Lecture #6 Control of Microbial Growth
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Sterilization
The killing or removal of all viable organisms within a growth medium
destruction of EVERYTHING→ even endospores (which are very resistant)
Inhibition
Effectively limiting microbial growth, no killing taking place
Ex: bacteriostatic medication, Static → stops from growing
Ex: refrigeration
Decontamination
The treatment of an object to make it safe to handle
aka sanitation
Ex: untensils sitting on a table at a restaurant are decontaminated by the dishwasher but while sitting out they are prone to air contamination
Disinfection
Directly targets the removal of all pathogens (disease causing) , not necessarily all microorganisms
Ex: antiseptic products→ more gentle, longer application time but is not too harsh on human tissue/ preserves it
disinfections is not necessarily more gentle
Heat Sterilization
Heat sterilization: is the most widely used method of controlling microbial growth. High temperature denature macromolecules
Decimal reduction time (D): the amount of time required to reduce viability tenfold/ time it takes for a 10 fold reduction in bacterial numbers
some bacteria produce resistant cells (endospores) that’s can survive heat that would rapidly kill vegetative cells.
Endospores are dormant during the harsh conditions but after the temperature decreases the endospores will “wake up” to become vegetative cells
Pasteurization
Pasteurization: is the process of using precisely controlled heat to
reduce the microbial load in heat-sensitive liquids.
Does not kill all organisms-> not sterilization, rather is disinfection
Describe the different methods of pasteurization in milk
In the case of milk many different time and temperature combinations can be used.
LTLT (low-temperature/long-time): 63oC for 30 minutes
HTST (high-temperature/short-time): 72oC for 15 seconds
• Both processes kill Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever, which is the most heat resistant pathogen found in milk
What is an autoclave?
autoclave: a sealed Chamber pressure device that uses steam under pressure, allows temperatures of water to get above 100 C. To ensure sterility, the point that takes the longest to heat must stay at 121 for 15 mins.
Steam at 121C for 15 mins at 15 pounds per square inch of pressure is typically used
What is radiation?
Radiation: Physical method of growth control. Radiation is used for sterilization in the medical field and food industry
Ex: Radiation is approved by the WHO and is used in the USA for
decontaminating foods particularly susceptible to microbial contamination
• Hamburger, chicken, spices may all be irradiated
Microwaves, UV, X-rays, gamma rays, and electrons: reduce
microbial growth
UV: has sufficient energy to cause modifications and breaks in
DNA, is useful for decontaminating surfaces
• UV Cannot penetrate solid, opaque, or light-absorbing surfaces
Sources of radiation include cathode ray tubes, X-rays, and radioactive nuclides
What is ionizing radiation?
Ionizing radiation: Electromagnetic radiation that produces
ions and other reactive molecules generates electrons, hydroxyl radicals, and hydride radicals.
• Some microorganisms are moreresistant to radiation than others.
• amount of energy required to reduce viability tenfold is analogous to D value
What is filtration?
Filtration: avoids the use of heat on sensitive liquids and gases. Pores of filter are too small for organisms to pass through
Ex: HEPA filters, membrane filters
• Allow liquid or gas to pass through by exploiting size→ bacteria at top of filter but the protein is let through
Pore size: Note the size of the pores relative
if the pore size is 5 µm, is this an appropriate filter to prevent bacteria from going through?
If the pore size 0.2 µm (Note the pore size relative to
Leptospira (0.1 x 20 µm) is this an appropriate filter to prevent bacteria from going through?
5 µm filter → too large → bacteria pass through
0.2 µm filter → effective for most bacteria
What are the methods membrane filters accomplish filtration with?
With membrane filters, filtration can be accomplished by:
• Syringe
• Pump
• Vacuum
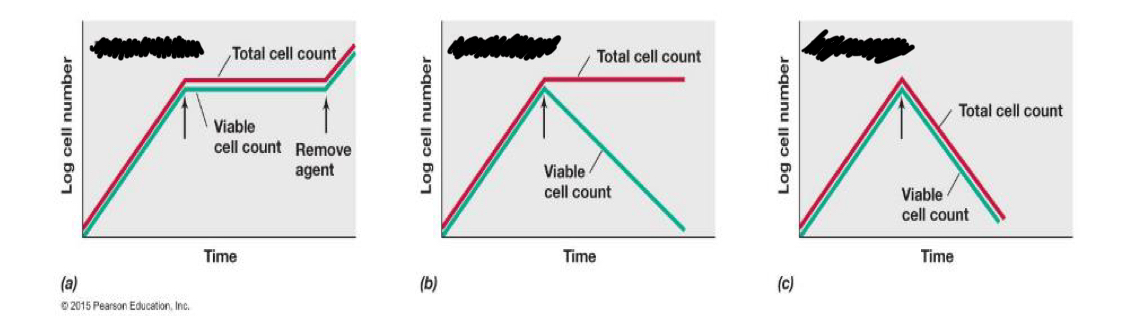
What are the different classes of antimicrobial agents?
Bacteriostatic: prevents cell growth as long as the antimicrobial agent is present.
stays the same, only stops the growth of bacteria
Bacteriocidal: kills the cells (does not lyse them)
Bacteriolytic: kills and lyses the cells
in the image a= bacteriostatic, b= bacteria ideal, c= bacteriolytic
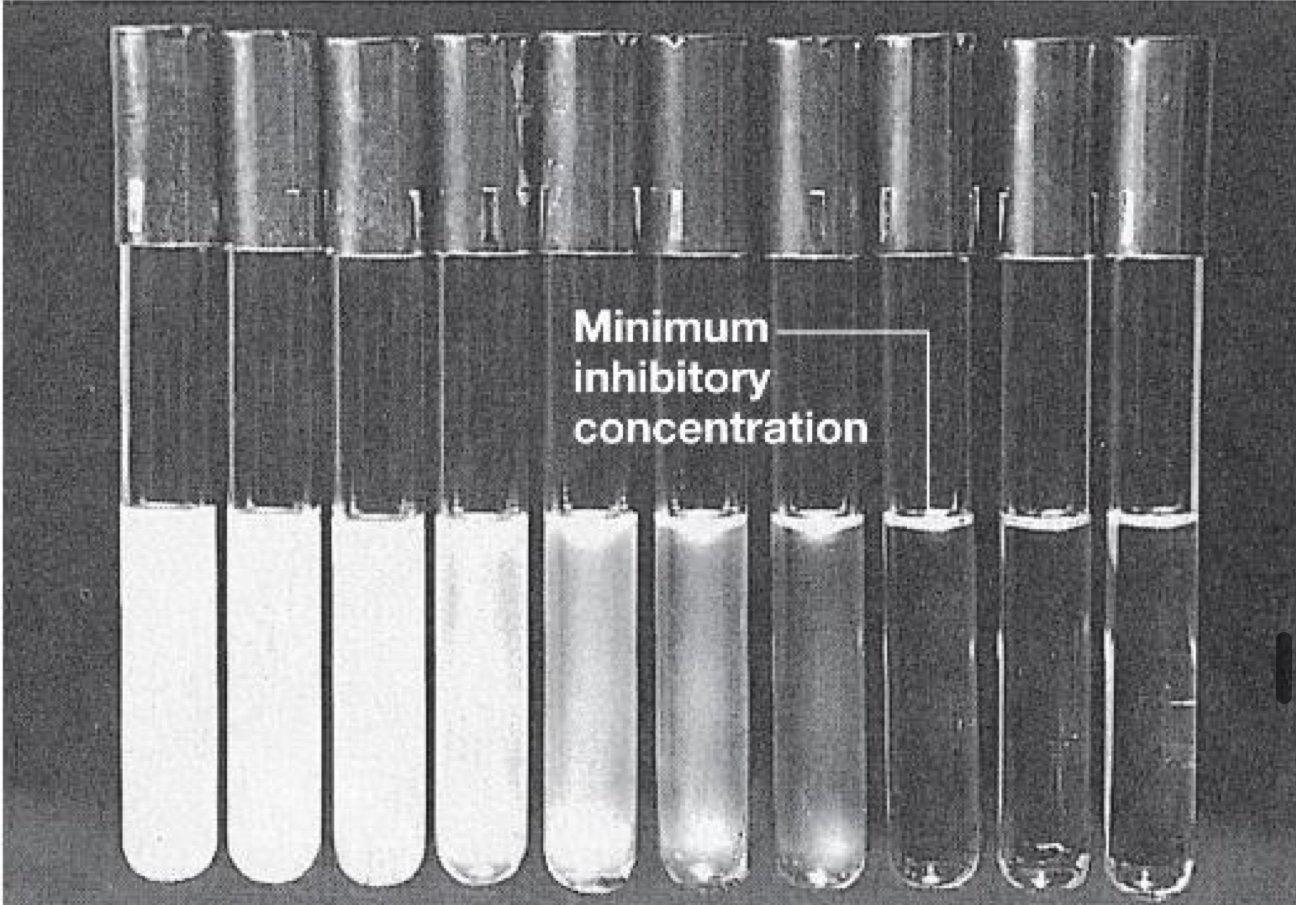
What is minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)?
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC): is the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent that inhibits visible growth of a microorganism. To determine if the agent is lethal, samples from the MIC and higher concentrations are plated on nutrient agar without antibiotic:
If colonies grow → the organisms were inhibited but not killed (bacteriostatic).
If no colonies grow → that concentration is the Minimal Lethal Concentration (MLC), which is usually higher than the MIC.
The MIC depends on factors such as the organism type, inoculum size, temperature, and pH, and the antibiotic must reach the site of infection at or above the MIC to be effective.
What is a disc diffusion assay?
Uses solid media, Antimicrobial agent is added to filter paper disc
• The MIC is reached at some distance, forms a zone of inhibition: area of no growth around disc
What are the different categories of antimicrobial agents?
1. Products used to control microorganisms in commercial and industrial applications
• Ex) chemicals in foods, air conditioning cooling towers, textile and paper products, fuel tanks
2. Products designed to prevent growth of human pathogens in inanimate environments and on external body surfaces
Sterilant: destroys all microorganisms including endospores
Disinfectant: kills microorganisms but not all endspores.
used on inanimate objects
Sanitizer: reduces the numbers of microorganisms on surfaces (e.g. hand
Antiseptic: kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms (non-toxic enough to be applied on living tissue (e.g. mouth wash))