RMS Macromolecules Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
2
New cards
Elements in macromolecules
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, (sulfur)
3
New cards
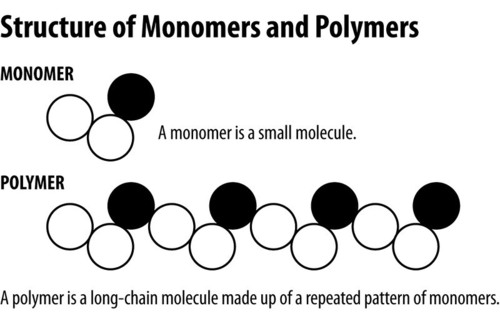
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
4
New cards
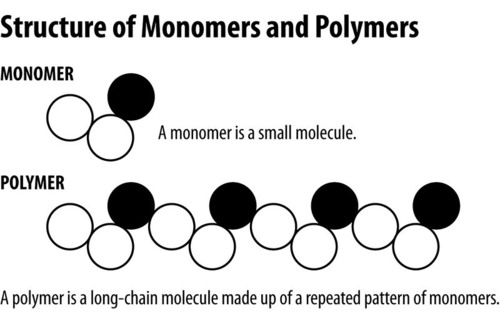
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
5
New cards
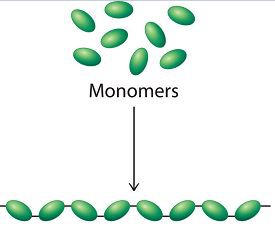
Polymerization
a chemical process that combines several monomers to form a polymer
6
New cards
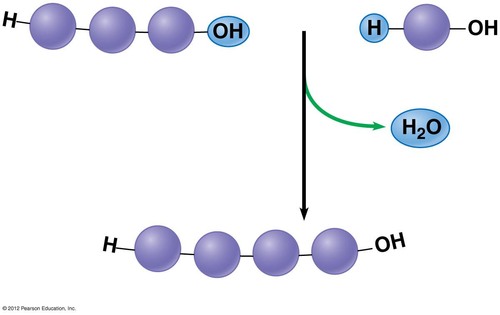
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
7
New cards
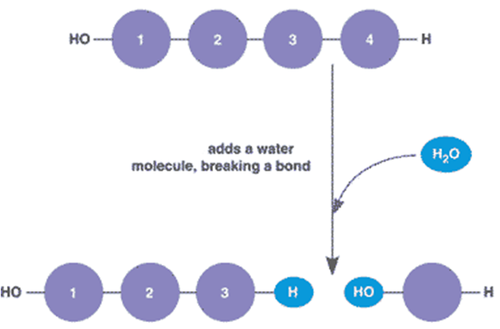
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
8
New cards
Carbohydrates (elements)
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (1:2:1)
9
New cards
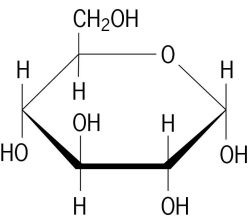
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide (Ex: glucose)
10
New cards
Carbohydrate dimer
disaccharide (sucrose, maltose, lactose)
11
New cards
carbohydrate polymer
polysaccharide (starch, cellulose, glycogen)
12
New cards
Carbohydrate function in the body
immediate energy source, short term storage
13
New cards
Carbohydrate food sources
Breads, Cereals, Pasta, Rice, Potato's and Bananas
14
New cards
Saccharides
sugars
15
New cards
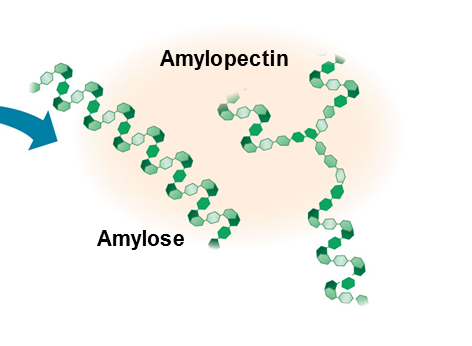
starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
16
New cards
Cellulose
Carbohydrate component of plant cell walls
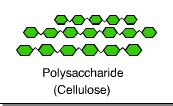
17
New cards
Glycogen
storage form of glucose in animals
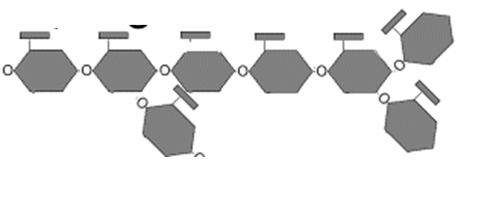
18
New cards
Lipids elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
19
New cards
Lipids examples
fats, oils, waxes
20
New cards
Lipids function
long term energy storage, cell membrane, insulation
21
New cards
Lipid monomer
glycerol and fatty acids
22
New cards
Carbohydrate bond
glycosidic bond
23
New cards
Lipids Bond Type
ester bond
24
New cards
saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid in which all carbons in the hydrocarbon tail are connected by single bonds, thus maximizing the number of hydrogen atoms that can attach to the carbon skeleton.
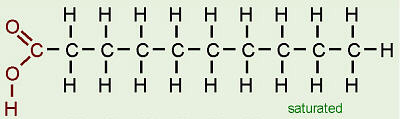
25
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
A fatty acid possessing one or more double bonds between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tail. Such bonding reduces the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton.
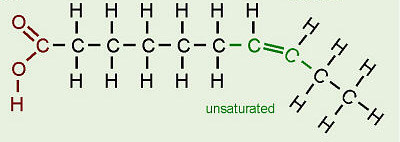
26
New cards
Protein elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
27
New cards
Protein examples
hemoglobin, enzymes, insulin, muscles, nails, hair
28
New cards
protein functions
structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances
29
New cards
Protein monomer
amino acids
30
New cards
Protein bond
peptide bond
31
New cards
Lipids in food
butter, oil
32
New cards
Proteins food sources
nuts, meat, milk, cheese
33
New cards
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
34
New cards
nucleic acids example
DNA and RNA
35
New cards
nucleic acid function
store and transmit genetic information
36
New cards
nucleic acid monomer
nucleotide
37
New cards
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
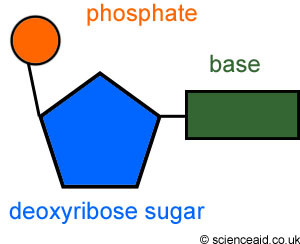
38
New cards
nucleic acid bond
phosphodiester bond