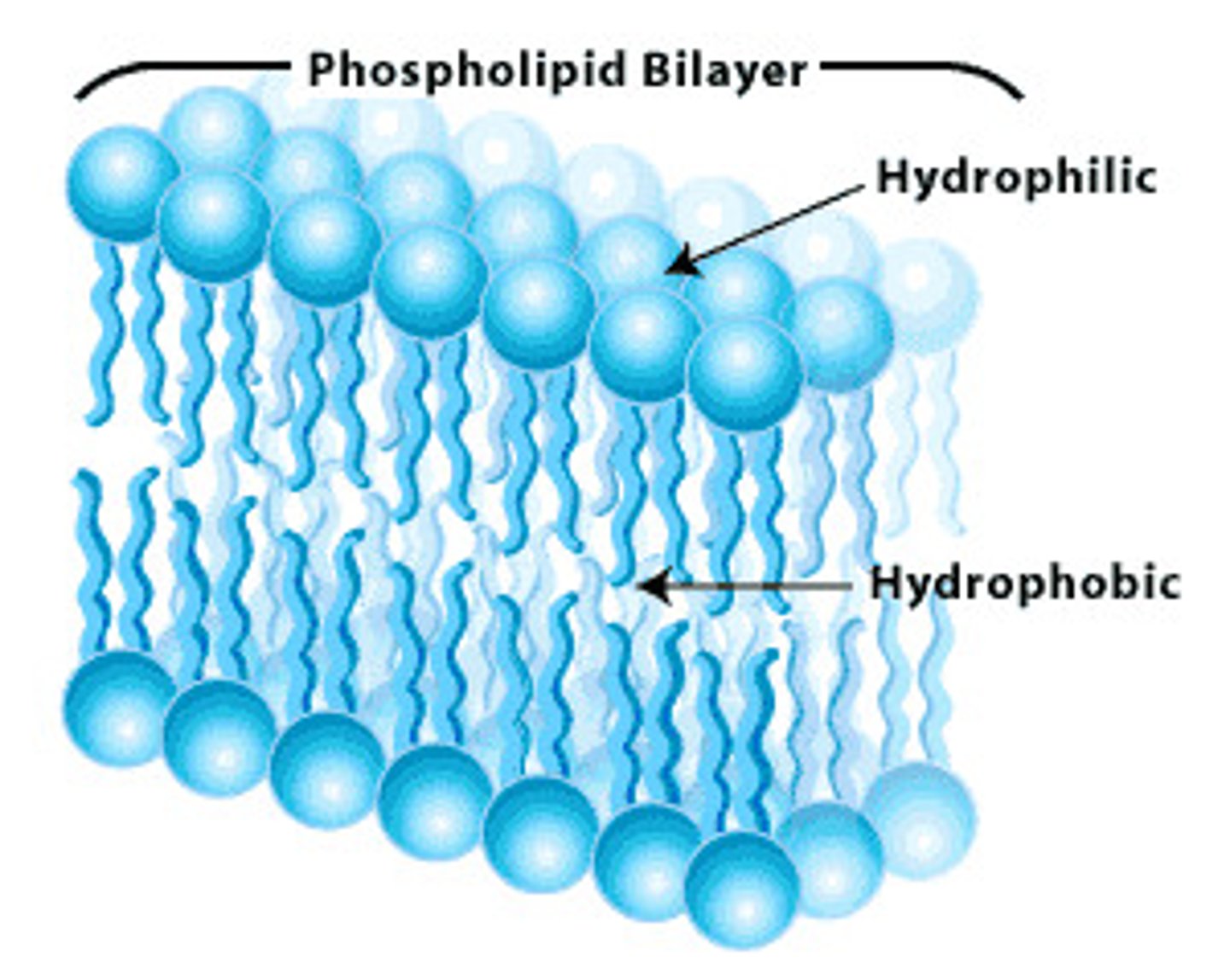
Plasma membrane
serves as boundary between the outside and the inside of a cell.
It is a selective barrier passage of gases, nutrients, and waste
Phospholipid bilayer
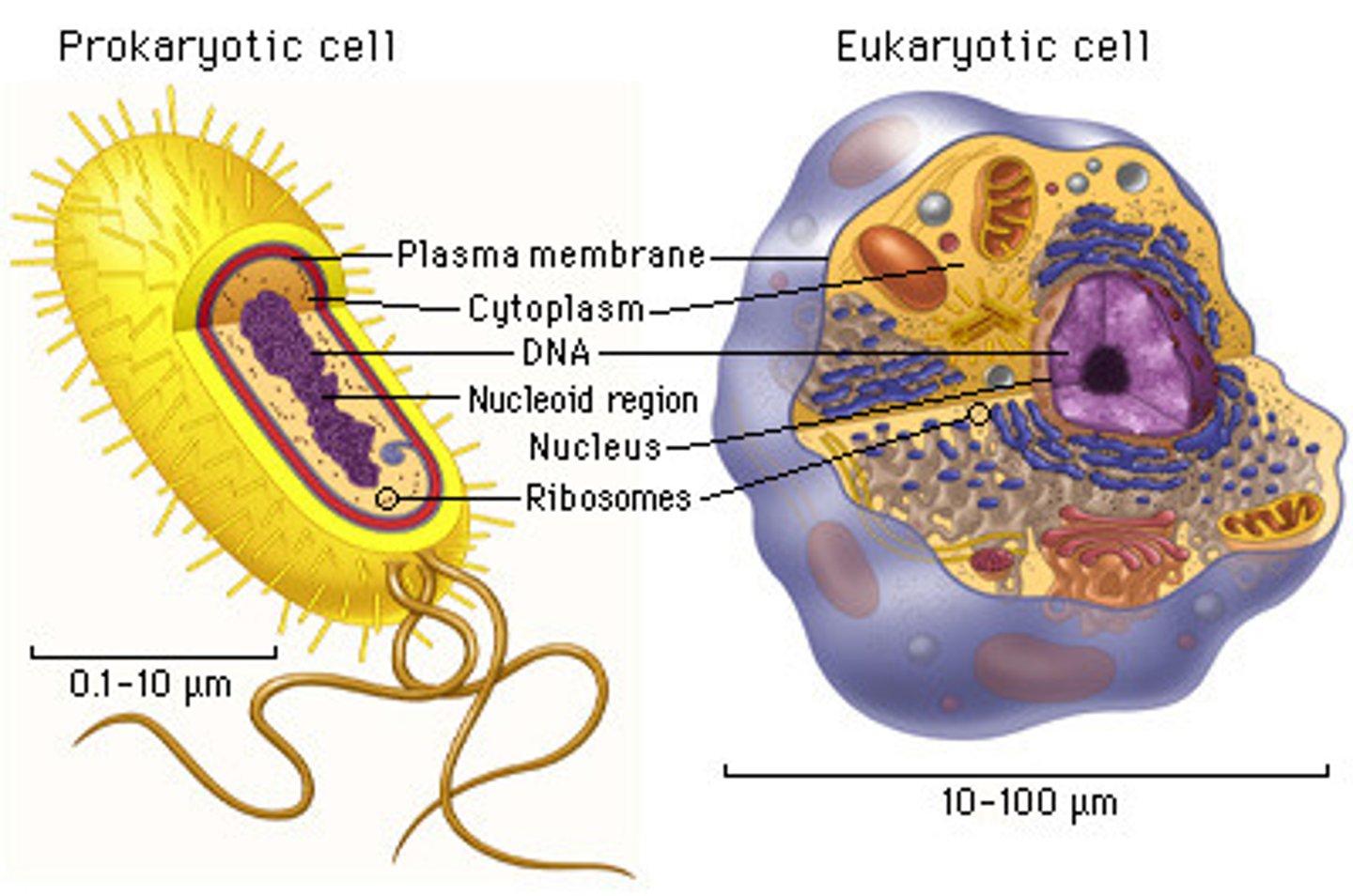
Prokaryotic
Found in Domain Archaea and Bacteria
No nucleus, but has Nucleoid (DNA in a single circled chromosome), No membrane-bound organelles, Cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane.
Eukaryotic
Found in Domain Eukarya
DNA is in the nucleus (a membranous nuclear envelope), has membrane-bound organelles, cytoplasm is between plasma membrane and nucleus, has a larger size the prokaryotic
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
has lipid bilayer, has cytosol (inner fluid), chromosomes (genes), and Ribosomes (make proteins)
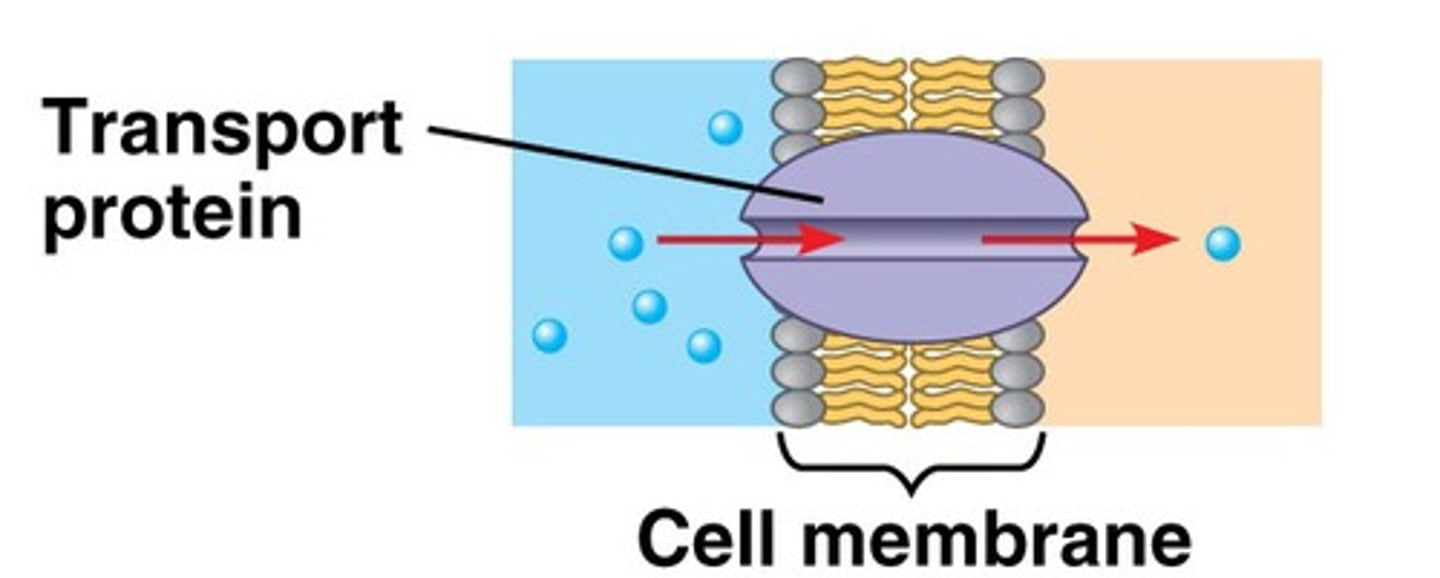
membrane proteins
Embedded proteins that perform specific functions for the cell membrane.
Junction = assist in cell-to-cell adhesion and communication
channel protein
allows passage of only one or a few specific molecules to move readily through the membrane (ex: aquaporins in kidneys)
transport proteins
allow passage of hydrophilic substances across the membrane
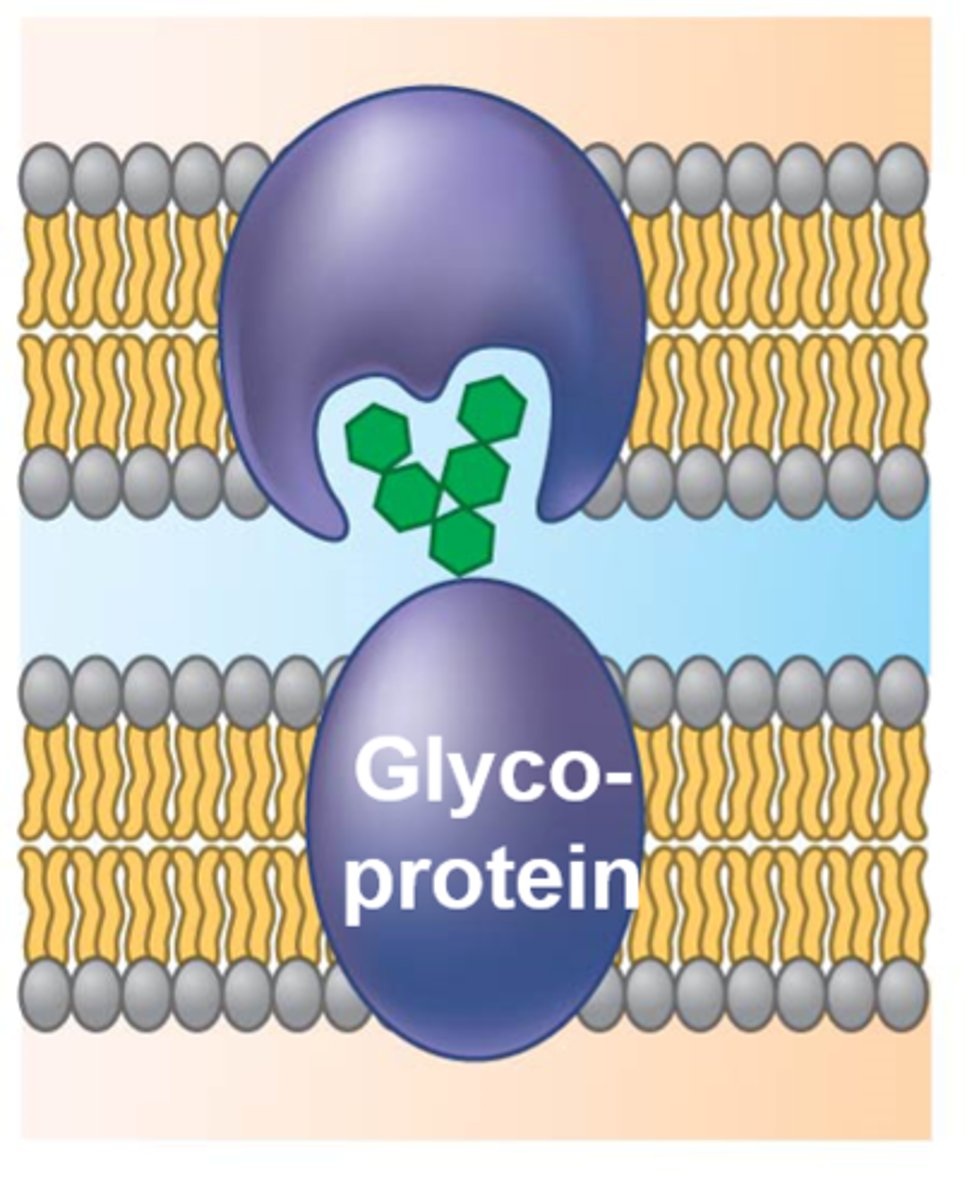
cell recognition proteins
recognizes our own cells from foreign cells (ex: glycoproteins)
receptor proteins
needs signal molecules to change shape and bring cellular response
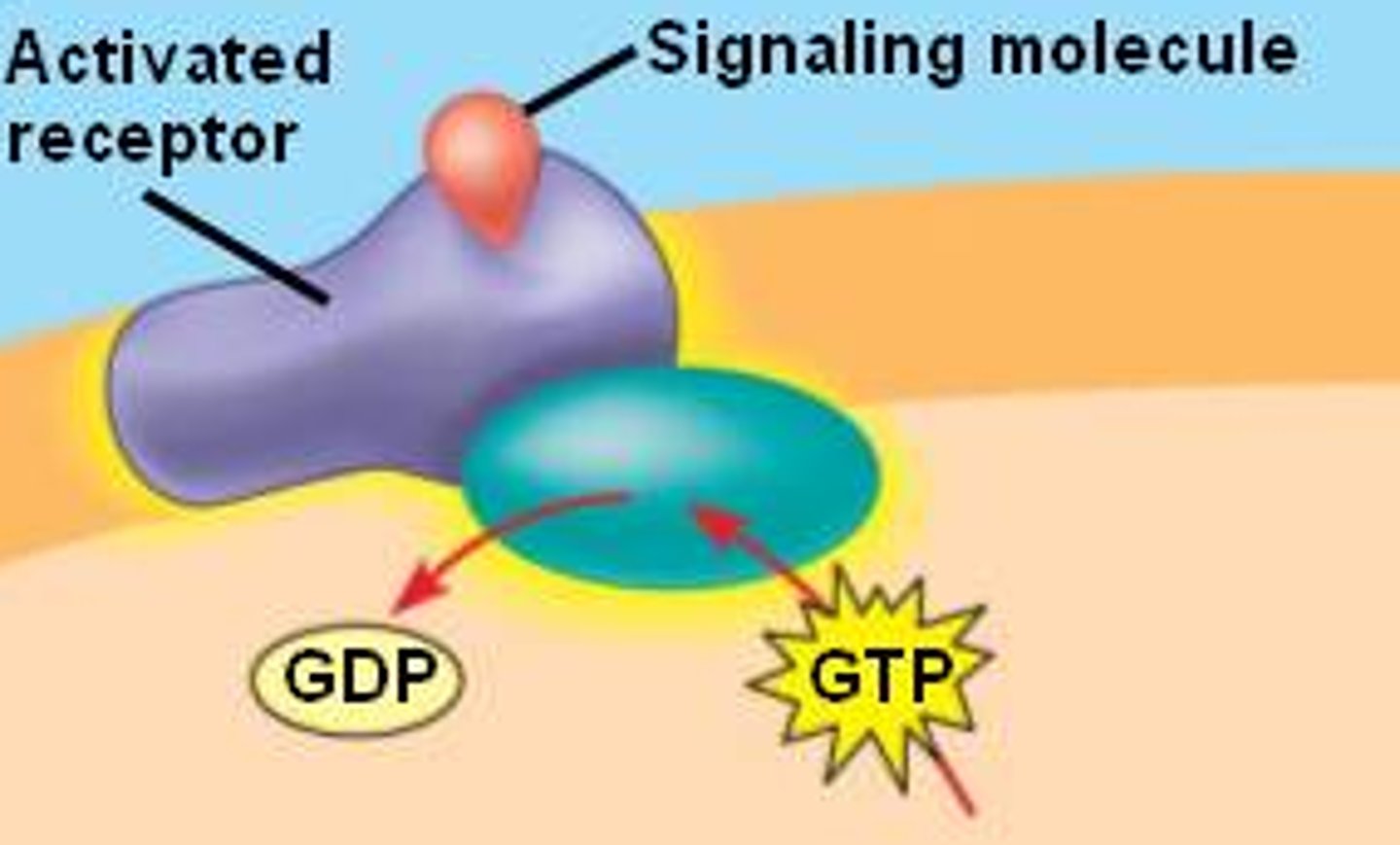
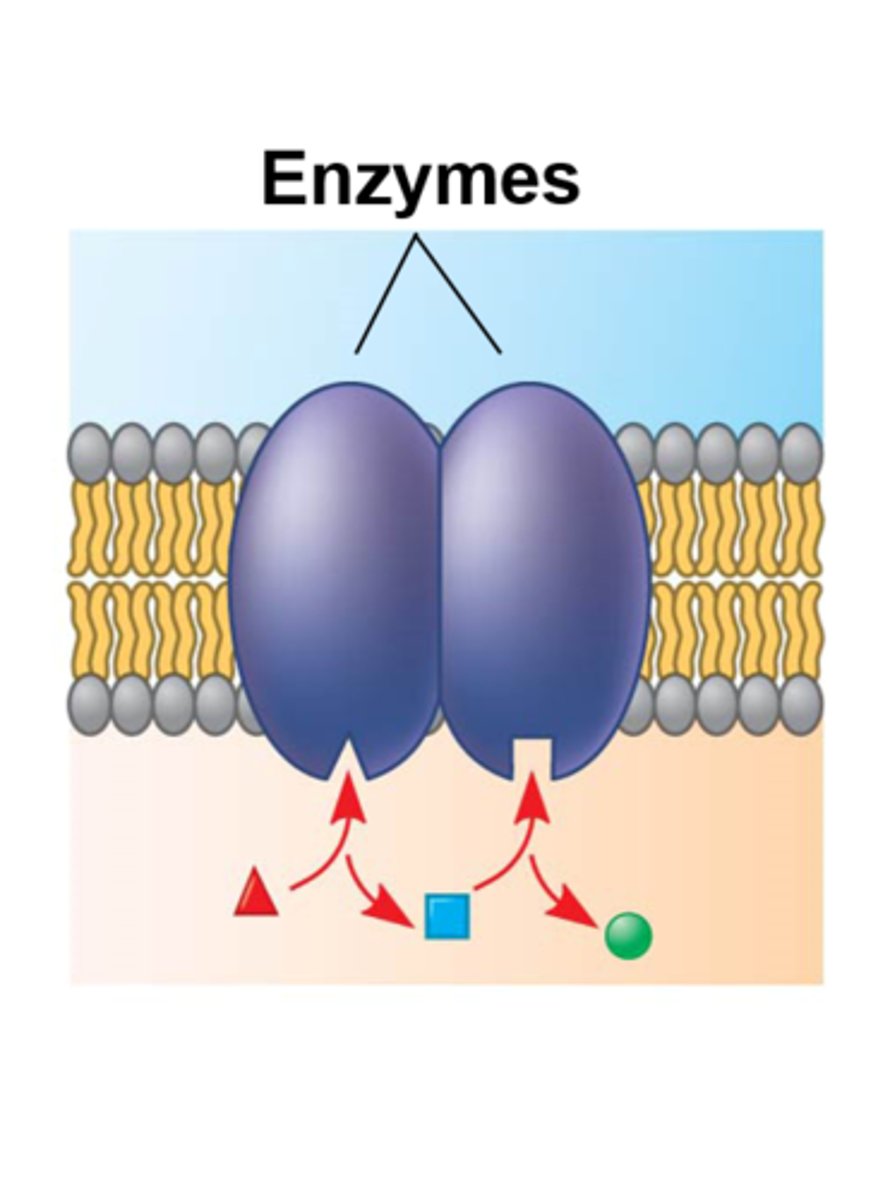
enzymatic proteins
participate in metabolic reactions
junction proteins
assist in cell-to-cell adhesion and communication
Nucleus
Stores genetic information (DNA)
Site of DNA transcription
Nucleolus
where rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is made
nuclear envelope
A double membrane with pores that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum
assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
(Biosynthesis Factory)
Smooth ER
Makes lipids, detoxifies poisons and enzyme production
Rough ER
studded with ribosomes and synthesizes membrane-bound proteins (membrane factory) and makes transport vesicles
Golgi apparatus
Flattened membranous sacs
it receives, modifies and ships materials into transport vesicles (warehouse)
Vesicles
small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
Lysosomes
digestive compartments
digests macromolecules or old cell parts
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
contractile vacuole
pump water out of cell (in protists)
central vacuole
in a mature plant cell, stores water and organic molecules
Food vacuoles are formed by
phagocytosis (cell-eating)
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
has its own DNA and ribosomes
has chlorophyll
Solar energy is used to synthesize carbs
Mitochondria
breakdown carbs to produce ATP
site of cellular respiration
present in BOTH animals and plants
has its own DNA and ribosomes
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
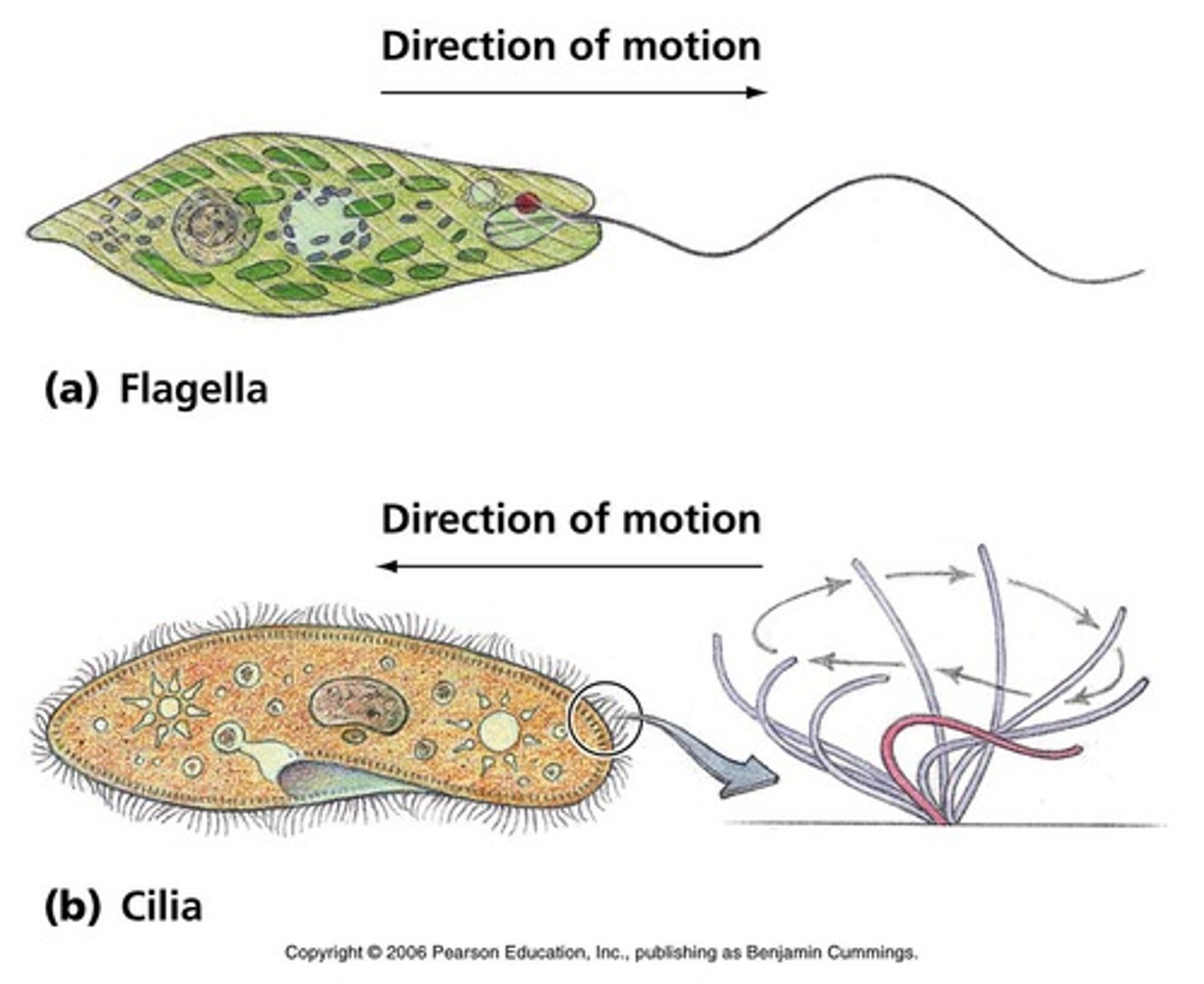
cilia and flagella function
movement of cell
Cilia is shorter than flagella
Cell Wall (NOT found in ANIMALS)
maintains shape and provides support to the cell
Plasmodesmata
channels between adjacent plant cells that allows exchange of water and small molecules between cells