B6: CM Repro Exam 4
1/515
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
516 Terms
respiratory distress syndrome
leading cause of death in preterm infants
produce phospholipids that are packaged into lamellar bodies
alveoli are lined by type II pneumocytes that produce
surfactant
-phospholipid compound released from lamellar bodies
-reduces surface tension with in alveolar spaces allowing for maximal gas exchange
•Lecithin
•Sphingomyelin
•Phosphatidylglycerol: appears later in gestation
predominant components of surfactant
-lecithin:sphingomyelin ratio (>2)
-tests for presence of phoshatidylglycerol
-lamellar body number density
amniocentesis tests for fetal lung maturity
phosphatidyglycerol
•If present <1-5% of infants will develop respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)
28 days
60% infants born 24-25 weeks survive at least
-activation of maternal/fetal HPA axis
-inflammation/infection
-decidual hemorrhage
-pathologic uterine distention
potential pathophysiologies of pre-term labor
•short cervical length
•multiple gestations
•vaginal bleeding
•UTIs
•genital track infections
•Periodontal disease
risks of pre-term labor during pregnancy
•smoking
•substance abuse
•short interpregnancy interval
•low maternal pre-pregnancy weight
behavioral risks that result in preterm labor
-birth 20-37 weeks
-regular contractions
-cervical change: effacement, dilation
the 3 criteria to preterm labor
•No effective interventions for prevention regardless of risk factors.
-may try hydroxyprogesterone caproate, compounded product
meds to prevent preterm labor
vaginal progesterone supplementation
drug to prevent pre term labor in women with shortened cervix
•OB Exam including speculum exam
•Digital cervical exam if no ruptured membranes
•GBBS testing vaginal and rectal
•Chlamydia/GC testing based on H&PE
•Urinalysis and culture
workup associated with evaluation of pre term labor
less than 30 mm
cervical length that increases risk of preterm labor
fetal fibronectin
•Protein produced by throphoblasts and chorioamniotic membranes
•Acts like "glue" to maintain integrity of the membranes
fetal fibronectin
•However, interventions based on fFN have not improved perinatal outcome
protein with a high negative predictive value for pre term labor
-IV fluids: increased hydration decreases uterine muscle activity
-steroids to promote fetal lung maturity, decreasse necrotizing enterocolitiss
initial management of pre term labor
steroids
med indicated from weeks 24-34 if t is at risk for delivery within 7 days
antibiotics
recommended med for PTL pt with ruptured membranes and GBS
Magnesium sulfate
med used in cases of pre term labor for neuroprotection (24-32 weeks)
magnesium sulfate
•Given for neuroprotection if < 32 weeks @ risk for delivery
•Decreases risk of cerebral palsy and motor dysfunction in preterm infants
•Works by stabilizing fetal circulation and normalized cerebral blood flow
when benefit of delaying delivery is greater than risk of therapy, not indicated prior to viability, no evidence has direct effect on neonatal outcomes or neonatal benefit
indication for tocolytics
lethal anomaly, chorioamnionitis, fetal demise, severe pre-eclampsia, abruption, PPROM, maternal contraindications to medications
contraindications for tocolytics
tocolytics
-used to prolong latency period for 48 hours to promote steroid activity on lung maturity
-muscle relaxers to prevent uterine contractions
-beta agonist: terbutaline, ritodrine
-calcium channel blockers
-prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors
-magnesium sulfate
examples of tocolytics
hyperglycemia (not for diabetics)
key side effect of beta agonist
hypotension
key side effect of calcium channel blocker
thrombocytopenia, anemia
key maternal side effects of prostaglandin inhibitors
necrotizing enterocolitis
key fetal side effects of prostaglandin inhibitor tocolytic
myasthenia gravis
magnesium sulfate is contraindicated in pts with
-depressed reflexes, flushing, shortness of breath
rare: pulmonary edema
key side effects of magnesium sulfate
24
at the best facilities, it is safe to deliver at ____ weeks
cervical insufficiency: painless dilation of cervix with no contracitons
sign of PPROM in which tocolytics have no place in management
cervical insufficiency --> PPROM
-finding amninotic fluid bulging into cervical canal is predictive
-1st trimester ultrasound shortening of cervix <2.5 cm
-previous preterm delivery
-earlier delivery in subsequent pregnancies
-cervical procedures
-uterine anomalies
risk factors for cervical insufficiency
cervical dilation or PPROM in 2nd trimester
clinical presentation of cervical insufficiency
cervical cerclage
-a surgical suture placed in purse string fashion placed near internal cervical os
-placed by 14 weeks for cervical insufficiency
prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM)
•rupture of membranes before onset of labor
•Historically referred to as premature rupture of membranes
PPROM (preterm premature rupture of membranes)
•Preterm rupture
•PROM before 37 weeks
•rupture preterm AND prior to labor
•associated with 30% preterm deliveries
-infections
-history of PPROM
-uterine distention: twins, polyhydamninoss, fibroids
-short cervix
-2nd or 3rd trimester bleeding
-lower BMI, lower SES, smokers and drug users
risk factors for pre-labor rupture of membranes
tests pooling fluid in vagina on fern test and nitrazine test
-arborization and pH >7.1 indicates rupture of membranes
how do you diagnose pre-labor rupture of membranes?
blood, mucus, or semen present in vaginal fluid raising the pH
what could cause a false positive nitrazine test
-intrauterine infection: increases with duration of latency
-cord prolapse
-placental abruption
main risks of term PROM
latency period
• time from PROM to labor
inversely related to gestational age
24 hours
if there is PROM at term, spontaneous labor typically occurs within
•Placental abruption
•Postpartum endometritis
•sepsis
maternal complications of PPROm
•Mortality 34% <26 weeks 15% >26 weeks
•Pulmonary hypoplasia
•Musculoskeletal deformities
•Cord prolapse
neonatal complications of PPROM
NO digital exam if membranes are ruptured and not in active labor
should you do a digital exam if pt present PPROM?
expectant management (in hospital) until maternal or fetal signs require delivery
-GBS prophylaxis, NSTs, ultrasound
typical management of PPROM
fever, non-reassuring NST, poor BPP, spontaneous labor, reach 37 weeks gestation
indications to deliver a PPROM pt
-all pregnancies at risk for delivery prior to 37 weeks
-no signs of chorioamnionitis
-reduce risk of RDS and intraventricular hemorrhage
indications for PPROM steroids
celestone
most commonly used PPROM steroid
give antivirals
•if recurrent disease- expectant management
•if active lesion when labors - cesarean delivery
management of PPROM ppt with HSV
antiretroviral therapy
•zidovudine during labor
• evaluate viral load to determine risk of vertical transmission
management of PPROM pt with HIV
ascending infection from vagina/cervix
maternal blood
penetrating trauma
sources of vertical transmission
•Toxoplasmosis
•Other (varicella, parvovirus B19, listeria)
•Rubella
•Cytomegalovirus
•HIV
•Herpes, Hepatitis B & C
•Syphilis
list the TORCHHeS infections
rubella and syphilis at first prenatal visit
-some countries also screen for toxoplasmosis
pregnant women should be screened during 1st trimester for these TORCH infections at their first prenatal visit
HIV
syphilis
hep B and C
chlamydia
ALL women are screened for these during first trimester
HHSV and gonorrhea
diseases screened during first prenatal visit only if high risk
group B strep
screened in ALL women during 36-37 weeks gestation
HIV, syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea
screened during third trimester if high risk
-rubella
-toxo and CMV
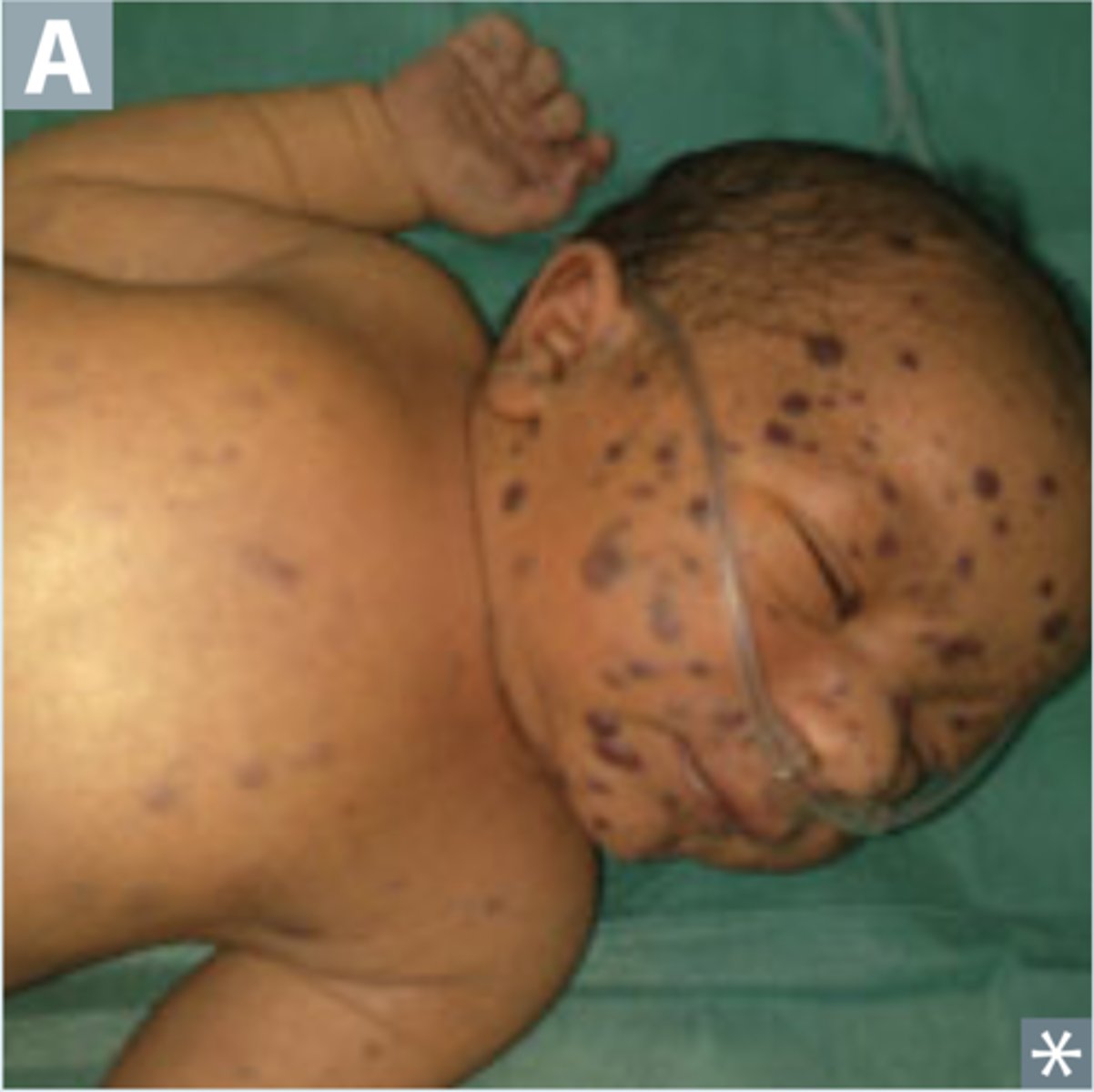
TORCH infections associated with blueberry muffin rash
blueberry muffin rash
extramedullary hematopoiesis in the dermis
T. gondii
-intracellular parasite found in undercooked meat, unwashed fruit, and litter box
-cats the only definitive hosts
oocyts--> tachyzoites in acute form---> bradyzoites (chronic)
-oocytes infectious found in feces, contaminated foods
acute and chronic forms of T. gondii
-typically asymptomatic and self limited; symptoms are typically mono like
-prior infection results in immunity
presentation of maternal toxoplasmosis
•Tachyzoite replication destroys infected cells
•Necrosis can become tissue calcification---> intracranial calcifications
pathogenesis of congenital toxoplasmosis
chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications
-chorioretinitis is later sequelae
classic diagnostic triad of congenital toxoplasmosis
congenital toxoplasmosis
-more severe manifestations usually indicate infection earlier in gestation
-no symptoms at birth= still at risk
-PREVENTION
-treatment of acutely infected women reduce risk of fetal transmission, reduce severity
best option of toxoplasmosis treatment
-RNA virus, familly matonaviridae, genus rubivirus
-aka german measles
virus family of rubella
children: generalized maculopapular rash on face, spreads to trunk
adults: prodrome fever, generaliized rashes, polyarthralgias
presentation of rubella
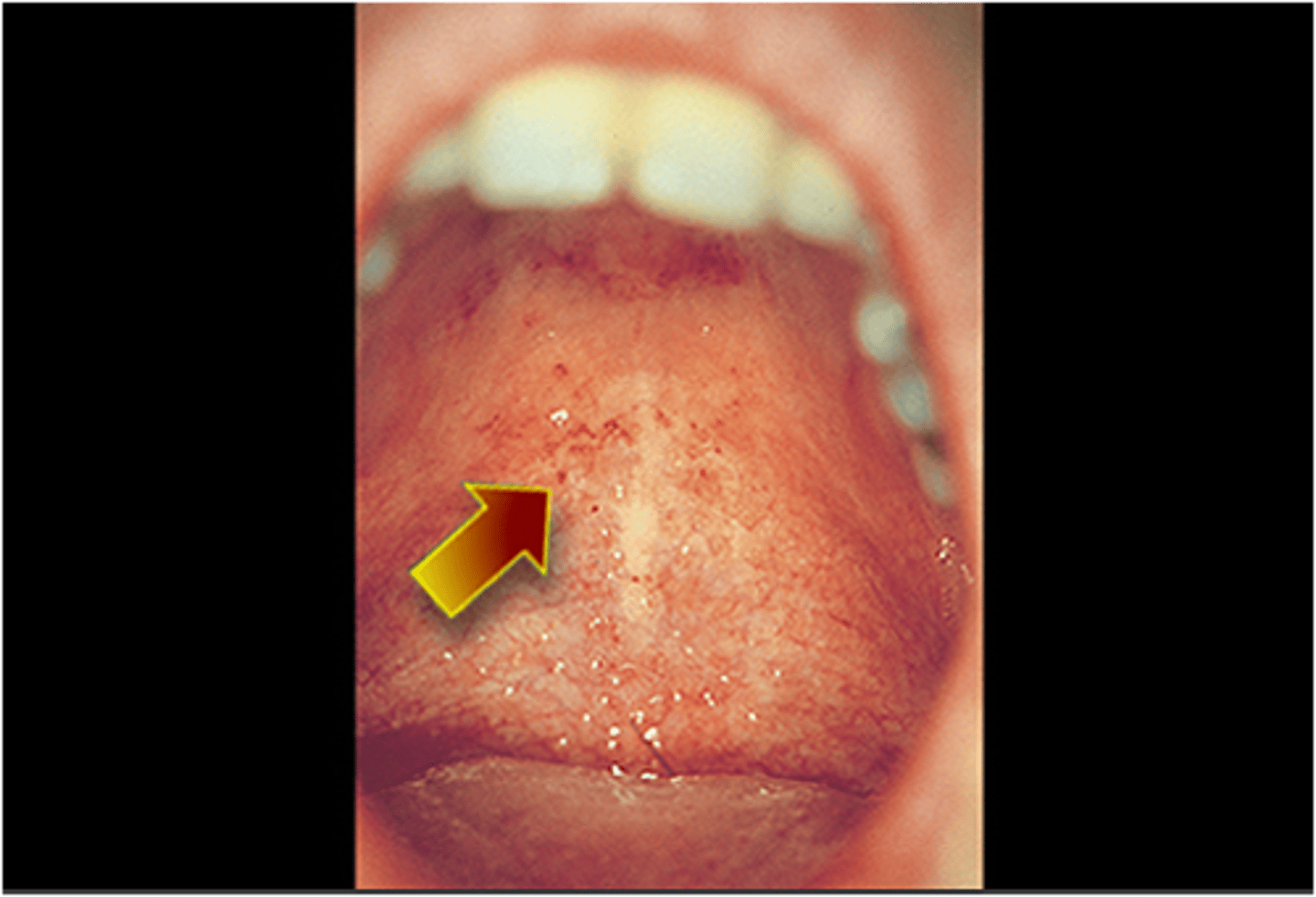
rubella
-associated with forchheimer spots (rose spots) on the soft palate
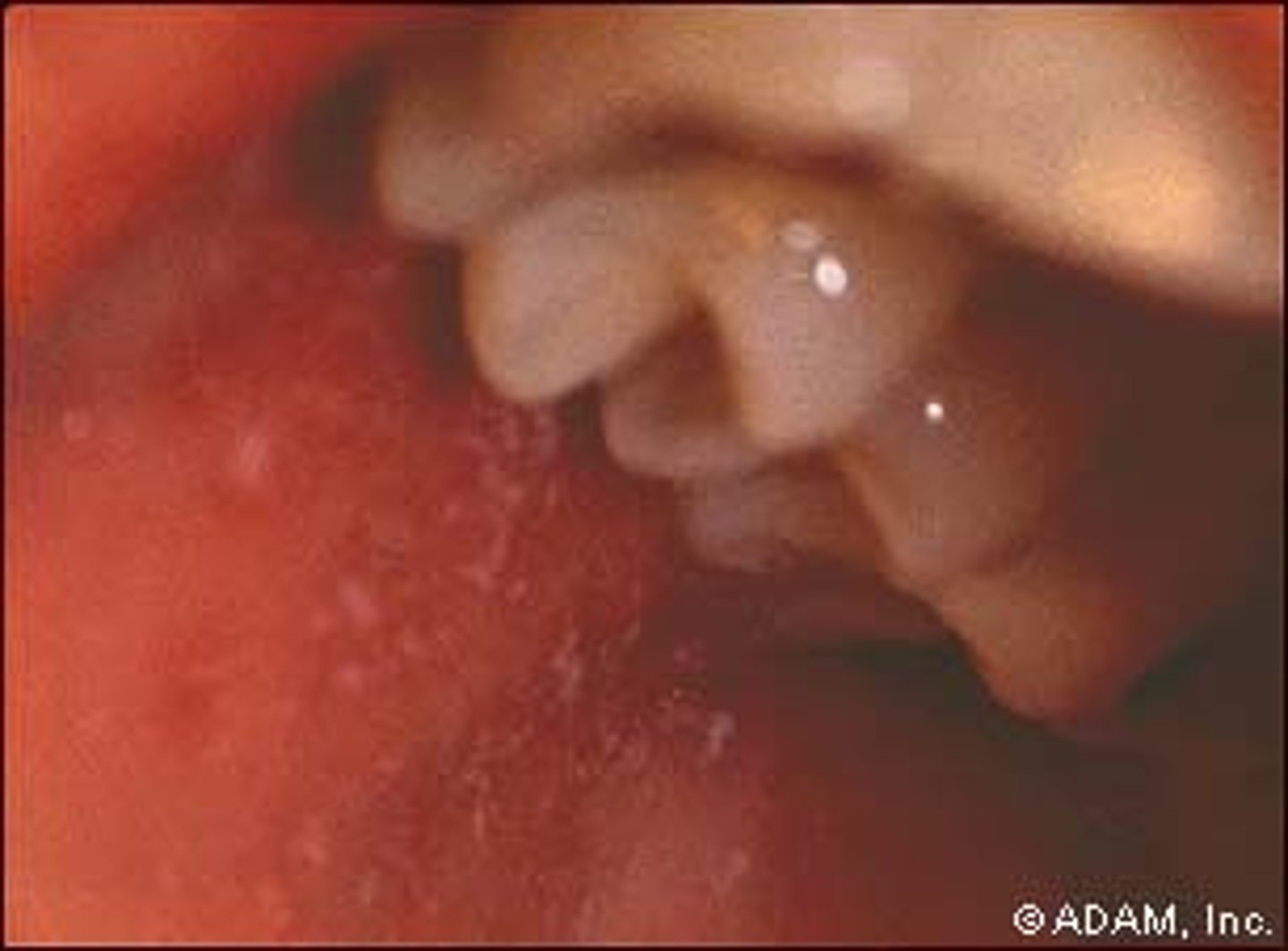
rubeola
associated with koplik spots, white spots on buccal mucosa
-pathognomonic for measles
highest risk in first 12 weeks
when is the highest risk of congenital rubella transmission?
sensorineural deafness, cataracts, congenital heat disease (eye <3 ruby earrings)
clinical triad of congenital rubella syndrome
-prevent with vaccine prior to pregnancy and avoidance
-supportive care only, close monitoring of infant over first year; no effective antiviral for baby
-isolate infected mom, shed virus in urine, stools secretions for one year
treatment of congenital rubella
rubella
virus that can be isolated from blood, urine, CSF, and throat swab specimens
human herpesvirus-5
-family herpesviridae; enveloped, dsDNA
virus family of CMV
cytomegalovirus
leading cause of nonhereditary sensorineural hearing loss; most common congenital viral infection
cytomegalovirus
•Lytic replication inside endothelial cells results in owl’s eye inclusion bodies
•Viral protein UL16 prevents expression of NK cell activating receptor ligands
cytomegalovirus
symptoms/presentation is inversely proportional to gestational age at time of transmission
-usually asymptomatic or subclinical
-symptomatic = mononucleosis (not EBV)
-primary infections have higher risk of transmission to baby
presentation of CMV in mom
congenital CMV
Chorioretinitis, Microcephaly, periVentricular calcifications
-petichiae, microcephaly
-intracranial calcifications, chorioretinitis
-hearing loss
-blueberry muffin rash
-hepatomegaly
-IV ganciclovir for infants with symptomatic congenital CMV
-maternal antiviral therapy not routinely recommended
treatment for congenital CMV
ssRNA, enveloped human retrovirus
virus type of HIV
-very LOW with combination of low viral load and ART therapy
-may occur antepartum, intrapartum, or posttpartum through breastfeeding
rate of vertical transmissio nof HIV
5 months
In untreated infants, the mean incubation period for developing an AIDS-defining condition after vertical transmission is
•Treat with ART within 12 hours of birth
•Bathe infant prior to administering vaccines
tx of HIV in neonates
38 weeks
•Planned cesarean delivery at ____ weeks of gestation is recommended for women who have a HIV viral load greater than 1,000 copies/mL
•Failure to thrive, neurodevelopmental delay, lymphadenopathy, Opportunistic infections (thrush, diaper rash), interstitial pneumonitis, frequent diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly
-molluscum contagiosum
presentation of congenital HIV
HIV
congenital infection defined by recurrent bacterial infections, lymphoid hyperplasia, chronic parotid swelling, progressive neurologic deterioration, pneumocystis jirovecii
dsDNA virus
•HSV-1 primarily cold sores; HSV-2 primarily genital herpes
•Either strain can cause genital herpes
viral family of herpes simplex
gingivostomatitis
inflammation of the mouth and gums associated with HSV 1
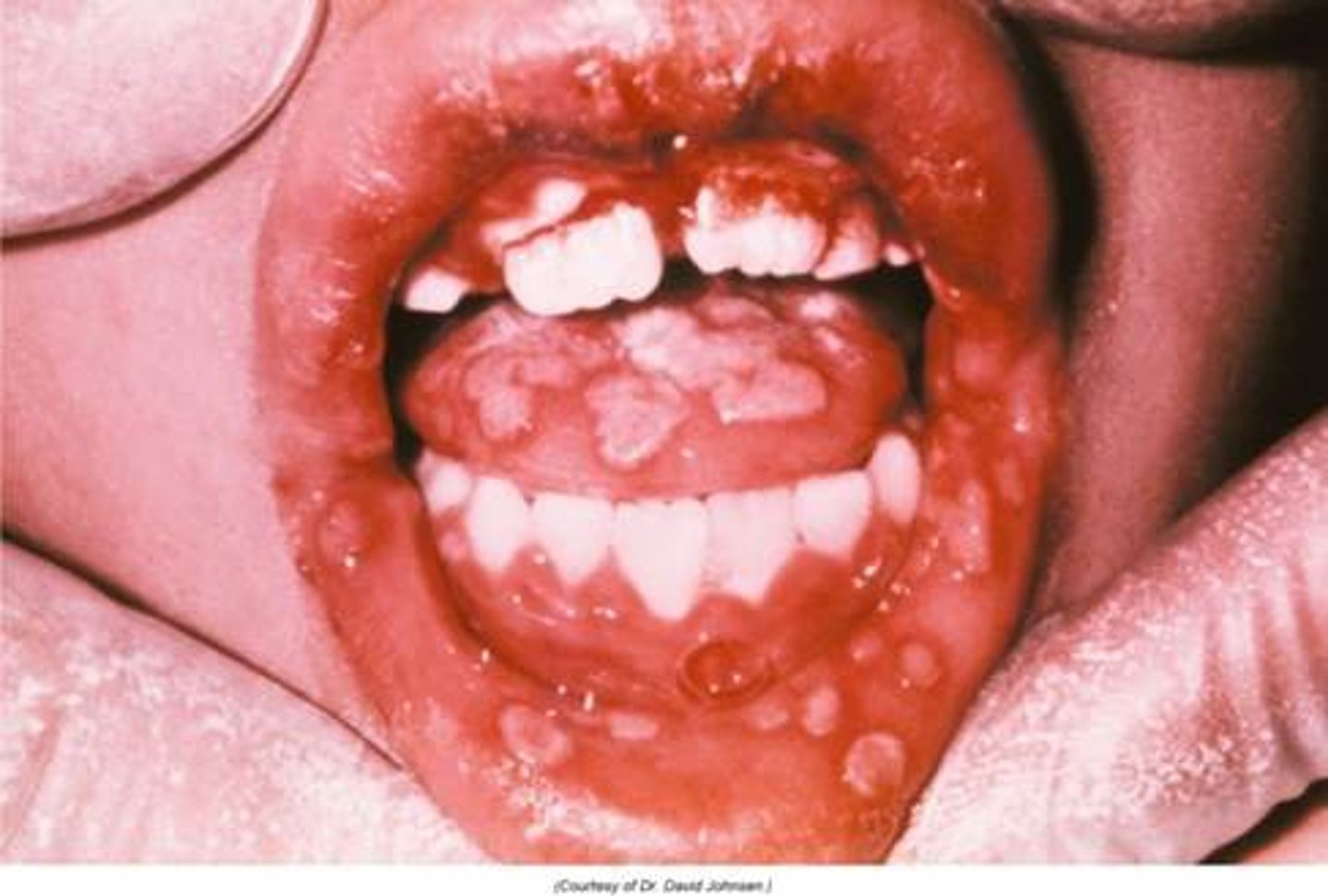
primary HSV
infection type of HSV that causes the greatest risk to fetus
•C-section recommended if herpes lesions are identified on the cervix, in the vagina, or on the vulva at the time of labor or spontaneous rupture of membranes
•Acyclovir is safe and can be used during pregnancy if symptoms are severe and to reduce risk of viral shedding or C-section delivery
prevention of congenital HSV
-rash of skin, eyes, and mouth
-localized CNS disease
-disseminated disease involvign multiple organs
3 patterns of presentation of neonatal HSV
IV acyclovir unntil PCR of CSF is negative ---> then long erm antiviral therapy
treatment of neonatal HSV
motile spirochete treponema pallidum
cause of syphilis